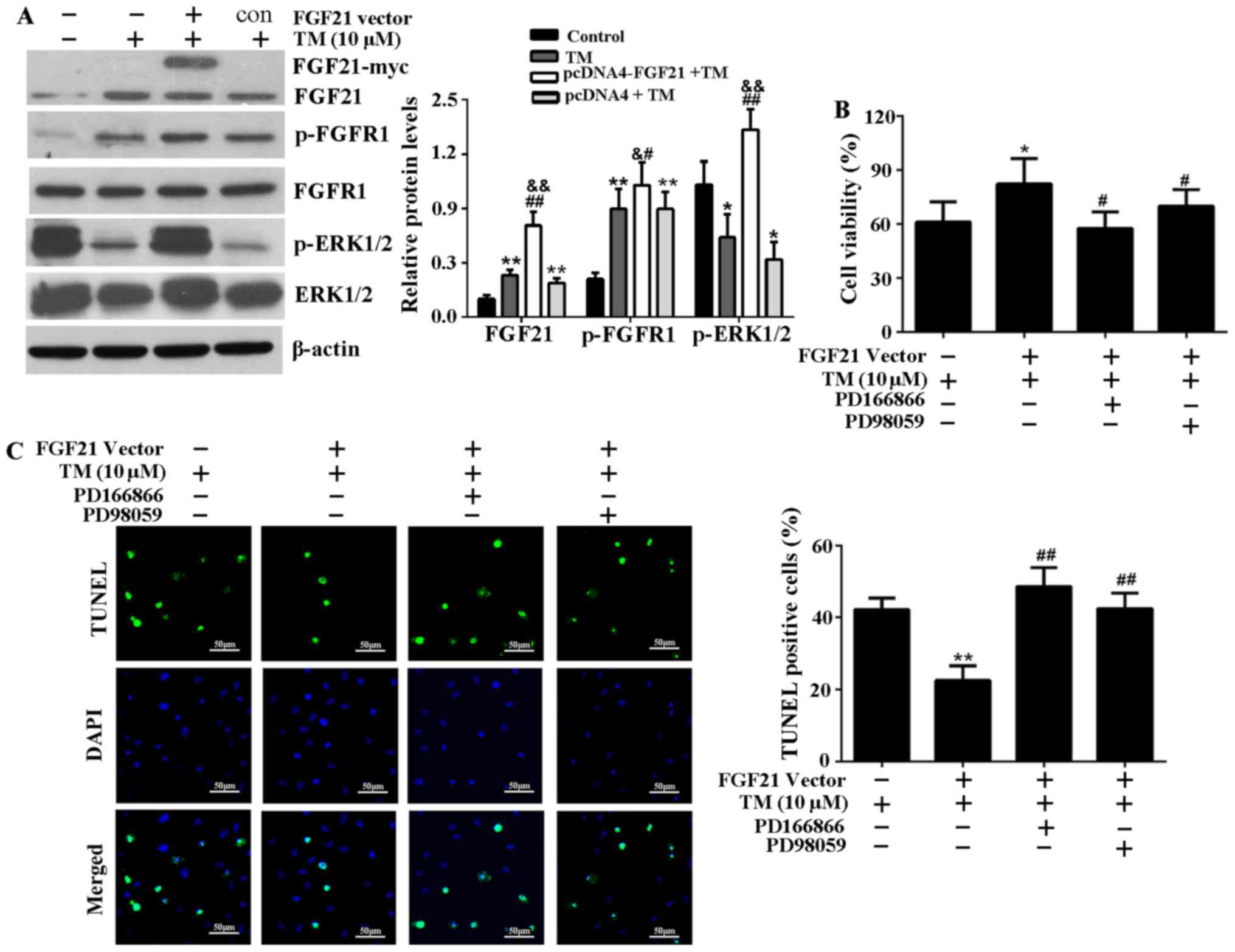
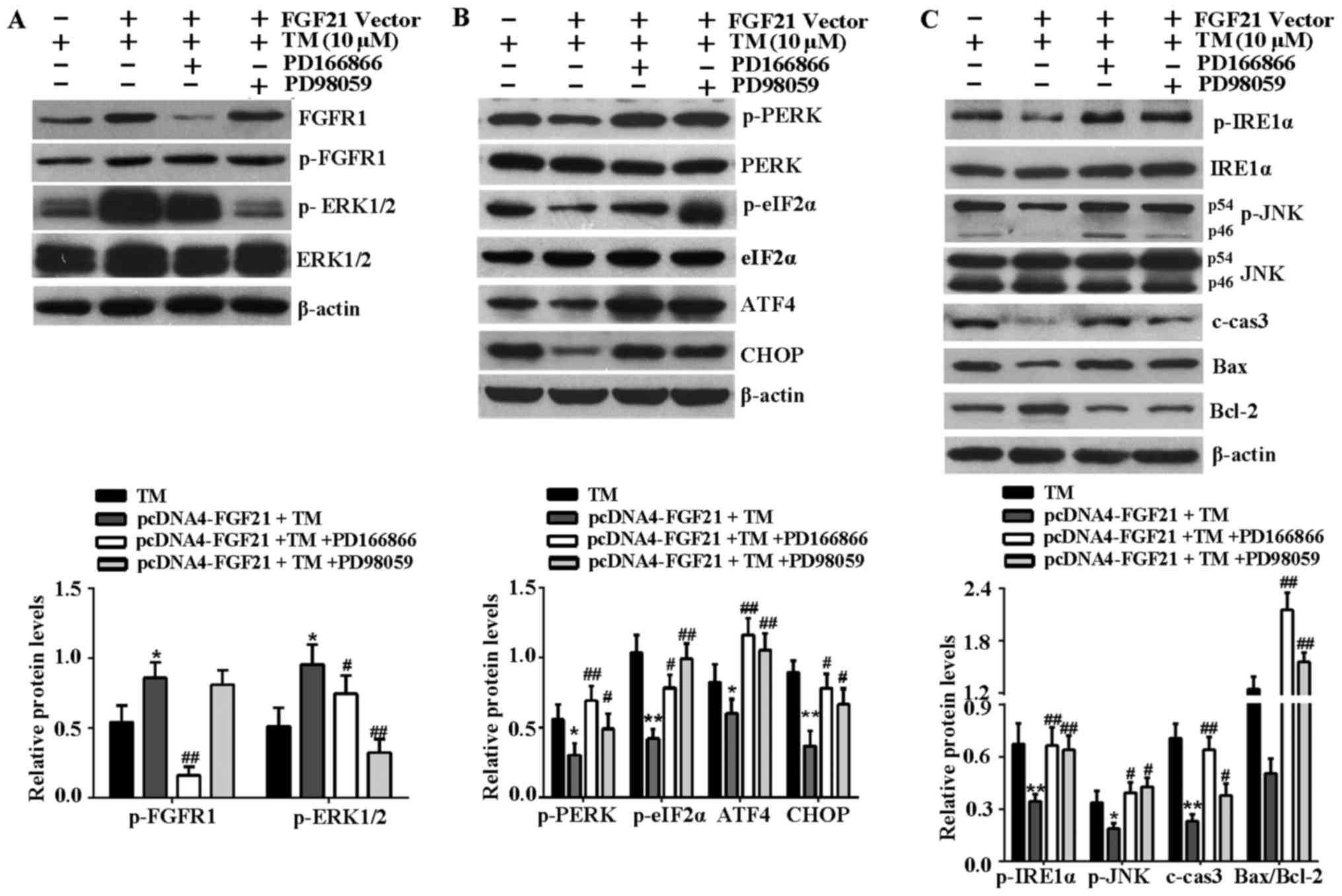
|
1
|
Kharitonenkov A, Shiyanova TL, Koester A,
Ford AM, Micanovic R, Galbreath EJ, Sandusky GE, Hammond LJ, Moyers
JS, Owens RA, et al: FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J Clin
Invest. 115:1627–1635. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fon Tacer K, Bookout AL, Ding X, Kurosu H,
John GB, Wang L, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Kuro-o M, Mangelsdorf DJ, et
al: Research resource: Comprehensive expression atlas of the
fibroblast growth factor system in adult mouse. Mol Endocrinol.
24:2050–2064. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ogawa Y, Kurosu H, Yamamoto M, Nandi A,
Rosenblatt KP, Goetz R, Eliseenkova AV, Mohammadi M and Kuro-o M:
BetaKlotho is required for metabolic activity of fibroblast growth
factor 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:7432–7437. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Foltz IN, Hu S, King C, Wu X, Yang C, Wang
W, Weiszmann J, Stevens J, Chen JS, Nuanmanee N, et al: Treating
diabetes and obesity with an FGF21-mimetic antibody activating the
βKlotho/FGFR1c receptor complex. Sci Transl Med. 4:162ra1532012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liu SQ, Roberts D, Kharitonenkov A, Zhang
B, Hanson SM, Li YC, Zhang LQ and Wu YH: Endocrine protection of
ischemic myocardium by FGF21 from the liver and adipose tissue. Sci
Rep. 3:27672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shen Y, Ma X, Zhou J, Pan X, Hao Y, Zhou
M, Lu Z, Gao M, Bao Y and Jia W: Additive relationship between
serum fibroblast growth factor 21 level and coronary artery
disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 12:1242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang W, Chu S, Ding W and Wang F: Serum
level of fibroblast growth factor 21 is independently associated
with acute myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 10:e01297912015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Di Lisa F and Itoh N: Cardiac Fgf21
synthesis and release: An autocrine loop for boosting up
antioxidant defenses in failing hearts. Cardiovasc Res. 106:1–3.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lü Y, Liu JH, Zhang LK, Du J, Zeng XJ, Hao
G, Huang J, Zhao DH, Wang GZ and Zhang YC: Fibroblast growth factor
21 as a possible endogenous factor inhibits apoptosis in cardiac
endothelial cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 123:3417–3421. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Cong WT, Ling J, Tian HS, Ling R, Wang Y,
Huang BB, Zhao T, Duan YM, Jin LT and Li XK: Proteomic study on the
protective mechanism of fibroblast growth factor 21 to
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 91:973–984.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Walter P and Ron D: The unfolded protein
response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science.
334:1081–1086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Faitova J, Krekac D, Hrstka R and Vojtesek
B: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
11:488–505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chaudhari N, Talwar P, Parimisetty A,
Lefebvre d'Hellencourt C and Ravanan P: A molecular web:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation, and oxidative stress.
Front Cell Neurosci. 8:2132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee WK, Chakraborty PK, Roussa E, Wolff NA
and Thévenod F: ERK1/2-dependent bestrophin-3 expression prevents
ER-stress-induced cell death in renal epithelial cells by reducing
CHOP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1823:1864–1876. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y,
Chung P, Harding HP and Ron D: Coupling of stress in the ER to
activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase
IRE1. Science. 287:664–666. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Brozzi F, Gerlo S, Grieco FA, Juusola M,
Balhuizen A, Lievens S, Gysemans C, Bugliani M, Mathieu C,
Marchetti P, et al: Ubiquitin D regulates IRE1α/c-Jun N-terminal
kinase (JNK) protein-dependent apoptosis in pancreatic beta cells.
J Biol Chem. 291:12040–12056. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Joo H, Lee HJ, Shin EA, Kim H, Seo KH,
Baek NI, Kim B and Kim SH: c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent
endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway is critically involved in
arjunic acid Induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Phytother Res. 30:596–603. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Minamino T and Kitakaze M: ER stress in
cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 48:1105–1110. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Brahma MK, Adam RC, Pollak NM, Jaeger D,
Zierler KA, Pöcher N, Schreiber R, Romauch M, Moustafa T, Eder S,
et al: Fibroblast growth factor 21 is induced upon cardiac stress
and alters cardiac lipid homeostasis. J Lipid Res. 55:2229–2241.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hotamisligil GS: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress and atherosclerosis. Nat Med. 16:396–399. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kurian MV, Hamilton L, Keeven J, Mehl P
and Mullins JM: Enhanced cell survival and diminished apoptotic
response to simulated ischemia-reperfusion in H9c2 cells by
magnetic field preconditioning. Apoptosis. 17:1182–1196. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schaap FG, Kremer AE, Lamers WH, Jansen PL
and Gaemers IC: Fibroblast growth factor 21 is induced by
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochimie. 95:692–699. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Dong K, Li H, Zhang M, Jiang S, Chen S,
Zhou J, Dai Z, Fang Q and Jia W: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
induces up-regulation of hepatic β-Klotho expression through ATF4
signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 459:300–305. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang C, Lu T, Wang GD, Ma C and Zhou YF:
Costunolide, an active sesquiterpene lactone, induced apoptosis via
ROS-mediated ER stress and JNK pathway in human U2OS cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 80:253–259. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mhaidat NM, Thorne R, Zhang XD and Hersey
P: Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in Docetaxel-induced
JNK-dependent apoptosis of human melanoma. Apoptosis. 13:1505–1512.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen YJ, Su JH, Tsao CY, Hung CT, Chao HH,
Lin JJ, Liao MH, Yang ZY, Huang HH, Tsai FJ, et al: Sinulariolide
induced hepatocellular carcinoma apoptosis through activation of
mitochondrial-related apoptotic and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP pathway.
Molecules. 18:10146–10161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li K, Li L, Yang M, Liu H, Boden G and
Yang G: The effects of fibroblast growth factor-21 knockdown and
over-expression on its signaling pathway and glucose-lipid
metabolism in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 348:21–26. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lips DJ, Bueno OF, Wilkins BJ, Purcell NH,
Kaiser RA, Lorenz JN, Voisin L, Saba-El-Leil MK, Meloche S,
Pouysségur J, et al: MEK1-ERK2 signaling pathway protects
myocardium from ischemic injury in vivo. Circulation.
109:1938–1941. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bourke L, McCormick J, Taylor V,
Pericleous C, Blanchet B, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Stuckey D, Lythgoe
MF, Stephanou A and Ioannou Y: Hydroxychloroquine protects against
cardiac ischaemia/reperfusion injury in vivo via enhancement of
ERK1/2 phosphorylation. PLoS One. 10:e01437712015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang C, Jin C, Li X, Wang F, McKeehan WL
and Luo Y: Differential specificity of endocrine FGF19 and FGF21 to
FGFR1 and FGFR4 in complex with KLB. PLoS One. 7:e338702012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Z, Wang Y, Ye J, Lu X, Cheng Y, Xiang
L, Chen L, Feng W, Shi H, Yu X, et al: bFGF attenuates endoplasmic
reticulum stress and mitochondrial injury on myocardial
ischaemia/reperfusion via activation of PI3K/Akt/ERK1/2 pathway. J
Cell Mol Med. 19:595–607. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hu P, Han Z, Couvillon AD and Exton JH:
Critical role of endogenous Akt/IAPs and MEK1/ERK pathways in
counteracting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death. J
Biol Chem. 279:49420–49429. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang X, Zhang C, Xin Y, Huang Z, Tan Y,
Huang Y, Wang Y, Feng W, Li X, Li W, et al: Protective effect of
FGF21 on type 1 diabetes-induced testicular apoptotic cell death
probably via both mitochondrial- and endoplasmic reticulum
stress-dependent pathways in the mouse model. Toxicol Lett.
219:65–76. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|