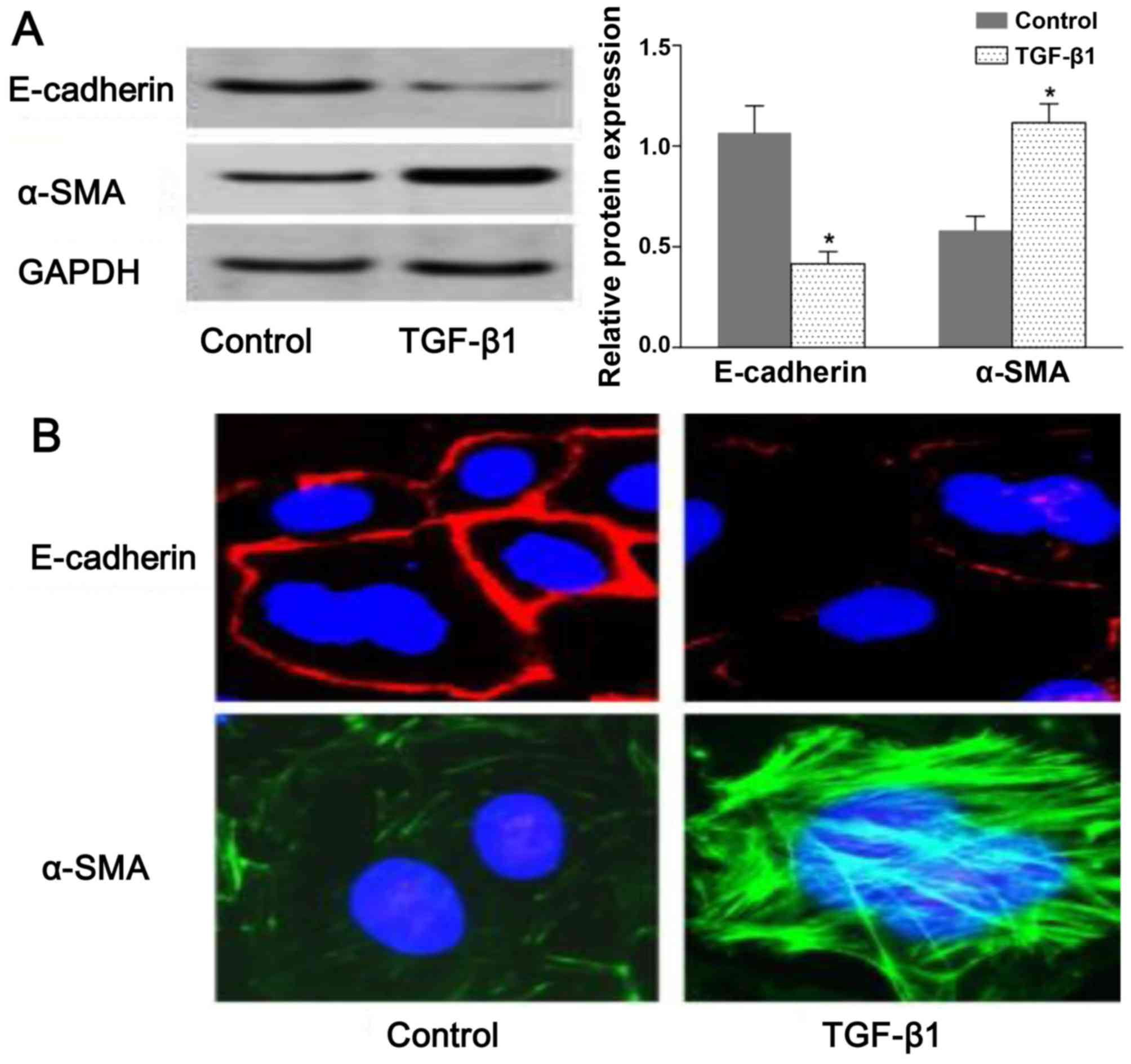
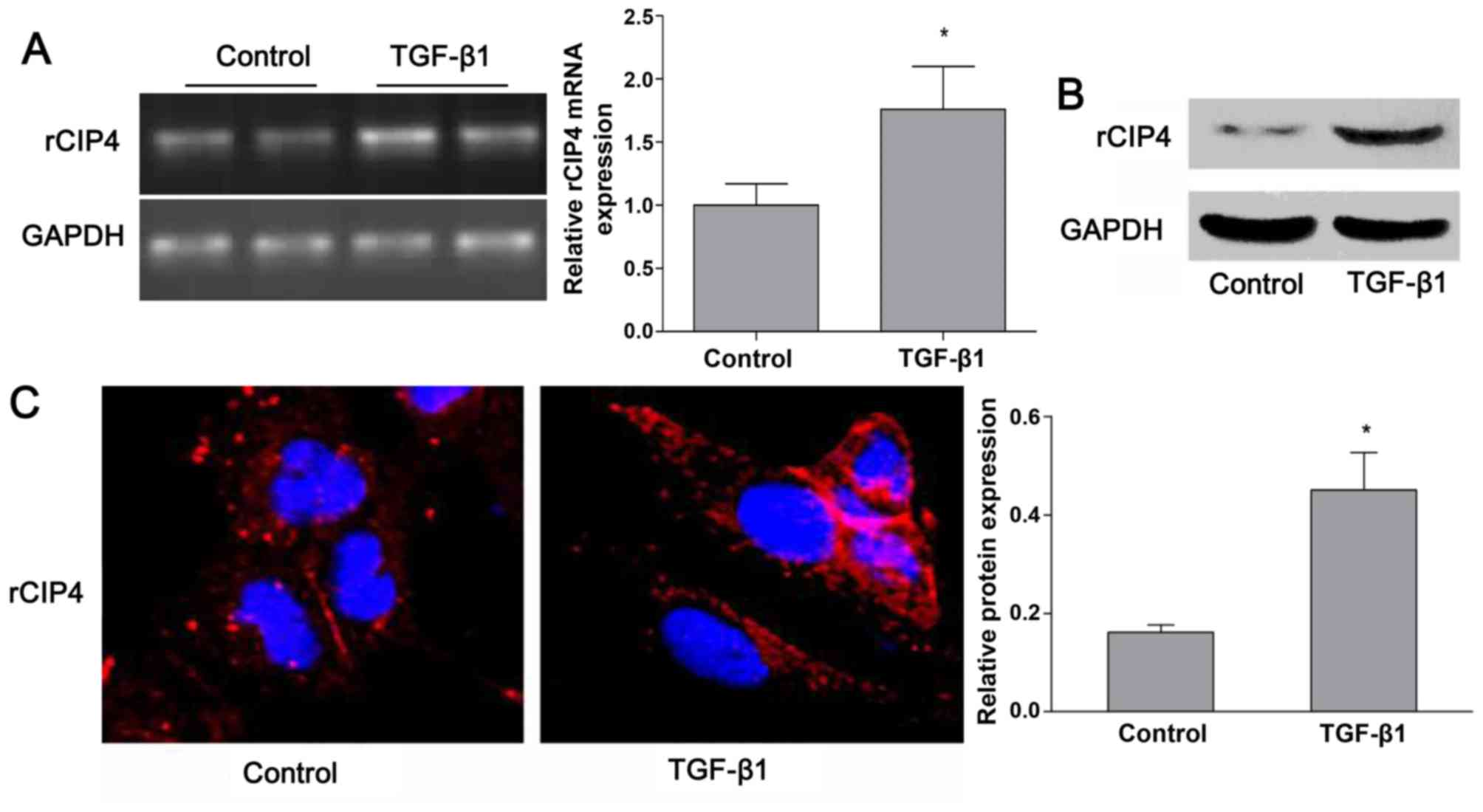
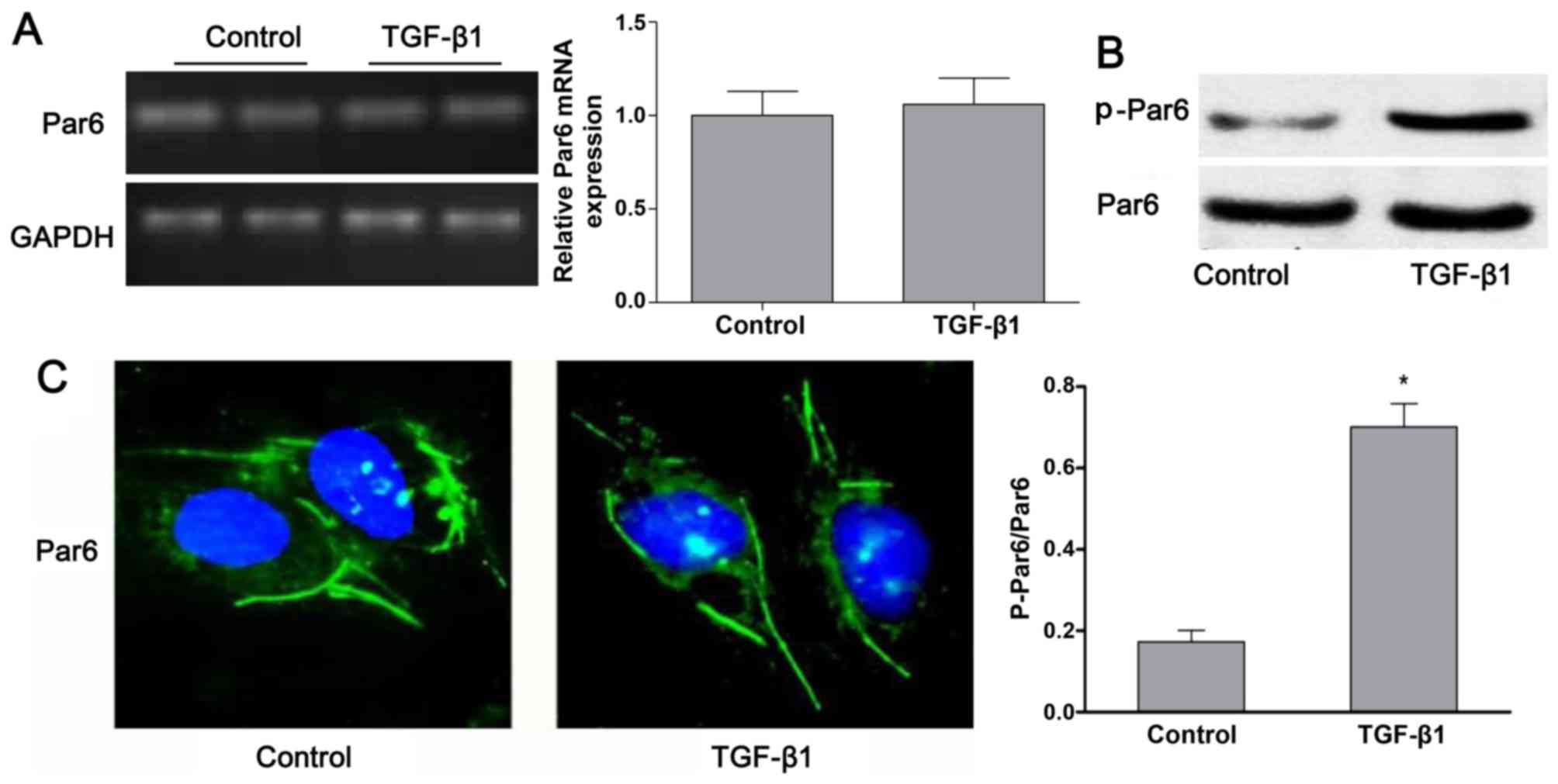
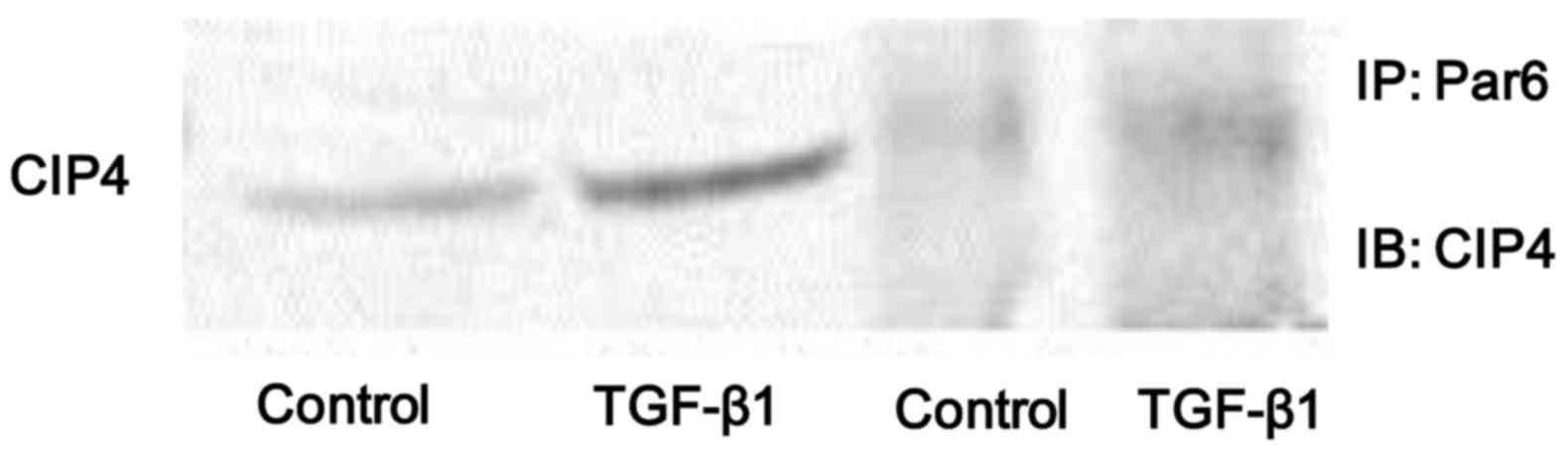
|
1
|
Baum B, Settleman J and Quinlan MP:
Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states in
development and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 19:294–308. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chua KN, Poon KL, Lim J, Sim WJ, Huang RY
and Thiery JP: Target cell movement in tumor and cardiovascular
diseases based on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition concept.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 63:558–567. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Simic P, Williams EO, Bell EL, Gong JJ,
Bonkowski M and Guarente L: SIRT1 suppresses the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis and organ
fibrosis. Cell Reports. 3:1175–1186. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guarino M, Tosoni A and Nebuloni M: Direct
contribution of epithelium to organ fibrosis:
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Hum Pathol. 40:1365–1376. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhao D, Besser AH, Wander SA, Sun J, Zhou
W, Wang B, Ince T, Durante MA, Guo W, Mills G, et al: Cytoplasmic
p27 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis
via STAT3-mediated Twist1 upregulation. Oncogene. 43:5447–5459.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ma J, Fang B, Zeng F, Ma C, Pang H, Cheng
L, Shi Y, Wang H, Yin B, Xia J, et al: Down-regulation of miR-223
reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant
pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget. 6:1740–1749. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chung H, Choi HS, Seo EK, Kang DH and Oh
ES: Baicalin and baicalein inhibit transforming growth
factor-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human
breast epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 458:707–713.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Liu N, Su X, Zhou G, Sun G, Du F,
Bian X and Wang B: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates
transforming growth factor-beta1 induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via Nrf2 regulation in renal tubular epithelial cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 70:260–267. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Piek E, Moustakas A, Kurisaki A, Heldin CH
and ten Dijke P: TGF-(beta) type I receptor/ALK-5 and Smad proteins
mediate epithelial to mesenchymal transdifferentiation in NMuMG
breast epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 112:4557–4568. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bae E, Kim SJ, Hong S, Liu F and Ooshima
A: Smad3 linker phosphorylation attenuates Smad3 transcriptional
activity and TGF-β1/Smad3-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in renal epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 427:593–599.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meng XM, Huang XR, Chung AC, Qin W, Shao
X, Igarashi P, Ju W, Bottinger EP and Lan HY: Smad2 protects
against TGF-beta/Smad3-mediated renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
21:1477–1487. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang YE: Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta
signaling. Cell Res. 19:128–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Avery-Cooper G, Doerr M, Gilbert RW,
Youssef M, Richard A, Huether P and Viloria-Petit AM: Par6 is an
essential mediator of apoptotic response to transforming growth
factor beta in NMuMG immortalized mammary cells. Cancer Cell Int.
14:192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ozdamar B, Bose R, Barrios-Rodiles M, Wang
HR, Zhang Y and Wrana JL: Regulation of the polarity protein Par6
by TGFbeta receptors controls epithelial cell plasticity. Science.
307:1603–1609. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Viloria-Petit AM, David L, Jia JY, Erdemir
T, Bane AL, Pinnaduwage D, Roncari L, Narimatsu M, Bose R, Moffat
J, et al: A role for the TGFbeta-Par6 polarity pathway in breast
cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:14028–14033. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai S, Zeng R, Zhou Q, Liao W, Zhang Y, Xu
C, Han M, Pei G, Liu L, Liu X, et al: Cdc42-interacting protein-4
promotes TGF-B1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
extracellular matrix deposition in renal proximal tubular
epithelial cells. Int J Biol Sci. 8:859–869. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Leibfried A, Fricke R, Morgan MJ, Bogdan S
and Bellaiche Y: Drosophila Cip4 and WASp define a branch of the
Cdc42-Par6-aPKC pathway regulating E-cadherin endocytosis. Curr
Biol. 18:1639–1648. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wirtz-Peitz F and Zallen JA: Junctional
trafficking and epithelial morphogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
19:350–356. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu H and Bilder D: Endocytic control of
epithelial polarity and proliferation in Drosophila. Nat Cell Biol.
7:1232–1239. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Aspenström P: A Cdc42 target protein with
homology to the non-kinase domain of FER has a potential role in
regulating the actin cytoskeleton. Curr Biol. 7:479–487. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu J, Kimura A, Baumann CA and Saltiel
AR: APS facilitates c-Cbl tyrosine phosphorylation and GLUT4
translocation in response to insulin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell
Biol. 22:3599–3609. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang D, He C, Stoykovich MP and Schwartz
DK: Nanoscale topography influences polymer surface diffusion. ACS
Nano. 9:1656–1664. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu C, Zhou Q, Liu L, Liu P, Pei G, Zeng R,
Han M and Xu G: Cdc42-interacting protein 4 represses E-Cadherin
expression by promoting β-Catenin translocation to the nucleus in
murine renal tubular epithelial cells. Int J Mol Sci.
16:19170–19183. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng G, Lyons JG, Tan TK, Wang Y, Hsu TT,
Min D, Succar L, Rangan GK, Hu M, Henderson BR, et al: Disruption
of E-cadherin by matrix metalloproteinase directly mediates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition downstream of transforming growth
factor-beta1 in renal tubular epithelial cells. Am J Pathol.
175:580–591. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gunaratne A and Di Guglielmo GM: Par6 is
phosphorylated by aPKC to facilitate EMT. Cell Adhes Migr.
7:357–361. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Nolan ME, Aranda V, Lee S, Lakshmi B, Basu
S, Allred DC and Muthuswamy SK: The polarity protein Par6 induces
cell proliferation and is overexpressed in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 68:8201–8209. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ruan L, Shen Y, Lu Z, Shang D, Zhao Z, Lu
Y, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Tu Z and Liu H: Roles of partitioning-defective
protein 6 (Par6) and its complexes in the proliferation, migration
and invasion of cancer cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
44:909–913. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gunaratne A, Thai BL and Di Guglielmo GM:
Atypical protein kinase C phosphorylates Par6 and facilitates
transforming growth factor β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Mol Cell Biol. 33:874–886. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|