|
1
|
Maher EA, Furnari FB, Bachoo RM, Rowitch
DH, Louis DN, Cavenee WK and DePinho RA: Malignant glioma: Genetics
and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev. 15:1311–1333. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Emdad L, Dent P, Sarkar D and Fisher PB:
Future approaches for the therapy of malignant glioma: Targeting
genes mediating invasion. Future Oncol. 8:343–346. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent
MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B,
Belanger K, et al European Organisation for Research and Treatment
of Cancer Brain Tumour and Radiation Oncology Groups; National
Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group: Effects of
radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus
radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised
phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet
Oncol. 10:459–466. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lefranc F, Brotchi J and Kiss R: Possible
future issues in the treatment of glioblastomas: Special emphasis
on cell migration and the resistance of migrating glioblastoma
cells to apoptosis. J Clin Oncol. 23:2411–2422. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Friedl P and Wolf K: Tumour-cell invasion
and migration: Diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:362–374. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Snyder GL and Greenberg S: Effect of
anaesthetic technique and other perioperative factors on cancer
recurrence. Br J Anaesth. 105:106–115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kvolik S, Glavas-Obrovac L, Bares V and
Karner I: Effects of inhalation anesthetics halothane, sevoflurane,
and isoflurane on human cell lines. Life Sci. 77:2369–2383. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kvolik S, Dobrosevic B, Marczi S, Prlic L
and Glavas-Obrovac L: Different apoptosis ratios and gene
expressions in two human cell lines after sevoflurane anaesthesia.
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 53:1192–1199. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang H, Gu M, Yang C, Wang H, Wen X and
Zhou Q: Sevoflurane inhibits invasion and migration of lung cancer
cells by inactivating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. J Anesth.
26:381–392. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jansson MD and Lund AH: MicroRNA and
cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:590–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Zhou Y, Feng X, An P, Quan X, Wang
H, Ye S, Yu C, He Y and Luo H: MicroRNA-126 functions as a tumor
suppressor in colorectal cancer cells by targeting CXCR4 via the
AKT and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 44:203–210.
2014.
|
|
12
|
Gu JJ, Gao GZ and Zhang SM: miR-218
inhibits the migration and invasion of glioma U87 cells through the
Slit2-Robo1 pathway. Oncol Lett. 9:1561–1566. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
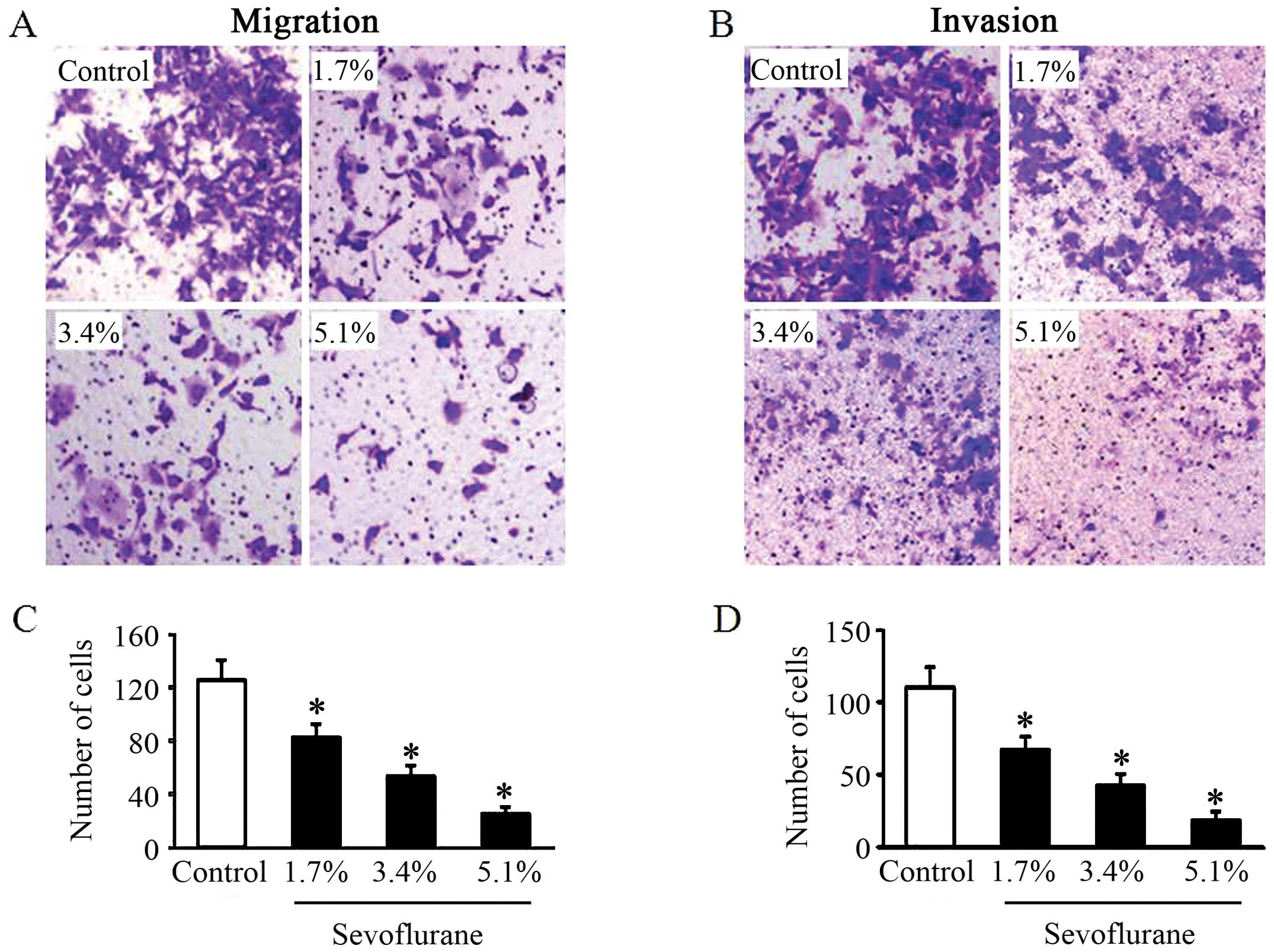
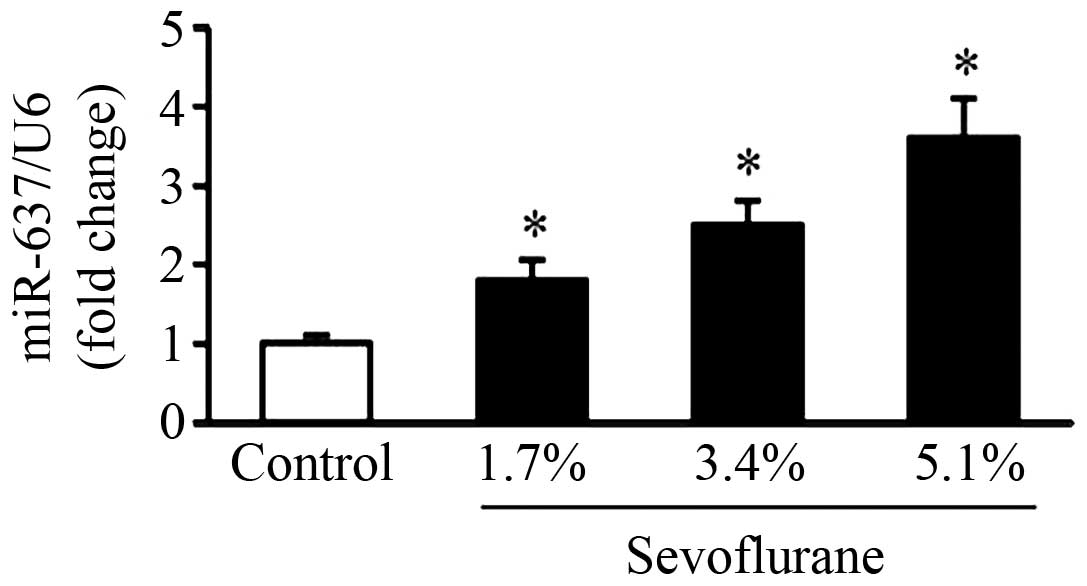
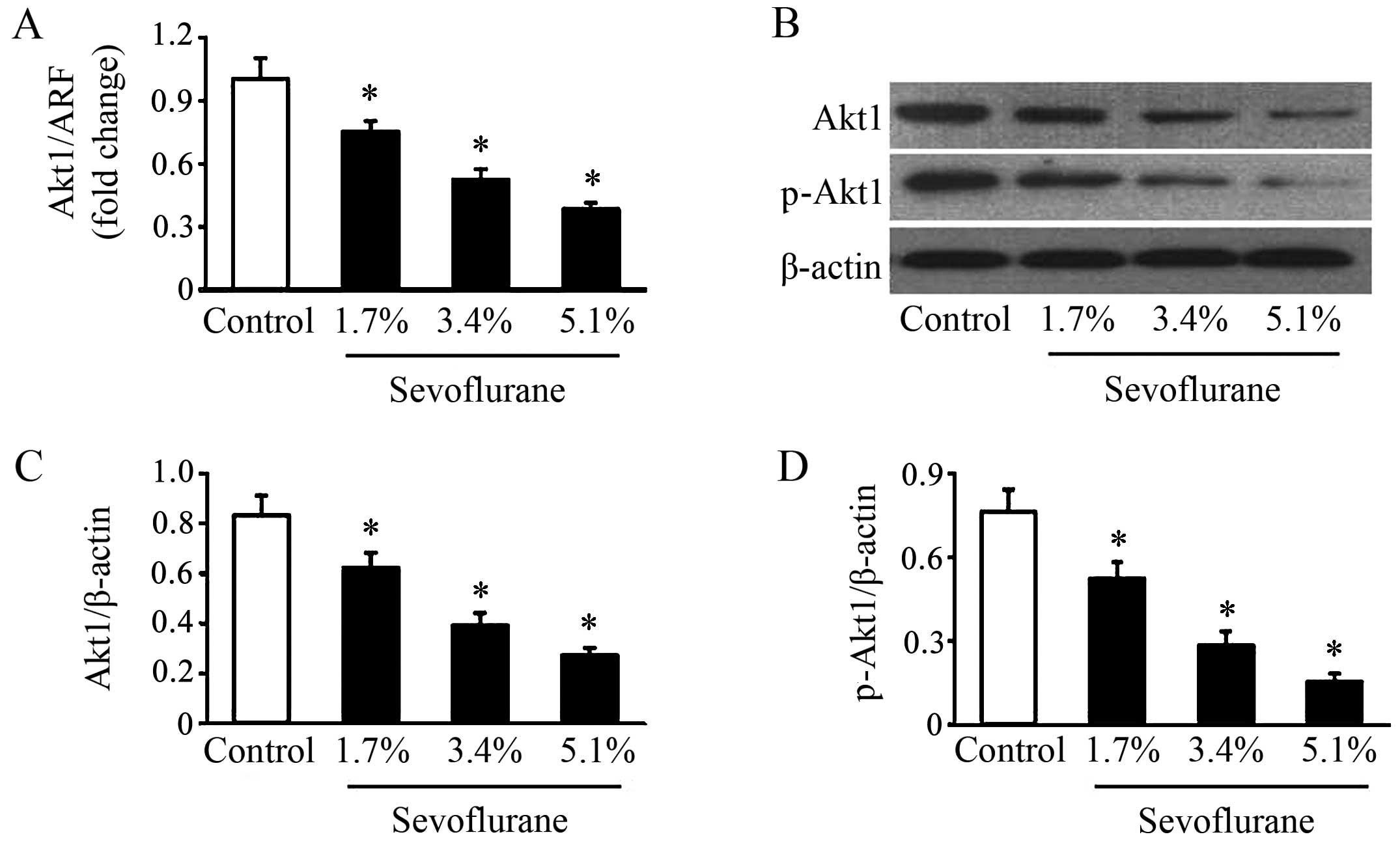
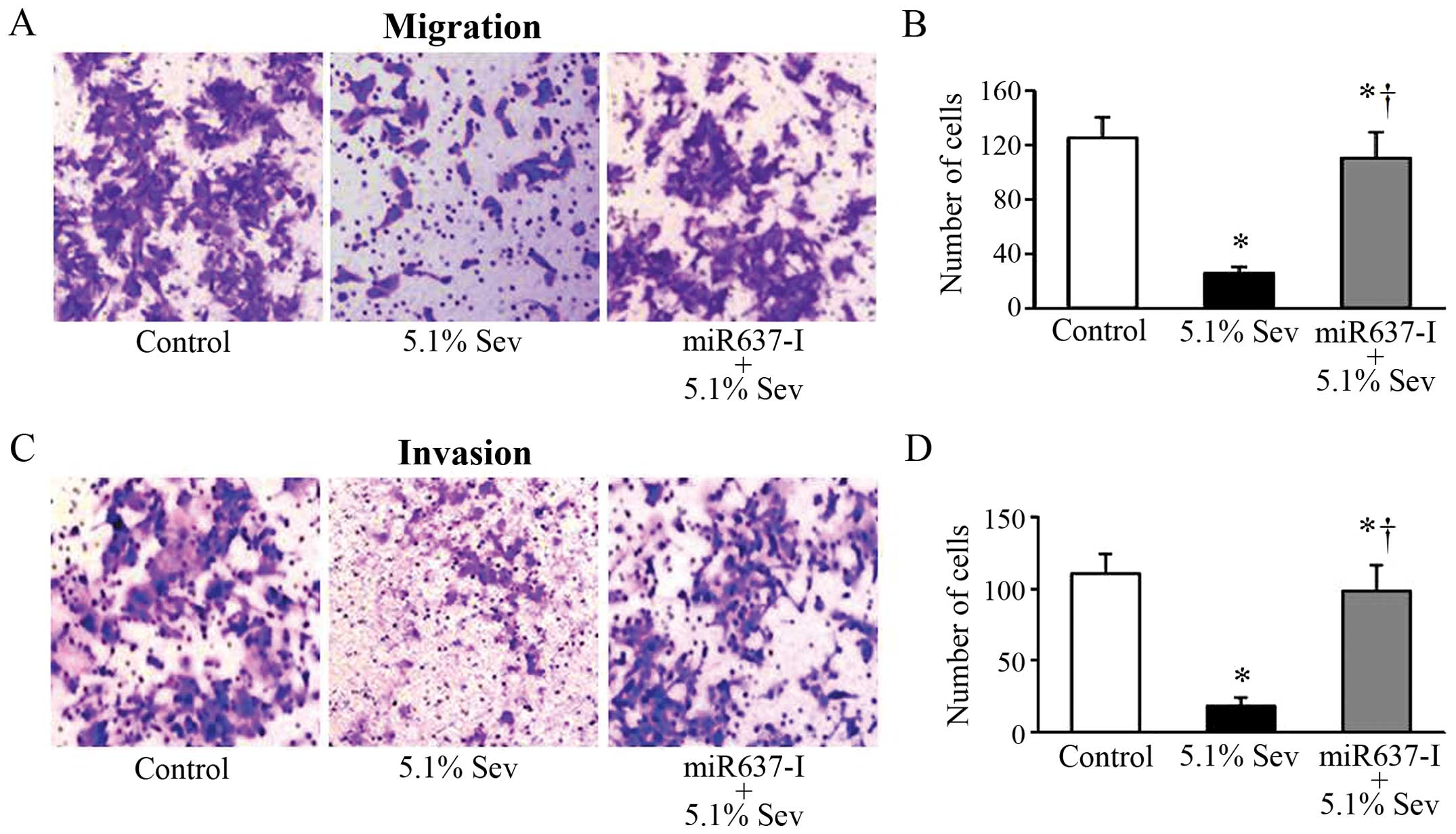
Que T, Song Y, Liu Z, Zheng S, Long H, Li
Z, Liu Y, Wang G, Liu Y, Zhou J, et al: Decreased miRNA-637 is an
unfavorable prognosis marker and promotes glioma cell growth,
migration and invasion via direct targeting Akt1. Oncogene.
34:4952–4963. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takeuchi J, Sakamoto A and Takizawa T:
Sevoflurane anesthesia persistently downregulates muscle-specific
microRNAs in rat plasma. Int J Mol Med. 34:291–298. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Goto G, Hori Y, Ishikawa M, Tanaka S and
Sakamoto A: Changes in the gene expression levels of microRNAs in
the rat hippocampus by sevoflurane and propofol anesthesia. Mol Med
Rep. 9:1715–1722. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Otsuki T, Ishikawa M, Hori Y, Goto G and
Sakamoto A: Volatile anesthetic sevoflurane ameliorates
endotoxin-induced acute lung injury via microRNA modulation in
rats. Biomed Rep. 3:408–412. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roesslein M1, Frick M, Auwaerter V, Humar
M, Goebel U, Schwer C, Geiger KK, Pahl HL, Pannen BH and Loop T:
Sevoflurane-mediated activation of p38-mitogen-activated
stresskinase is independent of apoptosis in Jurkat T-cells. Anesth
Analg. 106:1150–1160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li D, Wang C, Li N and Zhang L: Propofol
selectively inhibits nuclear factor-κB activity by suppressing p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in human EA.hy926
endothelial cells during intermittent hypoxia/reoxygenation. Mol
Med Rep. 9:1460–1466. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li GQ, Zhang Y, Liu D, Qian YY, Zhang H,
Guo SY, Sunagawa M, Hisamitsu T and Liu YQ: PI3 kinase/Akt/HIF-1α
pathway is associated with hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis.
Mol Cell Biochem. 372:221–231. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bozzuto G, Ruggieri P and Molinari A:
Molecular aspects of tumor cell migration and invasion. Ann Ist
Super Sanita. 46:66–80. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Coffey JC, Wang JH, Smith MJ,
Bouchier-Hayes D, Cotter TG and Redmond HP: Excisional surgery for
cancer cure: Therapy at a cost. Lancet Oncol. 4:760–768. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamaguchi K, Takagi Y, Aoki S, Futamura M
and Saji S: Significant detection of circulating cancer cells in
the blood by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction during
colorectal cancer resection. Ann Surg. 232:58–65. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hobert O: miRNAs play a tune. Cell.
131:22–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yin D, Ogawa S, Kawamata N, Leiter A, Ham
M, Li D, Doan NB, Said JW, Black KL and Phillip Koeffler H: miR-34a
functions as a tumor suppressor modulating EGFR in glioblastoma
multiforme. Oncogene. 32:1155–1163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen Z, Li D, Cheng Q, Ma Z, Jiang B, Peng
R, Chen R, Cao Y and Wan X: MicroRNA-203 inhibits the proliferation
and invasion of U251 glioblastoma cells by directly targeting PLD2.
Mol Med Rep. 9:503–508. 2014.
|
|
27
|
Fang L, Deng Z, Shatseva T, Yang J, Peng
C, Du WW, Yee AJ, Ang LC, He C, Shan SW and Yang BB: MicroRNA
miR-93 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting
integrin-β8. Oncogene. 30:806–821. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Dontula R, Dinasarapu A, Chetty C, Pannuru
P, Herbert E, Ozer H and Lakka SS: MicroRNA 203 modulates glioma
cell migration via Robo1/ERK/MMP-9 signaling. Genes Cancer.
4:285–296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu S, Lin Y, Xu D, Chen J, Shu M, Zhou Y,
Zhu W, Su X, Zhou Y, Qiu P, et al: MiR-135a functions as a
selective killer of malignant glioma. Oncogene. 31:3866–3874. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang JF, He ML, Fu WM, Wang H, Chen LZ,
Zhu X, Chen Y, Xie D, Lai P, Chen G, et al: Primate-specific
microRNA-637 inhibits tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by
disrupting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
signaling. Hepatology. 54:2137–2148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leivonen SK, Sahlberg KK, Mäkelä R, Due
EU, Kallioniemi O, Børresen-Dale AL and Perälä M: High-throughput
screens identify microRNAs essential for HER2 positive breast
cancer cell growth. Mol Oncol. 8:93–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Stokowy T, Wojtaś B, Fujarewicz K, Jarząb
B, Eszlinger M and Paschke R: miRNAs with the potential to
distinguish follicular thyroid carcinomas from benign follicular
thyroid tumors: Results of a meta-analysis. Horm Metab Res.
46:171–180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ishikawa M, Tanaka S, Arai M, Genda Y and
Sakamoto A: Differences in microRNA changes of healthy rat liver
between sevoflurane and propofol anesthesia. Anesthesiology.
117:1245–1252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Włodarski P, Grajkowska W, Łojek M, Rainko
K and Jóźwiak J: Activation of Akt and Erk pathways in
medulloblastoma. Folia Neuropathol. 44:214–220. 2006.
|
|
35
|
Schlegel J, Piontek G, Budde B, Neff F and
Kraus A: The Akt/protein kinase B-dependent anti-apoptotic pathway
and the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade are alternatively
activated in human glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Lett.
158:103–108. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|