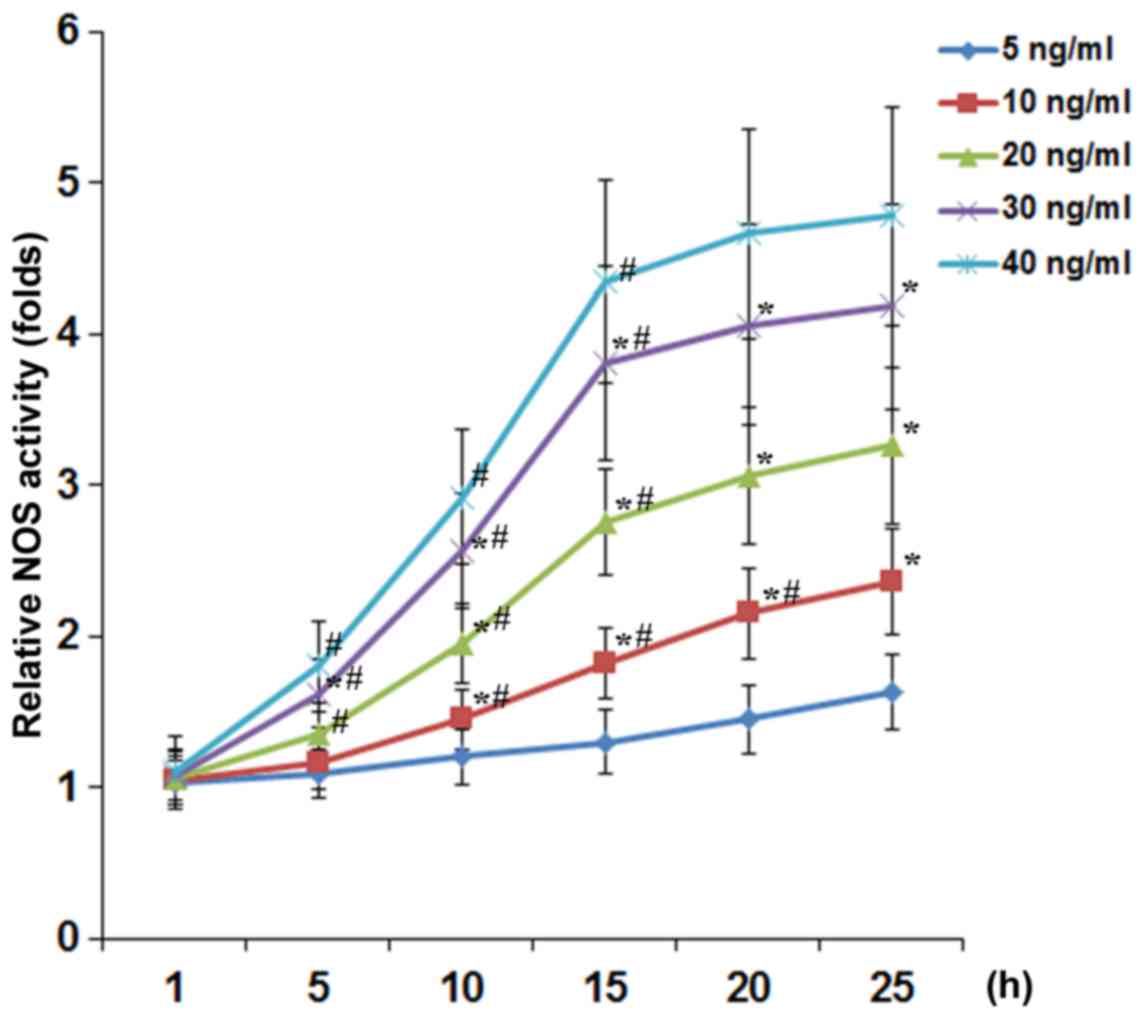
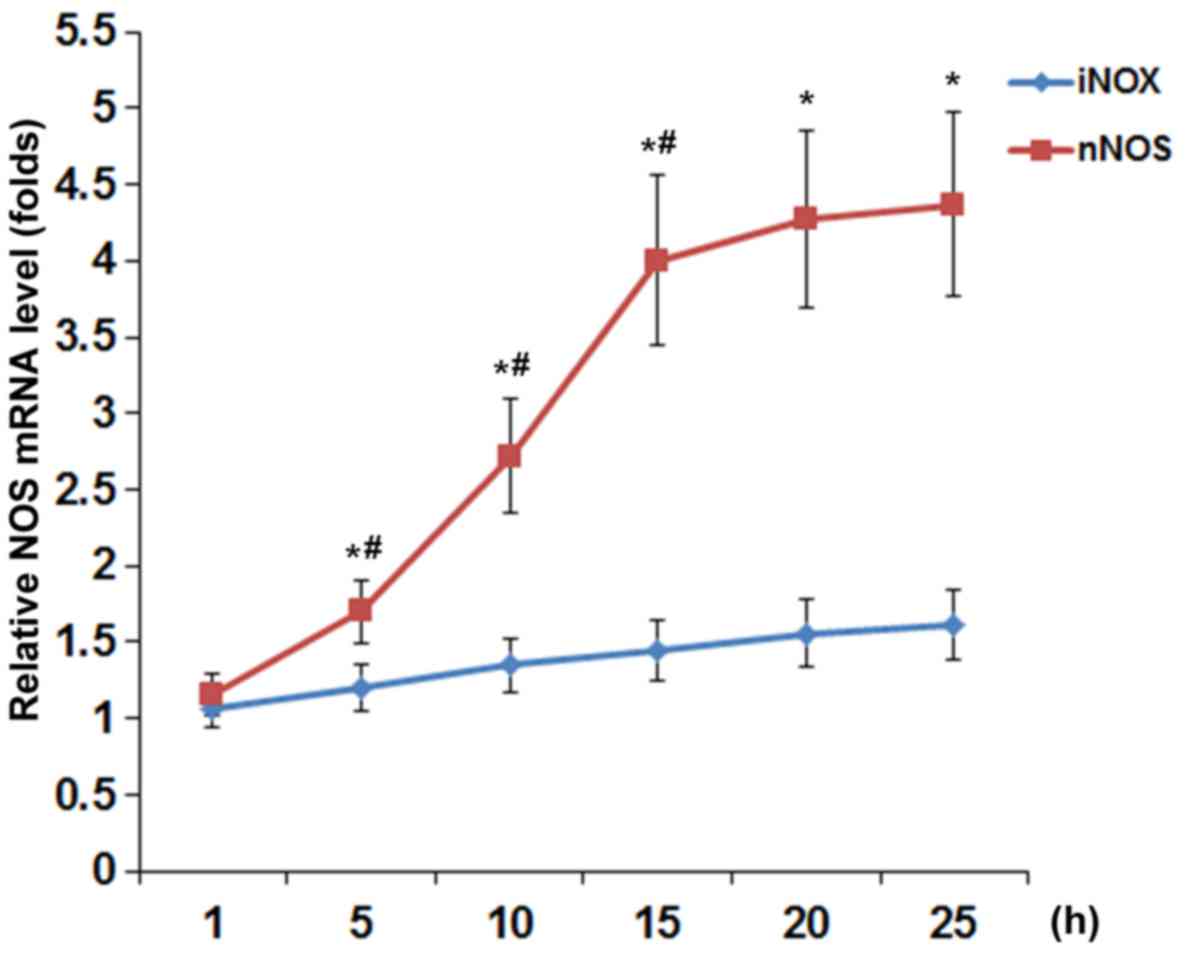
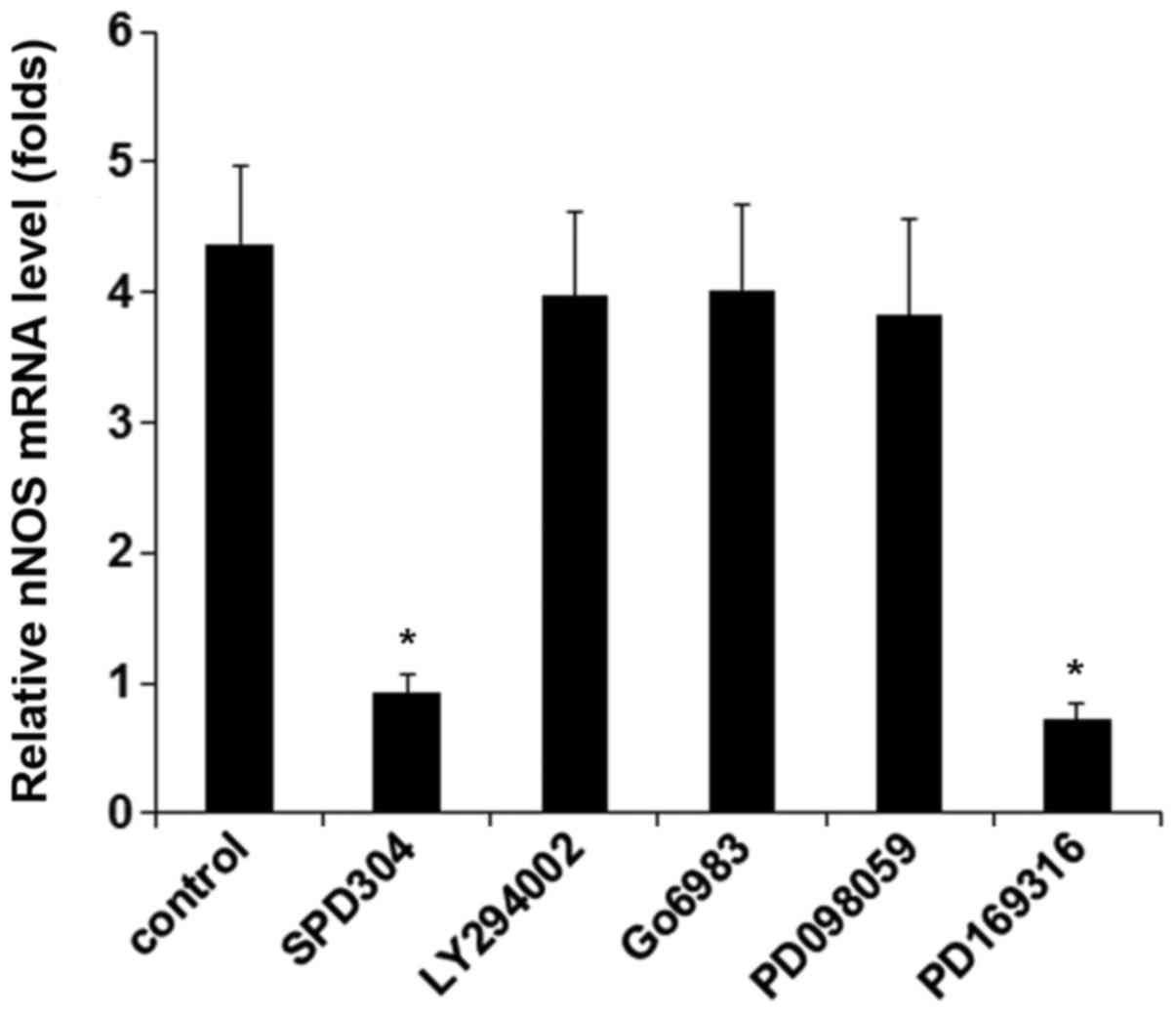
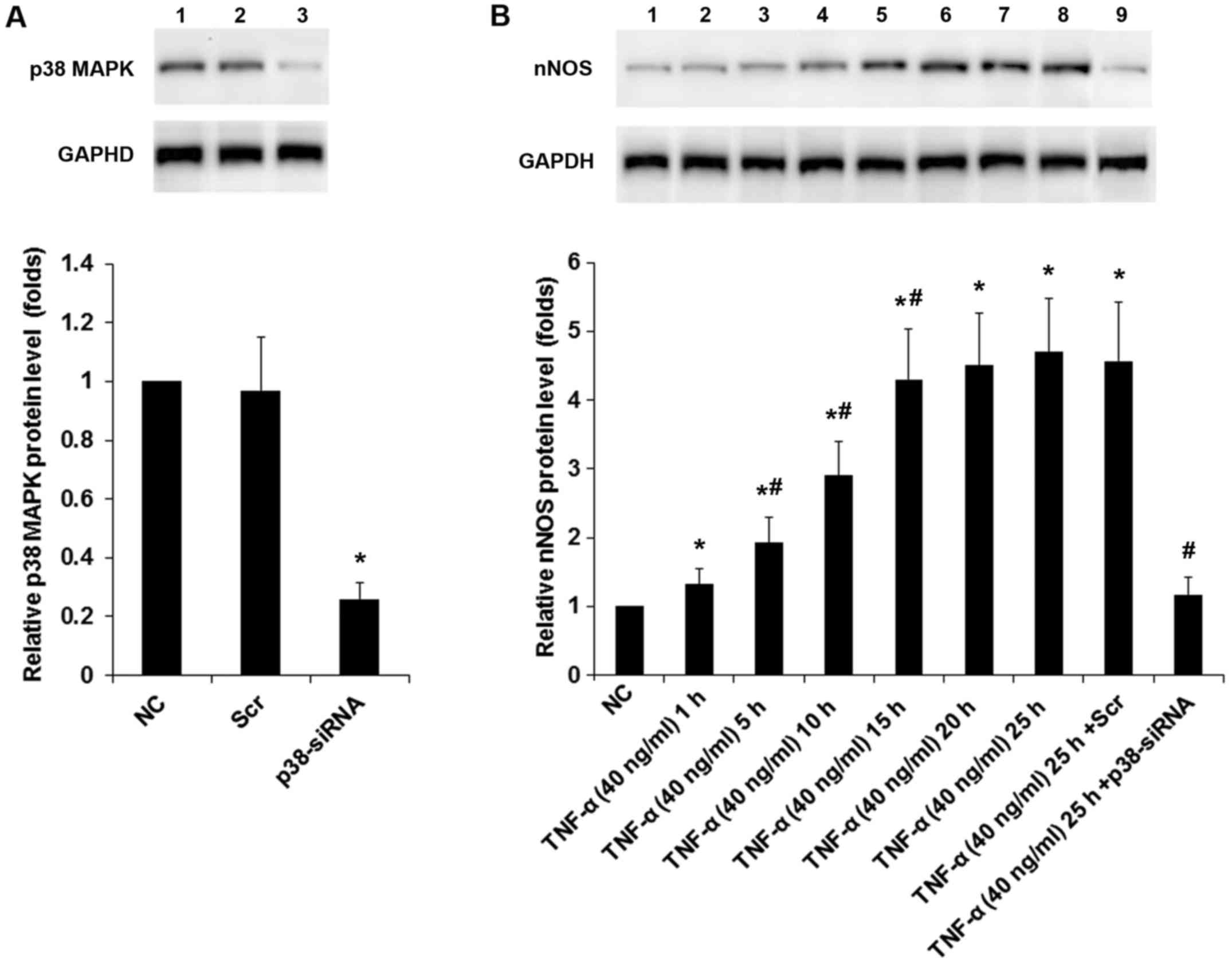
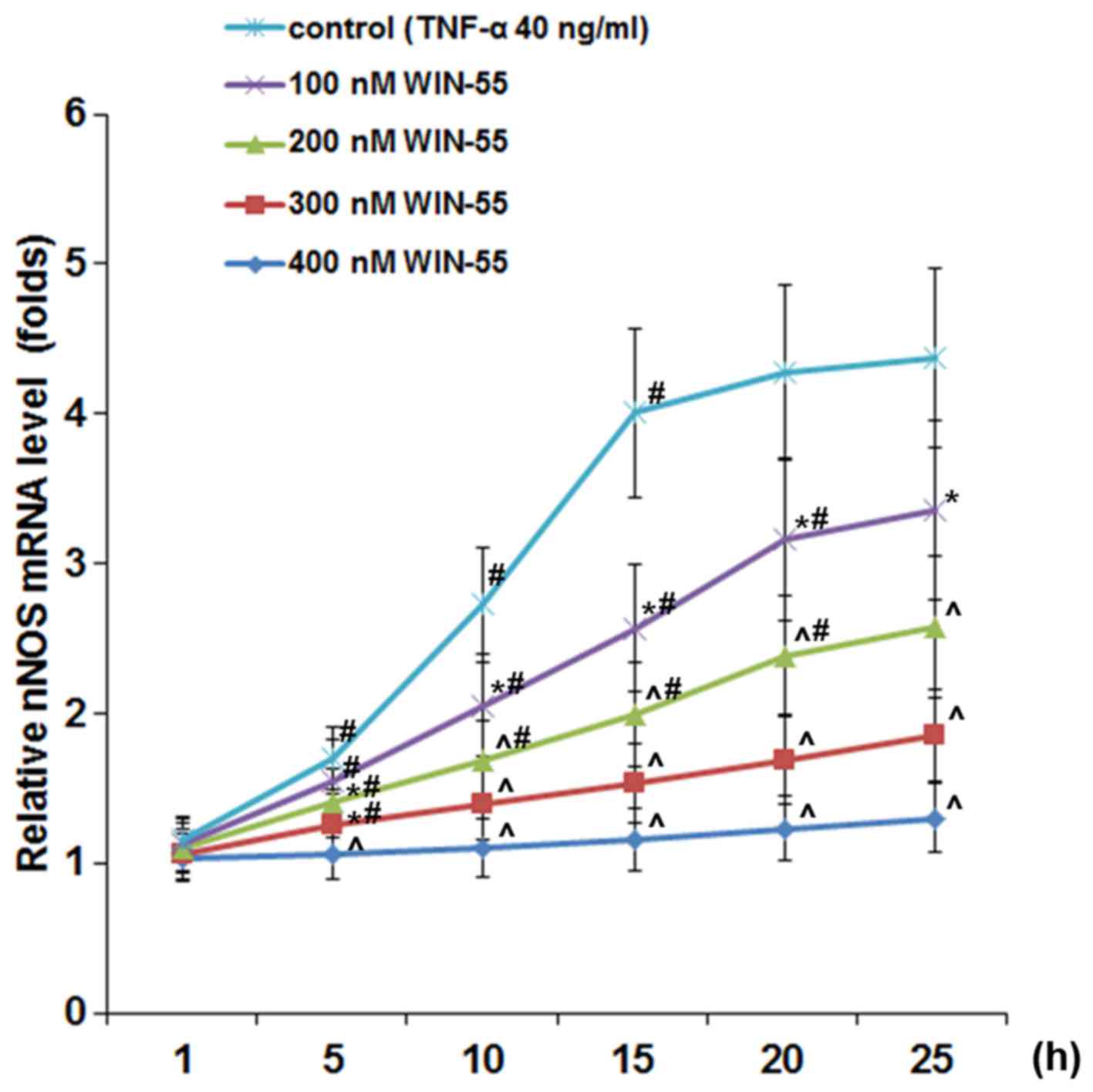
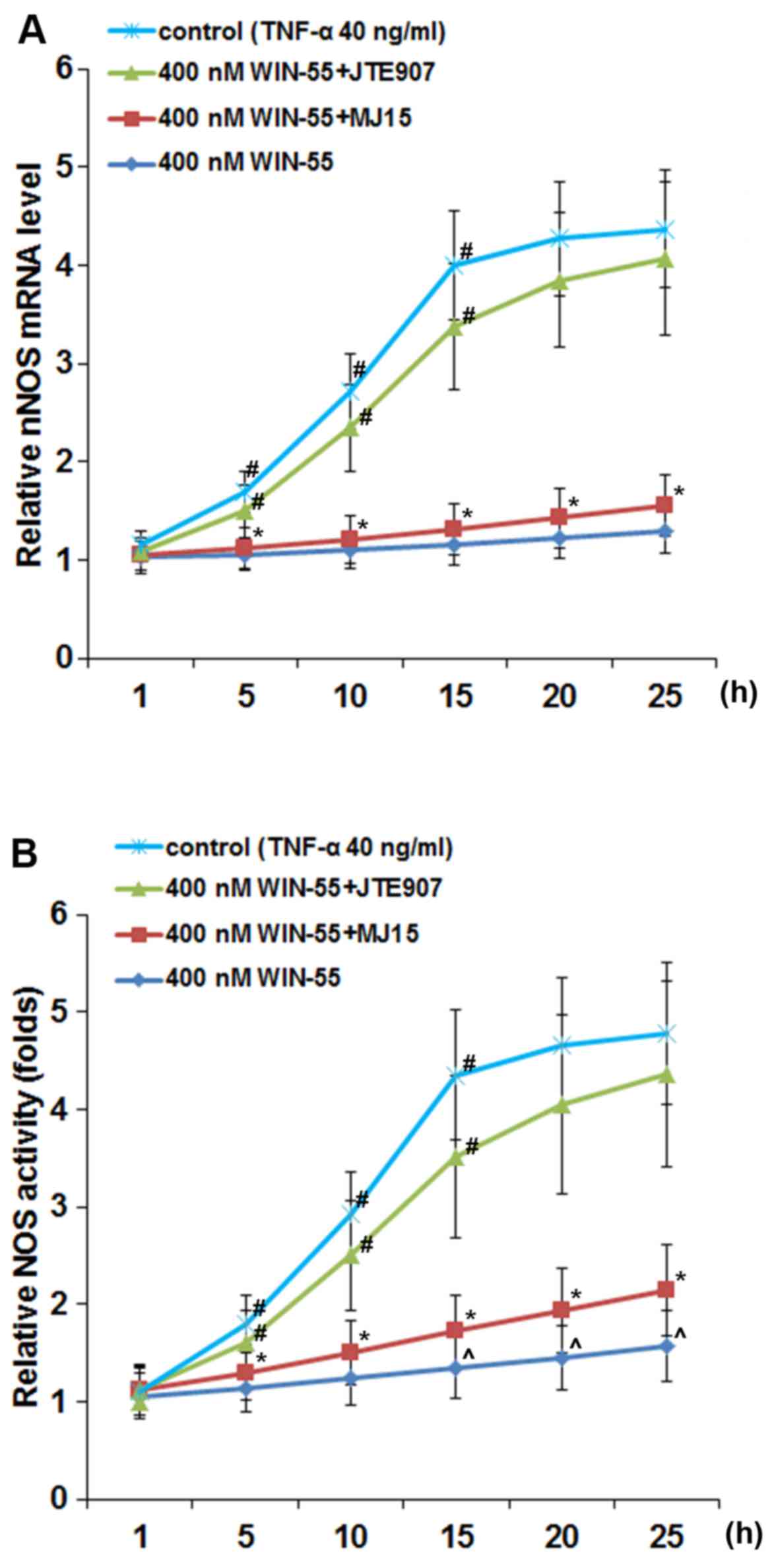
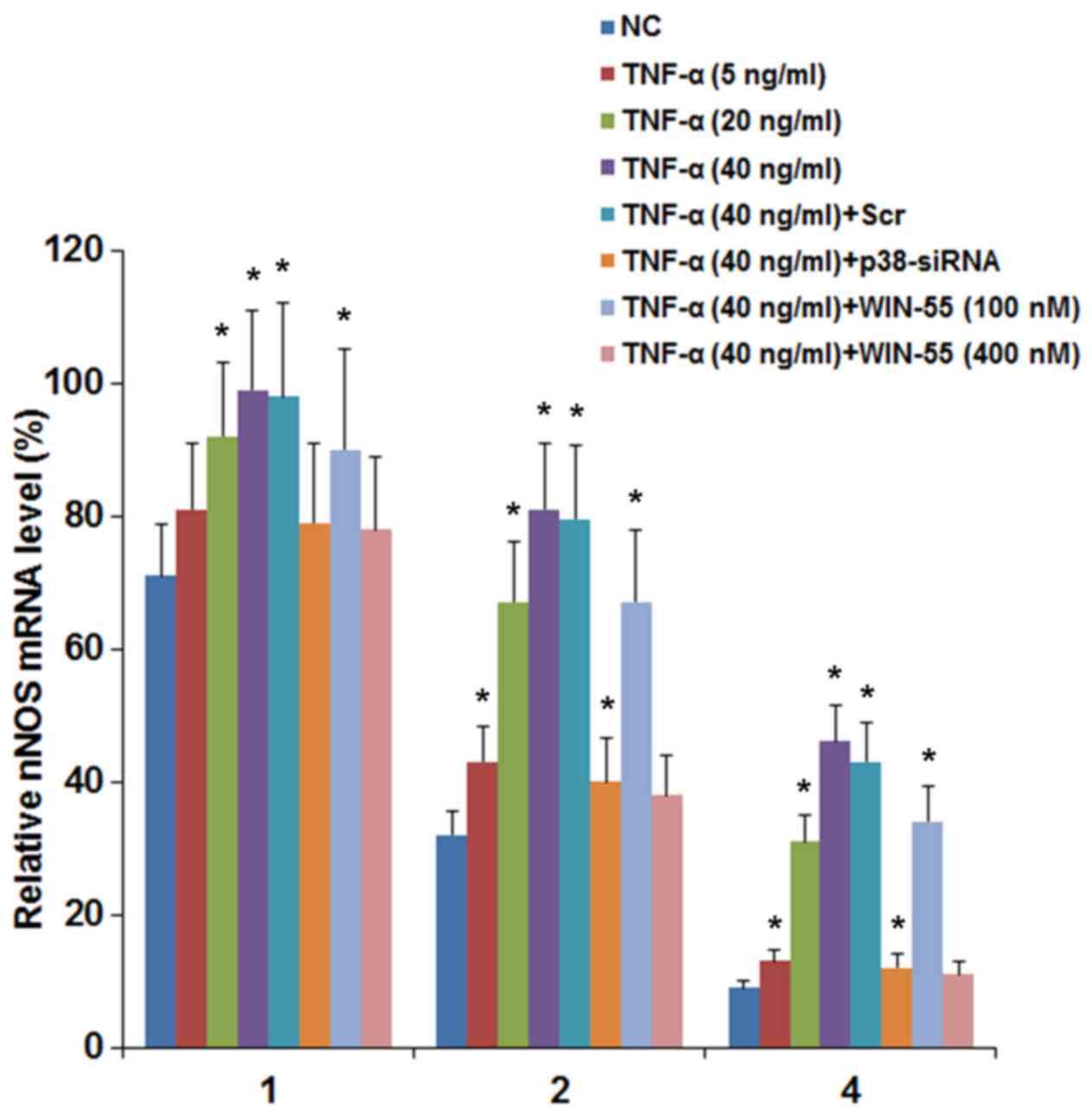
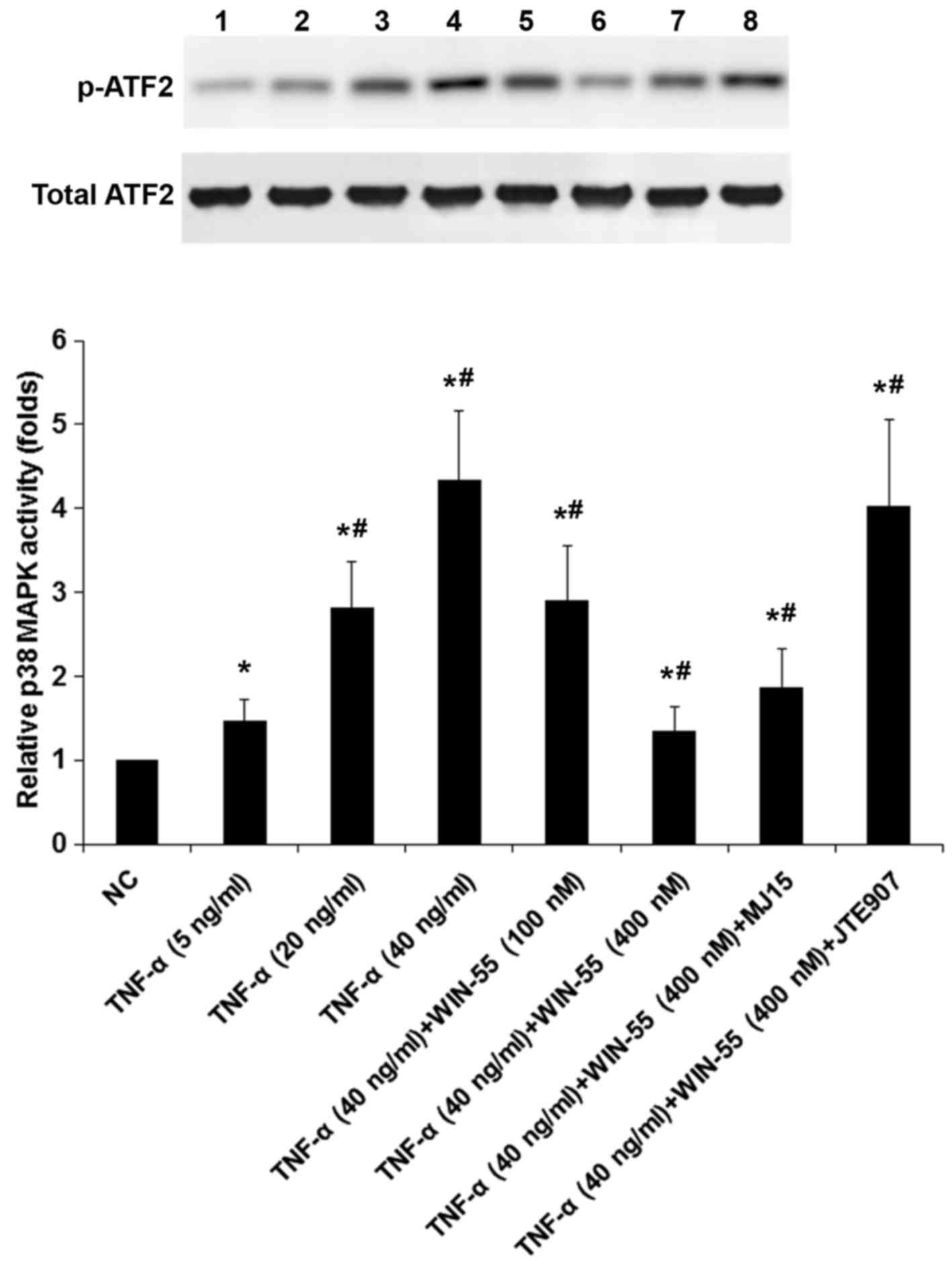
|
1
|
Saarto T and Wiffen PJ: Antidepressants
for neuropathic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
3:CD0054542005.
|
|
2
|
Lin HC, Huang YH, Chao TH, Lin WY, Sun WZ
and Yen CT: Gabapentin reverses central hypersensitivity and
suppresses medial prefrontal cortical glucose metabolism in rats
with neuropathic pain. Mol Pain. 10:632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Przewlocki R and Przewlocka B: Opioids in
neuropathic pain. Curr Pharm Des. 11:3013–3025. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chu LW, Chen JY, Wu PC and Wu BN:
Atorvastatin prevents neuroinflammation in chronic constriction
injury rats through nuclear NFκB downregulation in the dorsal root
ganglion and spinal cord. ACS Chem Neurosci. 6:889–898. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yang Y, Wu H, Yan JQ, Song ZB and Guo QL:
Tumor necrosis factor-α inhibits angiotensin II receptor type 1
expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons via β-catenin signaling.
Neuroscience. 248:383–391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Westacott CI, Atkins RM, Dieppe PA and
Elson CJ: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor expression on
chondrocytes isolated from human articular cartilage. J Rheumatol.
21:1710–1715. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boettger MK, Uceyler N, Zelenka M, Schmitt
A, Reif A, Chen Y and Sommer C: Differences in inflammatory pain in
nNOS-, iNOS- and eNOS-deficient mice. Eur J Pain. 11:810–818. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tao F, Tao YX, Zhao C, Doré S, Liaw WJ,
Raja SN and Johns RA: Differential roles of neuronal and
endothelial nitric oxide synthases during carrageenan-induced
inflammatory hyperalgesia. Neuroscience. 128:421–430. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hama A and Sagen J: Antinociceptive effect
of cannabinoid agonist WIN 55,212-2 in rats with a spinal cord
injury. Exp Neurol. 204:454–457. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rahn EJ and Hohmann AG: Cannabinoids as
pharmacotherapies for neuropathic pain: From the bench to the
bedside. Neurotherapeutics. 6:713–737. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hegyi Z, Kis G, Holló K, Ledent C and
Antal M: Neuronal and glial localization of the cannabinoid-1
receptor in the superficial spinal dorsal horn of the rodent spinal
cord. Eur J Neurosci. 30:251–262. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsieh GC, Pai M, Chandran P, Hooker BA,
Zhu CZ, Salyers AK, Wensink EJ, Zhan C, Carroll WA, Dart MJ, et al:
Central and peripheral sites of action for CB2 receptor mediated
analgesic activity in chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain
models in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 162:428–440. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Lim G, Sung B, Ji RR and Mao J:
Upregulation of spinal cannabinoid-1-receptors following nerve
injury enhances the effects of Win 55,212-2 on neuropathic pain
behaviors in rats. Pain. 105:275–283. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Amaya F, Shimosato G, Kawasaki Y,
Hashimoto S, Tanaka Y, Ji RR and Tanaka M: Induction of CB1
cannabinoid receptor by inflammation in primary afferent neurons
facilitates antihyperalgesic effect of peripheral CB1 agonist.
Pain. 124:175–183. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fernández-Ruiz J, Pazos MR,
García-Arencibia M, Sagredo O and Ramos JA: Role of CB2 receptors
in neuroprotective effects of cannabinoids. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
286(Suppl 1): S91–S96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mbvundula EC, Bunning RA and Rainsford KD:
Arthritis and cannabinoids: HU-210 and Win-55,212-2 prevent
IL-1alpha-induced matrix degradation in bovine articular
chondrocytes in-vitro. J Pharm Pharmacol. 58:351–358. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu Q, Bhat M, Bowen WD and Cheng J:
Signaling pathways from cannabinoid receptor-1 activation to
inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid mediated calcium influx and
neurotoxicity in dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 331:1062–1070. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Anand U, Otto WR, Sanchez-Herrera D, Facer
P, Yiangou Y, Korchev Y, Birch R, Benham C, Bountra C, Chessell IP,
et al: Cannabinoid receptor CB2 localisation and agonist-mediated
inhibition of capsaicin responses in human sensory neurons. Pain.
138:667–680. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Paszcuk AF, Dutra RC, da Silva KA, Quintão
L, Campos MM and Calixto JB: Cannabinoid agonists inhibit
neuropathic pain induced by brachial plexus avulsion in mice by
affecting glial cells and MAP kinases. PLoS One. 6:e240342011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang X, Wu H and Miller AH: Interleukin
1alpha (IL-1alpha) induced activation of p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase inhibits glucocorticoid receptor function. Mol
Psychiatry. 9:65–75. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jia P, Wang J, Wang L, Chen X, Chen Y, Li
WZ, Long R, Chen J, Shu YW, Liu K, et al: TNF-α upregulates Fgl2
expression in rat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Microcirculation. 20:524–533. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang RK, Zhang QQ, Pan YD and Guo QL:
Etanercept decreases HMGB1 expression in dorsal root ganglion
neuron cells in a rat chronic constriction injury model. Exp Ther
Med. 5:581–585. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu JT, Xin WJ, Wei XH, Wu CY, Ge YX, Liu
YL, Zang Y, Zhang T, Li YY and Liu XG: p38 activation in uninjured
primary afferent neurons and in spinal microglia contributes to the
development of neuropathic pain induced by selective motor fiber
injury. Exp Neurol. 204:355–365. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wilkerson JL, Gentry KR, Dengler EC,
Wallace JA, Kerwin AA, Kuhn MN, Zvonok AM, Thakur GA, Makriyannis A
and Milligan ED: Immunofluorescent spectral analysis reveals the
intrathecal cannabinoid agonist, AM1241, produces spinal
anti-inflammatory cytokine responses in neuropathic rats exhibiting
relief from allodynia. Brain Behav. 2:155–177. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wilkerson JL, Gentry KR, Dengler EC,
Wallace JA, Kerwin AA, Armijo LM, Kuhn MN, Thakur GA, Makriyannis A
and Milligan ED: Intrathecal cannabilactone CB(2)R agonist, AM1710,
controls pathological pain and restores basal cytokine levels.
Pain. 153:1091–1106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|