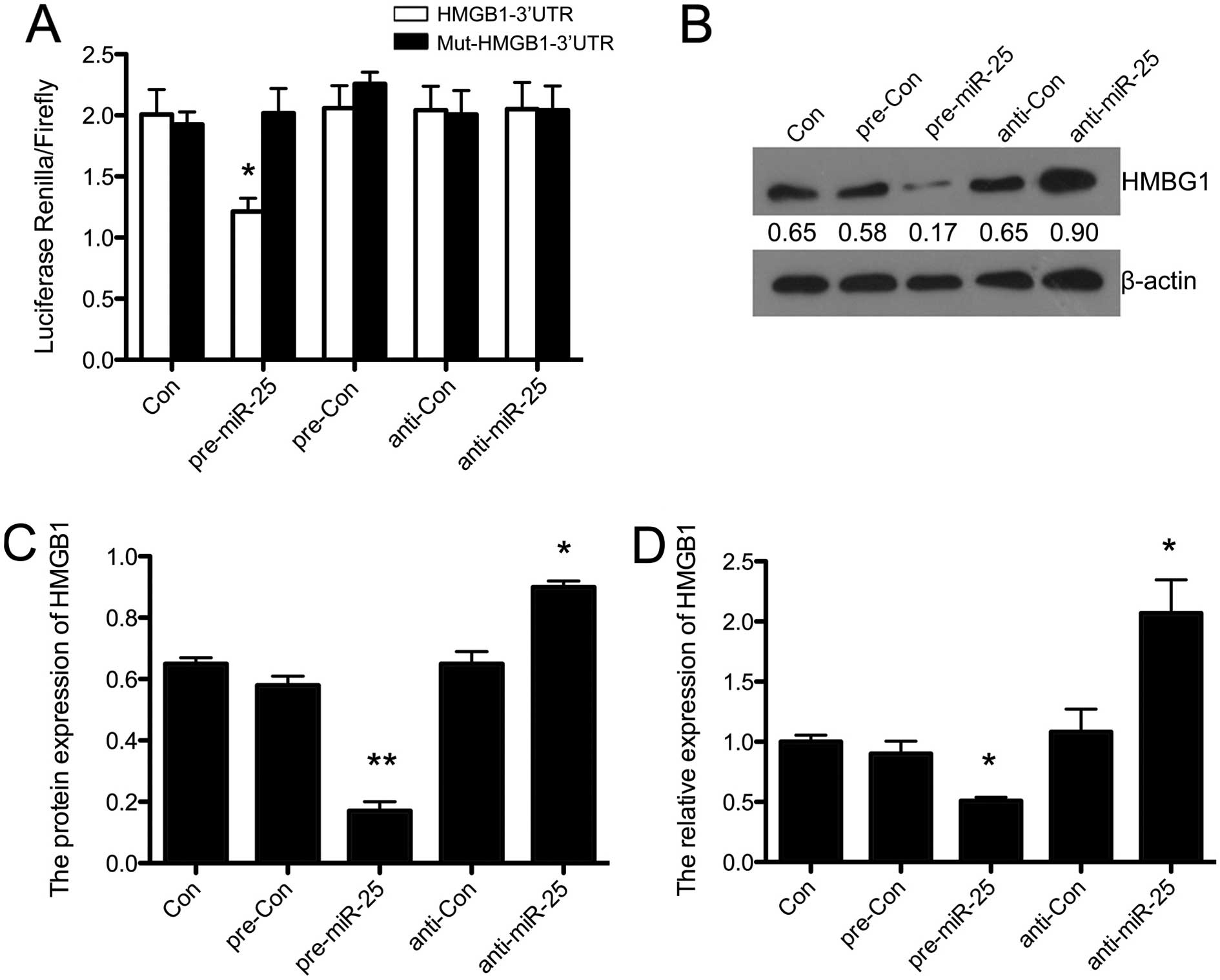
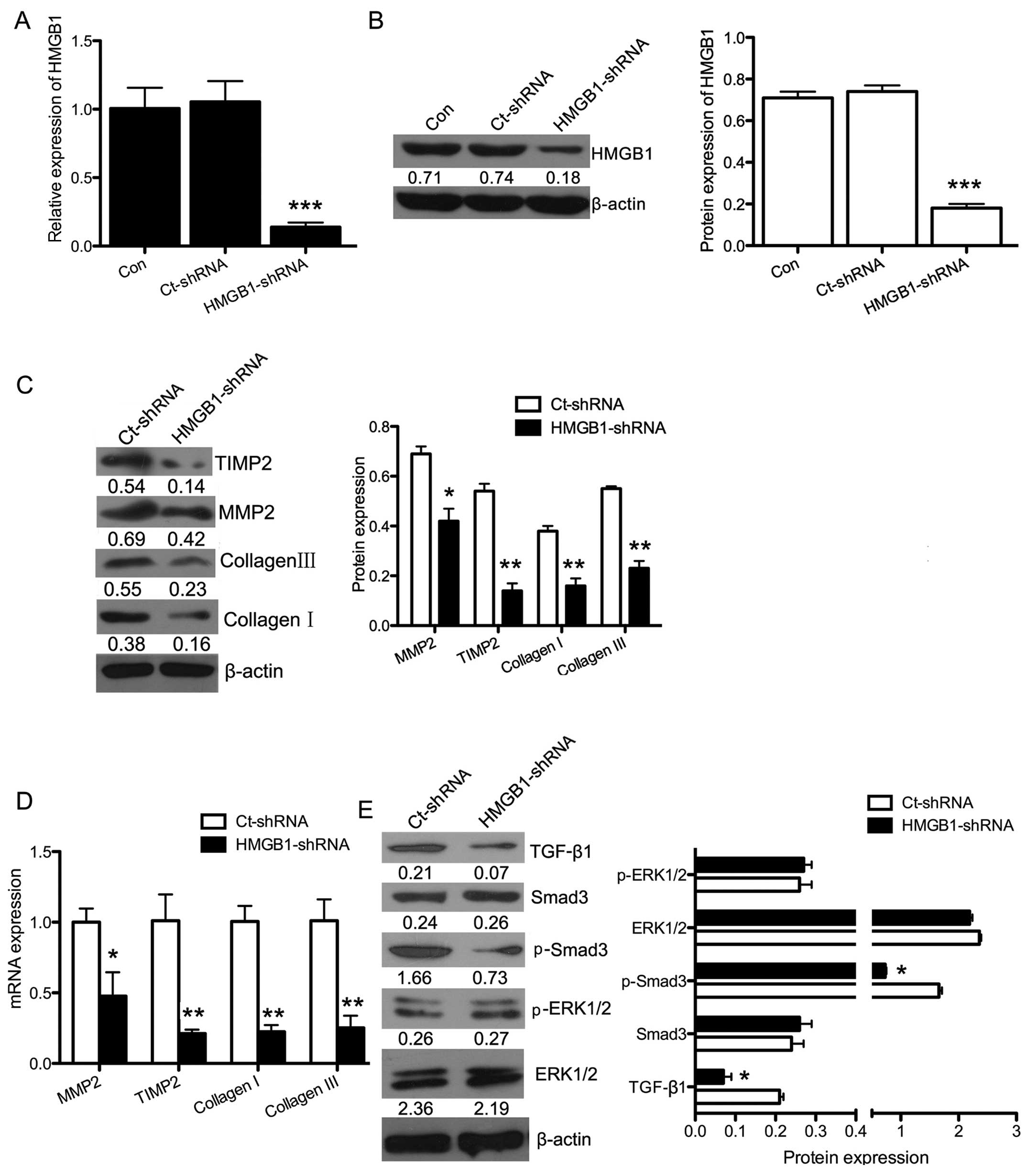
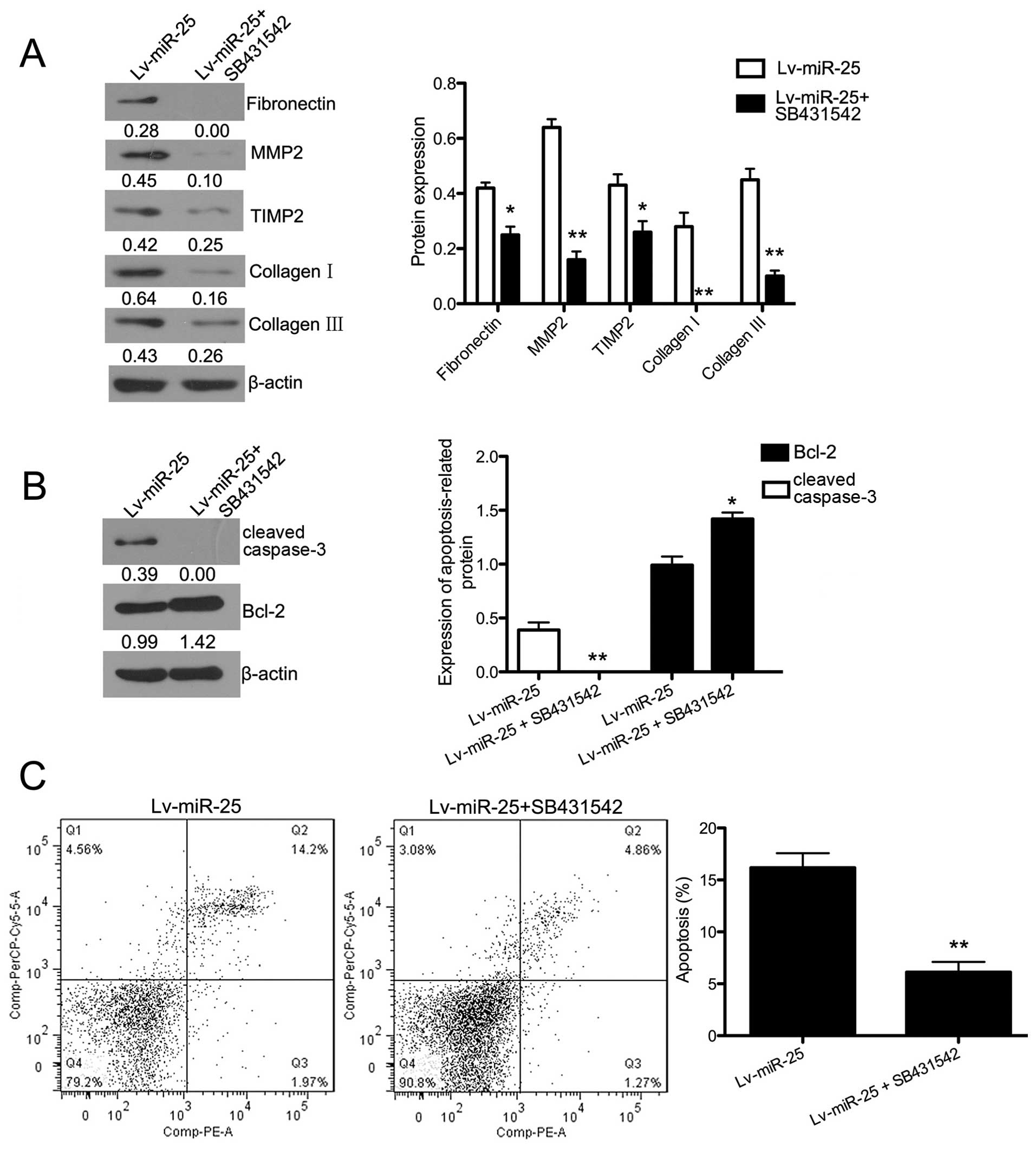
|
1
|
Lee SW, Won JY, Kim WJ, Lee J, Kim KH,
Youn SW, Kim JY, Lee EJ, Kim YJ, Kim KW and Kim HS: Snail as a
potential target molecule in cardiac fibrosis: paracrine action of
endothelial cells on fibroblasts through snail and CTGF axis. Mol
Ther. 21:1767–1777. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dhooghe B, Noël S, Huaux F and Leal T:
Lung inflammation in cystic fibrosis: pathogenesis and novel
therapies. Clin Biochem. 47:539–546. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Srivastava SP, Koya D and Kanasaki K:
MicroRNAs in kidney fibrosis and diabetic nephropathy: roles on EMT
and EndMT. BioMed Res Int. 2013:1254692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
López-Novoa JM and Nieto MA: Inflammation
and EMT: an alliance towards organ fibrosis and cancer progression.
EMBO Mol Med. 1:303–314. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Andersson U and Tracey KJ: HMGB1 is a
therapeutic target for sterile inflammation and infection. Annual
Rev Immunol. 29:139–162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lynch J, Nolan S, Slattery C, Feighery R,
Ryan MP and McMorrow T: High-mobility group box protein 1: a novel
mediator of inflammatory-induced renal epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Am J Nephrol. 32:590–602. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Andrassy M, Volz HC, Igwe JC, Funke B,
Eichberger SN, Kaya Z, Buss S, Autschbach F, Pleger ST, Lukic IK,
et al: High-mobility group box-1 in ischemia-reperfusion injury of
the heart. Circulation. 117:3216–3226. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roush S and Slack FJ: The let-7 family of
microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 18:505–516. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao J, Tang N, Wu K, Dai W, Ye C, Shi J,
Zhang J, Ning B, Zeng X and Lin Y: MiR-21 simultaneously regulates
ERK1 signaling in HSC activation and hepatocyte EMT in hepatic
fibrosis. PLoS One. 9:e1080052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brønnum H, Andersen DC, Schneider M,
Sandberg MB, Eskildsen T, Nielsen SB, Kalluri R and Sheikh SP:
miR-21 promotes fibrogenic epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of
epicardial mesothelial cells involving Programmed Cell Death 4 and
Sprouty-1. PLoS One. 8:e562802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang Y, Huang JQ, Zhang X and Shen LF:
MiR-129-2 functions as a tumor suppressor in glioma cells by
targeting HMGB1 and is down-regulated by DNA methylation. Mol Cell
Biochem. 404:229–239. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu F, Zhang J, Ji M, Li P, Du Y, Wang H,
Zang S, Ma D, Sun X and Ji C: miR-181b increases drug sensitivity
in acute myeloid leukemia via targeting HMGB1 and Mcl-1. Int J
Oncol. 45:383–392. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li X, Wang S, Chen Y, Liu G and Yang X:
miR-22 targets the 3′UTR of HMGB1 and inhibits the HMGB1-associated
autophagy in osteosarcoma cells during chemotherapy. Tumour Biol.
35:6021–6028. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang Q, Zhong H, Xie F, Xie J, Chen H and
Yao G: Expression of miR-106b-25 induced by salvianolic acid B
inhibits epithelial- to-mesenchymal transition in HK-2 cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 741:97–103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Divakaran V, Adrogue J, Ishiyama M, Entman
ML, Haudek S, Sivasubramanian N and Mann DL: Adaptive and
maladptive effects of SMAD3 signaling in the adult heart after
hemodynamic pressure overloading. Circ Heart Fail. 2:633–642. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barallobre-Barreiro J, Didangelos A,
Schoendube FA, Drozdov I, Yin X, Fernández-Caggiano M, Willeit P,
Puntmann VO, Aldama-López G, Shah AM, et al: Proteomics analysis of
cardiac extracellular matrix remodeling in a porcine model of
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation. 125:789–802. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen Z, Hu Z, Lu Z, Cai S, Gu X, Zhuang H,
Ruan Z, Xia Z, Irwin MG, Feng D and Zhang L: Differential microRNA
profiling in a cellular hypoxia reoxygenation model upon
posthypoxic propofol treatment reveals alterations in autophagy
signaling network. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:3784842013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Di Y, Lei Y, Yu F, Changfeng F, Song W and
Xuming M: MicroRNA expression and function in cerebral ischemia
reperfusion injury. J Mol Neurosci. 53:242–250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, Ren JY, Chen H and Han GP:
Statins decrease expression of five inflammation-associated
microRNAs in the plasma of patients with unstable angina. Beijing
Da. Xue Xue Bao. 47:761–768. 2015.In Chinese.
|
|
20
|
Dirkx E, Gladka MM, Philippen LE, Armand
AS, Kinet V, Leptidis S, El Azzouzi H, Salic K, Bourajjaj M, da
Silva GJ, et al: Nfat and miR-25 cooperate to reactivate the
transcription factor Hand2 in heart failure. Nat Cell Biol.
15:1282–1293. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Klune JR, Dhupar R, Cardinal J, Billiar TR
and Tsung A: HMGB1: endogenous danger signaling. Mol Med.
14:476–484. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsung A, Klune JR, Zhang X, Jeyabalan G,
Cao Z, Peng X, Stolz DB, Geller DA, Rosengart MR and Billiar TR:
HMGB1 release induced by liver ischemia involves Toll-like receptor
4-dependent reactive oxygen species production and calcium-mediated
signaling. J Exp Med. 204:2913–2923. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu H, Su Z, Wu J, Yang M, Penninger JM,
Martin CM, Kvietys PR and Rui T: The alarmin cytokine, high
mobility group box 1, is produced by viable cardiomyocytes and
mediates the lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial dysfunction via
a TLR4/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase gamma pathway. J Immunol.
184:1492–1498. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hu X, Jiang H, Bai Q, Zhou X, Xu C, Lu Z,
Cui B and Wen H: Increased serum HMGB1 is related to the severity
of coronary artery stenosis. Clin Chim Acta. 406:139–142. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Andrassy M, Volz HC, Riedle N, Gitsioudis
G, Seidel C, Laohachewin D, Zankl AR, Kaya Z, Bierhaus A,
Giannitsis E, et al: HMGB1 as a predictor of infarct transmurality
and functional recovery in patients with myocardial infarction. J
Intern Med. 270:245–253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao D, Wang Y and Xu Y: Decreased serum
endogenous secretory receptor for advanced glycation endproducts
and increased cleaved receptor for advanced glycation endproducts
levels in patients with atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol.
158:471–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Frangogiannis NG, Smith CW and Entman ML:
The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res.
53:31–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hu X, Fu W and Jiang H: HMGB1: A potential
therapeutic target for myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury.
Int J Cardiol. 155:4892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Su Z, Yin J, Wang T, Sun Y, Ni P, Ma R,
Zhu H, Zheng D, Shen H, Xu W and Xu H: Up-regulated HMGB1 in EAM
directly led to collagen deposition by a PKCβ/Erk1/2-dependent
pathway: cardiac fibroblast/myofibroblast may be another source of
HMGB1. J Cell Mol Med. 18:1740–1751. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saltis J, Agrotis A and Bobik A:
Regulation and interactions of transforming growth factor-beta with
cardiovascular cells: implications for development and disease.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 23:193–200. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Petrocca F, Vecchione A and Croce CM:
Emerging role of miR-106b-25/miR-17-92 clusters in the control of
transforming growth factor beta signaling. Cancer Res.
68:8191–8194. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|