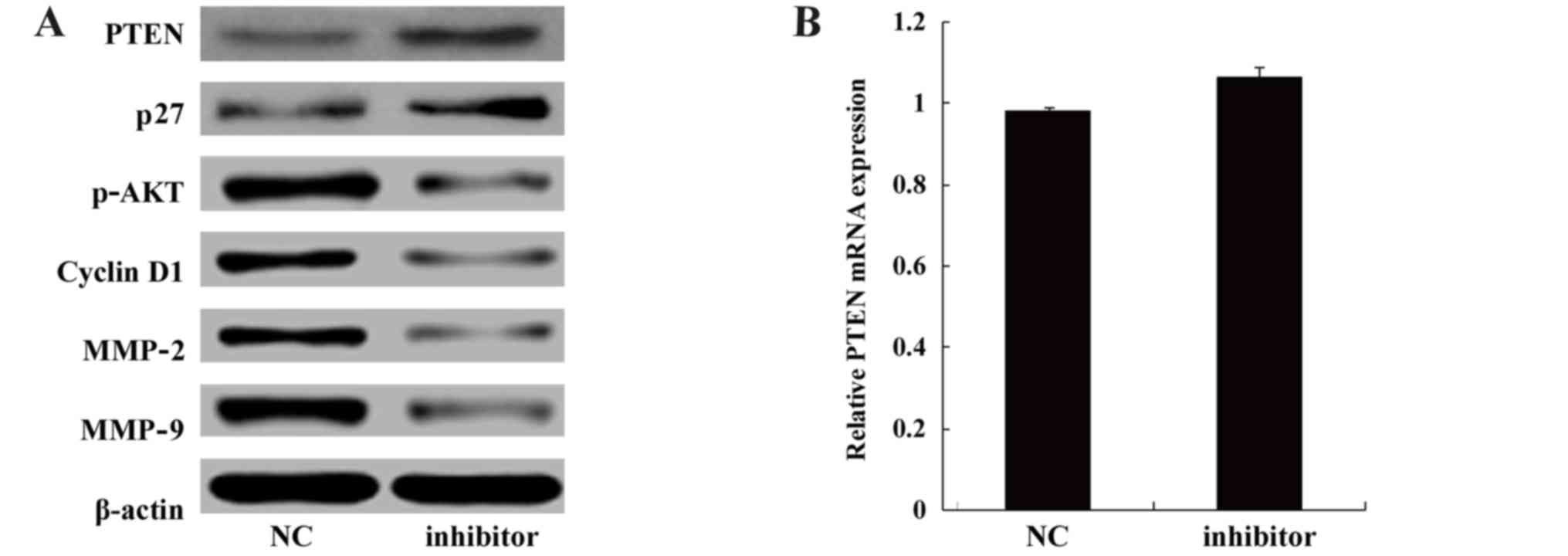
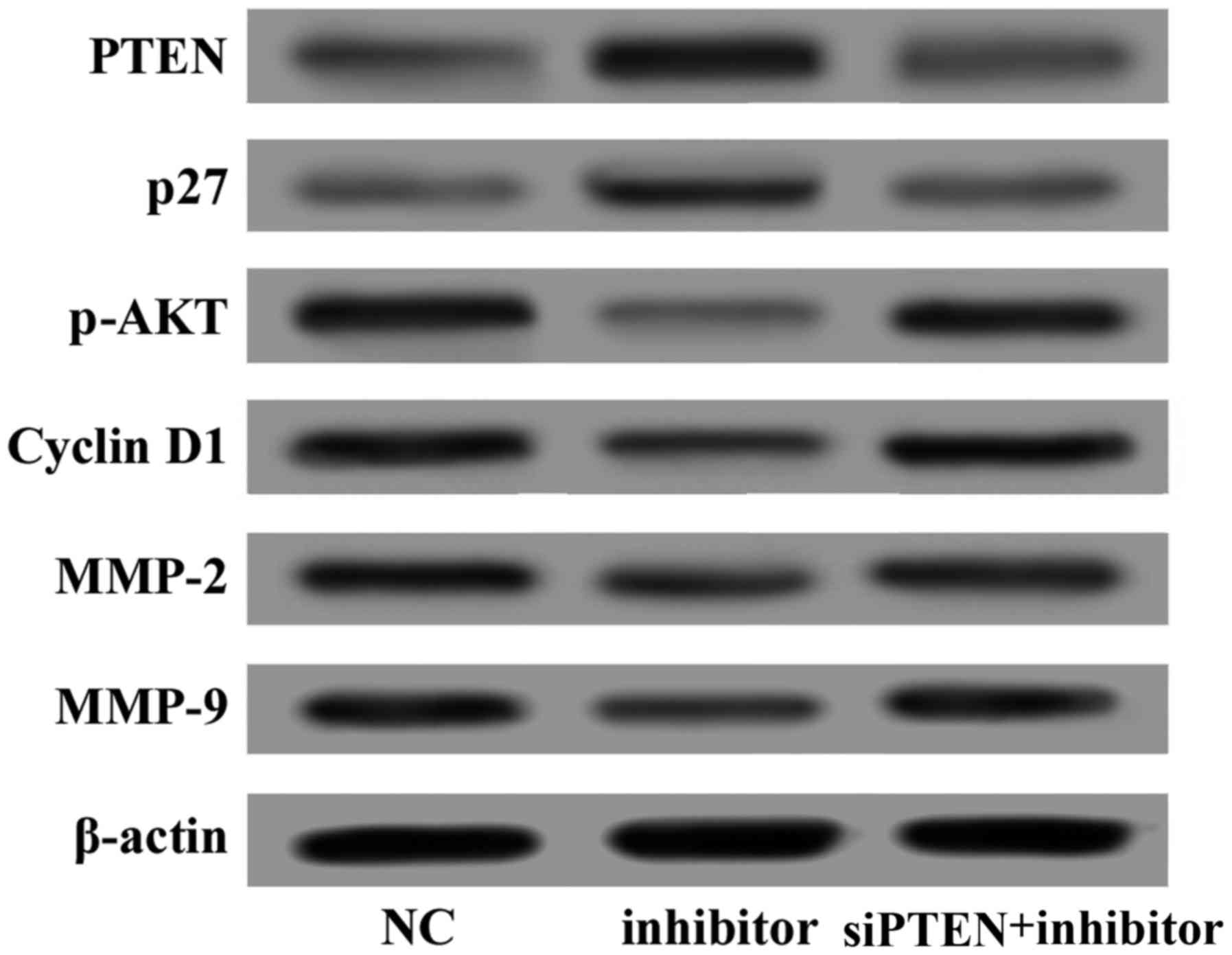
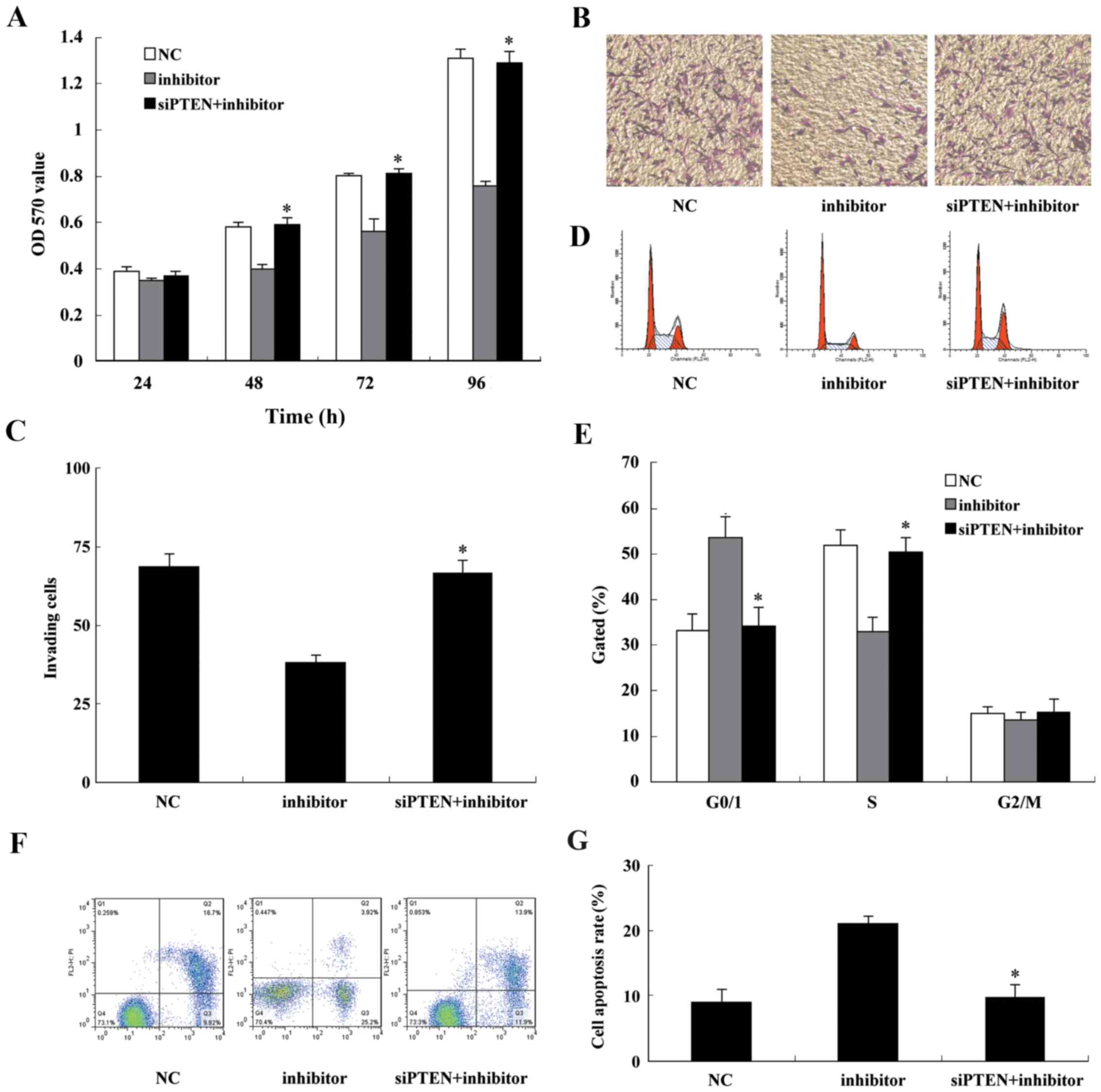
|
1
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Epidemiology and
etiology of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 109:93–108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou X, Ren Y, Moore L, Mei M, You Y, Xu
P, Wang B, Wang G, Jia Z, Pu P, et al: Downregulation of miR-21
inhibits EGFR pathway and suppresses the growth of human
glioblastoma cells independent of PTEN status. Lab Invest.
90:144–155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu Y, Yan W, Zhang W, Chen L, You G, Bao
Z, Wang Y, Wang H, Kang C and Jiang T: miR-218 reverses high
invasiveness of glioblastoma cells by targeting the oncogenic
transcription factor LEF1. Oncol Rep. 28:1013–1021. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gu JJ, Gao GZ and Zhang SM: miR-218
inhibits the migration and invasion of glioma U87 cells through the
Slit2-Robo1 pathway. Oncol Lett. 9:1561–1566. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang L, Wang C, Lei F, Zhang L, Zhang X,
Liu A, Wu G, Zhu J and Song L: miR-93 promotes cell proliferation
in gliomas through activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Oncotarget. 6:8286–8299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Borgdorff V, Lleonart ME, Bishop CL,
Fessart D, Bergin AH, Overhoff MG and Beach DH: Multiple microRNAs
rescue from Ras-induced senescence by inhibiting p21(Waf1/Cip1).
Oncogene. 29:2262–2271. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dong P, Karaayvaz M, Jia N, Kaneuchi M,
Hamada J, Watari H, Sudo S, Ju J and Sakuragi N: Mutant p53
gain-of-function induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
modulation of the miR-130b-ZEB1 axis. Oncogene. 32:3286–3295. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Malzkorn B, Wolter M, Liesenberg F,
Grzendowski M, Stühler K, Meyer HE and Reifenberger G:
Identification and functional characterization of microRNAs
involved in the malignant progression of gliomas. Brain Pathol.
20:539–550. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yu T, Cao R, Li S, Fu M, Ren L, Chen W,
Zhu H, Zhan Q and Shi R: MiR-130b plays an oncogenic role by
repressing PTEN expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
cells. BMC Cancer. 15:292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y and Jiang T: Understanding high
grade glioma: molecular mechanism, therapy and comprehensive
management. Cancer Lett. 331:139–146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carlsson SK, Brothers SP and Wahlestedt C:
Emerging treatment strategies for glioblastoma multiforme. EMBO Mol
Med. 6:1359–1370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li R and Li X, Ning S, Ye J, Han L, Kang C
and Li X: Identification of a core miRNA-pathway regulatory network
in glioma by therap eutically targeting miR-181d, miR-21, miR-23b,
β-catenin, CBP, and STAT3. PLoS One. 9:e1019032014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jun GJ, Zhong GG and Ming ZS: miR-218
inhibits the proliferation of glioma U87 cells through the
inactivation of the CDK6/cyclin D1/p21Cip1/Waf1 pathway.
Oncol Lett. 9:2743–2749. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Lee EK, Lee MJ, Abdelmohsen K, Kim W, Kim
MM, Srikantan S, Martindale JL, Hutchison ER, Kim HH, Marasa BS, et
al: miR-130 suppresses adipogenesis by inhibiting peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma expression. Mol Cell Biol.
31:626–638. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sand M, Skrygan M, Sand D, Georgas D,
Gambichler T, Hahn SA, Altmeyer P and Bechara FG: Comparative
microarray analysis of microRNA expression profiles in primary
cutaneous malignant melanoma, cutaneous malignant melanoma
metastases, and benign melanocytic nevi. Cell Tissue Res.
351:85–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lai KW, Koh KX, Loh M, Tada K, Subramaniam
MM, Lim XY, Vaithilingam A, Salto-Tellez M, Iacopetta B, Ito Y, et
al: Singapore Gastric Cancer Consortium: MicroRNA-130b regulates
the tumour suppressor RUNX3 in gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer.
46:1456–1463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Scheffer AR, Holdenrieder S, Kristiansen
G, von Ruecker A, Müller SC and Ellinger J: Circulating microRNAs
in serum: novel biomarkers for patients with bladder cancer. World
J Urol. 32:353–358. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Colangelo T, Fucci A, Votino C, Sabatino
L, Pancione M, Laudanna C, Binaschi M, Bigioni M, Maggi CA, Parente
D, et al: MicroRNA-130b promotes tumor development and is
associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Neoplasia.
15:1218–1231. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu X, Weng L, Li X, Guo C, Pal SK, Jin JM,
Li Y, Nelson RA, Mu B, Onami SH, et al: Identification of a
4-microRNA signature for clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis
and prognosis. PLoS One. 7:e356612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yip L, Kelly L, Shuai Y, Armstrong MJ,
Nikiforov YE, Carty SE and Nikiforova MN: MicroRNA signature
distinguishes the degree of aggressiveness of papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2035–2041. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leone V, Langella C, D'Angelo D, Mussnich
P, Wierinckx A, Terracciano L, Raverot G, Lachuer J, Rotondi S,
Jaffrain-Rea ML, et al: miR-23b and miR-130b expression is
downregulated in pituitary adenomas. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 390:1–7.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao G, Zhang JG, Shi Y, Qin Q, Liu Y,
Wang B, Tian K, Deng SC, Li X, Zhu S, et al: miR-130b is a
prognostic marker and inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in
pancreatic cancer through targeting STAT3. PLoS One. 8:e738032013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shacka JJ, Roth KA and Zhang J: The
autophagy-lysosomal degradation pathway: role in neurodegenerative
disease and therapy. Front Biosci. 13:718–736. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tu K, Zheng X, Dou C, Li C, Yang W, Yao Y
and Liu Q: MicroRNA-130b promotes cell aggressiveness by inhibiting
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 15:20486–20499. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen Z, Trotman LC, Shaffer D, Lin HK,
Dotan ZA, Niki M, Koutcher JA, Scher HI, Ludwig T, Gerald W, et al:
Crucial role of p53-dependent cellular senescence in suppression of
Pten-deficient tumorigenesis. Nature. 436:725–730. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sansal I and Sellers WR: The biology and
clinical relevance of the PTEN tumor suppressor pathway. J Clin
Oncol. 22:2954–2963. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chung JH and Eng C: Nuclear-cytoplasmic
partitioning of phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on
chromosome 10 (PTEN) differentially regulates the cell cycle and
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 65:8096–8100. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamada KM and Araki M: Tumor suppressor
PTEN: modulator of cell signaling, growth, migration and apoptosis.
J Cell Sci. 114:2375–2382. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|