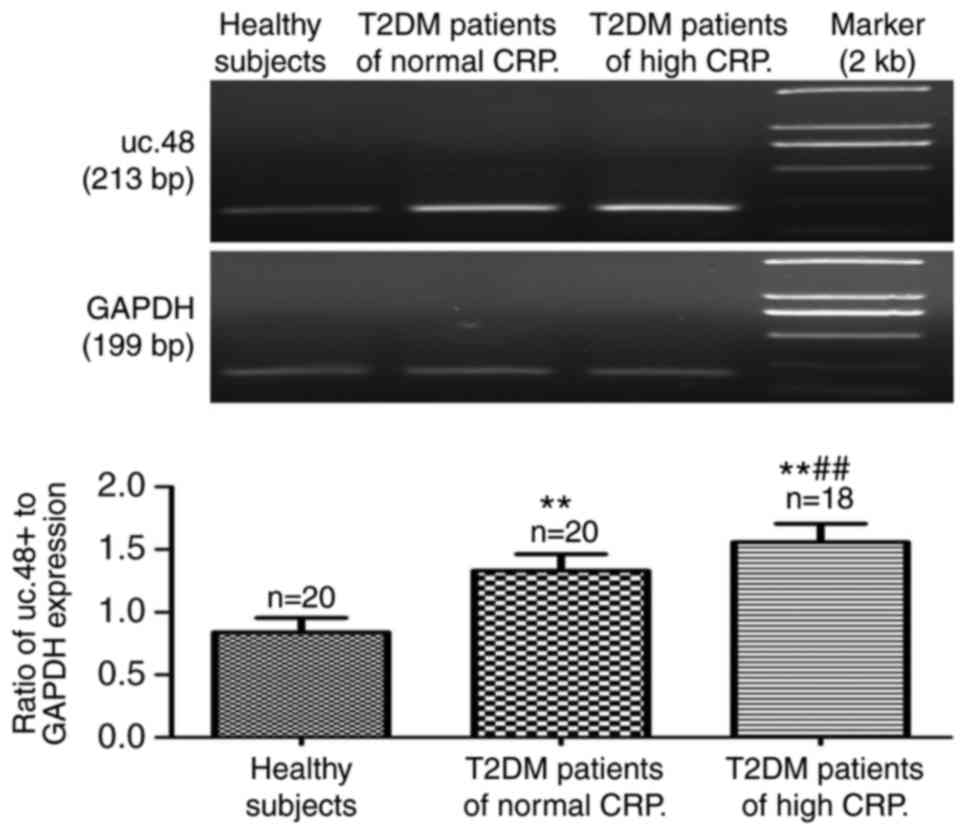
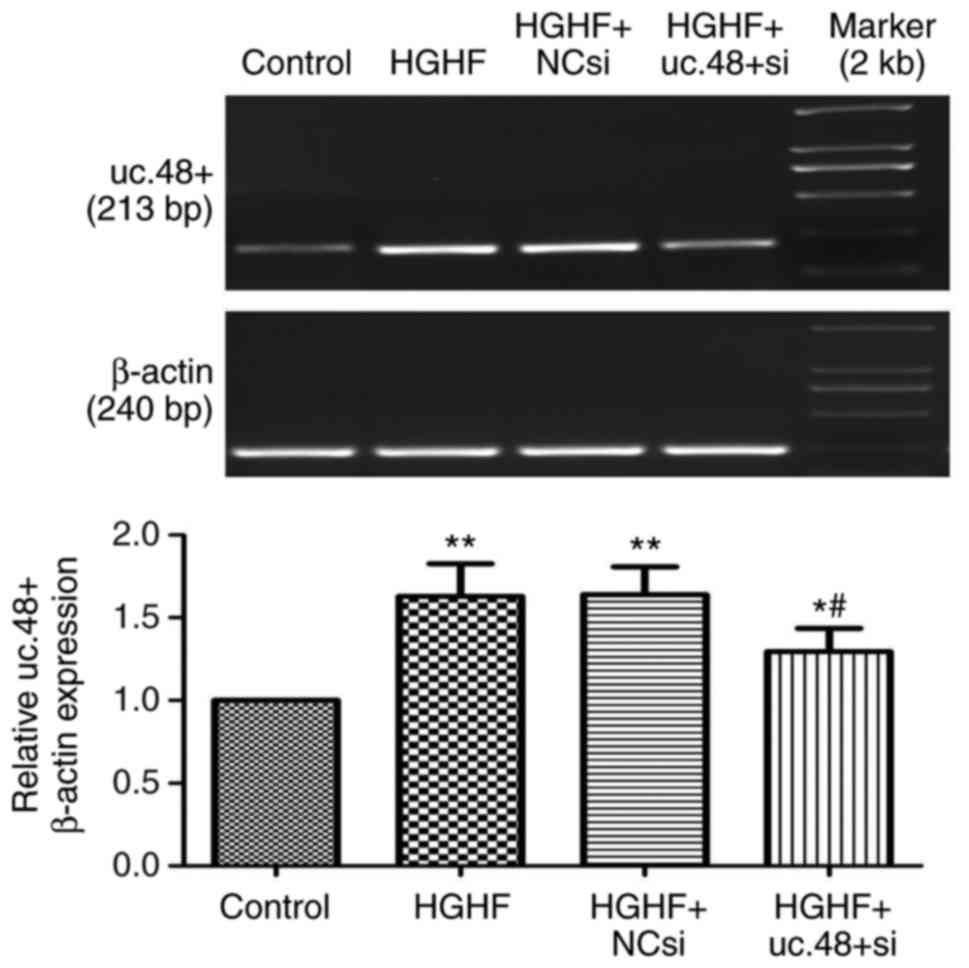
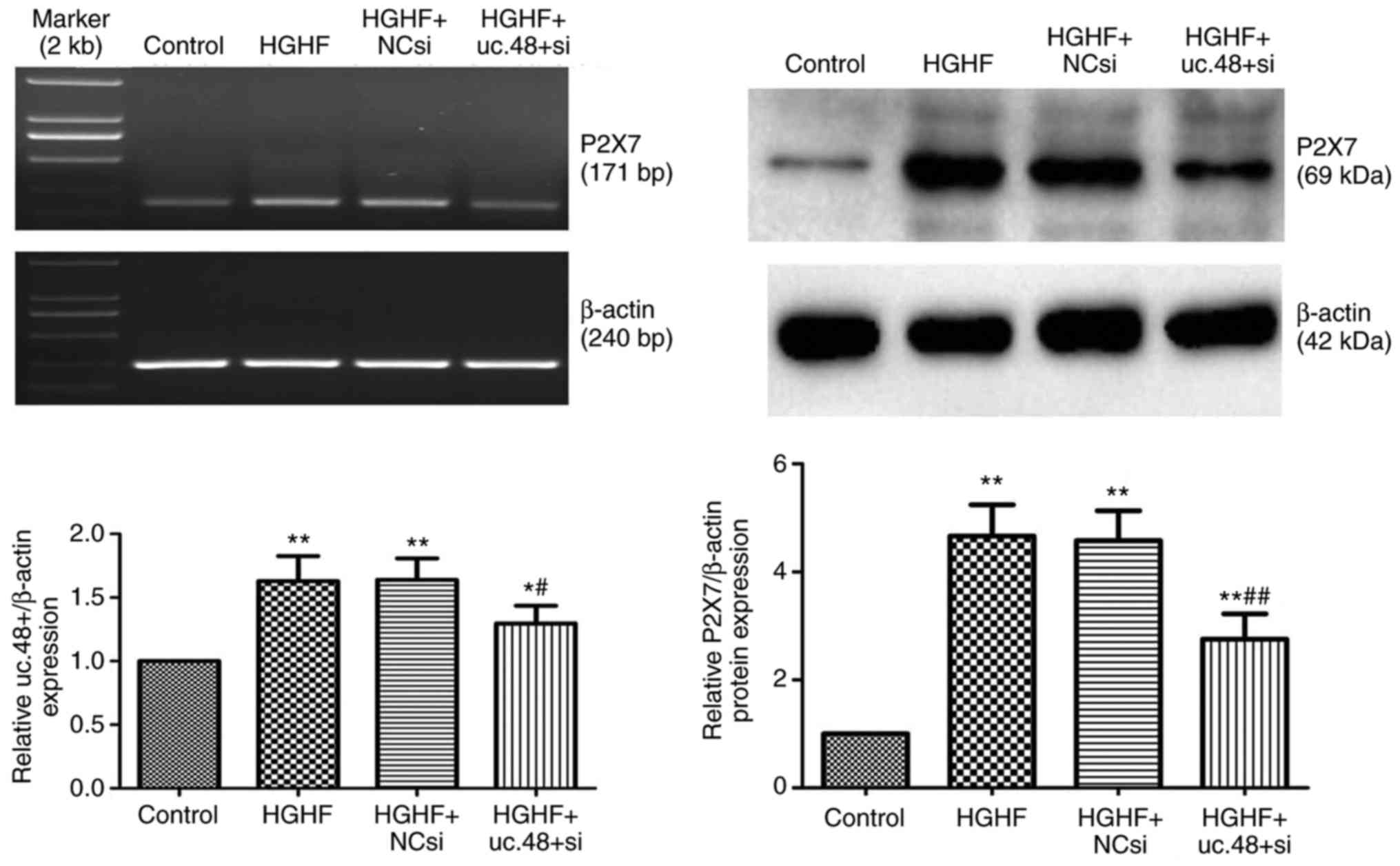
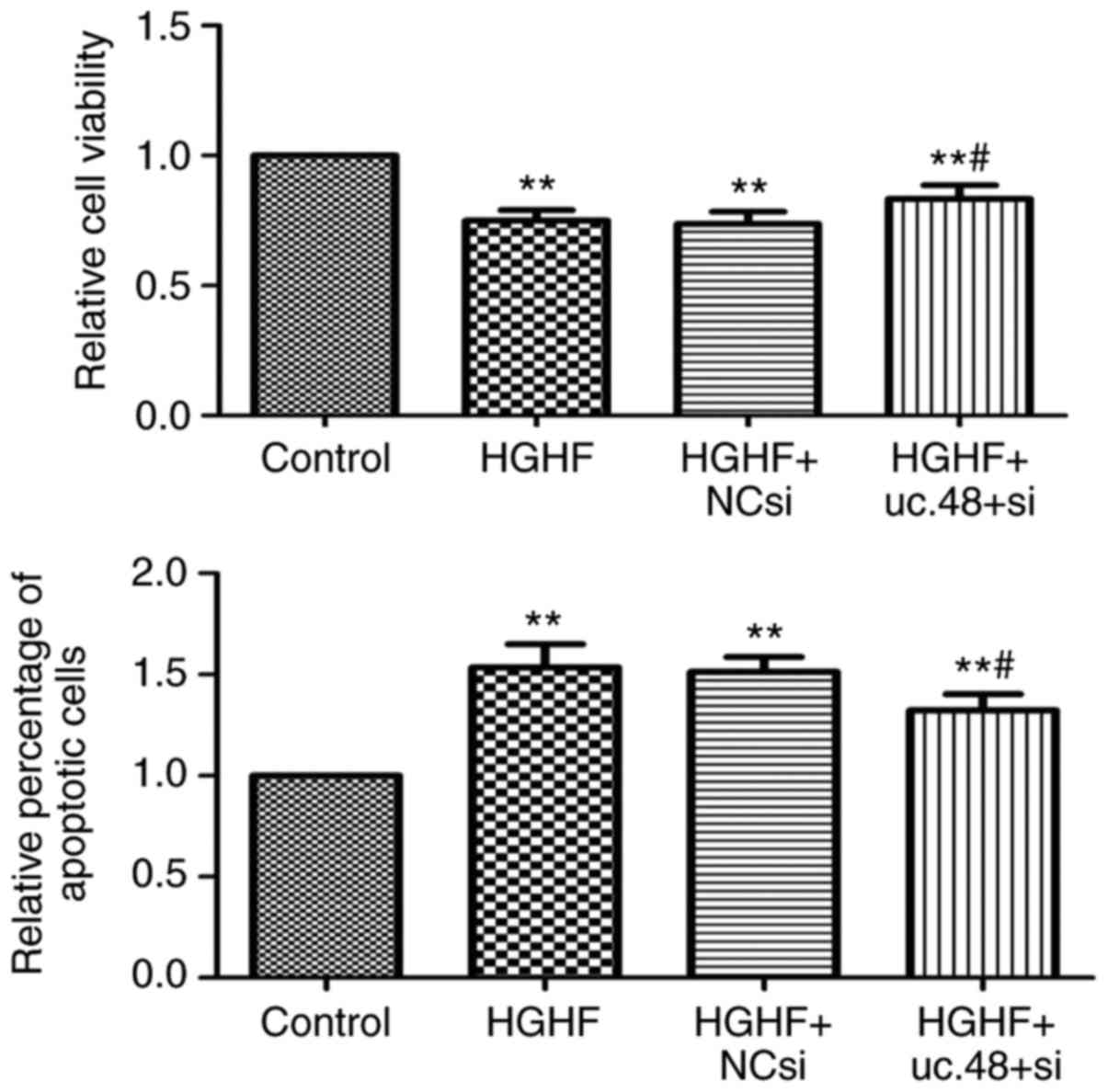
|
1
|
Czyżewska-Majchrzak Ł, Grzelak T,
Kramkowska M, Czyżewska K and Witmanowski H: The use of
low-carbohydrate diet in type 2 diabetes-benefits and risks. Ann
Agr Env Med. 21:320–326. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zonszein J, Lombardero M, Ismail-Beigi F,
Palumbo P, Foucher S, Groenewoud Y, Cushing G, Wajchenberg B and
Genuth S; Bari 2D Study Group: Triglyceride high-density
lipoprotein ratios predict glycemia-lowering in response to insulin
sensitizing drugs in type 2 diabetes: A post hoc analysis of the
BARI 2D. J Diabetes Res. 2015:1298912015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martins AR, Nachbar RT, Gorjao R, Vinolo
MA, Festuccia WT, Lambertucci RH, Cury-Boaventura MF, Silveira LR,
Curi R and Hirabara SM: Mechanisms underlying skeletal muscle
insulin resistance induced by fatty acids: Importance of the
mitochondrial function. Lipids Health Dis. 11:302012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Esser N, Legrand-Poels S, Piette J, Scheen
AJ and Paquot N: Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic
syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 105:141–150.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jansen HJ, Stienstra R, van Diepen JA,
Hijmans A, van der Laak JA, Vervoort GM and Tack CJ: Start of
insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus promotes
the influx of macrophages into subcutaneous adipose tissue.
Diabetologia. 56:2573–2581. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu H, Nie Y, Xiong H, Liu S, Li G, Huang
A, Guo L, Wang S, Xue Y, Wu B, et al: P2X7 receptor expression in
peripheral blood monocytes is correlated with plasma C-reactive
protein and cytokine levels in patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus: A preliminary report. Inflammation. 38:2076–2081. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Solini A, Chiozzi P, Morelli A, Adinolfi
E, Rizzo R, Baricordi OR and Di Virgilio F: Enhanced P2X7 activity
in human fibroblasts from diabetic patients: A possible
pathogenetic mechanism for vascular damage in diabetes. Arterioscl
Throm Vas. 24:1240–1245. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Stolz M, Klapperstuck M, Kendzierski T,
Detro-Dassen S, Panning A, Schmalzing G and Markwardt F:
Homodimeric anoctamin-1, but not homodimeric anoctamin-6, is
activated by calcium increases mediated by the P2Y1 and P2X7
receptors. Pflug Arch. 467:2121–2140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Huang SW, Walker C, Pennock J, Else K,
Muller W, Daniels MJ, Pellegrini C, Brough D, Lopez-Castejon G and
Cruickshank SM: P2X7 receptor-dependent tuning of gut epithelial
responses to infection. Immunol Cell Biol. 95:178–188. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jiang L, Liu W, Zhu A, Zhang J, Zhou J and
Wu C: Transcriptome analysis demonstrate widespread differential
expression of long noncoding RNAs involve in Larimichthys crocea
immune response. Fish Shellfish Immun. 51:1–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Boysen A, Møller-Jensen J, Kallipolitis B,
Valentin-Hansen P and Overgaard M: Translational regulation of gene
expression by an anaerobically induced small non-coding RNA in
Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 285:10690–10702. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lutz BM, Bekker A and Tao YX: Noncoding
RNAs: New players in chronic pain. Anesthesiology. 121:409–417.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song G, Shen Y, Ruan Z, Li X, Chen Y, Yuan
W, Ding X, Zhu L and Qian L: LncRNA-uc.167 influences cell
proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation of P19 cells by
regulating Mef2c. Gene. 590:97–108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bejerano G, Pheasant M, Makunin I, Stephen
S, Kent WJ, Mattick JS and Haussler D: Ultraconserved elements in
the human genome. Science. 304:1321–1325. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu C, Wang J, Yuan X, Qian W, Zhang B,
Shi M, Xie J, Shen B, Xu H, Hou Z and Chen H: Long noncoding RNA
uc.345 promotes tumorigenesis of pancreatic cancer by upregulation
of hnRNPL expression. Oncotarget. 7:71556–71566. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang S, Xu H, Zou L, Xie J, Wu H, Wu B, Yi
Z, Lv Q, Zhang X, Ying M, et al: LncRNA uc.48+ is involved in
diabetic neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X3 receptor in the
dorsal root ganglia. Purinerg Signal. 12:139–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lv Q, Xue Y, Li G, Zou L, Zhang X, Ying M,
Wang S, Guo L, Gao Y, Li G, et al: Beneficial effects of evodiamine
on P2X(4)-mediated inflammatory injury of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells due to high glucose. Int Immunopharmacol.
28:1044–1049. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu H, Wu B, Jiang F, Xiong S, Zhang B, Li
G, Liu S, Gao Y, Xu C, Tu G, et al: High fatty acids modulate
P2X(7) expression and IL-6 release via the p38 MAPK pathway in PC12
cells. Brain Res Bull. 94:63–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao Y, Liu H, Deng L, Zhu G, Xu C, Li G,
Liu S, Xie J, Liu J, Kong F, et al: Effect of emodin on neuropathic
pain transmission mediated by P2X2/3 receptor of primary sensory
neurons. Brain Res Bull. 84:406–413. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Suryadevara S, Ueno M, Tello-Montoliu A,
Ferreiro JL, Desai B, Rollini F, Box LC, Zenni M, Guzman LA, Bass
TA and Angiolillo DJ: Effects of pioglitazone on platelet
P2Y12-mediated signalling in clopidogrel-treated patients with type
2 diabetes mellitus. Thromb Haemostasis. 108:930–936. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Burnstock G and Novak I: Purinergic
signalling and diabetes. Purinerg Signal. 9:307–324. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jaé N and Dimmeler S: Long noncoding RNAs
in diabetic retinopathy. Circ Res. 116:1104–1106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang GJ, Zhang T, An T, Zhao DD, Yang XY,
Zhang DW, Zhang Y, Mu QQ, Yu N, Ma XS and Gao SH: Differential
expression of long noncoding RNAs between sperm samples from
diabetic and non-diabetic mice. PloS One. 11:e01540282016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao W, Wang ZM, Zhu M, Lian XQ, Zhao H,
Zhao D, Yang ZJ, Lu X and Wang LS: Altered long noncoding RNA
expression profiles in the myocardium of rats with ischemic heart
failure. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 16:473–479. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Younce CW, Wang K and Kolattukudy PE:
Hyperglycaemiainduced cardiomyocyte death is mediated via MCP-1
production and induction of a novel zinc-finger protein MCPIP.
Cardiovasc Res. 87:665–674. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Glas R, Sauter NS, Schulthess FT, Shu L,
Oberholzer J and Maedler K: Purinergic P2X7 receptors regulate
secretion of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and beta cell
function and survival. Diabetologia. 52:1579–1588. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu S, Zou L, Xie J, Xie W, Wen S, Xie Q,
Gao Y, Li G, Zhang C, Xu C, et al: LncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA
regulates neuropathic pain behaviors in type 2 diabetic rats
through the P2X7 receptor in dorsal root ganglia. Mol Brain.
9:442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fernández-Real JM and Pickup JC: Innate
immunity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia.
55:273–278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mirza S, Hossain M, Mathews C, Martinez P,
Pino P, Gay JL, Rentfro A, McCormick JB and Fisher-Hoch SP: Type
2-diabetes is associated with elevated levels of TNF-alpha, IL-6
and adiponectin and low levels of leptin in a population of Mexican
Americans: A cross-sectional study. Cytokine. 57:136–142. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Saraswathi V, Ramnanan CJ, Wilks AW,
Desouza CV, Eller AA, Murali G, Ramalingam R, Milne GL, Coate KC
and Edgerton DS: Impact of hematopoietic cyclooxygenase-1
deficiency on obesity-linked adipose tissue inflammation and
metabolic disorders in mice. Metabolism. 62:1673–1685. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dinarello CA: Immunological and
inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu Rev
Immunol. 27:519–550. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ciraci C, Janczy JR, Sutterwala FS and
Cassel SL: Control of innate and adaptive immunity by the
inflammasome. Microbes Infect. 14:1263–1270. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dinarello CA: Blocking interleukin-1β in
acute and chronic autoinflammatory diseases. J Intern Med.
269:16–28. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Ponnusamy M, Liu N, Gong R, Yan H and
Zhuang S: ERK pathway mediates P2X7 expression and cell death in
renal interstitial fibroblasts exposed to necrotic renal epithelial
cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 301:F650–F659. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zanin RF, Bergamin LS, Morrone FB,
Coutinho-Silva R, de Souza Wyse AT and Battastini AM: Pathological
concentrations of homocysteine increases IL-1β production in
macrophages in a P2X7, NF-κB, and erk-dependent manner. Purinerg
Signal. 11:463–470. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wu B, Zhang C, Zou L, Ma Y, Huang K, Lv Q,
Zhang X, Wang S, Xue Y, Yi Z, et al: LncRNA uc.48+ siRNA improved
diabetic sympathetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetic rats mediated by
P2X7, receptor in SCG. Auton Neurosci. 197:14–18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|