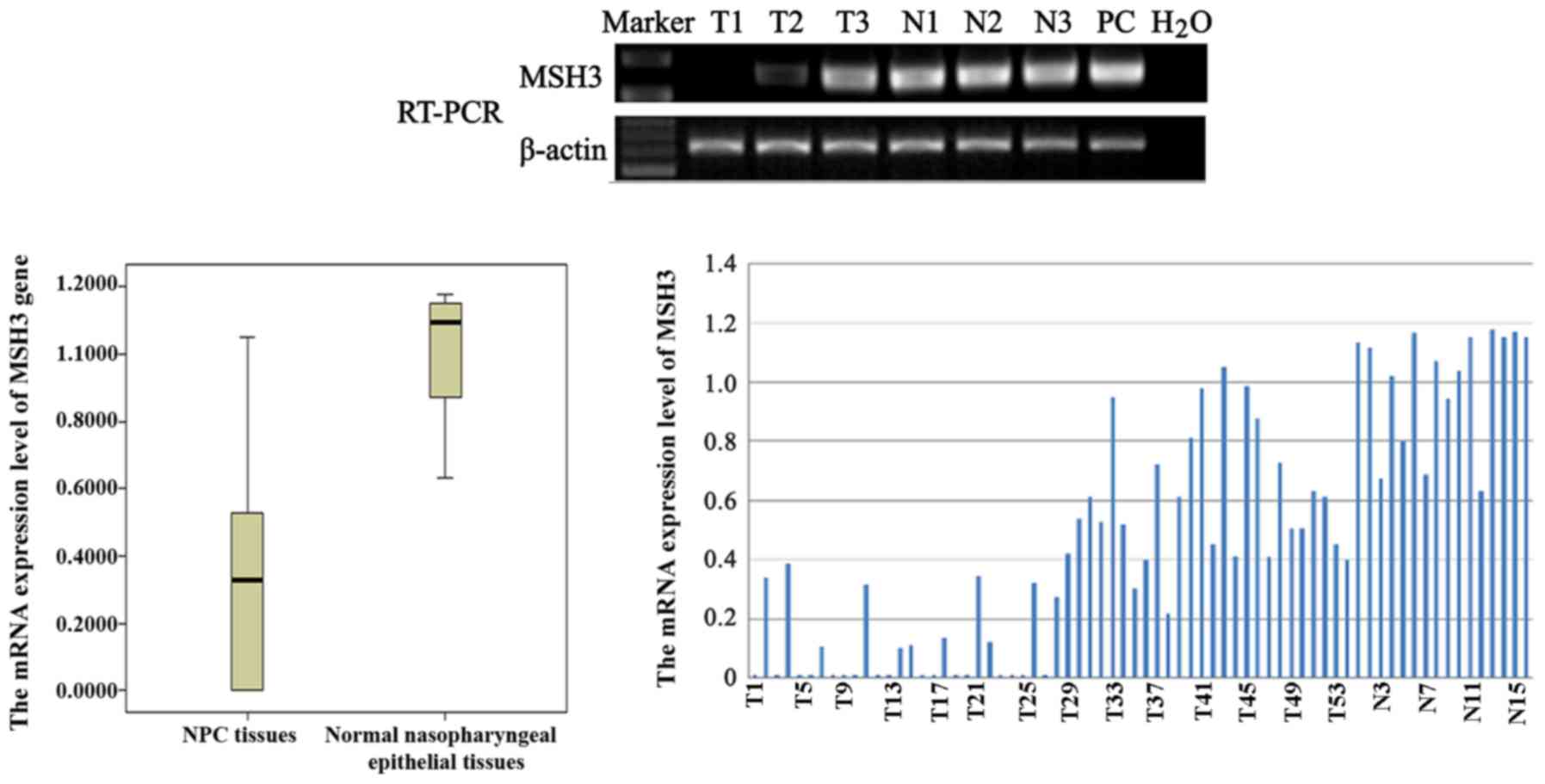
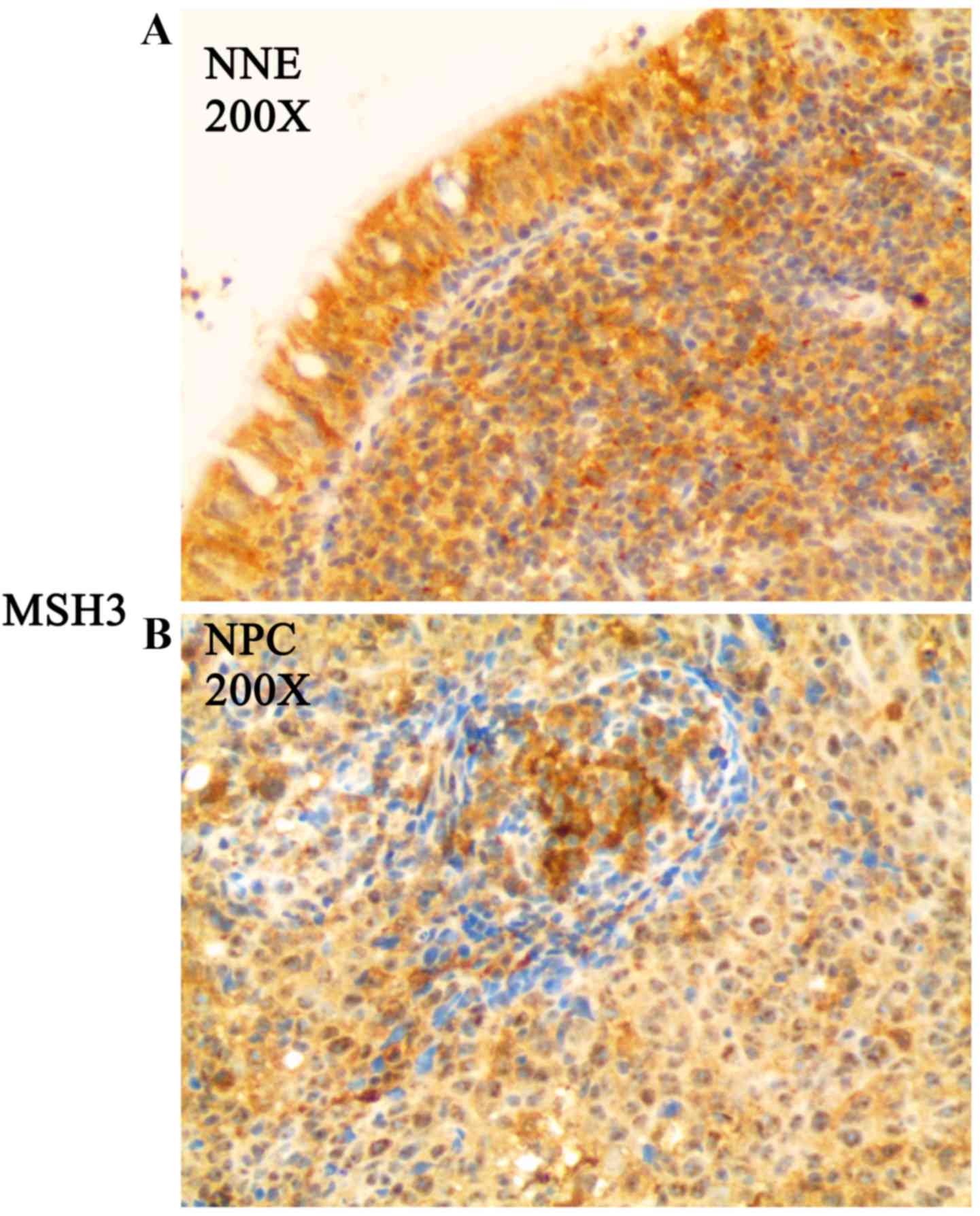
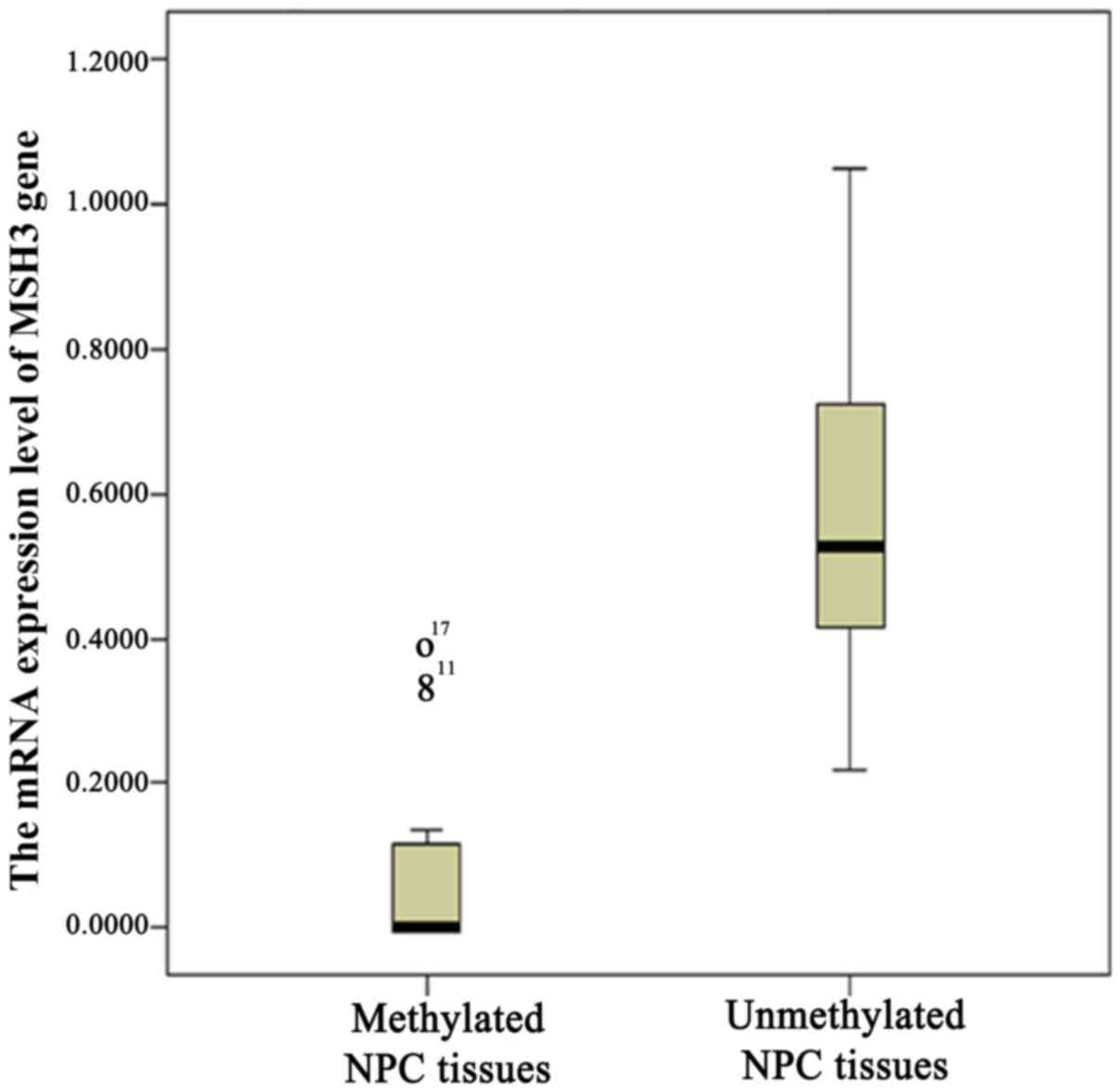
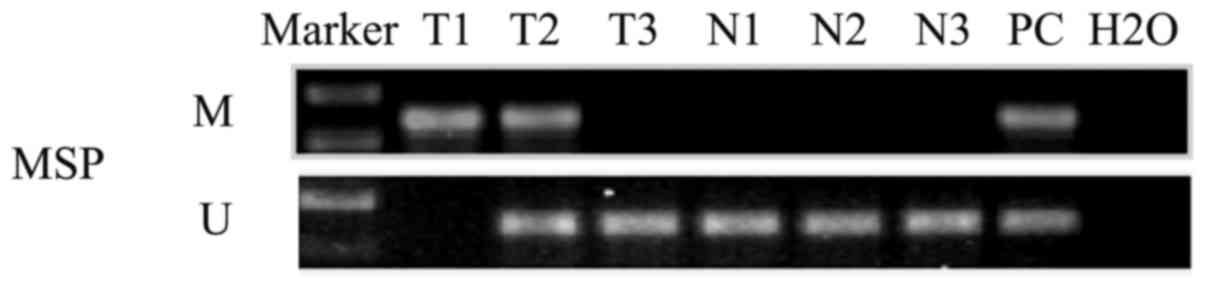
|
1
|
Tao Q and Chan AT: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic developments.
Expert Rev Mol Med. 9:1–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lung HL, Cheung AK, Ko JM, Cheng Y,
Stanbridge EJ and Lung ML: Deciphering the molecular genetic basis
of NPC through functional approaches. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:87–95.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lo KW, Chung GT and To KF: Deciphering the
molecular genetic basis of NPC through molecular, cytogenetic, and
epigenetic approaches. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:79–86. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fishel R: The selection for mismatch
repair defects in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer:
revising the mutator hypothesis. Cancer Res. 61:7369–7374.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jensen LE, Jauert PA and Kirkpatrick DT:
The large loop repair and mismatch repair pathways of Saccharomyces
cerevisiae act on distinct substrates during meiosis. Genetics.
170:1033–1043. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gupta S, Gellert M and Yang W: Mechanism
of mismatch recognition revealed by human MutSβ bound to unpaired
DNA loops. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 19:72–78. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
van Oers JM, Edwards Y, Chahwan R, Zhang
W, Smith C, Pechuan X, Schaetzlein S, Jin B, Wang Y, Bergman A, et
al: The MutSβ complex is a modulator of p53-driven tumorigenesis
through its functions in both DNA double-strand break repair and
mismatch repair. Oncogene. 33:3939–3946. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Owen BA, H Lang W and McMurray CT: The
nucleotide binding dynamics of human MSH2–MSH3 are lesion
dependent. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 16:550–557. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park JM, Huang S, Tougeron D and Sinicrope
FA: MSH3 mismatch repair protein regulates sensitivity to cytotoxic
drugs and a histone deacetylase inhibitor in human colon carcinoma
cells. PLoS One. 8:e653692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mangoni M, Bisanzi S, Carozzi F, Sani C,
Biti G, Livi L, Barletta E, Costantini AS and Gorini G: Association
between genetic polymorphisms in the XRCC1, XRCC3, XPD, GSTM1,
GSTT1, MSH2, MLH1, MSH3, and MGMT genes and radiosensitivity in
breast cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 81:52–58.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang SC, Lee JK, Smith EJ, Doctolero RT,
Tajima A, Beck SE, Weidner N and Carethers JM: Evidence for an
hMSH3 defect in familial hamartomatous polyps. Cancer. 117:492–500.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Campregher C, Schmid G, Ferk F, Knasmüller
S, Khare V, Kortüm B, Dammann K, Lang M, Scharl T, Spittler A, et
al: MSH3-deficiency initiates EMAST without oncogenic
transformation of human colon epithelial cells. PLoS One.
7:e505412012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
de Wind N, Dekker M, Claij N, Jansen L,
van Klink Y, Radman M, Riggins G, van der Valk M, van't Wout K and
te Riele H: HNPCC-like cancer predisposition in mice through
simultaneous loss of Msh3 and Msh6 mismatch-repair protein
functions. Nat Genet. 23:359–362. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Edelmann W, Umar A, Yang K, Heyer J,
Kucherlapati M, Lia M, Kneitz B, Avdievich E, Fan K, Wong E, et al:
The DNA mismatch repair genes Msh3 and Msh6 cooperate in intestinal
tumor suppression. Cancer Res. 60:803–807. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jones PA and Laird PW: Cancer epigenetics
comes of age. Nat Genet. 21:163–167. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Plaschke J, Preußler M, Ziegler A and
Schackert HK: Aberrant protein expression and frequent allelic loss
of MSH3 in colorectal cancer with low-level microsatellite
instability. Int J Colorectal Dis. 27:911–919. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim HG, Lee S, Kim DY, Ryu SY, Joo JK, Kim
JC, Lee KH and Lee JH: Aberrant methylation of DNA mismatch repair
genes in elderly patients with sporadic gastric carcinoma: a
comparison with younger patients. J Surg Oncol. 101:28–35. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kawakami T, Shiina H, Igawa M, Deguchi M,
Nakajima K, Ogishima T, Tokizane T, Urakami S, Enokida H, Miura K,
et al: Inactivation of the hMSH3 mismatch repair gene in bladder
cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 325:934–942. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun X, Chen C, Vessella RL and Dong JT:
Microsatellite instability and mismatch repair target gene
mutations in cell lines and xenografts of prostate cancer.
Prostate. 66:660–666. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xiao X, Melton DW and Gourley C: Mismatch
repair deficiency in ovarian cancer - molecular characteristics and
clinical implications. Gynecol Oncol. 132:506–512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Heinen CD: Genotype to phenotype:
analyzing the effects of inherited mutations in colorectal cancer
families. Mutat Res. 693:32–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Nunn J, Nagini S, Risk JM, Prime W,
Maloney P, Liloglou T, Jones AS, Rogers SR, Gosney JR, Woolgar J
and Field JK: Allelic imbalance at the DNA mismatch repair loci,
hMSH2, hMLH1, hPMS1, hPMS2 and hMSH3, in squamous cell carcinoma of
the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 39:115–129. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Sun D, Van N, Tang A, Hu L and
Huang G: Inactivation of RASSF2A by promoter methylation correlates
with lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 120:32–38. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Huang XM, Dai CB, Mou ZL, Wang LJ, Wen WP,
Lin SG, Xu G and Li HB: Overproduction of cyclin D1 is dependent on
activated mTORC1 signal in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: implication
for therapy. Cancer Lett. 279:47–56. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Olek A, Oswald J and Walter J: A modified
and improved method for bisulphite based cytosine methylation
analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 24:5064–5066. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vymetalkova VP, Slyskova J, Korenkova V,
Bielik L, Langerova L, Prochazka P, Rejhova A, Schwarzova L,
Pardini B, Naccarati A and Vodicka P: Molecular characteristics of
mismatch repair genes in sporadic colorectal tumors in Czech
patients. BMC Med Genet. 15:172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Conde J, Silva SN, Azevedo AP, Teixeira V,
Pina JE, Rueff J and Gaspar JF: Association of common variants in
mismatch repair genes and breast cancer susceptibility: a multigene
study. BMC Cancer. 9:3442009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jafary F, Salehi M, Sedghi M, Nouri N,
Jafary F, Sadeghi F, Motamedi S and Talebi M: Association between
mismatch repair gene MSH3 codons 1036 and 222 polymorphisms and
sporadic prostate cancer in the Iranian population. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 13:6055–6057. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Kawamoto K, Kikuno N,
Suehiro Y, Okayama N, Tanaka Y and Dahiya R: Mismatch repair gene
MSH3 polymorphism is associated with the risk of sporadic prostate
cancer. J Urol. 179:2020–2024. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Michiels S, Danoy P, Dessen P, Bera A,
Boulet T, Bouchardy C, Lathrop M, Sarasin A and Benhamou S:
Polymorphism discovery in 62 DNA repair genes and haplotype
associations with risks for lung and head and neck cancers.
Carcinogenesis. 28:1731–1739. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Koessler T, Azzato EM, Perkins B, Macinnis
RJ, Greenberg D, Easton DF and Pharoah PD: Common germline
variation in mismatch repair genes and survival after a diagnosis
of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 124:1887–1891. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Dong X, Li Y, Hess KR, Abbruzzese JL and
Li D: DNA mismatch repair gene polymorphisms affect survival in
pancreatic cancer. Oncologist. 16:61–70. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Verma M, Maruvada P and Srivastava S:
Epigenetics and cancer. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 41:585–607. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|