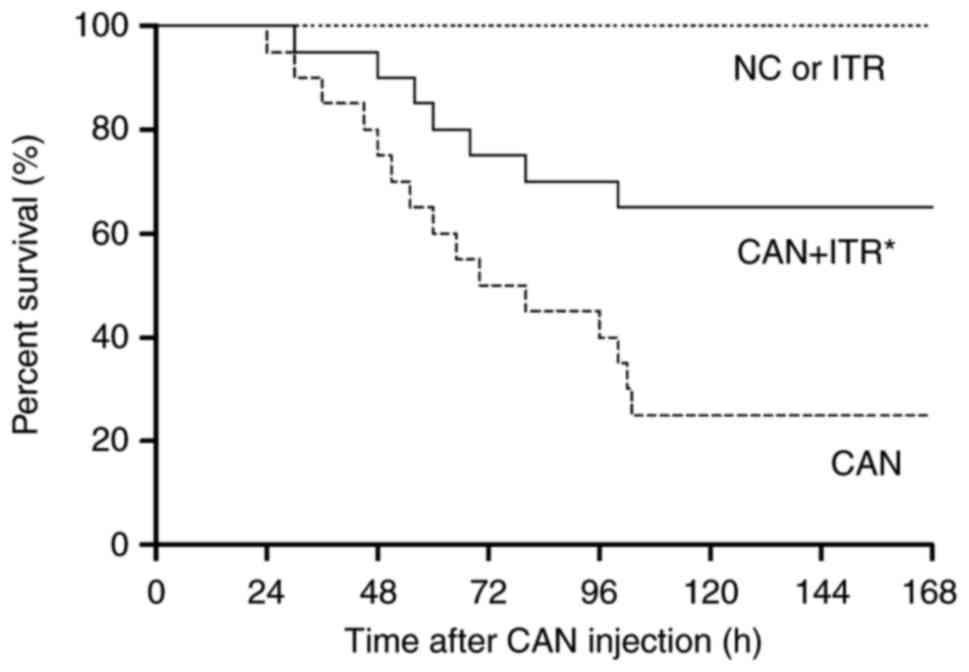
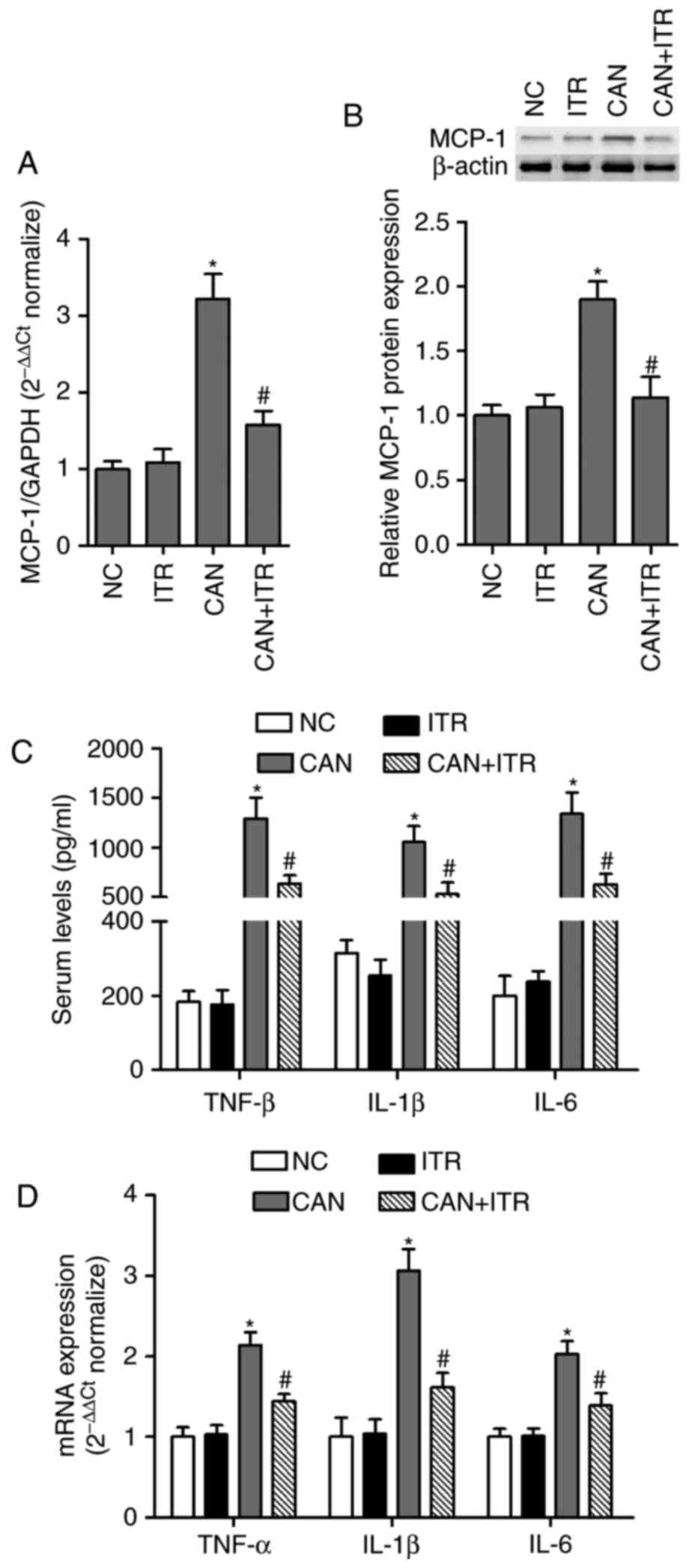
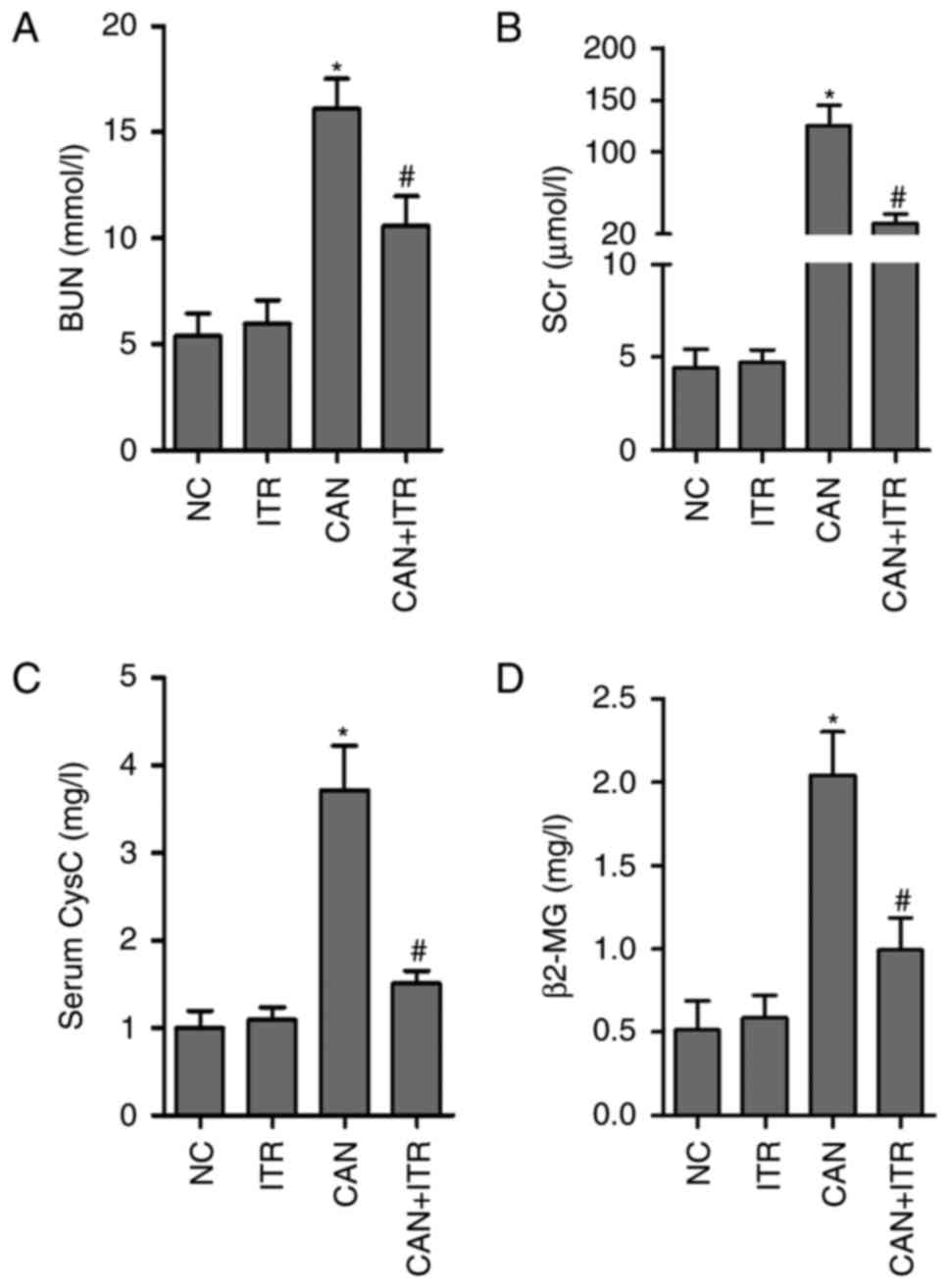
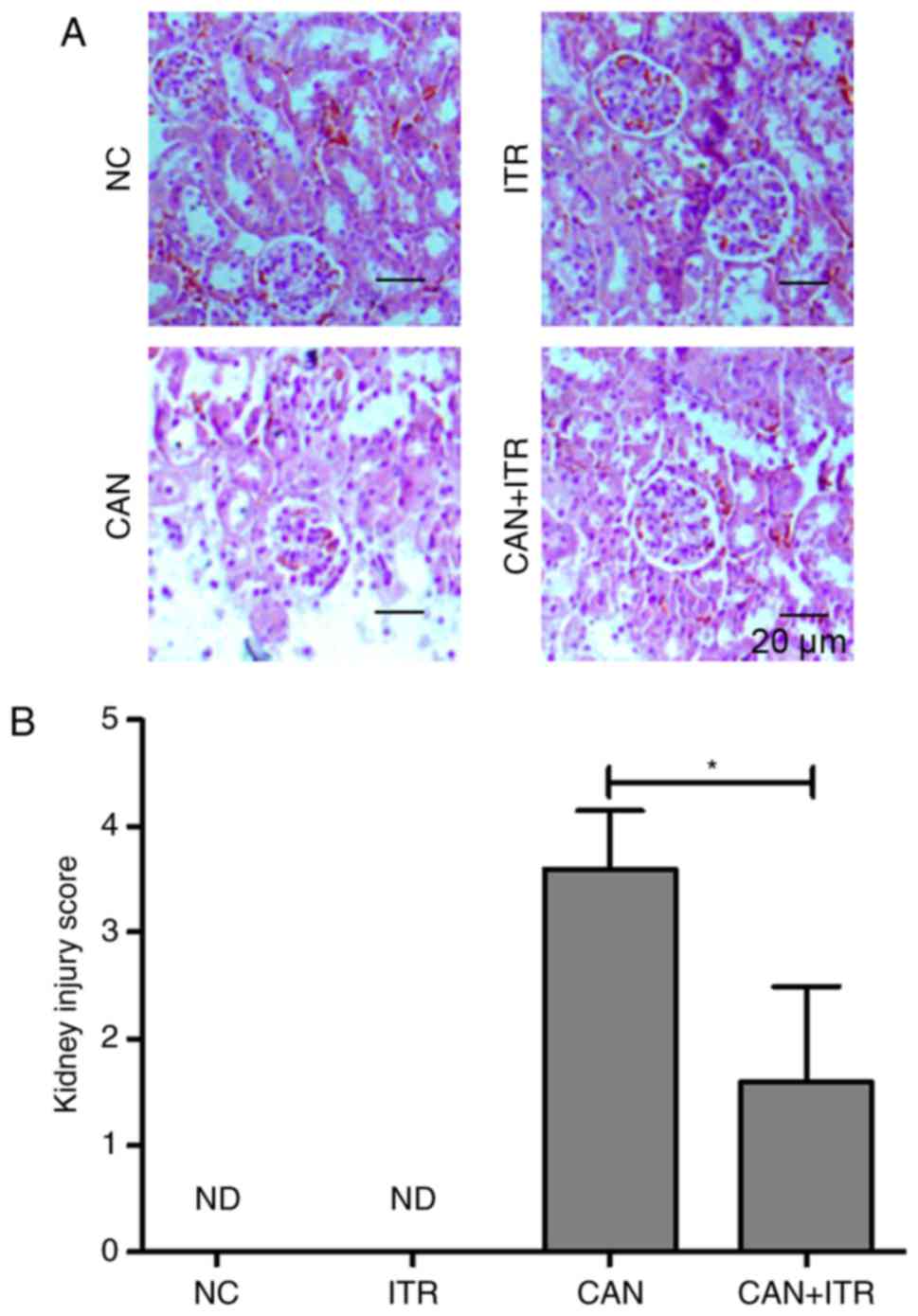
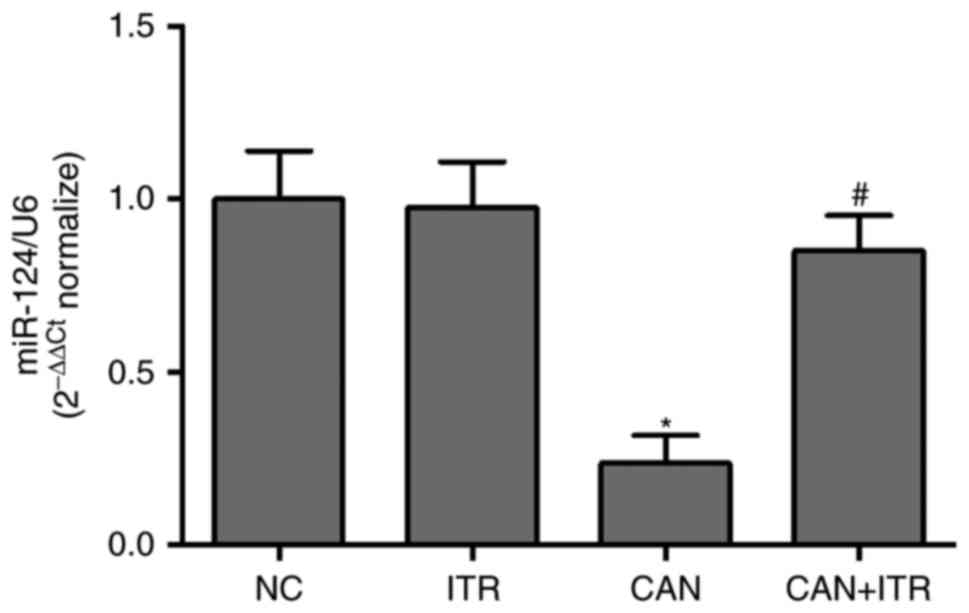
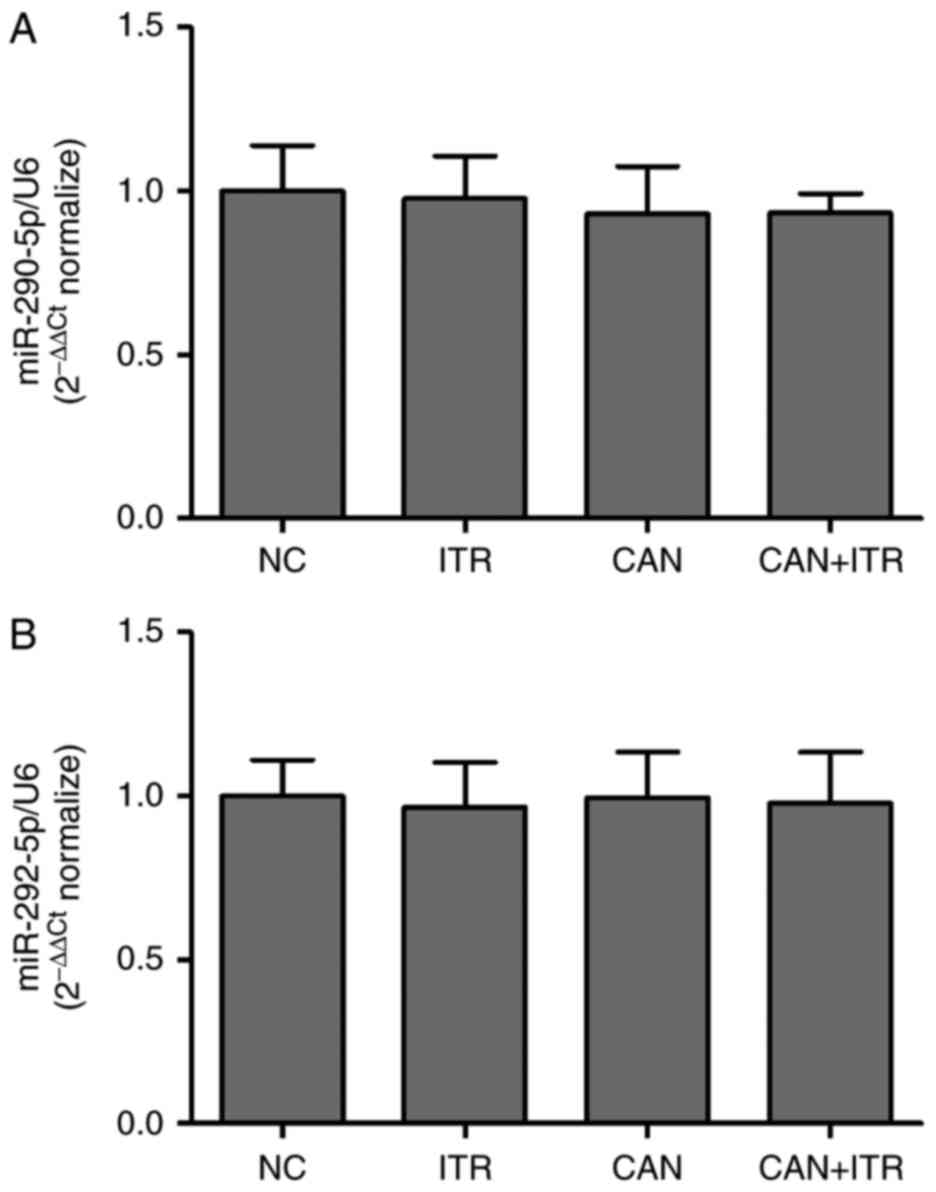
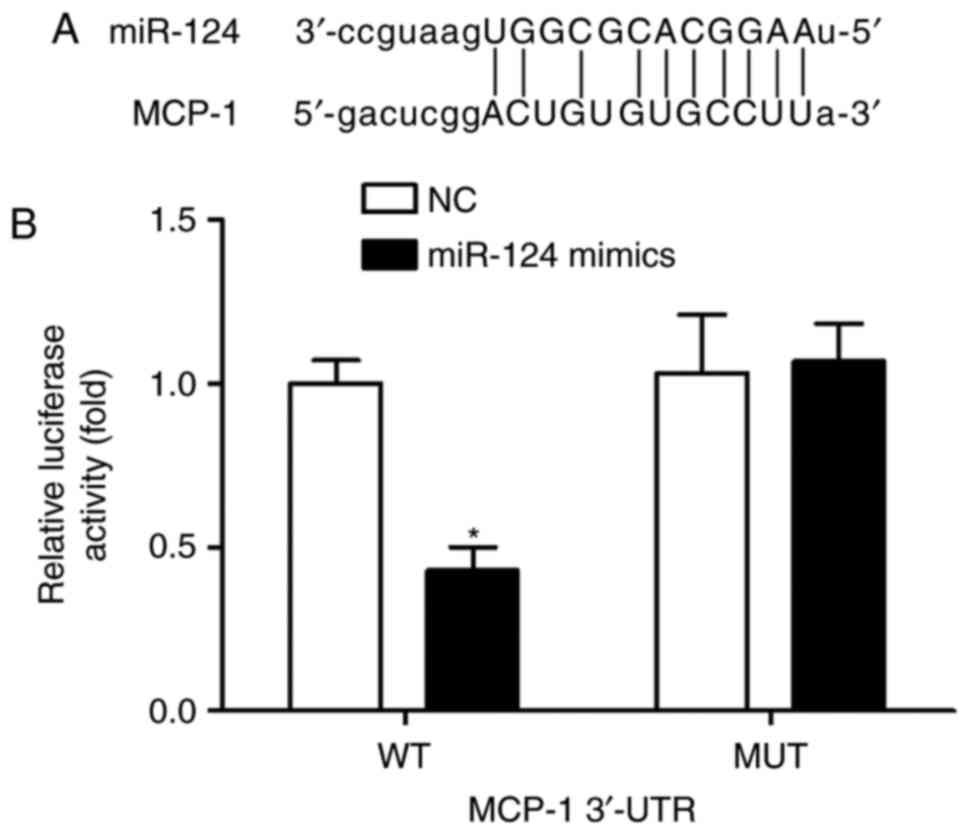
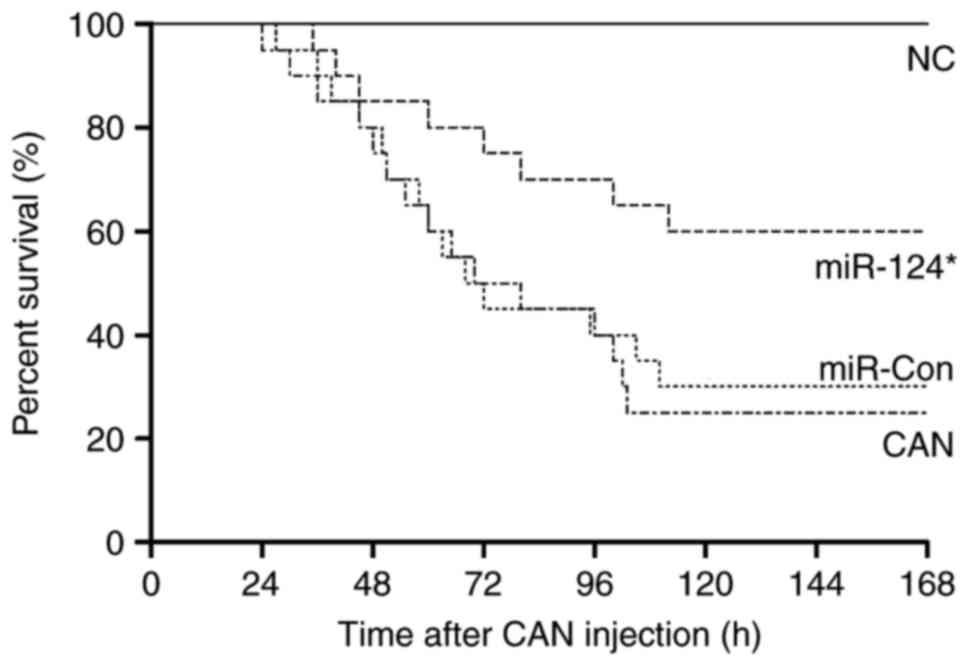
|
1
|
Leelahavanichkul A, Somparn P, Bootprapan
T, Tu H, Tangtanatakul P, Nuengjumnong R, Worasilchai N,
Tiranathanagul K, Eiam-ong S, Levine M, et al: High-dose ascorbate
with low-dose amphotericin B attenuates severity of disease in a
model of the reappearance of candidemia during sepsis in the mouse.
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 309:R223–R234. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pfaller MA and Diekema DJ: Epidemiology of
invasive candidiasis: A persistent public health problem. Clin
Microbiol Rev. 20:133–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lionakis MS, Swamydas M, Fischer BG,
Plantinga TS, Johnson MD, Jaeger M, Green NM, Masedunskas A,
Weigert R, Mikelis C, et al: CX3CR1-dependent renal macrophage
survival promotes Candida control and host survival. J Clin Invest.
123:5035–5051. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Spellberg B, Ibrahim AS, Edwards JE Jr and
Filler SG: Mice with disseminated candidiasis die of progressive
sepsis. J Infect Dis. 192:336–343. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ngo LY, Kasahara S, Kumasaka DK, Knoblaugh
SE, Jhingran A and Hohl TM: Inflammatory monocytes mediate early
and organ-specific innate defense during systemic candidiasis. J
Infect Dis. 209:109–119. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Navarathna DH, Stein EV, Lessey-Morillon
EC, Nayak D, Martin-Manso G and Roberts DD: CD47 promotes
protective innate and adaptive immunity in a mouse model of
disseminated candidiasis. PLoS One. 10:e01282202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lionakis MS, Fischer BG, Lim JK, Swamydas
M, Wan W, Richard Lee CC, Cohen JI, Scheinberg P, Gao JL and Murphy
PM: Chemokine receptor Ccr1 drives neutrophil-mediated kidney
immunopathology and mortality in invasive candidiasis. PLoS Pathog.
8:e10028652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Castillo L, MacCallum DM, Brown AJ, Gow NA
and Odds FC: Differential regulation of kidney and spleen cytokine
responses in mice challenged with pathology-standardized doses of
Candida albicans mannosylation mutants. Infect Immun. 79:146–152.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Imbert F, Jardin M, Fernandez C, Gantier
JC, Dromer F, Baron G, Mentre F, Van Beijsterveldt L, Singlas E and
Gimenez F: Effect of efflux inhibition on brain uptake of
itraconazole in mice infected with Cryptococcus neoformans. Drug
Metab Dispos. 31:319–325. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Carrer DP, Samonis G, Droggiti DI,
Tsaganos T, Pistiki A and Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ: Intravenous
itraconazole against experimental neutropenic Candida parapsilosis
infection: Efficacy after suppression of bacterial translocation. J
Infect Chemother. 19:1080–1086. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sharifzadeh A, Khosravi AR, Shokri H and
Tari PS: Synergistic anticandidal activity of menthol in
combination with itraconazole and nystatin against clinical Candida
glabrata and Candida krusei isolates. Microb Pathog. 107:390–396.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Inoue H, Iwasaki H, Abe S, Yamaguchi H and
Ueda T: Modulation of the human interleukin-12p40 response by a
triazole antifungal derivative, itraconazole. Scand J Infect Dis.
36:607–609. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wark PA, Hensley MJ, Saltos N, Boyle MJ,
Toneguzzi RC, Epid GD, Simpson JL, McElduff P and Gibson PG:
Anti-inflammatory effect of itraconazole in stable allergic
bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: A randomized controlled trial. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 111:952–957. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Oliveira AH, de Oliveira GG, Carnevale
Neto F, Portuondo DF, Batista-Duharte A and Carlos IZ:
Anti-inflammatory activity of Vismia guianensis (Aubl.) Pers
Extracts and antifungal activity against Sporothrix schenckii. J
Ethnopharmacol. 195:266–274. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Friccius H, Pohla H, Adibzadeh M,
Siegels-Hubenthal P, Schenk A and Pawelec G: The effects of the
antifungal azoles itraconazole, fluconazole, ketoconazole and
miconazole on cytokine gene expression in human lymphoid cells. Int
J Immunopharmacol. 14:791–799. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ohta K, Ishida Y, Fukui A, Nishi H, Naruse
T, Takechi M and Kamata N: Itraconazole inhibits TNF-α-induced
CXCL10 expression in oral fibroblasts. Oral Dis. 21:106–112. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Naranjo TW, Lopera DE, Diaz-Granados LR,
Duque JJ, Restrepo A and Cano LE: Histopathologic and immunologic
effects of the itraconazole treatment in a murine model of chronic
pulmonary paracoccidioidomycosis. Microbes Infect. 12:1153–1162.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu J, Shi K, Chen M, Xu L, Hong J, Hu B,
Yang X and Sun R: Elevated miR-155 expression induces
immunosuppression via CD39(+) regulatory T-cells in sepsis patient.
Int J Infect Dis. 40:135–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pan S, Yang X, Jia Y, Li Y, Chen R, Wang
M, Cai D and Zhao R: Intravenous injection of microvesicle-delivery
miR-130b alleviates high-fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice
through translational repression of PPAR-γ. J Biomed Sci.
22:862015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ge QM, Huang CM, Zhu XY, Bian F and Pan
SM: Differentially expressed miRNAs in sepsis-induced acute kidney
injury target oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
pathways. PLoS One. 12:e01732922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Monk CE, Hutvagner G and Arthur JS:
Regulation of miRNA transcription in macrophages in response to
Candida albicans. PLoS One. 5:e136692010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li XY, Zhang K, Jiang ZY and Cai LH:
MiR-204/miR-211 downregulation contributes to candidemia-induced
kidney injuries via derepression of Hmx1 expression. Life Sci.
102:139–144. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Venturini J, de Camargo MR, Felix MC,
Vilani-Moreno FR and de Arruda MS: Influence of tumour condition on
the macrophage activity in Candida albicans infection. Scand J
Immunol. 70:10–17. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fan HY, Qi D, Yu C, Zhao F, Liu T, Zhang
ZK, Yang MY, Zhang LM, Chen DQ and Du Y: Paeonol protects
endotoxin-induced acute kidney injury: potential mechanism of
inhibiting TLR4-NF-κB signal pathway. Oncotarget. 7:39497–39510.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiao F, Huang Z, Li H, Yu J, Wang C, Chen
S, Meng Q, Cheng Y, Gao X and Li J: Leucine deprivation increases
hepatic insulin sensitivity via GCN2/mTOR/S6K1 and AMPK pathways.
Diabetes. 60:746–756. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
He J, Chen Y, Lin Y, Zhang W, Cai Y, Chen
F, Liao Q, Yin Z, Wang Y, Tao S, et al: Association study of MCP-1
promoter polymorphisms with the susceptibility and progression of
sepsis. PLoS One. 12:e01767812017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Labbe K, Danialou G, Gvozdic D, Demoule A,
Divangahi M, Boyd JH and Petrof BJ: Inhibition of monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 prevents diaphragmatic inflammation and
maintains contractile function during endotoxemia. Crit Care.
14:R1872010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dorso L, Bigot-Corbel E, Abadie J, Diab M,
Gouard S, Bruchertseifer F, Morgenstern A, Maurel C, Chérel M and
Davodeau F: Long-term toxicity of 213Bi-labelled BSA in mice. PLoS
One. 11:e01513302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kluger N, Kataja J, Aho H, Ronn AM, Krohn
K and Ranki A: Kidney involvement in autoimmune polyendocrinopath
y-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy in a Finnish cohort. Nephrol
Dial Transplant. 29:1750–1757. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Munshi R, Johnson A, Siew ED, Ikizler TA,
Ware LB, Wurfel MM, Himmelfarb J and Zager RA: MCP-1 gene
activation marks acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephro. 22:165–175.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Vianna HR, Soares CM, Silveira KD, Elmiro
GS, Mendes PM, de Sousa Tavares M, Teixeira MM, Miranda DM, Simões
E and Silva AC: Cytokines in chronic kidney disease: Potential link
of MCP-1 and dyslipidemia in glomerular diseases. Pediatr Nephrol.
28:463–469. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yu C, Qi D, Sun JF, Li P and Fan HY: Rhein
prevents endotoxin-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting NF-κB
activities. Sci Rep. 5:118222015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chen H, Zhu J, Liu Y, Dong Z, Liu H, Liu
Y, Zhou X, Liu F and Chen G: Lipopolysaccharide induces chronic
kidney injury and fibrosis through activation of mTOR signaling in
macrophages. Am J Nephrol. 42:305–317. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang D, Shi L, Xin W, Xu J, Xu J, Li Q, Xu
Z, Wang J, Wang G, Yao W, et al: Activation of PPARγ inhibits
pro-inflammatory cytokines production by upregulation of miR-124 in
vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 486:726–731. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li X, Fan Q, Li J, Song J and Gu Y:
MiR-124 down-regulation is critical for cancer associated
fibroblasts-enhanced tumor growth of oral carcinoma. Exp Cell Res.
351:100–108. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dong N, Xu B, Shi H and Tang X: Baicalein
inhibits amadori-glycated albumin-induced MCP-1 expression in
retinal ganglion cells via a microRNA-124-dependent mechanism.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 56:5844–5853. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang D, Zhang H, Li M, Frid MG, Flockton
AR, McKeon BA, Yeager ME, Fini MA, Morrell NW, Pullamsetti SS, et
al: MicroRNA-124 controls the proliferative, migratory, and
inflammatory phenotype of pulmonary vascular fibroblasts. Circ Res.
114:67–78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Fischer A: Gene therapy: Repair and
replace. Nature. 510:226–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhou Y, Song Y, Shaikh Z, Li H, Zhang H,
Caudle Y, Zheng S, Yan H, Hu D, Stuart C and Yin D: MicroRNA-155
attenuates late sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through JNK and
β-arrestin 2. Oncotarget. 8:47317–47329. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zheng D, Yu Y, Li M, Wang G, Chen R, Fan
GC, Martin C, Xiong S and Peng T: Inhibition of microRNA 195
prevents apoptosis and multiple-organ injury in mouse models of
sepsis. J Infect Dis. 213:1661–1670. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|