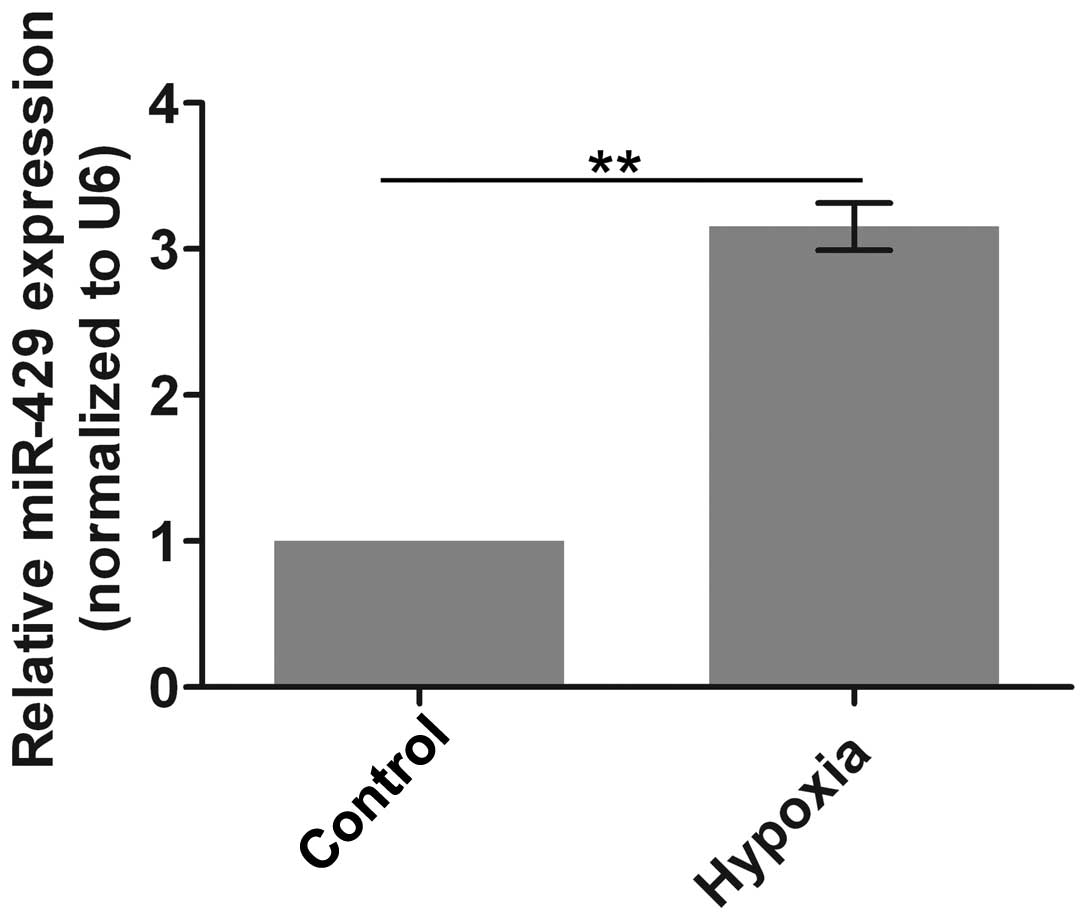
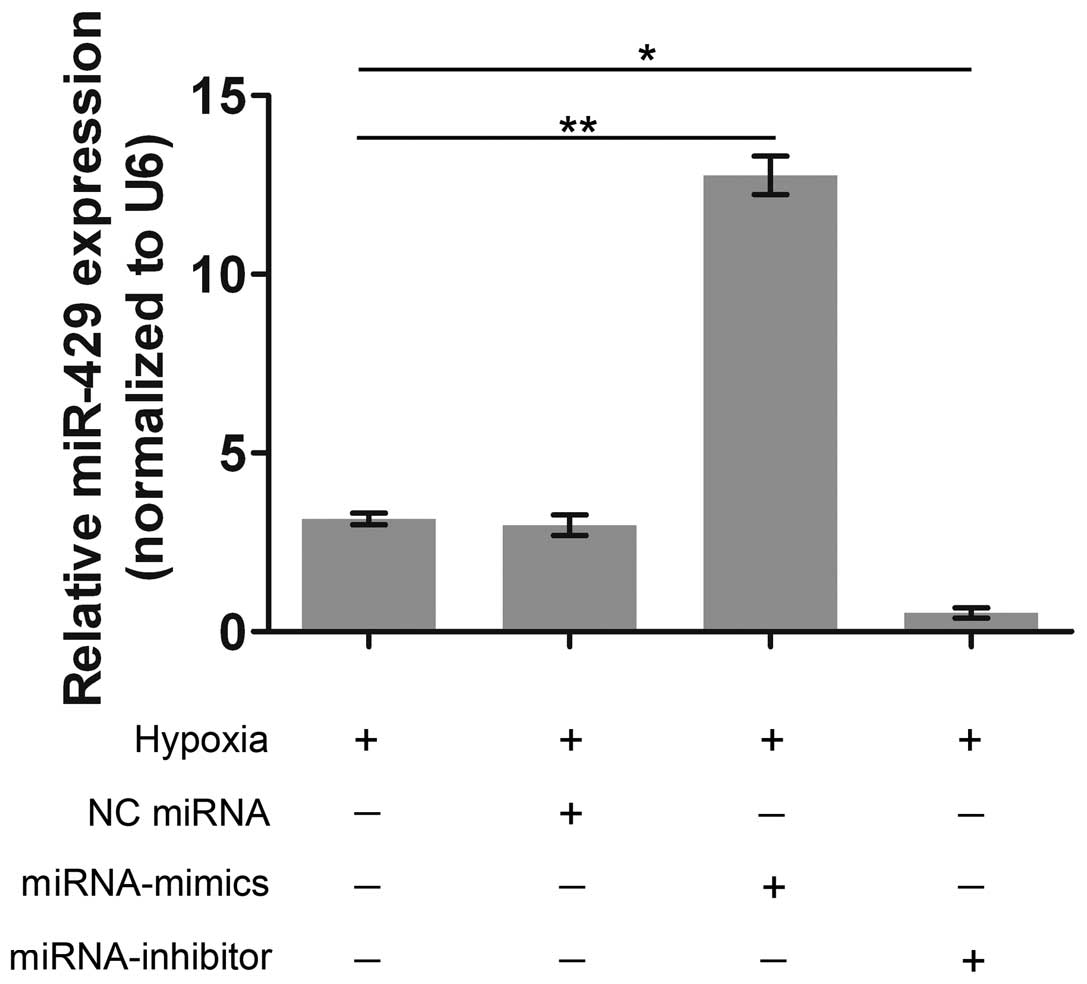
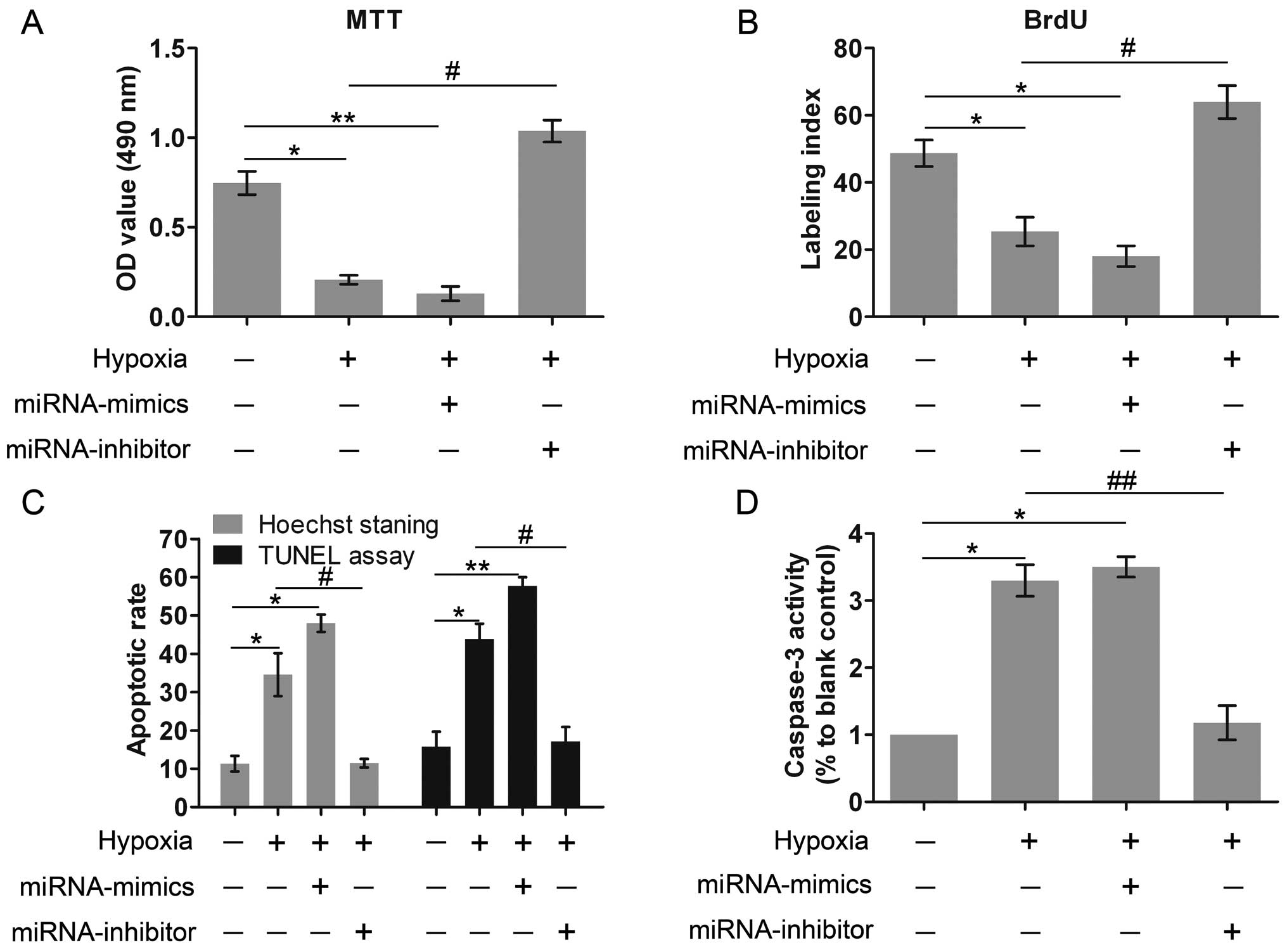
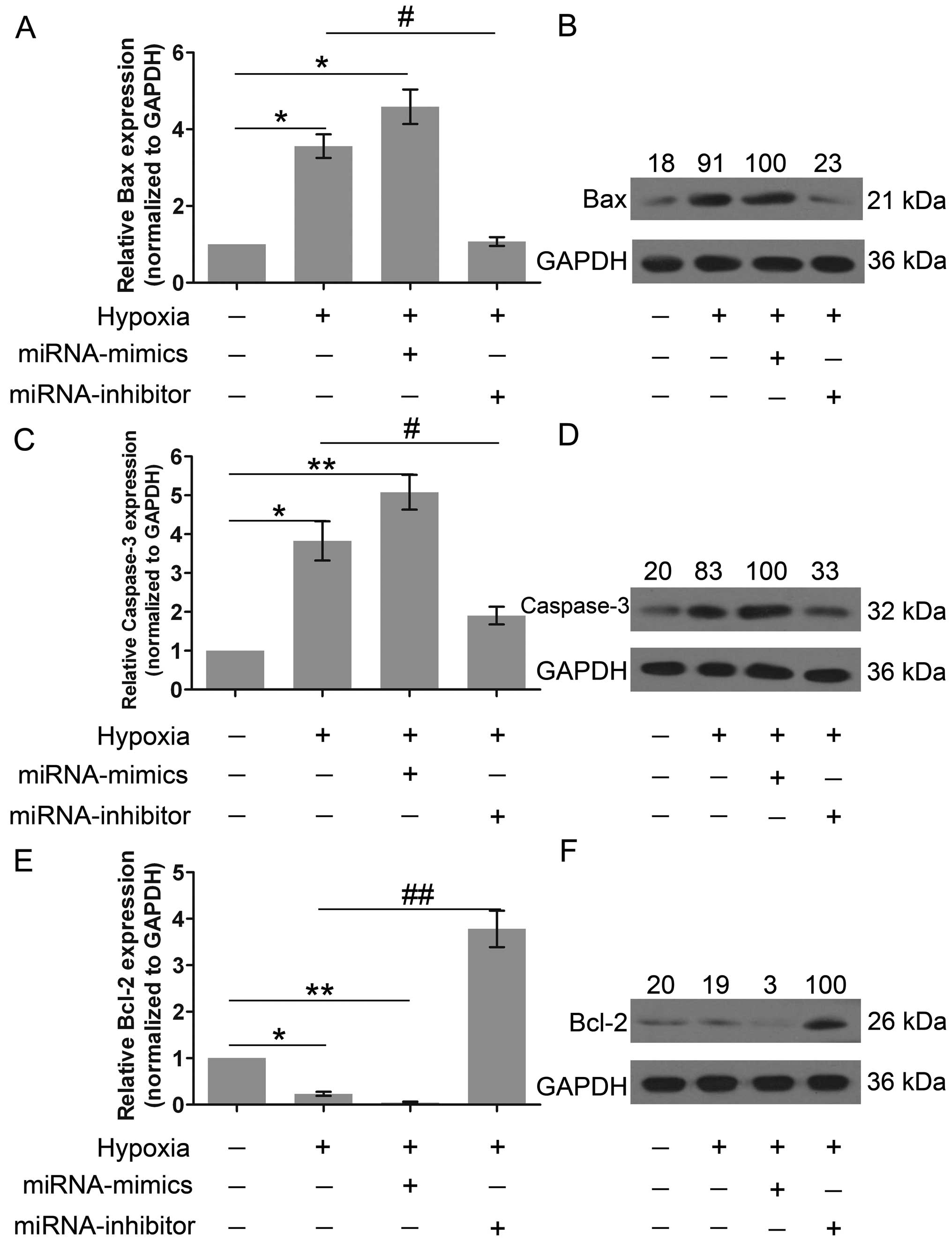
|
1
|
Jianqiang P, Ping Z, Xinmin F, Zhenhua Y,
Ming Z and Ying G: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha
ameliorate myocardial ischemia in rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
465:691–695. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Elsässer A, Suzuki K, Lorenz-Meyer S, Bode
C and Schaper J: The role of apoptosis in myocardial ischemia: A
critical appraisal. Basic Res Cardiol. 96:219–226. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Freude B, Masters TN, Robicsek F, Fokin A,
Kostin S, Zimmermann R, Ullmann C, Lorenz-Meyer S and Schaper J:
Apoptosis is initiated by myocardial ischemia and executed during
reperfusion. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 32:197–208. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kloner RA: Does reperfusion injury exist
in humans? J Am Coll Cardiol. 21:537–545. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bracken CP, Whitelaw ML and Peet DJ: The
hypoxia-inducible factors: Key transcriptional regulators of
hypoxic responses. Cell Mol Life Sci. 60:1376–1393. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Choudhuri S: Small noncoding RNAs:
Biogenesis, function, and emerging significance in toxicology. J
Biochem Mol Toxicol. 24:195–216. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fang J, Song XW, Tian J, Chen HY, Li DF,
Wang JF, Ren AJ, Yuan WJ and Lin L: Overexpression of microRNA-378
attenuates ischemia-induced apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3
expression in cardiac myocytes. Apoptosis. 17:410–423. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hu S, Huang M, Li Z, Jia F, Ghosh Z,
Lijkwan MA, Fasanaro P, Sun N, Wang X, Martelli F, et al:
MicroRNA-210 as a novel therapy for treatment of ischemic heart
disease. Circulation. 122(Suppl 11): S124–S131. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qian L, Van Laake LW, Huang Y, Liu S,
Wendland MF and Srivastava D: miR-24 inhibits apoptosis and
represses Bim in mouse cardiomyocytes. J Exp Med. 208:549–560.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li AY, Yang Q and Yang K: miR-133a
mediates the hypoxia-induced apoptosis by inhibiting TAGLN2
expression in cardiac myocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 400:173–181.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang X, Li C and Dai Q: Downregulation of
microRNA-26b rescued hypoxia-induced apoptosis in cultured neonatal
rat cardiac myocytes by regulating PTEN. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:4073–4079. 2015.
|
|
13
|
Tang J, Li L, Huang W, Sui C, Yang Y, Lin
X, Hou G, Chen X, Fu J, Yuan S, et al: MiR-429 increases the
metastatic capability of HCC via regulating classic Wnt pathway
rather than epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett.
364:33–43. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Du L, Yang Y, Wang C, Liu H, Wang L,
Zhang X, Li W, Zheng G and Dong Z: MiR-429 is an independent
prognostic factor in colorectal cancer and exerts its
anti-apoptotic function by targeting SOX2. Cancer Lett. 329:84–90.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gao H and Liu C: miR-429 represses cell
proliferation and induces apoptosis in HBV-related HCC. Biomed
Pharmacother. 68:943–949. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Li M, Zang W, Ma Y, Wang N, Li P,
Wang T and Zhao G: MiR-429 upregulation induces apoptosis and
suppresses invasion by targeting Bcl-2 and SP-1 in esophageal
carcinoma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 36:385–394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ye ZB, Ma G, Zhao YH, Xiao Y, Zhan Y, Jing
C, Gao K, Liu ZH and Yu SJ: miR-429 inhibits migration and invasion
of breast cancer cells in vitro. Int J Oncol. 46:531–538. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Lei W, Liu YE, Zheng Y and Qu L: MiR-429
inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma growth by targeting ZEB1. Med
Sci Monit. 21:383–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
von Boehmer H: Coming to grips with Notch.
J Exp Med. 194:F43–F46. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miele L and Osborne B: Arbiter of
differentiation and death: Notch signaling meets apoptosis. J Cell
Physiol. 181:393–409. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Hiroi Y and Liao JK: Notch signaling
as an important mediator of cardiac repair and regeneration after
myocardial infarction. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 20:228–231. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Del Monte G, Grego-Bessa J, González-Rajal
A, Bolós V and De La Pompa JL: Monitoring Notch1 activity in
development: Evidence for a feedback regulatory loop. Dev Dyn.
236:2594–2614. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grego-Bessa J, Luna-Zurita L, del Monte G,
Bolós V, Melgar P, Arandilla A, Garratt AN, Zang H, Mukouyama YS,
Chen H, et al: Notch signaling is essential for ventricular chamber
development. Dev Cell. 12:415–429. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gude NA, Emmanuel G, Wu W, Cottage CT,
Fischer K, Quijada P, Muraski JA, Alvarez R, Rubio M, Schaefer E
and Sussman MA: Activation of Notch-mediated protective signaling
in the myocardium. Circ Res. 102:1025–1035. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chiba S: Notch signaling in stem cell
systems. Stem Cells. 24:2437–2447. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
del Monte G, Casanova JC, Guadix JA,
MacGrogan D, Burch JB, Pérez-Pomares JM and de la Pompa JL:
Differential Notch signaling in the epicardium is required for
cardiac inflow development and coronary vessel morphogenesis. Circ
Res. 108:824–836. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bolós V, Grego-Bessa J and de la Pompa JL:
Notch signaling in development and cancer. Endocr Rev. 28:339–363.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Collesi C, Zentilin L, Sinagra G and
Giacca M: Notch1 signaling stimulates proliferation of immature
cardiomyocytes. J Cell Biol. 183:117–128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu B and Song B: Notch 1 signalling
inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis in ischaemic postconditioning.
Heart Lung Circ. 23:152–158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gersh BJ, Sliwa K, Mayosi BM and Yusuf S:
Novel therapeutic concepts: the epidemic of cardiovascular disease
in the developing world: global implications. Eur Heart J.
31:642–648. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eefting F, Rensing B, Wigman J, Pannekoek
WJ, Liu WM, Cramer MJ, Lips DJ and Doevendans PA: Role of apoptosis
in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 61:414–426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Velazquez EJ and Bonow RO:
Revascularization in severe left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 65:615–624. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang J, Guo X, Yang J, Ding JW, Li S, Yang
R, Fan ZX and Yang CJ: RP105 protects against apoptosis in
ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial damage in rats by
suppressing TLR4-mediated signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:2137–2148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen A, Li G, Chen L, Guo J and Liu Y:
Downregulation of microRNA-100 protects
H2O2-induced apoptosis in neonatal
cardiomyocytes. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:5491–5496. 2015.
|
|
35
|
Tong Z, Jiang B, Wu Y, Liu Y, Li Y, Gao M,
Jiang Y, Lv Q and Xiao X: MiR-21 protected cardiomyocytes against
doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by targeting BTG2. Int J Mol Sci.
16:14511–14525. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Boccalini G, Sassoli C, Formigli L, Bani D
and Nistri S: Relaxin protects cardiac muscle cells from
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury: Involvement of the Notch-1 pathway.
FASEB J. 29:239–249. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|