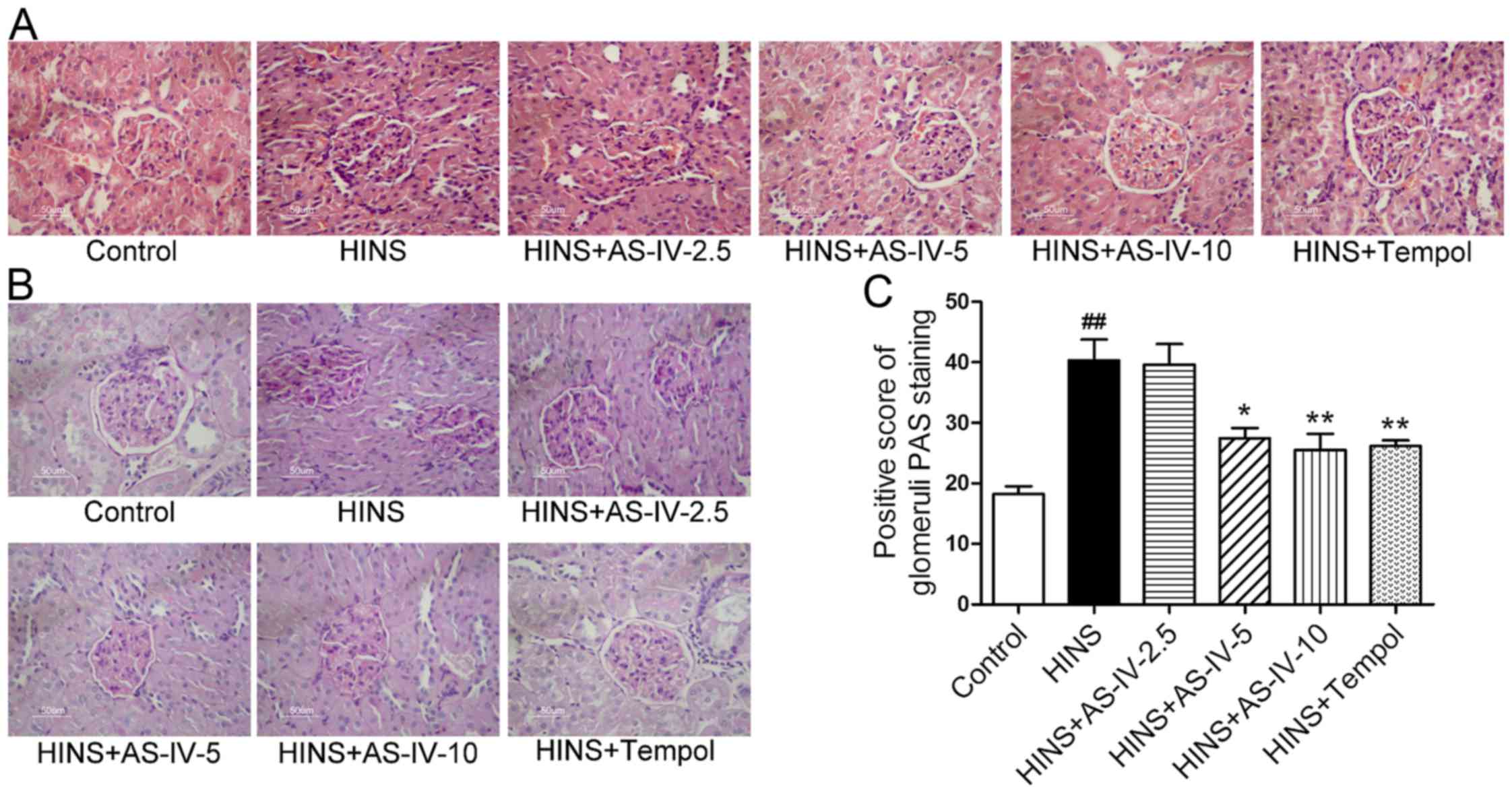
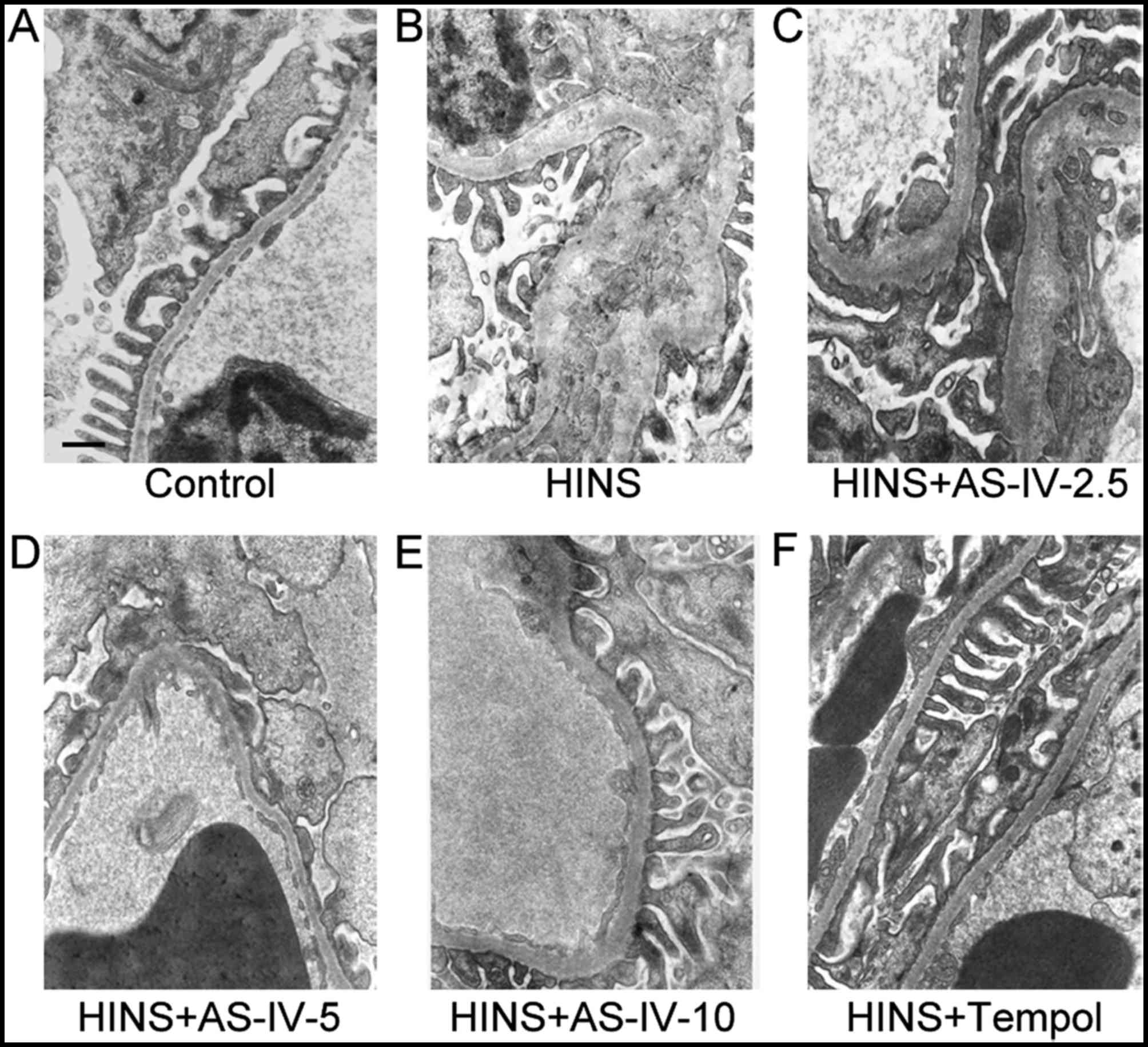
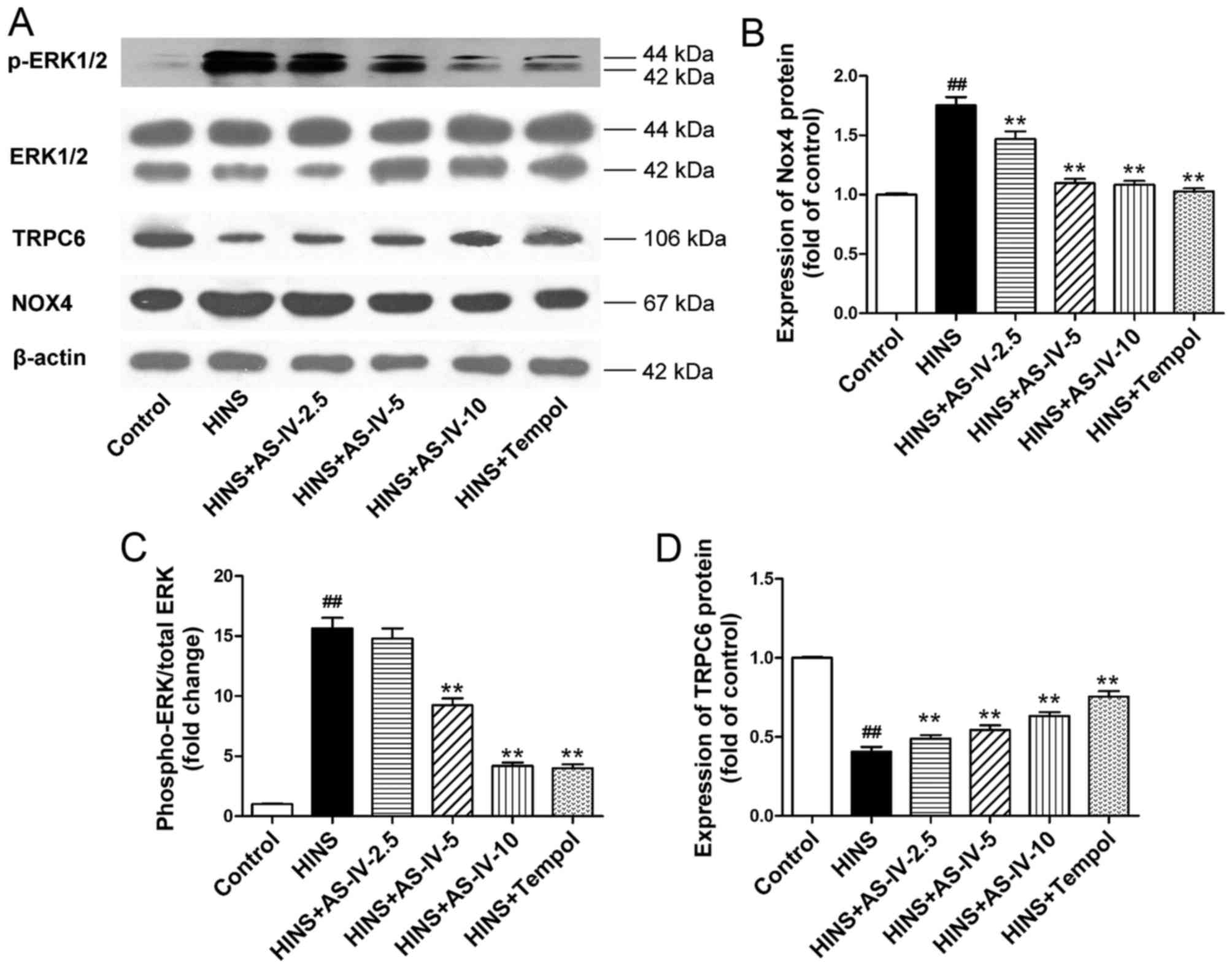
|
1
|
American Diabetes Association: Standards
of medical care in diabetes - 2011. Diabetes Care. 34(Suppl 1):
S11–S61. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Choudhury D, Tuncel M and Levi M: Diabetic
nephropathy - - a multifaceted target of new therapies. Discov Med.
10:406–415. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang MY, Yu X, Lee Y, McCorkle SK, Clark
GO, Strowig S, Unger RH and Raskin P: Iatrogenic hyperinsulinemia
in type 1 diabetes: Its effect on atherogenic risk markers. J
Diabetes Complications. 27:70–74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mariappan MM, DeSilva K, Sorice GP,
Muscogiuri G, Jimenez F, Ahuja S, Barnes JL, Choudhury GG, Musi N,
DeFronzo R, et al: Combined acute hyperglycemic and
hyperinsulinemic clamp induced profibrotic and proinflammatory
responses in the kidney. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 306:C202–C211.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Ngubane PS, Hadebe SI, Serumula MR and
Musabayane CT: The effects of transdermal insulin treatment of
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats on kidney function and renal
expression of glucose transporters. Ren Fail. 37:151–159. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Draznin B, Miles P, Kruszynska Y, Olefsky
J, Friedman J, Golovchenko I, Stjernholm R, Wall K, Reitman M,
Accili D, et al: Effects of insulin on prenylation as a mechanism
of potentially detrimental influence of hyperinsulinemia.
Endocrinology. 141:1310–1316. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun L, Li W, Li W, Xiong L, Li G and Ma R:
Astragaloside IV prevents damage to human mesangial cells through
the inhibition of the NADPH oxidase/ROS/Akt/NF-κB pathway under
high glucose conditions. Int J Mol Med. 34:167–176. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim EY, Anderson M and Dryer SE: Insulin
increases surface expression of TRPC6 channels in podocytes: Role
of NADPH oxidases and reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 302:F298–F307. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Hong OK, Lee SH, Rhee M, Ko SH, Cho JH,
Choi YH, Song KH, Son HY and Yoon KH: Hyperglycemia and
hyperinsulinemia have additive effects on activation and
proliferation of pancreatic stellate cells: Possible explanation of
islet-specific fibrosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Cell
Biochem. 101:665–675. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mariappan MM, Feliers D, Mummidi S,
Choudhury GG and Kasinath BS: High glucose, high insulin, and their
combination rapidly induce laminin-beta1 synthesis by regulation of
mRNA translation in renal epithelial cells. Diabetes. 56:476–485.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bondi CD, Manickam N, Lee DY, Block K,
Gorin Y, Abboud HE and Barnes JL: NAD(P)H oxidase mediates
TGF-beta1-induced activation of kidney myofibroblasts. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 21:93–102. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Asaba K, Tojo A, Onozato ML, Goto A, Quinn
MT, Fujita T and Wilcox CS: Effects of NADPH oxidase inhibitor in
diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 67:1890–1898. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gorin Y, Block K, Hernandez J, Bhandari B,
Wagner B, Barnes JL and Abboud HE: Nox4 NAD(P)H oxidase mediates
hypertrophy and fibronectin expression in the diabetic kidney. J
Biol Chem. 280:39616–39626. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nam SM, Lee MY, Koh JH, Park JH, Shin JY,
Shin YG, Koh SB, Lee EY and Chung CH: Effects of NADPH oxidase
inhibitor on diabetic nephropathy in OLETF rats: The role of
reducing oxidative stress in its protective property. Diabetes Res
Clin Pract. 83:176–182. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Mora C and Navarro JF: Inflammation and
pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Metabolism. 53:265–266;
author reply 266-267. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang Y, Zeng J, Chen G, Xie X, Guo W and
Tian W: Periodontitis contributes to adipose tissue inflammation
through the NF-kappaB, JNK and ERK pathways to promote insulin
resistance in a rat model. Microbes Infect. 18:804–812. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Smyth JT, Hwang SY, Tomita T, DeHaven WI,
Mercer JC and Putney JW: Activation and regulation of
store-operated calcium entry. J Cell Mol Med. 14:2337–2349. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nilius B and Owsianik G: The transient
receptor potential family of ion channels. Genome Biol. 12:2182011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ma R, Du J, Sours S and Ding M:
Store-operated Ca2+ channel in renal microcirculation
and glomeruli. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 231:145–153. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ren S, Zhang H, Mu Y, Sun M and Liu P:
Pharmacological effects of astragaloside IV: A literature review. J
Tradit Chin Med. 33:413–416. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gui D, Huang J, Liu W, Guo Y, Xiao W and
Wang N: Astragaloside IV prevents acute kidney injury in two rodent
models by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis pathways.
Apoptosis. 18:409–422. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Danda RS, Habiba NM, Rincon-Choles H,
Bhandari BK, Barnes JL, Abboud HE and Pergola PE: Kidney
involvement in a nongenetic rat model of type 2 diabetes. Kidney
Int. 68:2562–2571. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Banse HE, Frank N, Kwong GP and McFarlane
D: Relationship of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle with obesity
and obesity-associated hyperinsulinemia in horses. Can J Vet Res.
79:329–338. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Luan J, Li W, Han J, Zhang W, Gong H and
Ma R: Renal protection of in vivo administration of tempol in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Pharmacol Sci. 119:167–176.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chowdhury TA, O'Toole S and Yaqoob MM:
Managing blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes and renal
impairment. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 77:C10–C13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Velussi M, Cernigoi AM, De Monte A, Dapas
F, Caffau C and Zilli M: Long-term (12 months) treatment with an
anti-oxidant drug (silymarin) is effective on hyperinsulinemia,
exogenous insulin need and malondialdehyde levels in cirrhotic
diabetic patients. J Hepatol. 26:871–879. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Müssig K, Staiger H, Kantartzis K,
Fritsche A, Kanz L and Häring HU: Type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk
of malignancy: Is there a strategy to identify a subphenotype of
patients with increased susceptibility to endogenous and exogenous
hyperinsulinism? Diabet Med. 28:276–286. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gerstein HC, Bosch J, Dagenais GR, Díaz R,
Jung H, Maggioni AP, Pogue J, Probstfield J, Ramachandran A, Riddle
MC, et al ORIGIN Trial Investigators: Basal insulin and
cardiovascular and other outcomes in dysglycemia. N Engl J Med.
367:319–328. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Koulmanda M, Qipo A, Chebrolu S, O'Neil J,
Auchincloss H and Smith RN: The effect of low versus high dose of
streptozotocin in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascilularis). Am J
Transplant. 3:267–272. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma Y and Li W, Yin Y and Li W: AST IV
inhibits H2O2-induced human umbilical vein
endothelial cell apoptosis by suppressing Nox4 expression through
the TGF-β1/Smad2 pathway. Int J Mol Med. 35:1667–1674. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gluhovschi C, Gluhovschi G, Petrica L,
Timar R, Velciov S, Ionita I, Kaycsa A and Timar B: Urinary
biomarkers in the assessment of early diabetic nephropathy. J
Diabetes Res. 2016:46261252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gui D, Huang J, Guo Y, Chen J, Chen Y,
Xiao W, Liu X and Wang N: Astragaloside IV ameliorates renal injury
in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through inhibiting
NF-κB-mediated inflammatory genes expression. Cytokine. 61:970–977.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Voroneanu L, Nistor I, Dumea R, Apetrii M
and Covic A: Silymarin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A systematic
review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J
Diabetes Res. 2016:51474682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abhijit S, Bhaskaran R, Narayanasamy A,
Chakroborty A, Manickam N, Dixit M, Mohan V and Balasubramanyam M:
Hyperinsulinemia-induced vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC)
migration and proliferation is mediated by converging mechanisms of
mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biochem.
373:95–105. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xu L and Badr MZ: Enhanced potential for
oxidative stress in hyperinsulinemic rats: imbalance between
hepatic peroxisomal hydrogen peroxide production and decomposition
due to hyperinsulinemia. Horm Metab Res. 31:278–282. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Piwkowska A, Rogacka D, Kasztan M,
Angielski S and Jankowski M: Insulin increases glomerular
filtration barrier permeability through dimerization of protein
kinase G type Iα subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:791–804.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee HB, Yu MR, Yang Y, Jiang Z and Ha H:
Reactive oxygen species-regulated signaling pathways in diabetic
nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14(Suppl 3): S241–S245. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kedziora-Kornatowska K, Szram S,
Kornatowski T, Szadujkis-Szadurski L, Kedziora J and Bartosz G: The
effect of verapamil on the antioxidant defence system in diabetic
kidney. Clin Chim Acta. 322:105–112. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fridovich I: Superoxide radical and
superoxide dismutases. Annu Rev Biochem. 64:97–112. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu S, Zhang Q, Chen C, Ge D, Qu Y, Chen
R, Fan YM, Li N, Tang WW, Zhang W, et al: Hyperinsulinemia enhances
interleukin-17-induced inflammation to promote prostate cancer
development in obese mice through inhibiting glycogen synthase
kinase 3-mediated phosphorylation and degradation of interleukin-17
receptor. Oncotarget. 7:13651–13666. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hasegawa G, Nakano K, Sawada M, Uno K,
Shibayama Y, Ienaga K and Kondo M: Possible role of tumor necrosis
factor and interleukin-1 in the development of diabetic
nephropathy. Kidney Int. 40:1007–1012. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xiao H, Li Y, Qi J, Wang H and Liu K:
Peroxynitrite plays a key role in glomerular lesions in diabetic
rats. J Nephrol. 22:800–808. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pugliese G, Pricci F, Pugliese F, Mene P,
Lenti L, Andreani D, Galli G, Casini A, Bianchi S, Rotella CM, et
al: Mechanisms of glucose-enhanced extracellular matrix
accumulation in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Diabetes.
43:478–490. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Setty S, Michael AA, Fish AJ, Michael
Mauer S, Butkowski RJ, Virtanen I and Kim Y: Differential
expression of laminin isoforms in diabetic nephropathy and other
renal diseases. Mod Pathol. 25:859–868. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kinoshita Y, Kondo S, Urushihara M, Suga
K, Matsuura S, Takamatsu M, Shimizu M, Nishiyama A, Kawachi H and
Kagami S: Angiotensin II type I receptor blockade suppresses
glomerular renin-angiotensin system activation, oxidative stress,
and progressive glomerular injury in rat anti-glomerular basement
membrane glomerulonephritis. Transl Res. 158:235–248. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Singh LP, Cheng DW, Kowluru R, Levi E and
Jiang Y: Hexosamine induction of oxidative stress, hypertrophy and
laminin expression in renal mesangial cells: Effect of the
anti-oxidant alpha-lipoic acid. Cell Biochem Funct. 25:537–550.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ji K and Tsirka SE: Inflammation modulates
expression of laminin in the central nervous system following
ischemic injury. J Neuroinflammation. 9:1592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mariappan MM, Shetty M, Sataranatarajan K,
Choudhury GG and Kasinath BS: Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta is a
novel regulator of high glucose- and high insulin-induced
extracellular matrix protein synthesis in renal proximal tubular
epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 283:30566–30575. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane
WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Snapinn SM, Zhang Z and
Shahinfar S; RENAAL Study Investigators: Effects of losartan on
renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes
and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 345:861–869. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hu X, Wang H, Liu J, Fang X, Tao K, Wang
Y, Li N, Shi J, Wang Y, Ji P, et al: The role of ERK and JNK
signaling in connective tissue growth factor induced extracellular
matrix protein production and scar formation. Arch Dermatol Res.
305:433–445. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fernandez-Twinn DS, Blackmore HL, Siggens
L, Giussani DA, Cross CM, Foo R and Ozanne SE: The programming of
cardiac hypertrophy in the offspring by maternal obesity is
associated with hyperinsulinemia, AKT, ERK, and mTOR activation.
Endocrinology. 153:5961–5971. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
He T, Guan X, Wang S, Xiao T, Yang K, Xu
X, Wang J and Zhao J: Resveratrol prevents high glucose-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells
by inhibiting NADPH oxidase/ROS/ERK pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
402:13–20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Ma JQ, Ding J, Xiao ZH and Liu CM:
Puerarin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative DNA
damage and inflammation in mouse kidney through ERK/Nrf2/ARE
pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 71:264–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li G and Li W, Duan W and Li W: Protective
effects of As-IV on high insulin induced human mesangial cells
injury and its mechanisms. Acta Univ Medicinalis Anhui.
50:1629–1633. 2015.In Chinese.
|
|
55
|
Piwkowska A, Rogacka D, Audzeyenka I,
Kasztan M, Angielski S and Jankowski M: Insulin increases
glomerular filtration barrier permeability through PKGIα-dependent
mobilization of BKCa channels in cultured rat podocytes. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1852:1599–1609. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Reiser J, Polu KR, Möller CC, Kenlan P,
Altintas MM, Wei C, Faul C, Herbert S, Villegas I, Avila-Casado C,
et al: TRPC6 is a glomerular slit diaphragm-associated channel
required for normal renal function. Nat Genet. 37:739–744. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shen B, He Y, Zhou S, Zhao H, Mei M and Wu
X: TRPC6 may protect renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through
inhibiting necroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells. Med Sci
Monit. 22:633–641. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Graham S, Gorin Y, Abboud HE, Ding M, Lee
DY, Shi H, Ding Y and Ma R: Abundance of TRPC6 protein in
glomerular mesangial cells is decreased by ROS and PKC in diabetes.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 301:C304–C315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|