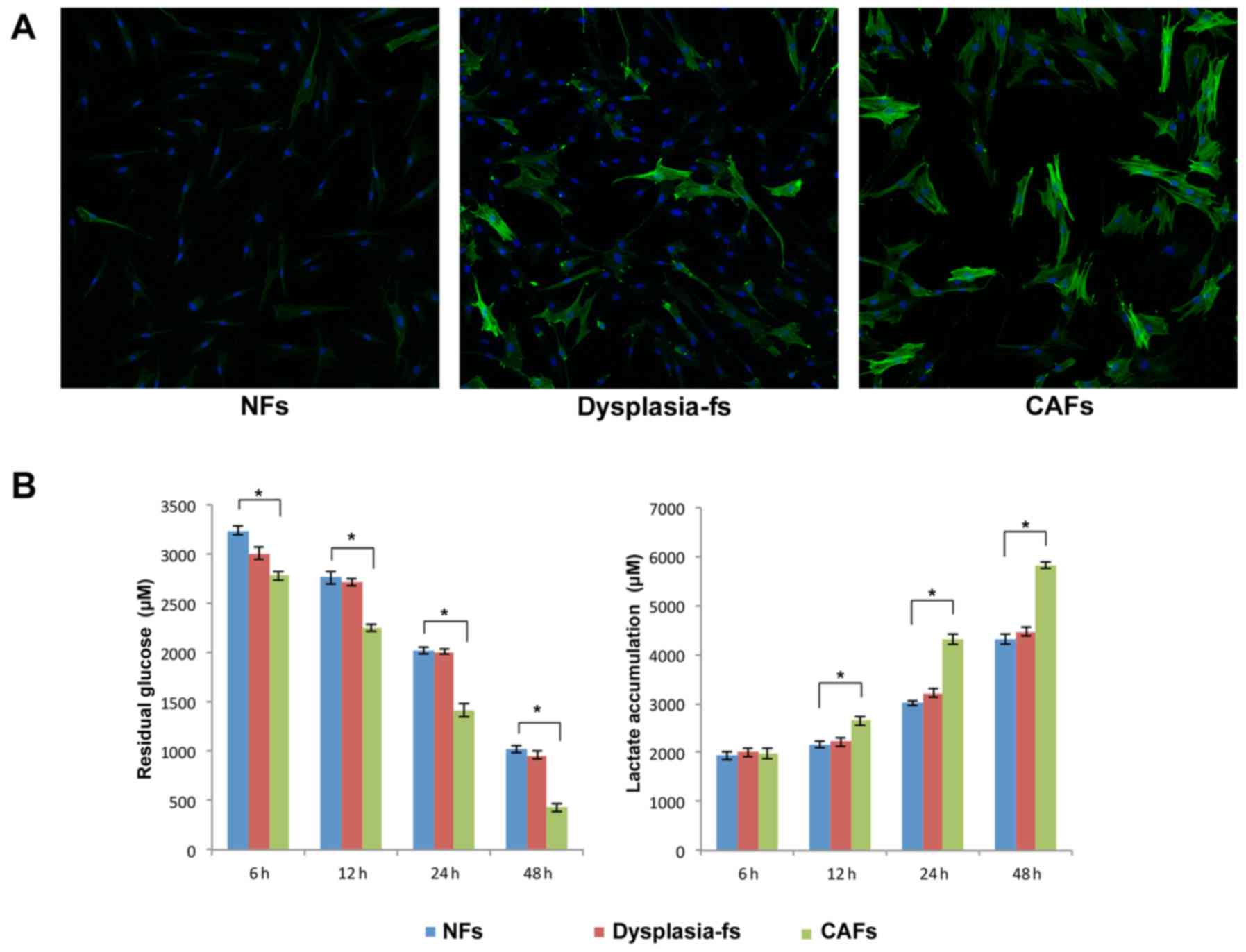
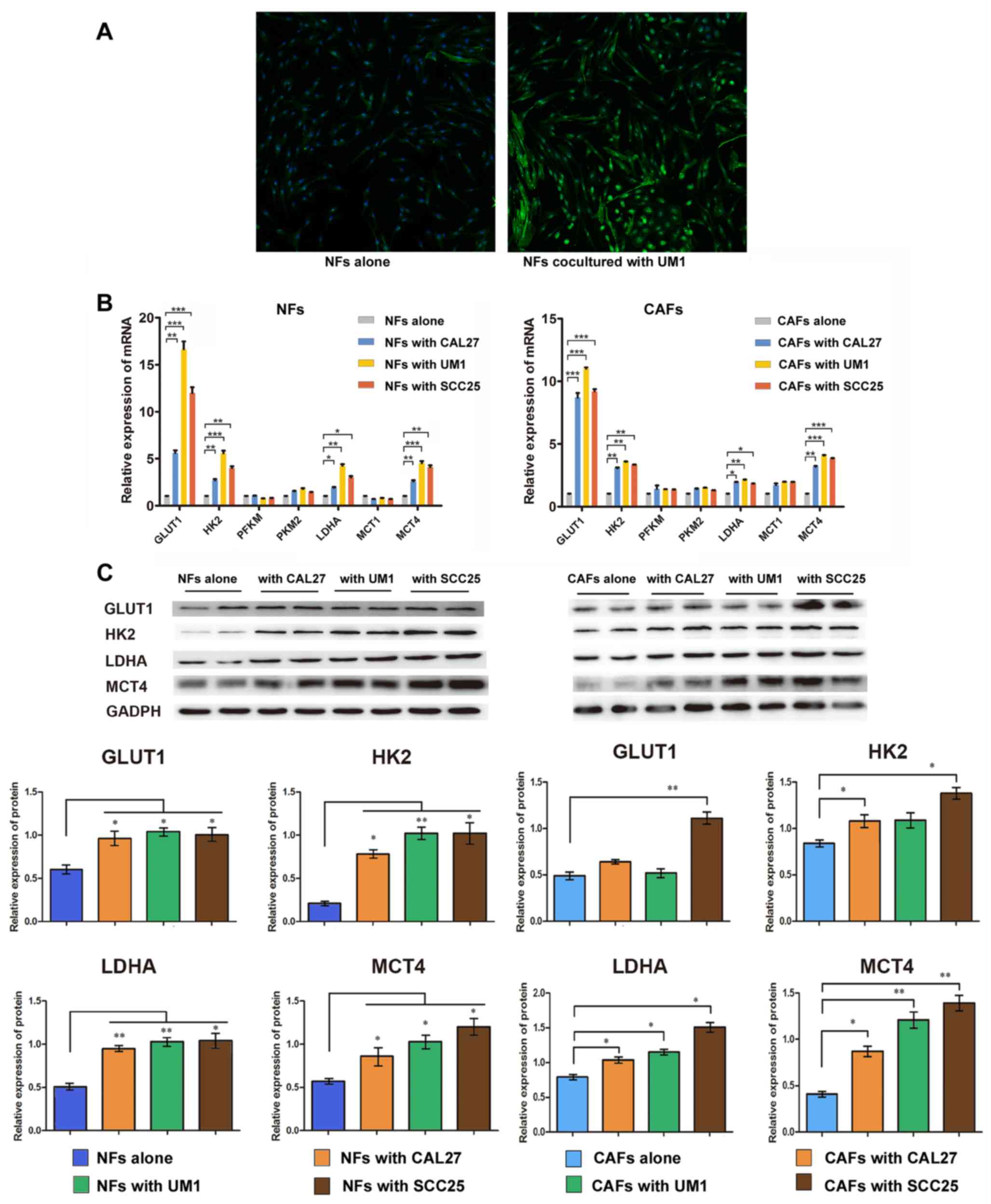
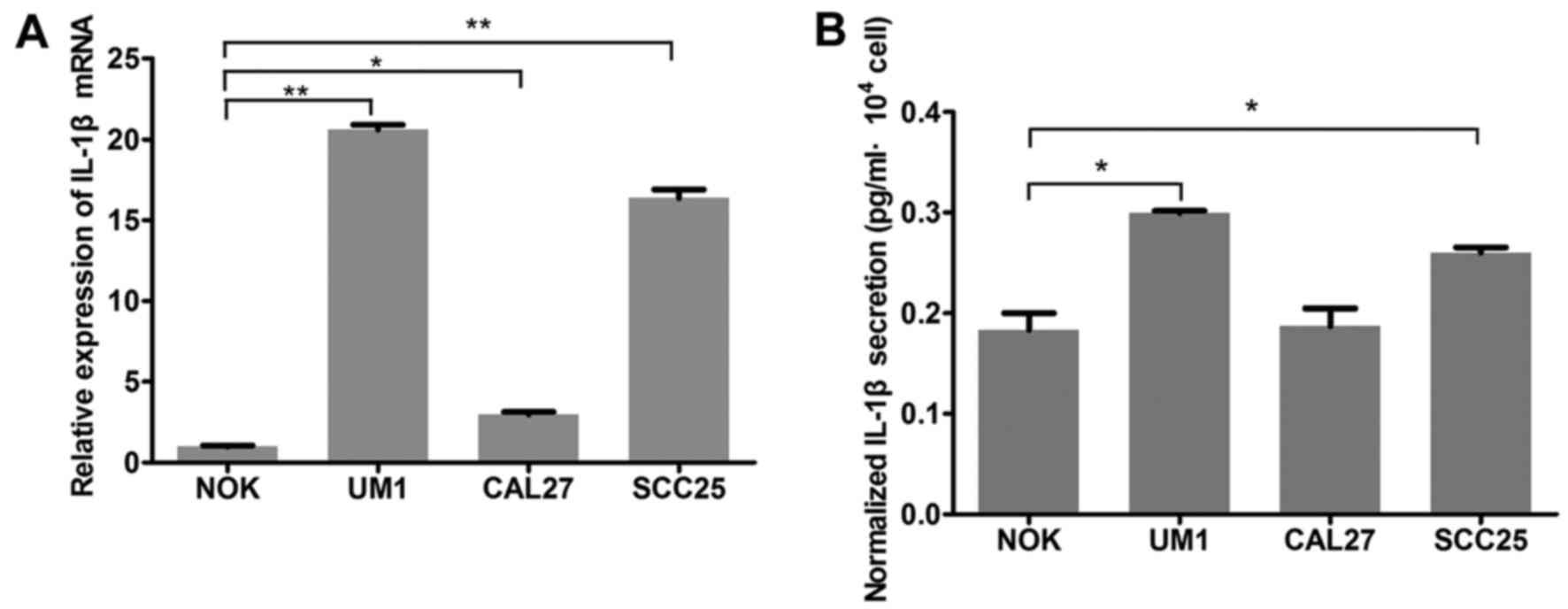
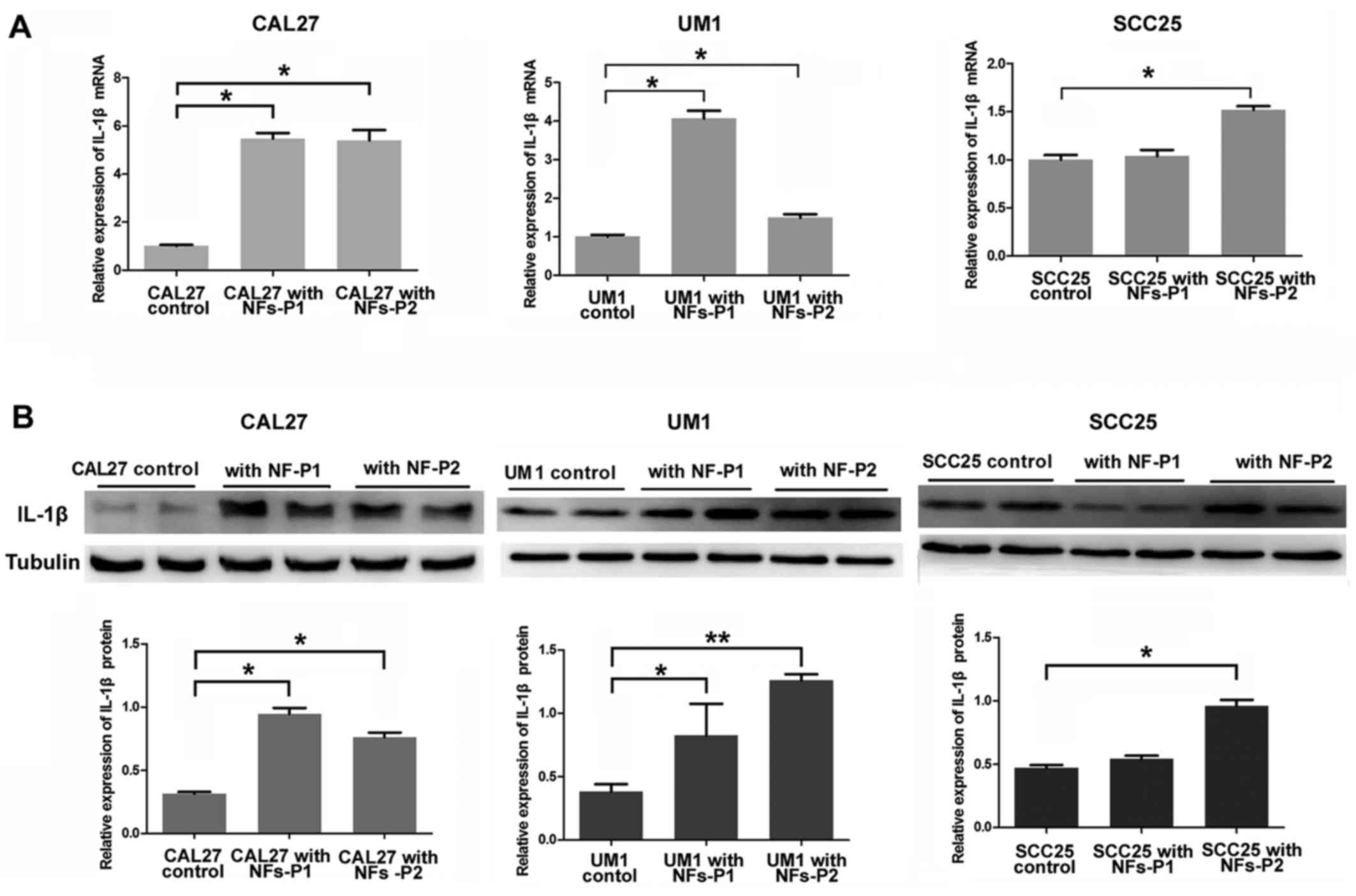
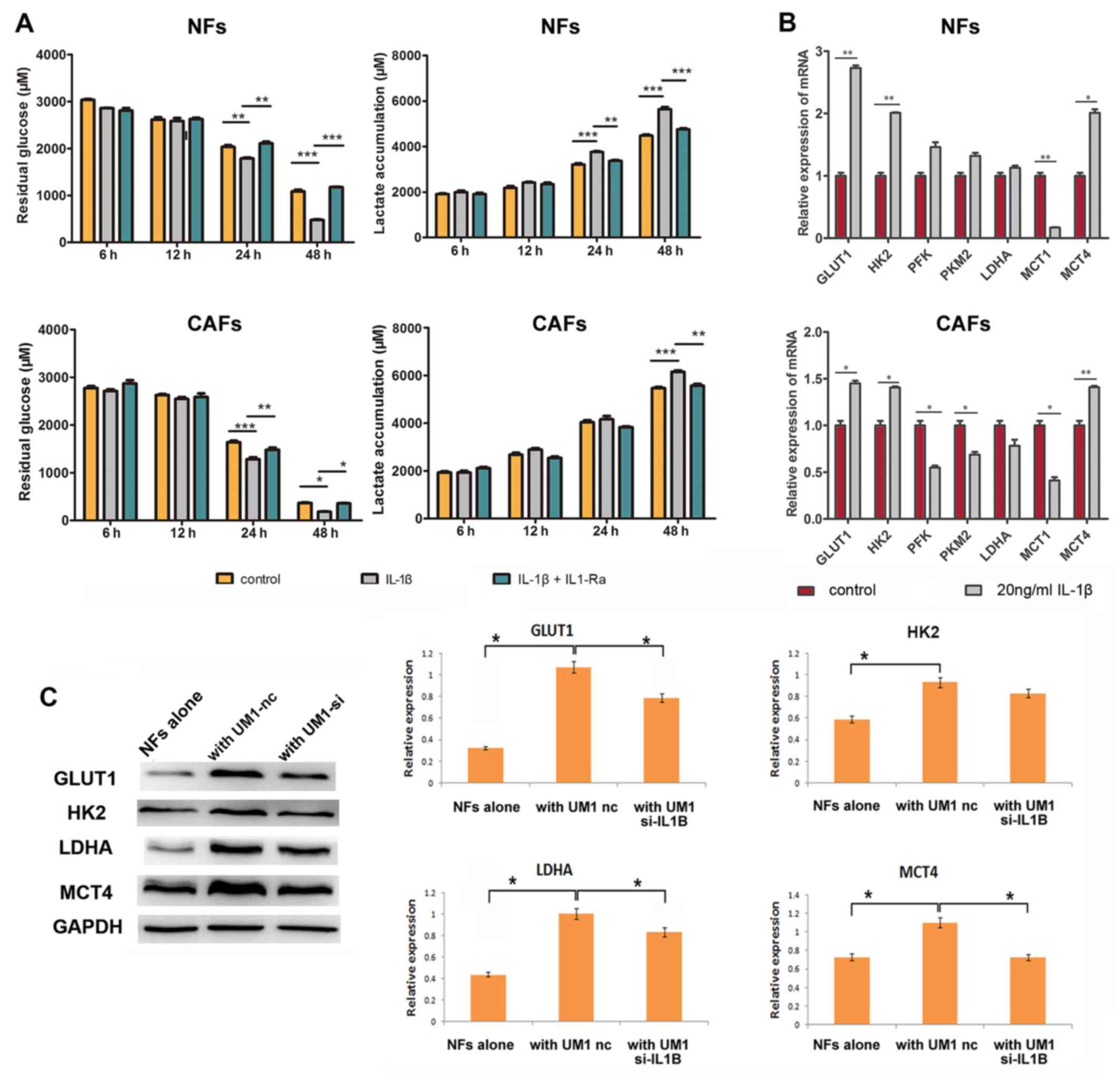
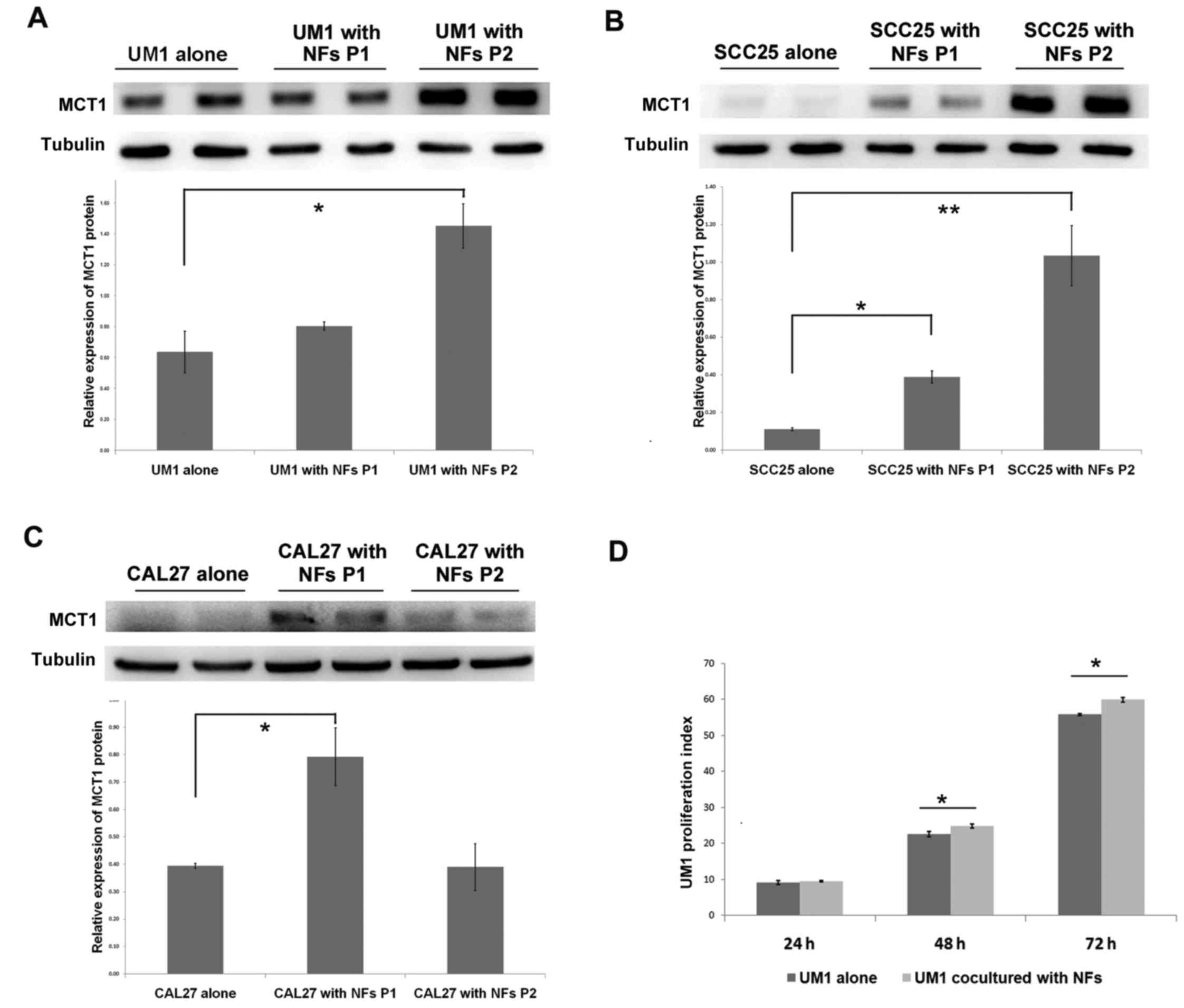
|
1
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Lisanti MP and
Sotgia F: Catabolic cancer-associated fibroblasts transfer energy
and biomass to anabolic cancer cells, fueling tumor growth. Semin
Cancer Biol. 25:47–60. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paolicchi E, Gemignani F, Krstic-Demonacos
M, Dedhar S, Mutti L and Landi S: Targeting hypoxic response for
cancer therapy. Oncotarget. 7:13464–13478. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Witkiewicz AK, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Dasgupta A, Philp NJ, Lin Z, Gandara R, Sneddon S,
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Using the 'reverse
Warburg effect' to identify high-risk breast cancer patients:
Stromal MCT4 predicts poor clinical outcome in triple-negative
breast cancers. Cell Cycle. 11:1108–1117. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bröer S, Rahman B, Pellegri G, Pellerin L,
Martin JL, Verleysdonk S, Hamprecht B and Magistretti PJ:
Comparison of lactate transport in astroglial cells and
monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT 1) expressing Xenopus laevis
oocytes. Expression of two different monocarboxylate transporters
in astroglial cells and neurons. J Biol Chem. 272:30096–30102.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pérez-Escuredo J, Van Hée VF, Sboarina M,
Falces J, Payen VL, Pellerin L and Sonveaux P: Monocarboxylate
transporters in the brain and in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:2481–2497. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Whitaker-Menezes D, Martinez-Outschoorn
UE, Lin Z, Ertel A, Flomenberg N, Witkiewicz AK, Birbe RC, Howell
A, Pavlides S, Gandara R, et al: Evidence for a stromal-epithelial
'lactate shuttle' in human tumors: MCT4 is a marker of oxidative
stress in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Cycle. 10:1772–1783.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang G, Qian G and Cheng D: The effect of
monocarboxylate transporter gene on the regulation of pHi and
growth character in cancer cells. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi.
24:666–670. 2001.In Chinese.
|
|
8
|
Baba M, Inoue M, Itoh K and Nishizawa Y:
Blocking CD147 induces cell death in cancer cells through
impairment of glycolytic energy metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 374:111–116. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
O'Callaghan K, Palagano E, Butini S,
Campiani G, Williams DC, Zisterer DM and O'Sullivan J: Induction of
apoptosis in oral squamous carcinoma cells by
pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepines. Mol Med Rep. 12:3748–3754. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu T, Hong Y, Jia L, Wu J, Xia J, Wang J,
Hu Q and Cheng B: Modulation of IL-1β reprogrammes the tumor
microenvironment to interrupt oral carcinogenesis. Sci Rep.
6:202082016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang SN, Xie GP, Qin CH, Chen YR, Zhang
KR, Li X, Wu Q, Dong WQ, Yang J and Yu B: Aucubin prevents
interleukin-1 beta induced inflammation and cartilage matrix
degradation via inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway in rat
articular chondrocytes. Int Immunopharmacol. 24:408–415. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shen XJ, Zhang H, Tang GS, Wang XD, Zheng
R, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Xue XC and Bi JW: Caveolin-1 is a modulator of
fibroblast activation and a potential biomarker for gastric cancer.
Int J Biol Sci. 11:370–379. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Al-Rakan MA, Colak D, Hendrayani SF,
Al-Bakheet A, Al-Mohanna FH, Kaya N, Al-Malik O and Aboussekhra A:
Breast stromal fibroblasts from histologically normal surgical
margins are pro-carcinogenic. J Pathol. 231:457–465. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mundim FG, Pasini FS, Nonogaki S, Rocha
RM, Soares FA, Brentani MM and Logullo AF: Breast
carcinoma-associated fibroblasts share similar biomarker profiles
in matched lymph node metastasis. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol.
24:712–720. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tang D, Gao J, Wang S, Ye N, Chong Y,
Huang Y, Wang J, Li B, Yin W and Wang D: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts promote angiogenesis in gastric cancer through
galectin-1 expression. Tumour Biol. 37:1889–1899. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Pavlides S, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Castello-Cros R, Flomenberg N, Witkiewicz AK, Frank PG, Casimiro
MC, Wang C, Fortina P, Addya S, et al: The reverse Warburg effect:
Aerobic glycolysis in cancer associated fibroblasts and the tumor
stroma. Cell Cycle. 8:3984–4001. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bonuccelli G, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Castello-Cros R, Pavlides S, Pestell RG, Fatatis A, Witkiewicz AK,
Vander Heiden MG, Migneco G, Chiavarina B, et al: The reverse
Warburg effect: Glycolysis inhibitors prevent the tumor promoting
effects of caveolin-1 deficient cancer associated fibroblasts. Cell
Cycle. 9:1960–1971. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pavlides S, Vera I, Gandara R, Sneddon S,
Pestell RG, Mercier I, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Howell A, Sotgia F, et al: Warburg meets autophagy:
Cancer-associated fibroblasts accelerate tumor growth and
metastasis via oxidative stress, mitophagy, and aerobic glycolysis.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:1264–1284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Capparelli C, Guido C, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Bonuccelli G, Balliet R, Pestell TG, Goldberg AF, Pestell RG,
Howell A, Sneddon S, et al: Autophagy and senescence in
cancer-associated fibroblasts metabolically supports tumor growth
and metastasis via glycolysis and ketone production. Cell Cycle.
11:2285–2302. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kamatani T, Shiogama S, Yoshihama Y, Kondo
S, Shirota T and Shintani S: Interleukin-1 beta in unstimulated
whole saliva is a potential biomarker for oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Cytokine. 64:497–502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Venturelli L, Nappini S, Bulfoni M,
Gianfranceschi G, Dal Zilio S, Coceano G, Del Ben F, Turetta M,
Scoles G, Vaccari L, et al: Glucose is a key driver for
GLUT1-mediated nanoparticles internalization in breast cancer
cells. Sci Rep. 6:216292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brito AF, Abrantes AM, Ribeiro M, Oliveira
R, Casalta-Lopes J, Gonçalves AC, Sarmento-Ribeiro AB, Tralhão JG
and Botelho MF: Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in
hepatocellular carcinoma: Correlation with glucose transporters and
53 expression. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 5:183–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma Y, Yu C, Mohamed EM, Shao H, Wang L,
Sundaresan G, Zweit J, Idowu M and Fang X: A causal link from ALK
to hexokinase II overexpression and hyperactive glycolysis in
EML4-ALK-positive lung cancer. Oncogene. 35:6132–6142. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Masoud GN and Li W: HIF-1α pathway: Role,
regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B.
5:378–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Choi SY, Xue H, Wu R, Fazli L, Lin D,
Collins CC, Gleave ME, Gout PW and Wang Y: The MCT4 gene: A novel,
potential target for therapy of advanced prostate cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 22:2721–2733. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lisanti MP, Sotgia F, Pestell RG, Howell A
and Martinez-Outschoorn UE: Stromal glycolysis and MCT4 are
hallmarks of DCIS progression to invasive breast cancer. Cell
Cycle. 12:2935–2936. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Andersen S, Solstad Ø, Moi L, Donnem T,
Eilertsen M, Nordby Y, Ness N, Richardsen E, Busund LT and Bremnes
RM: Organized metabolic crime in prostate cancer: The coexpression
of MCT1 in tumor and MCT4 in stroma is an independent
prognosticator for biochemical failure. Urol Onco. 33:338.e339–317.
2015.
|
|
29
|
Pértega-Gomes N, Vizcaíno JR, Attig J,
Jurmeister S, Lopes C and Baltazar F: A lactate shuttle system
between tumour and stromal cells is associated with poor prognosis
in prostate cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:3522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Trimmer C, Lin Z,
Whitaker-Menezes D, Chiavarina B, Zhou J, Wang C, Pavlides S,
Martinez-Cantarin MP, Capozza F, et al: Autophagy in cancer
associated fibroblasts promotes tumor cell survival: Role of
hypoxia, HIF1 induction and NFκB activation in the tumor stromal
microenvironment. Cell Cycle. 9:3515–3533. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vallejo S, Palacios E, Romacho T,
Villalobos L, Peiró C and Sánchez-Ferrer CF: The interleukin-1
receptor antagonist anakinra improves endothelial dysfunction in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
13:1582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vecile E, Dobrina A, Salloum FN, Van
Tassell BW, Falcione A, Gustini E, Secchiero S, Crovella S, Sinagra
G, Finato N, et al: Intracellular function of interleukin-1
receptor antagonist in ischemic cardiomyocytes. PLoS One.
8:e532652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|