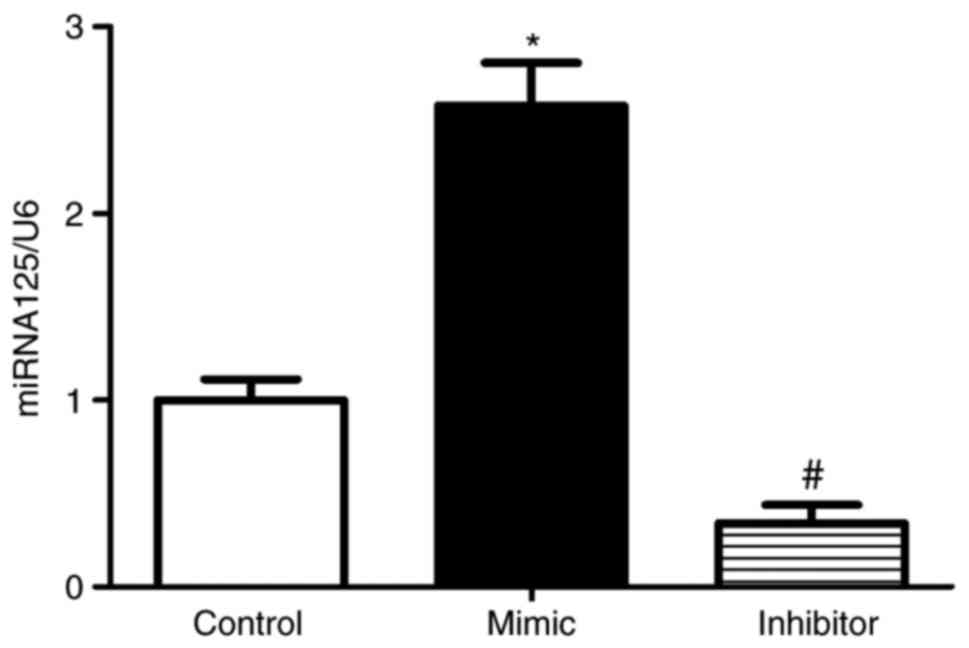
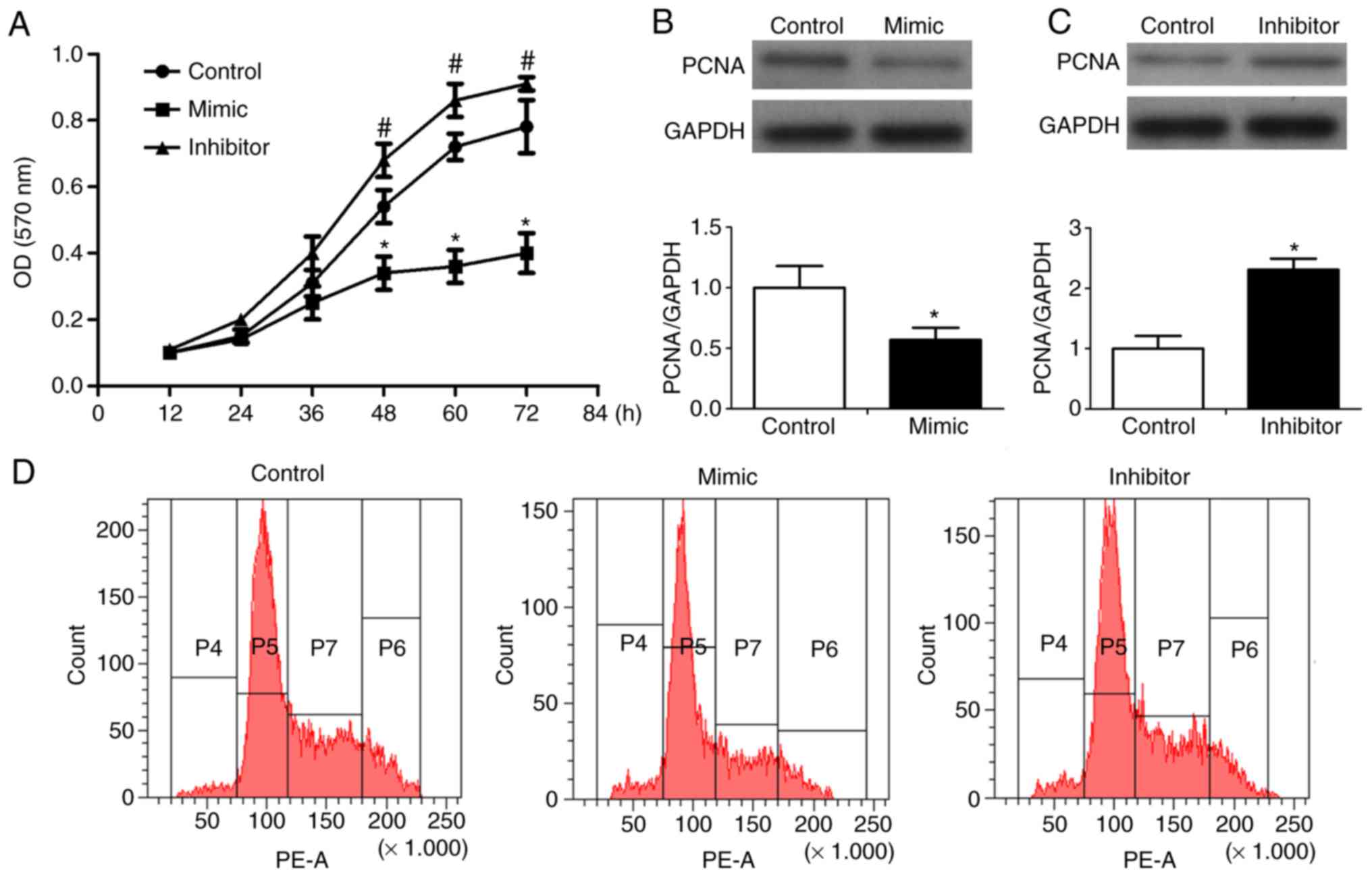
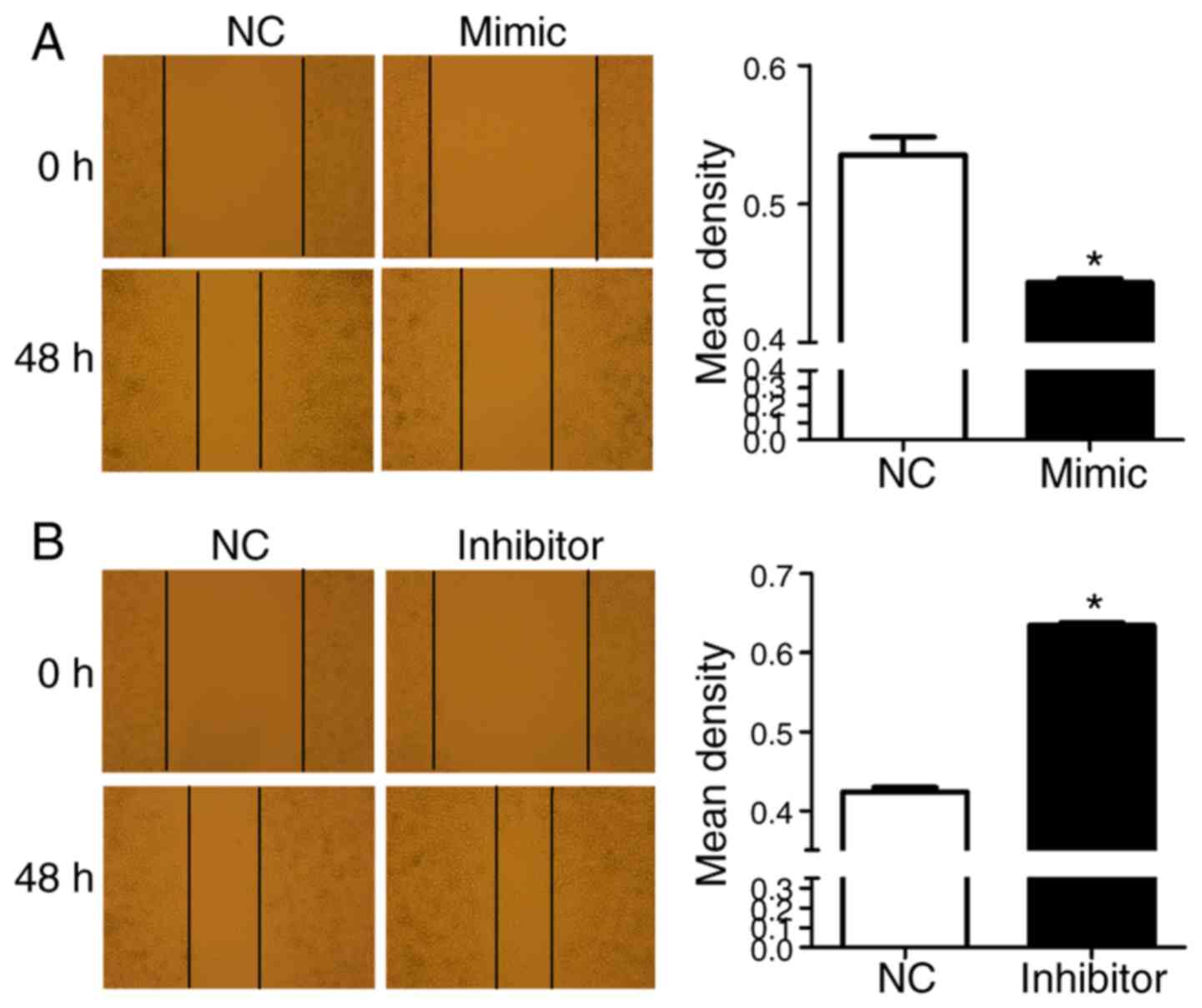
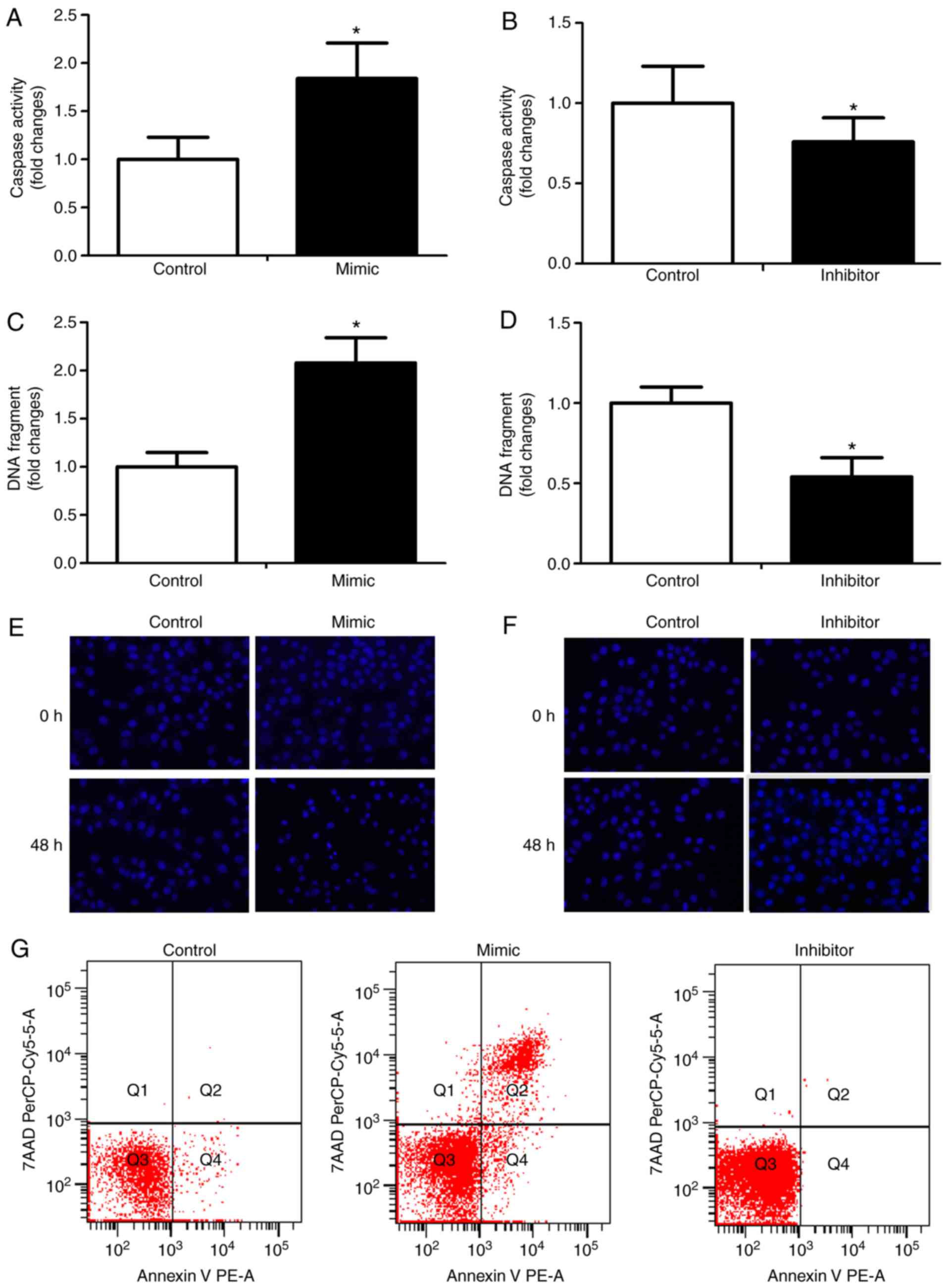
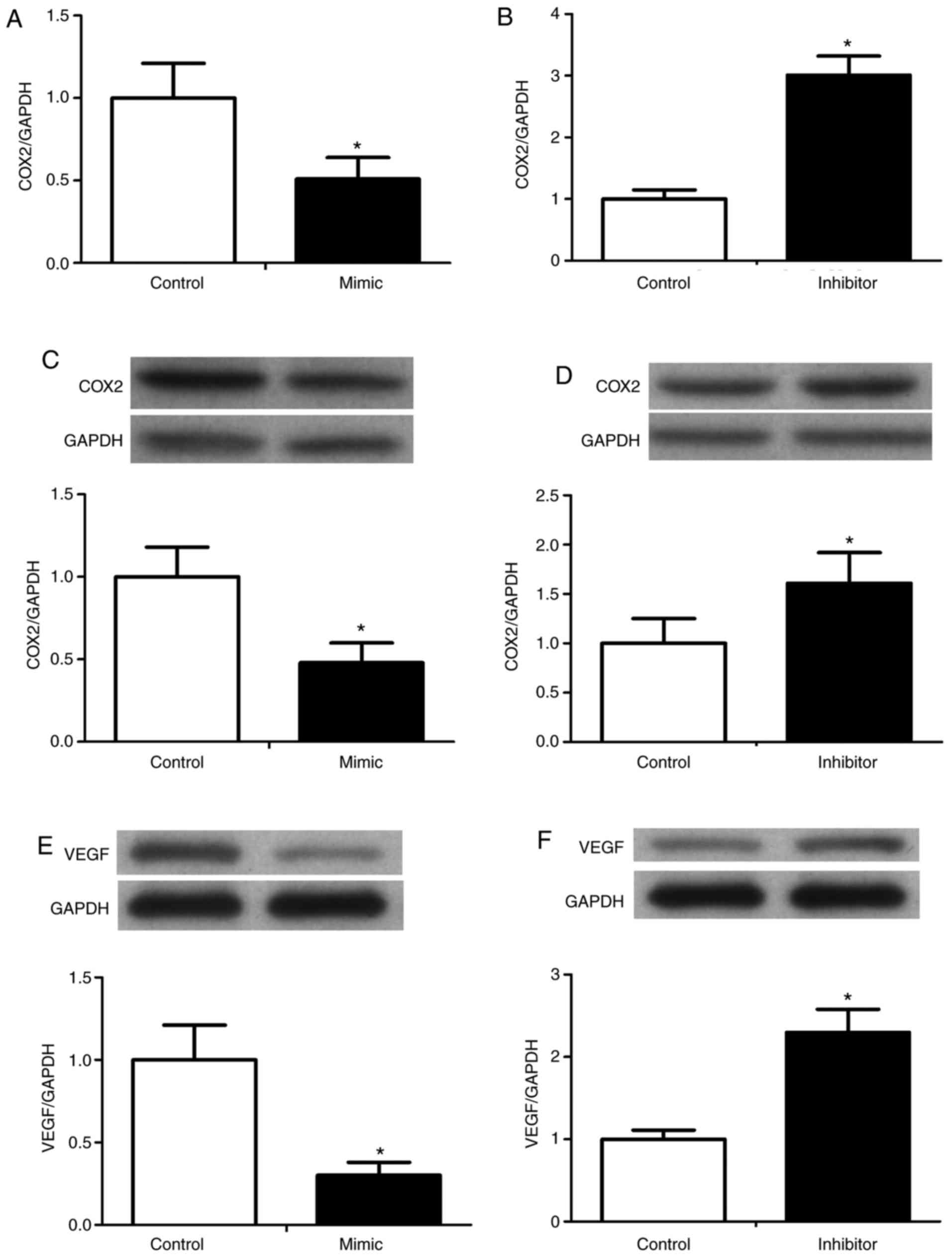
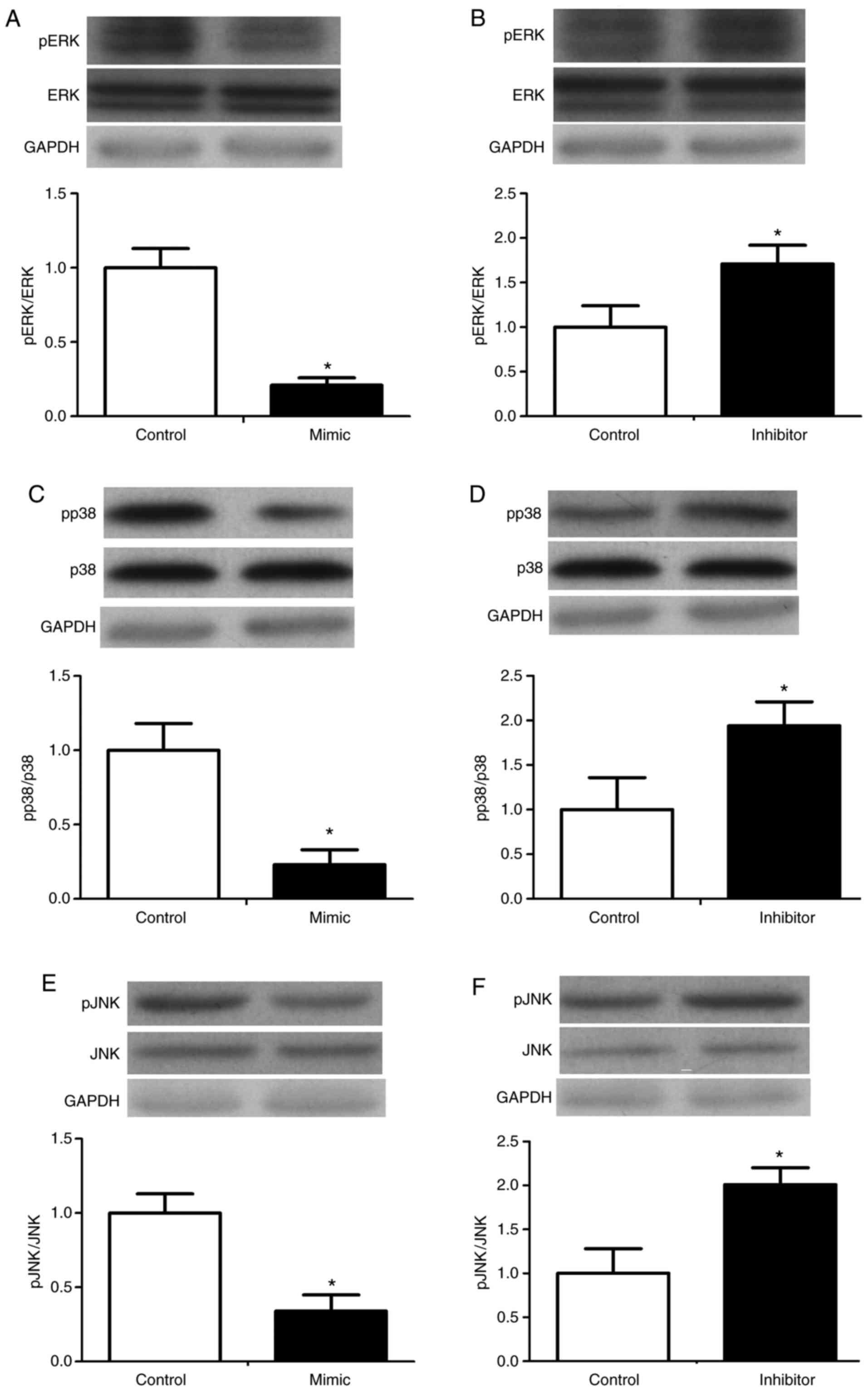
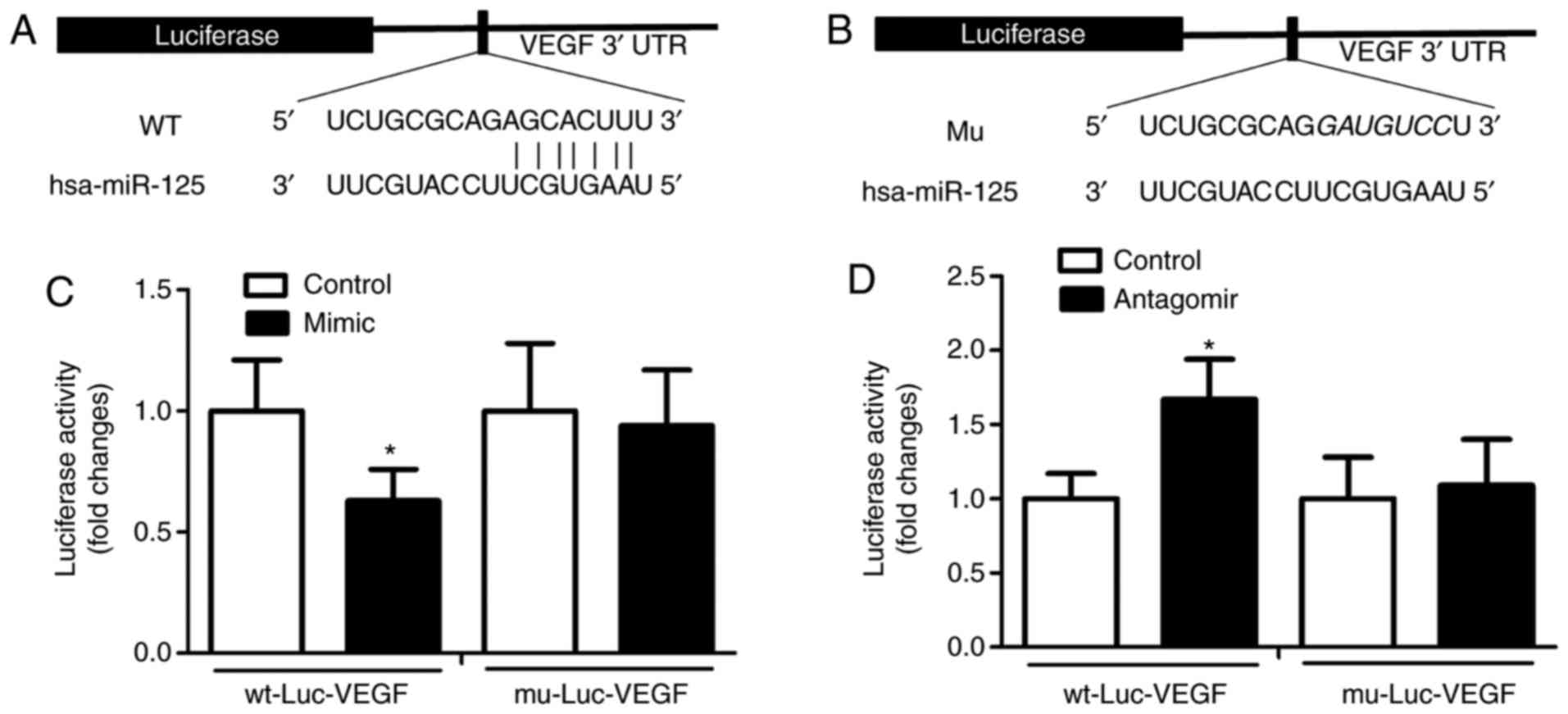
|
1
|
Haggar FA and Boushey RP: Colorectal
cancer epidemiology: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk
factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 22:191–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dean M: Cancer as a complex developmental
disorder-nineteenth Cornelius P. Rhoads memorial award lecture.
Cancer Res. 58:5633–5636. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meister G and Tuschl T: Mechanisms of gene
silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature. 431:343–349. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kumarswamy R and Thum T: Non-coding RNAs
in cardiac remodeling and heart failure. Circ Res. 113:676–689.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Quiat D and Olson EN: MicroRNAs in
cardiovascular disease: From pathogenesis to prevention and
treatment. J Clin Invest. 123:11–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E: Gene
silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression
and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. 12:99–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI and
Diederichs S: Many roads to maturity: MicroRNA biogenesis pathways
and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 11:228–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN and Filipowicz
W: Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: How many mechanisms?
Trends Cell Biol. 17:118–126. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Martínez-Acuña N, González-Torres A,
Tapia-Vieyra JV and Alvarez-Salas LM: MARK1 is a novel target for
miR-125a-5p: Implications for cell migration in cervical tumor
cells. Microrna. 2017.
|
|
13
|
Yin H, Sun Y, Wang X, Park J, Zhang Y, Li
M, Yin J, Liu Q and Wei M: Progress on the relationship between
miR-125 family and tumorigenesis. Exp Cell Res. 339:252–260. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aldebasi YH, Rahmani AH, Khan AA and Aly
SM: The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor in the
progression of bladder cancer and diabetic retinopathy. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 6:239–251. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stiegelbauer V, Perakis S, Deutsch A, Ling
H, Gerger A and Pichler M: MicroRNAs as novel predictive biomarkers
and therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:11727–11735. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bi Q, Tang S, Xia L, Du R, Fan R, Gao L,
Jin J, Liang S, Chen Z, Xu G, et al: Ectopic expression of miR-125a
inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting MMP11 and VEGF. PLos One. 7:e401692012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-(delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sun X, Zhang S and Ma X: Prognostic value
of MicroRNA-125 in various human malignant neoplasms: A
meta-analysis. Clin Lab. 61:1667–1674. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom
M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, Labourier E, Reinert KL, Brown D and Slack
FJ: RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell.
120:635–647. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tsang WP and Kwok TT: The miR-18a*
microRNA functions as a potential tumor suppressor by targeting on
K-Ras. Carcinogenesis. 30:953–959. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen X, Guo X, Zhang H, Xiang Y, Chen J,
Yin Y, Cai X, Wang K, Wang G, Ba Y, et al: Role of miR-143
targeting KRAS in colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 28:1385–1392.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yin Y, Yan ZP, Lu NN, Xu Q, He J, Qian X,
Yu J, Guan X, Jiang BH and Liu LZ: Downregulation of miR-145
associated with cancer progression and VEGF transcriptional
activation by targeting N-RAS and IRS1. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1829:239–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bousquet M, Harris MH, Zhou B and Lodish
HF: MicroRNA miR-125b causes leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:21558–21563. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cowden Dahl KD, Dahl R, Kruichak JN and
Hudson LG: The epidermal growth factor receptor responsive miR-125a
represses mesenchymal morphology in ovarian cancer cells.
Neoplasia. 11:1208–1215. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang L, Huang Q, Zhang S, Zhang Q, Chang
J, Qiu X and Wang E: Hsa-miR- 125a-3p and hsa-miR-125a-5p are
downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and have inverse
effects on invasion and migration of lung cancer cells. BMC Cancer.
10:3182010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jiang F, Liu T, He Y, Yan Q, Chen X, Wang
H and Wan X: MiR-125b promotes proliferation and migration of type
II endometrial carcinoma cells through targeting TP53INP1 tumor
suppressor in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer. 11:4252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guan Y, Yao H, Zheng Z, Qiu G and Sun K:
MiR-125b targets BCL3 and suppresses ovarian cancer proliferation.
Int J Cancer. 128:2274–2283. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang L, Luo J, Cai Q, Pan Q, Zeng H, Guo
Z, Dong W, Huang J and Lin T: MicroRNA-125b suppresses the
development of bladder cancer by targeting E2F3. Int J Cancer.
128:1758–1769. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu LH, Li H, Li JP, Zhong H, Zhang HC,
Chen J and Xiao T: MiR-125b suppresses the proliferation and
migration of osteosarcoma cells through down-regulation of STAT3.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 416:31–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li W, Duan R, Kooy F, Sherman SL, Zhou W
and Jin P: Germline mutation of microRNA-125a is associated with
breast cancer. J Med Genet. 46:358–360. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Scott GK, Goga A, Bhaumik D, Berger CE,
Sullivan CS and Benz CC: Coordinate suppression of ERBB2 and ERBB3
by enforced expression of micro-RNA miR-125a or miR-125b. J Biol
Chem. 282:1479–1486. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J, Sensinger K,
Wong L, Scott GK, Fedele V, Ginzinger D, Getts R and Haqq C:
Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides
novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer
biopsies. Mol Cancer. 5:242006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liang L, Wong CM, Ying Q, Fan DN, Huang S,
Ding J, Yao J, Yan M, Li J, Yao M, et al: MicroRNA-125b
suppressesed human liver cancer cell proliferation and metastasis
by directly targeting oncogene LIN28B2. Hepatology. 52:1731–1740.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jia HY, Wang YX, Yan WT, Li HY, Tian YZ,
Wang SM and Zhao HL: MicroRNA-125b functions as a tumor suppressor
in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Sci. 13:8762–8774.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kappelmann M, Kuphal S, Meister G,
Vardimon L and Bosserhoff AK: MicroRNA miR-125b controls melanoma
progression by direct regulation of c-Jun protein expression.
Oncogene. 32:2984–2991. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen H and Hu Z:
Hypermethylation-associated silencing of miR-125a and miR-125b: A
potential marker in colorectal cancer. Dis Markers.
2015:3450802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nagy JA, Dvorak AM and Dvorak HF: VEGF and
the induction of pathological angiogenesis. Annu Rev Pathol.
2:251–275. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Aragon-Ching JB and Dahut WL:
Anti-angiogenesis approach to genitourinary cancer treatment.
Update Cancer Ther. 3:182–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dormoy-Raclet V, Ménard I, Clair E, Kurban
G, Mazroui R, Di Marco S, von Roretz C, Pause A and Gallouzi IE:
The RNA-binding protein HuR promotes cell migration and cell
invasion by stabilizing the beta-actin mRNA in a
U-rich-element-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 27:5365–5380. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Denkert C, Weichert W, Pest S, Koch I,
Licht D, Köbel M, Reles A, Sehouli J, Dietel M and Hauptmann S:
Overexpression of the embryonic-le-thal abnormal vision-like
protein HuR in ovarian carcinoma is a prognostic factor and is
associated with increased cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Cancer Res.
64:189–195. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mrena J, Wiksten JP, Thiel A, Kokkola A,
Pohjola L, Lundin J, Nordling S, Ristimäki A and Haglund C:
Cyclooxygenase-2 is an independent prognostic factor in gastric
cancer and its expression is regulated by the messenger RNA
stability factor HuR. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7362–7368. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|