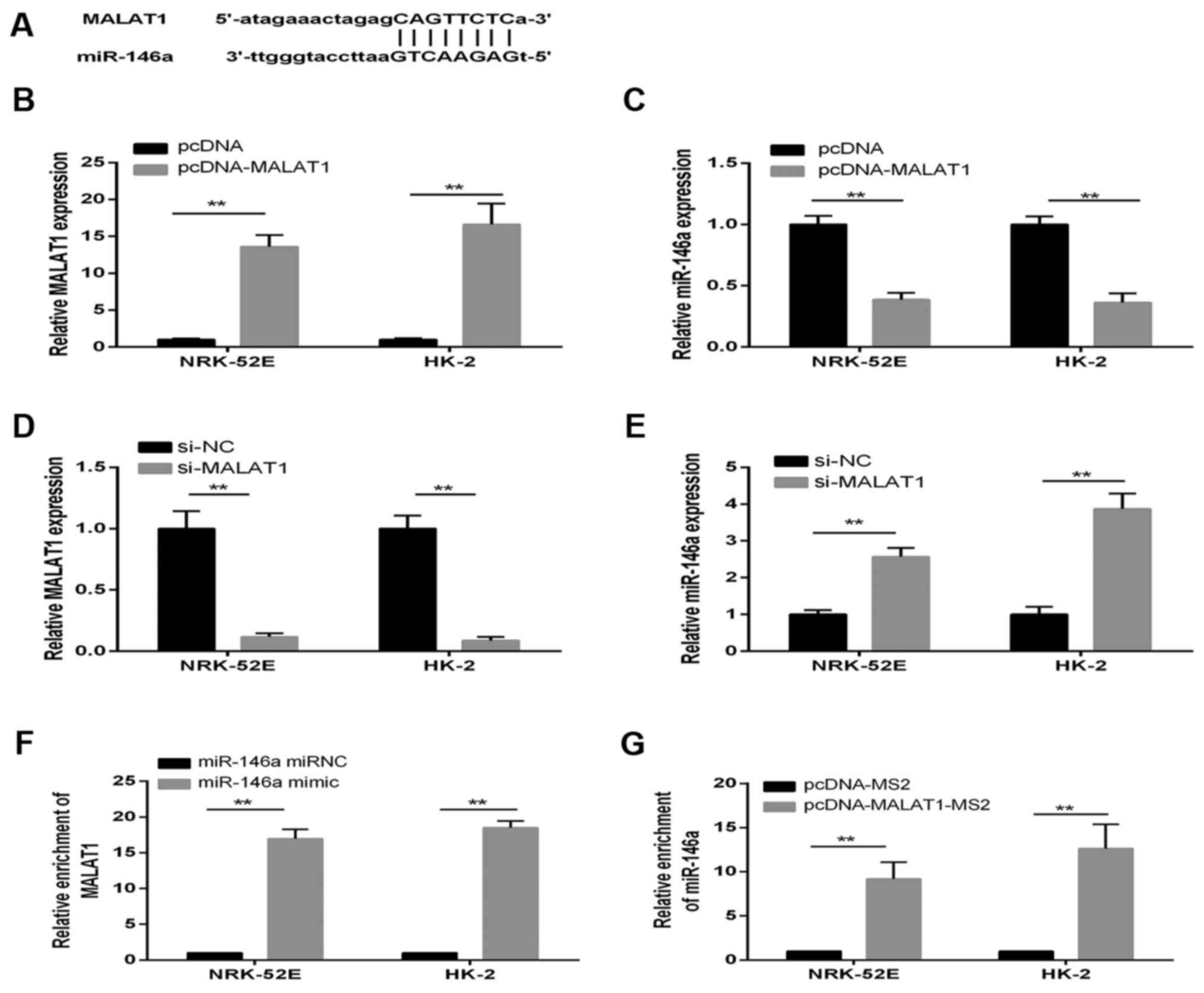
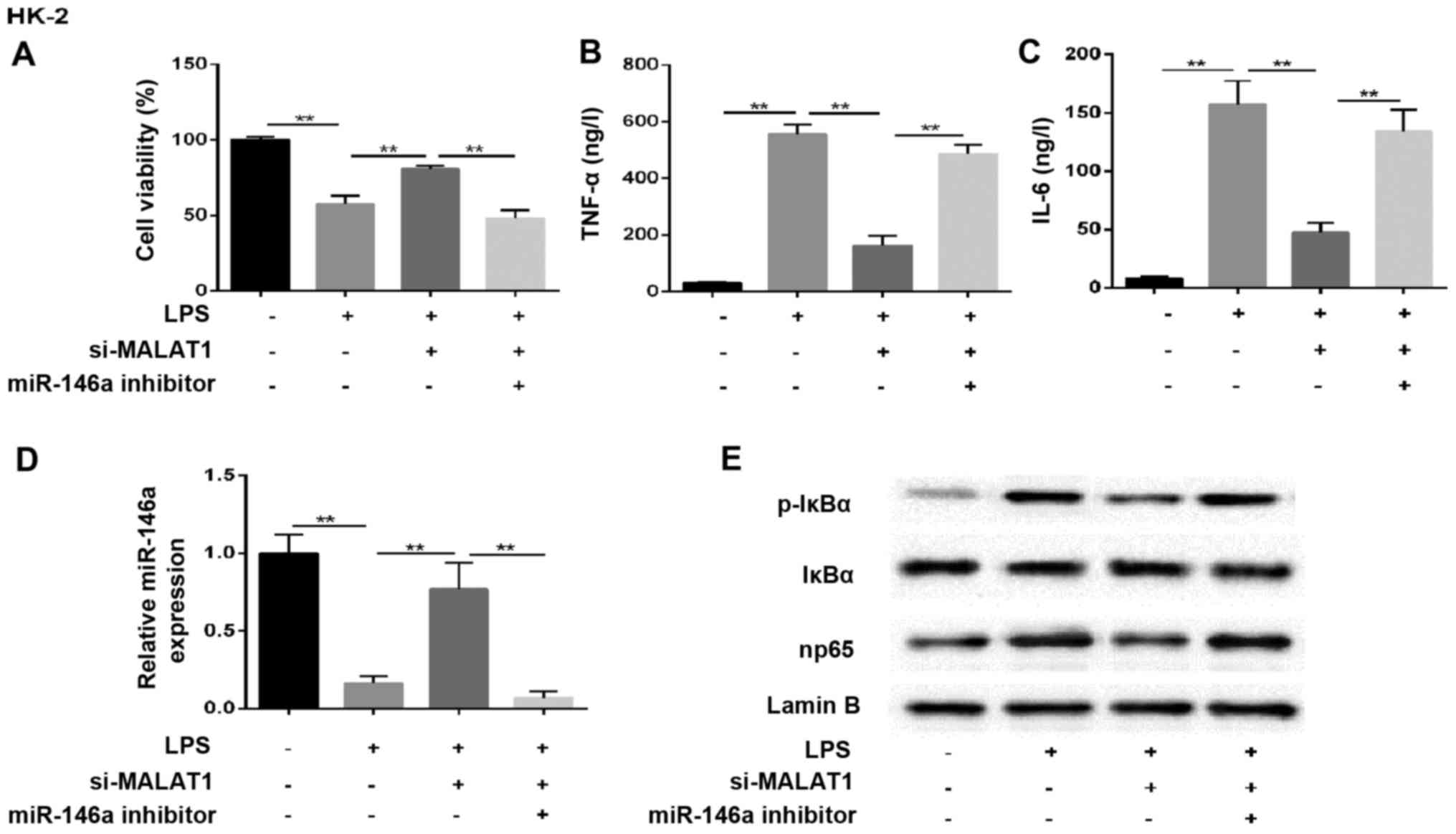
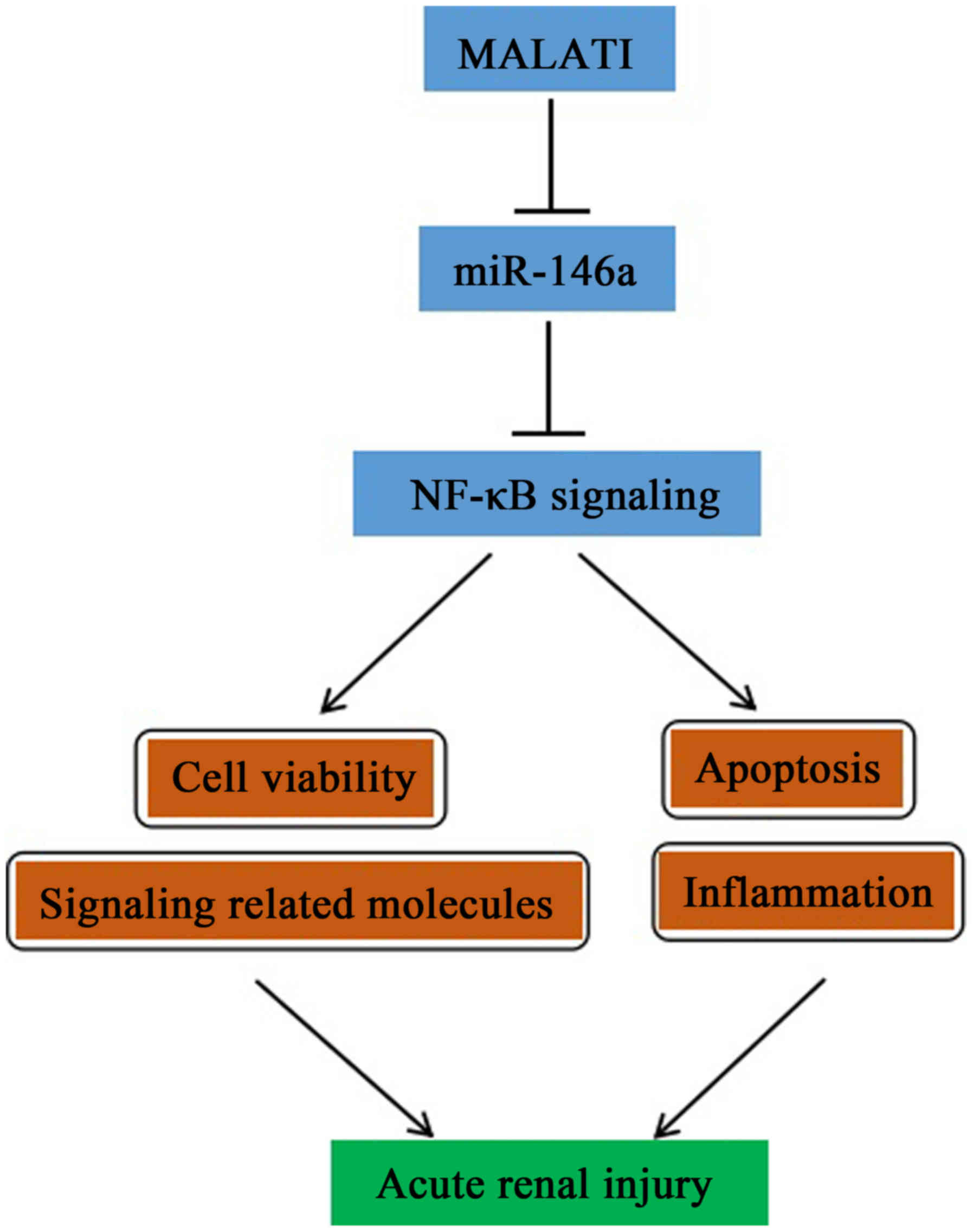
|
1
|
Segev G, Langston C, Takada K, Kass PH and
Cowgill LD: Validation of a clinical scoring system for outcome
prediction in dogs with acute kidney injury managed by
hemodialysis. J Vet Intern Med. 30:803–807. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Angeli P, Tonon M, Pilutti C, Morando F
and Piano S: Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury in patients with
cirrhosis. Hepatol Int. 10:115–123. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Linkermann A: Nonapoptotic cell death in
acute kidney injury and transplantation. Kidney Int. 89:46–57.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pistolesi V, Di Napoli A, Fiaccadori E,
Zeppilli L, Polistena F, Sacco MI, Regolisti G, Tritapepe L,
Pierucci A and Morabito S: Severe acute kidney injury following
cardiac surgery: short-term outcomes in patients undergoing
continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). J Nephrol. 29:229–239.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chalikias G, Drosos I and Tziakas DN:
Prevention of contrast-induced acute kidney injury: an update.
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 30:515–524. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu D, Chen M, Ren X, Ren X and Wu Y:
Leonurine ameliorates LPS-induced acute kidney injury via
suppressing ROS-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway. Fitoterapia.
97:148–155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kawara M, Matsunaga R, Yamamoto Y, Yoneda
G, Fujino R, Nishi K, Jono H and Saito H: Nephropreventive effect
of shikonin on murine LPS-induced septic acute kidney injury via
Nrf2 activation with antioxidative responses. J Clin Exp Nephrol.
1:192016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Heemskerk S, Masereeuw R, Russel FG and
Pickkers P: Selective iNOS inhibition for the treatment of
sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol. 5:629–640.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao G, Su Z, Song D, Mao Y and Mao X: The
long noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates the lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory response through its interaction with NF-κB. FEBS
Lett. 590:2884–2895. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Frixa T, Donzelli S and Blandino G:
Oncogenic microRNAs: key players in malignant transformation.
Cancers (Basel). 7:2466–2485. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Cheng HS, Sivachandran N, Lau A, Boudreau
E, Zhao JL, Baltimore D, Delgado-Olguin P, Cybulsky MI and Fish JE:
MicroRNA-146 represses endothelial activation by inhibiting
pro-inflammatory pathways. EMBO Mol Med. 5:1017–1034. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12481–12486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao JL, Rao DS, Boldin MP, Taganov KD,
O'Connell RM and Baltimore D: NF-kappaB dysregulation in
microRNA-146a-deficient mice drives the development of myeloid
malignancies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:9184–9189. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li K, Ching D, Luk FS and Raffai R:
Abstract 155: Micro-RNA-146a suppression of NF-κB-driven
monocyte/macrophage activation and atherosclerosis is regulated by
cellular ApoE expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
35:A1552015.
|
|
15
|
Yousefzadeh N, Alipour MR and Soufi FG:
Deregulation of NF-κB-miR-146a negative feedback loop may be
involved in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. J Physiol
Biochem. 71:51–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang YA, Chen X, You ZH, Huang DS and
Chan KC: ILNCSIM: improved lncRNA functional similarity calculation
model. Oncotarget. 7:25902–25914. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gong W, Zheng J, Liu X, Ma J, Liu Y and
Xue Y: Knockdown of NEAT1 restrained the malignant progression of
glioma stem cells by activating microRNA let-7e. Oncotarget.
7:62208–62223. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu TM, Palanisamy K, Sun KT, Day YJ, Shu
KH, Wang IK, Shyu WC, Chen P, Chen YL and Li CY: RANTES mediates
kidney ischemia reperfusion injury through a possible role of
HIF-1α and lncRNA PRINS. Sci Rep. 6:184242016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shao K, Shi T, Yang Y, Wang X, Xu D and
Zhou P: Highly expressed lncRNA CRNDE promotes cell proliferation
through Wnt/β-catenin signaling in renal cell carcinoma. Tumour
Biol. Oct 6–2016.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang L, Cai Y, Zhao X, Jia X, Zhang J, Liu
J, Zhen H, Wang T, Tang X, Liu Y, et al: Down-regulated long
non-coding RNA H19 inhibits carcinogenesis of renal cell carcinoma.
Neoplasma. 62:412–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang HM, Yang FQ, Chen SJ, Che J and
Zheng JH: Upregulation of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 correlates
with tumor progression and poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:2947–2955. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Nair AR, Masson GS, Ebenezer PJ, Del Piero
F and Francis J: Role of TLR4 in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
kidney injury: protection by blueberry. Free Radic Biol Med.
71:16–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shin S, Kim Y, Jeong S, Hong S, Kim I, Lee
W and Choi S: The therapeutic effect of human adult stem cells
derived from adipose tissue in endotoxemic rat model. Int J Med
Sci. 10:8–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qi M, Yin L, Xu L, Tao X, Qi Y, Han X,
Wang C, Xu Y, Sun H, Liu K, et al: Dioscin alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory kidney injury via the
microRNA let-7i/TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res.
111:509–522. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hei Z, Zhang A, Wei J, Gan X, Wang Y, Luo
G and Li X: Lipopolysaccharide effects on the proliferation of
NRK52E cells via alternations in gap-junction function. J Trauma
Acute Care Surg. 73:67–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Schrier RW, Wang W, Poole B and Mitra A:
Acute renal failure: definitions, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and
therapy. J Clin Invest. 114:5–14. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bihorac A, Baslanti TO, Cuenca AG, Hobson
CE, Ang D, Efron PA, Maier RV, Moore FA and Moldawer LL: Acute
kidney injury is associated with early cytokine changes after
trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 74:1005–1013. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Heyman SN, Khamaisi M, Rosen S and
Rosenberger C: In vivo models of acute kidney injury. Drug Discov
Today Dis Models. 7:51–56. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kurozumi A, Goto Y, Matsushita R, Fukumoto
I, Kato M, Nishikawa R, Sakamoto S, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, Ichikawa
T, et al: Tumor-suppressive microRNA-223 inhibits cancer cell
migration and invasion by targeting ITGA3/ITGB1 signaling in
prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 107:84–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ichii O, Otsuka S, Sasaki N, Namiki Y,
Hashimoto Y and Kon Y: Altered expression of microRNA miR-146a
correlates with the development of chronic renal inflammation.
Kidney Int. 81:280–292. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M:
Functional interactions among microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 34:9–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cao Y, Xu R, Xu X, Zhou Y, Cui L and He X:
Downregulation of lncRNA CASC2 by microRNA-21 increases the
proliferation and migration of renal cell carcinoma cells. Mol Med
Rep. 14:1019–1025. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chiyomaru T, Fukuhara S, Saini S, Majid S,
Deng G, Shahryary V, Chang I, Tanaka Y, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, et
al: Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR is targeted and regulated by
microRNA-141 in renal carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem.
289:12550–12565. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu Q, Han L, Yan W, Ji X, Han R, Yang J,
Yuan J and Ni C: miR-489 inhibits silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis
by targeting MyD88 and Smad3 and is negatively regulated by lncRNA
CHRF. Sci Rep. 6:309212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gutschner T, Hämmerle M and Diederichs S:
MALAT1 - a paradigm for long noncoding RNA function in cancer. J
Mol Med (Berl). 91:791–801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|