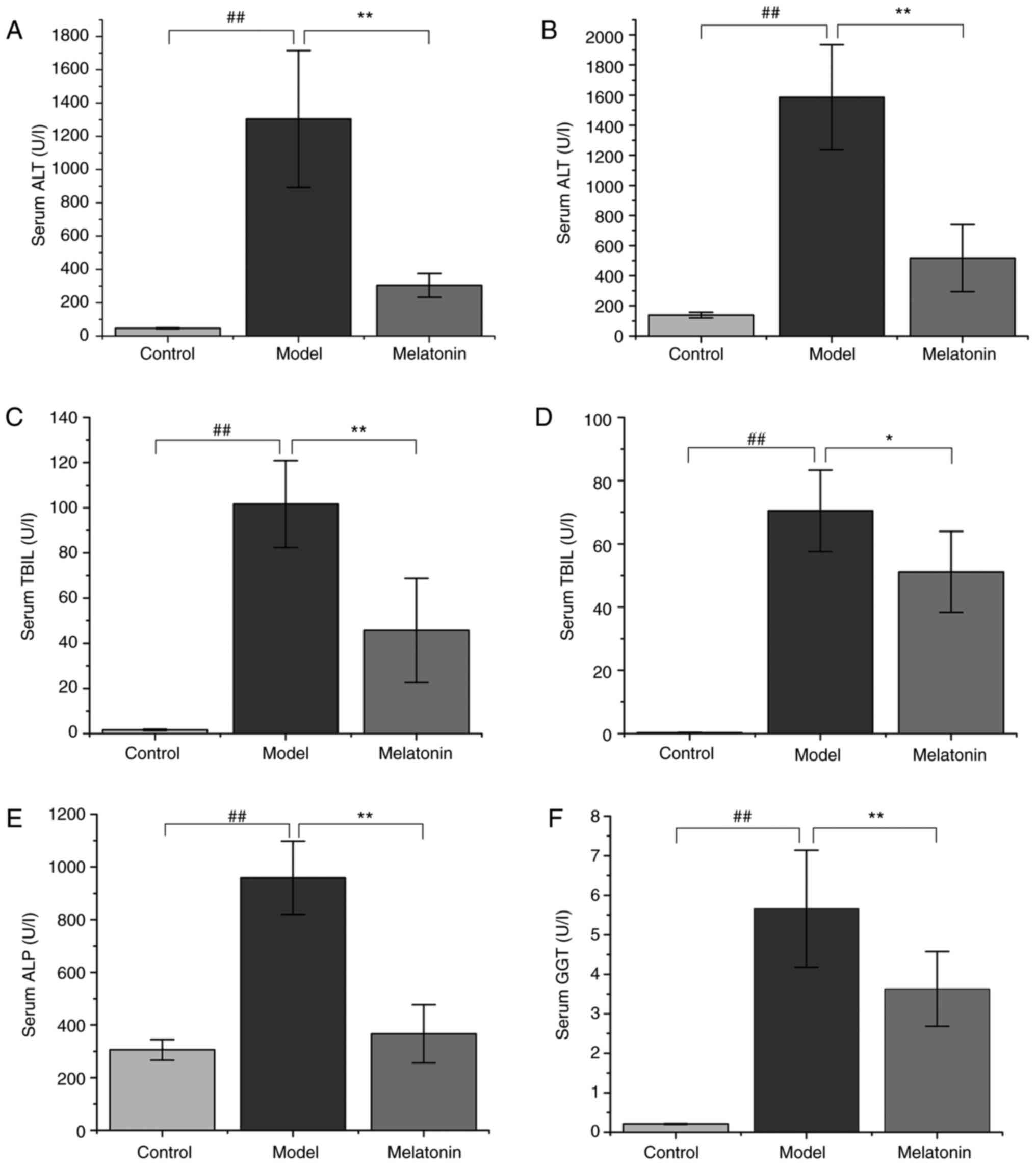
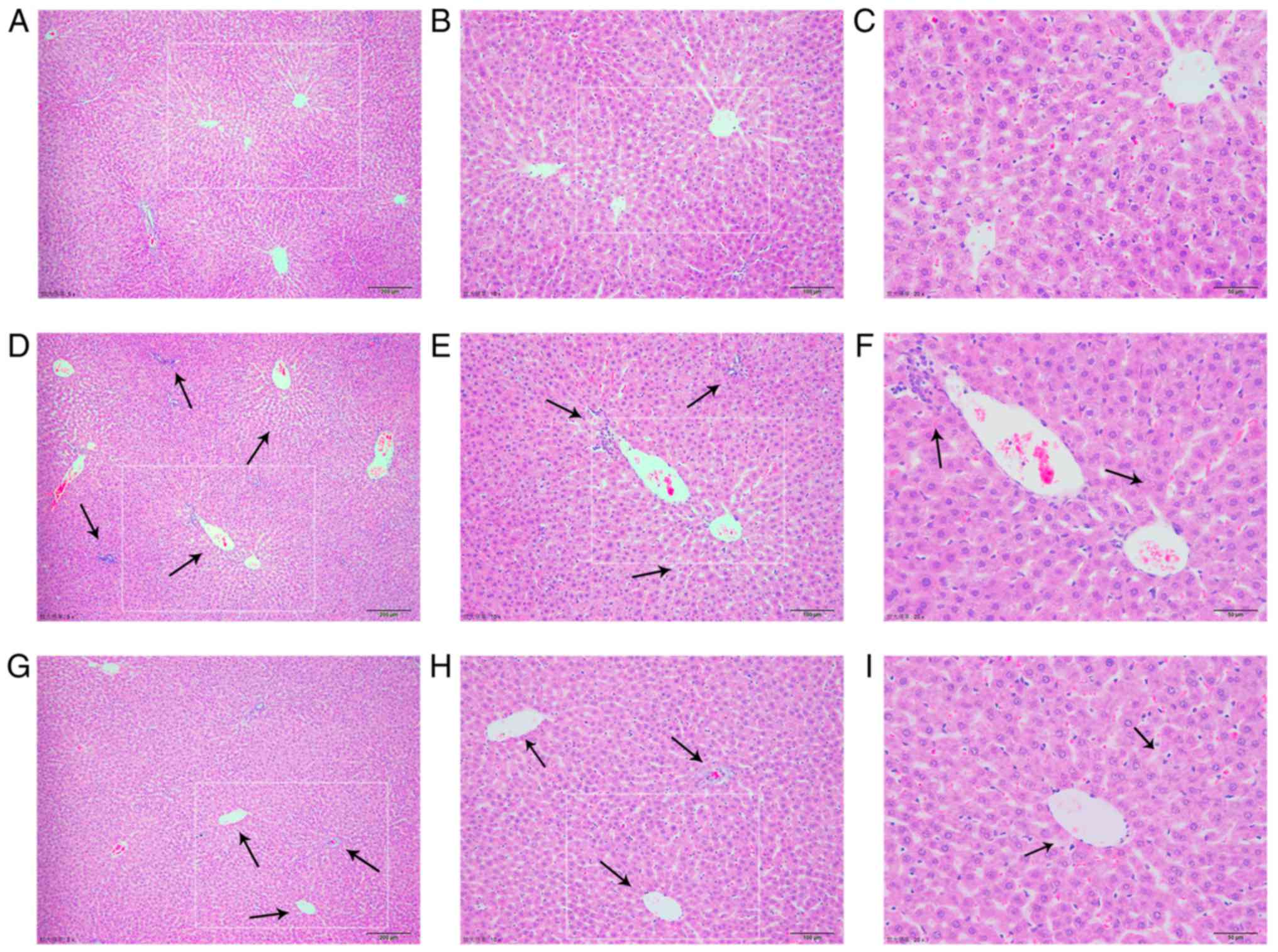
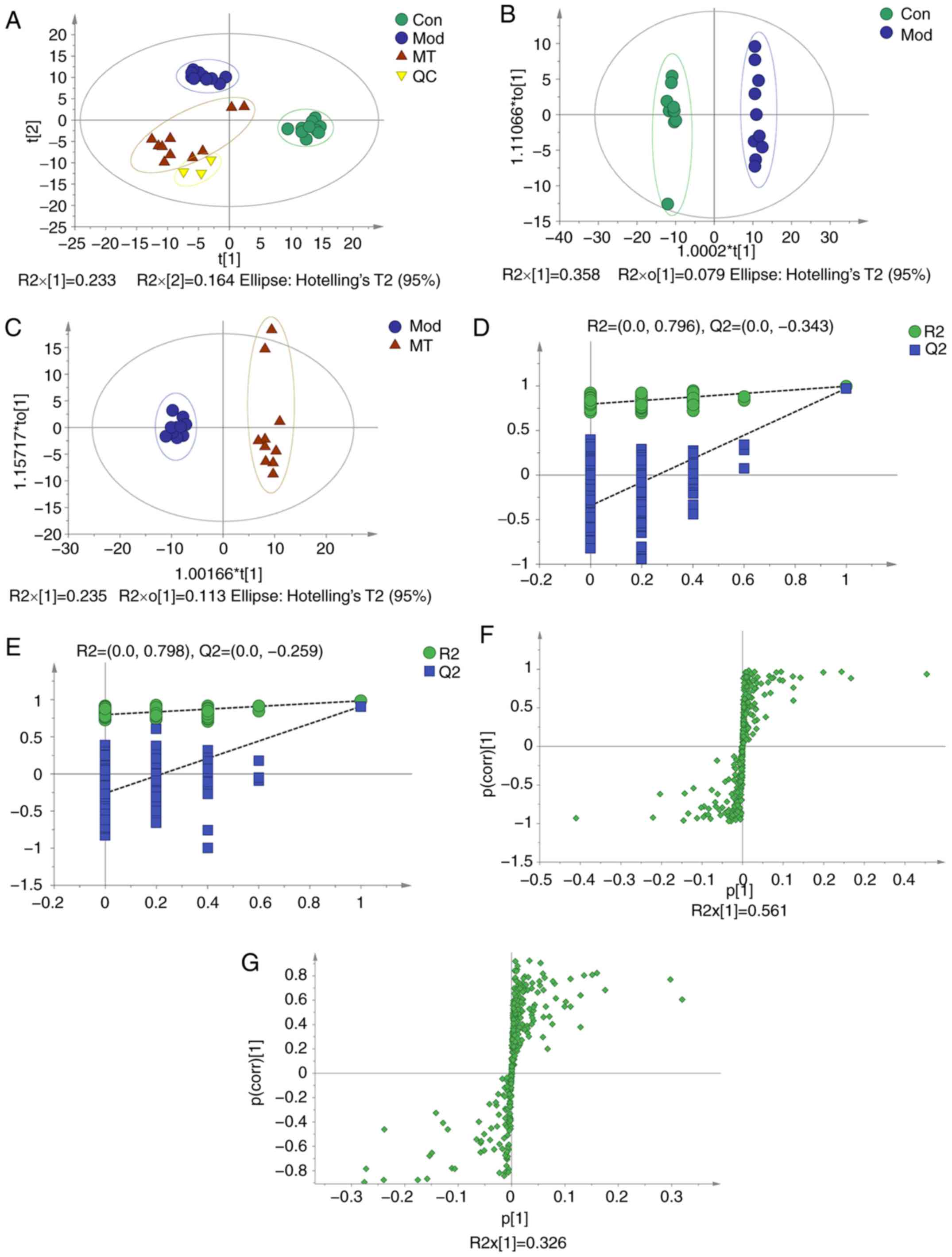
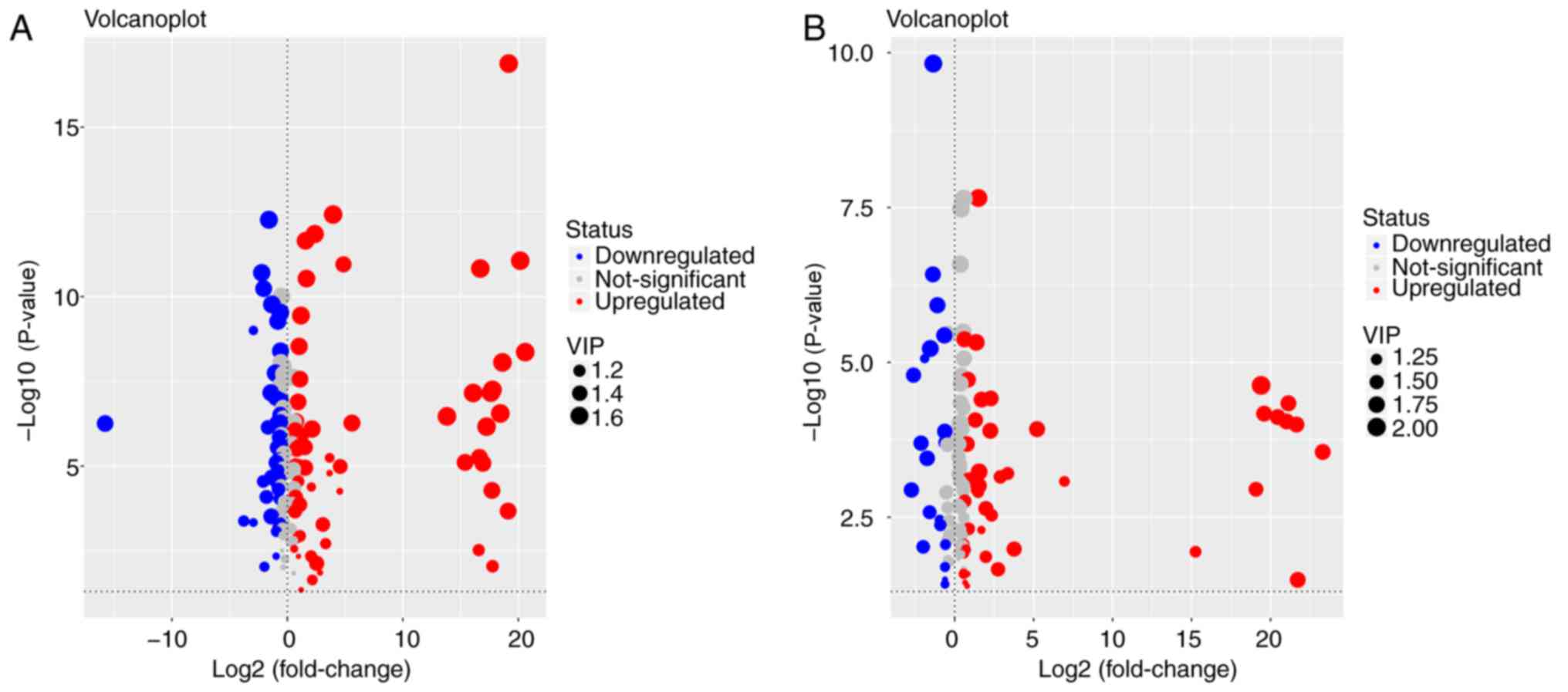
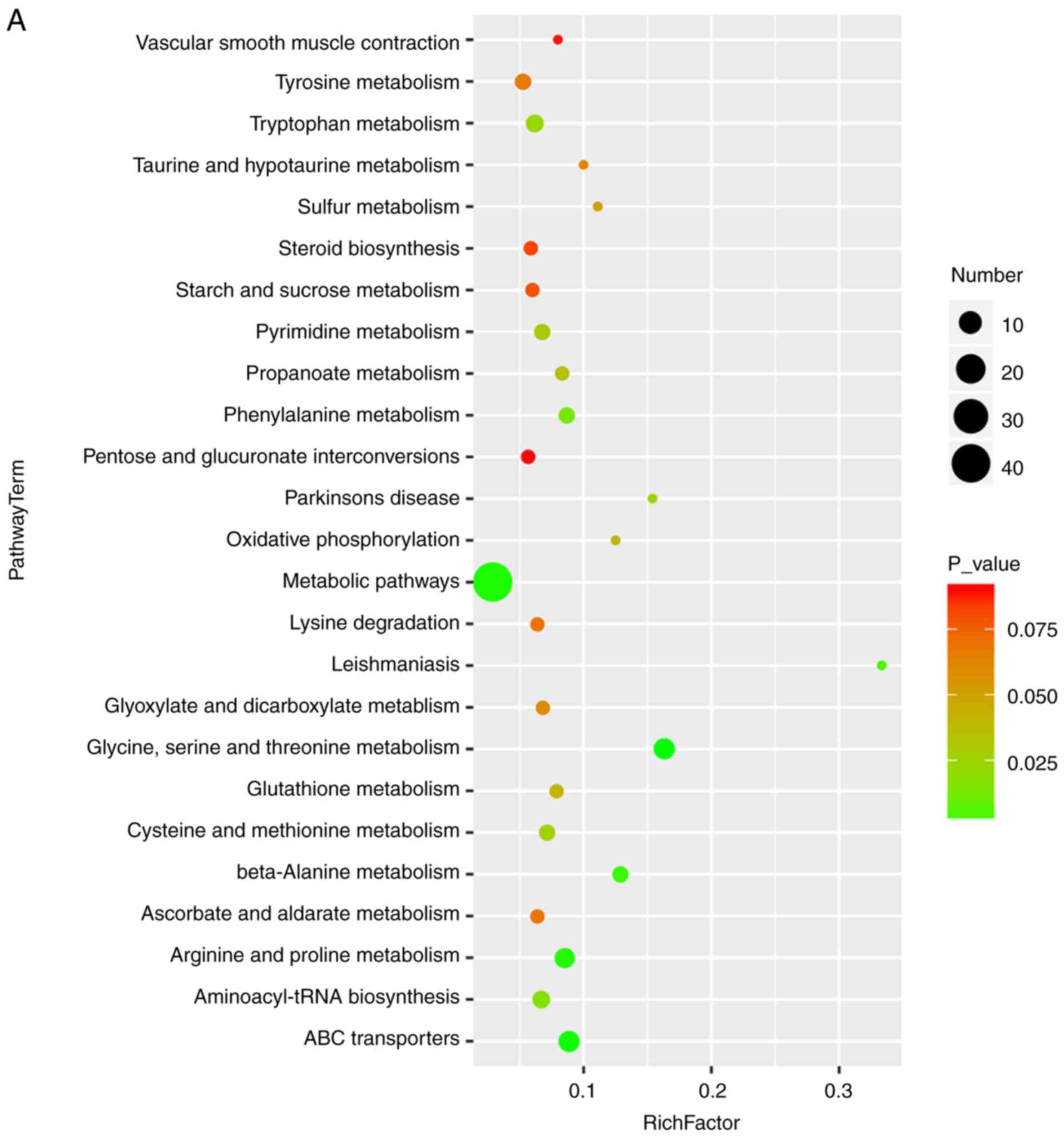
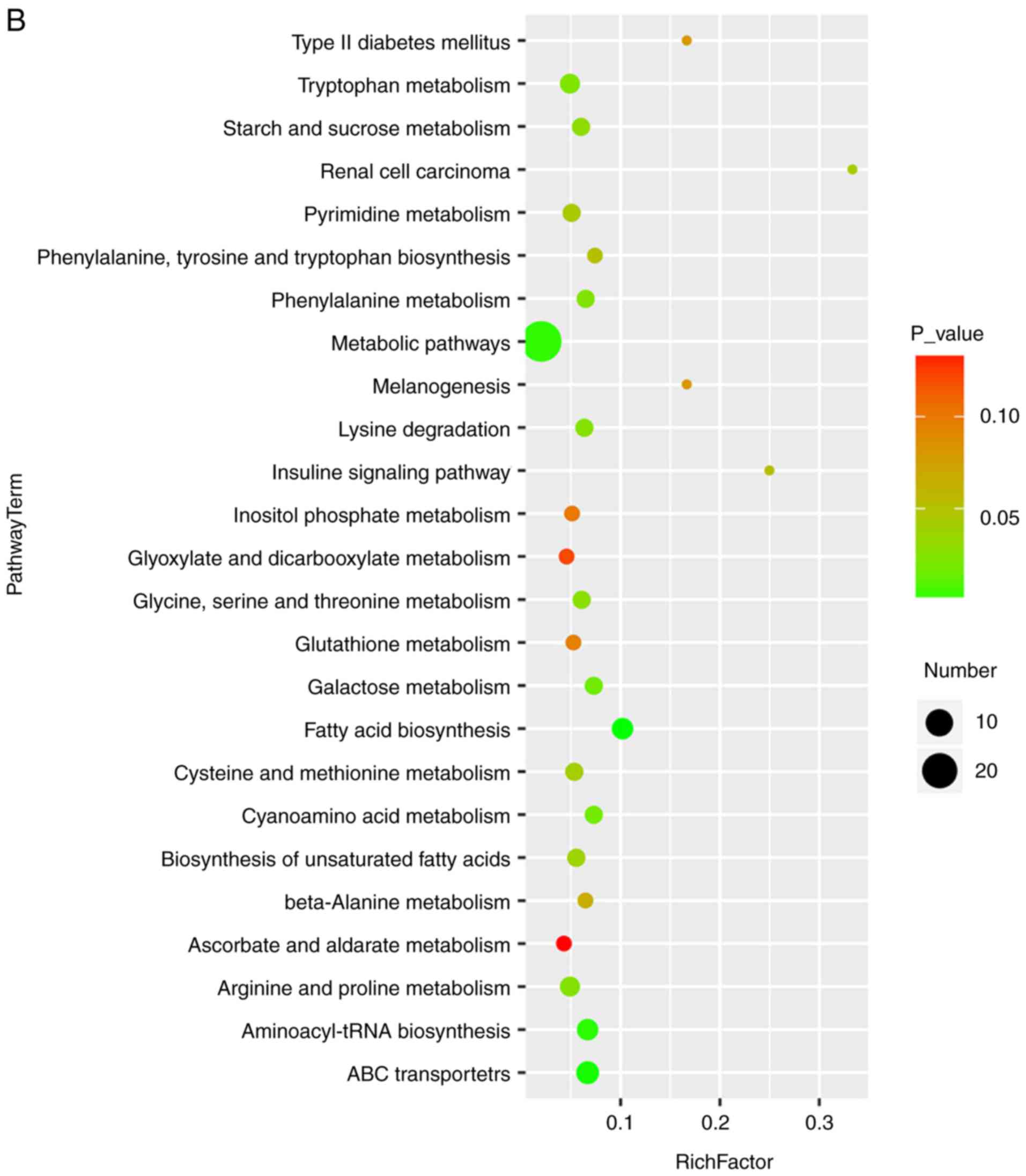
|
1
|
Cao X, Gao Y, Zhang W, Xu P, Fu Q, Chen C,
Li C, Yang C, Ma G, Qu Y, et al: Cholestasis morbidity rate in
first-hospitalized patients with chronic liver disease in Shanghai.
Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 23:569–573. 2015.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang K, Köck K, Sedykh A, Tropsha A and
Brouwer KL: An updated review on drug-induced cholestasis:
Mechanisms and investigation of physicochemical properties and
pharmacokinetic parameters. J Pharm Sci. 102:3037–3057. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver: EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of cholestatic
liver diseases. J Hepatol. 51:237–267. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park HW, Lee NM, Kim JH, Kim KS and Kim
SN: Parenteral fish oil-containing lipid emulsions may reverse
parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis in neonates: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nutr. 145:277–283. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boyer JL: New perspectives for the
treatment of cholestasis: Lessons from basic science applied
clinically. J Hepatol. 46:365–371. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pollock G and Minuk GY: Diagnostic
considerations for chole-static liver disease. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 32:1303–1309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Allen K, Jaeschke H and Copple BL: Bile
acids induce inflammatory genes in hepatocytes: A novel mechanism
of inflammation during obstructive cholestasis. Am J Pathol.
178:175–186. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weerachayaphorn J, Luo Y, Mennone A,
Soroka CJ, Harry K and Boyer JL: Deleterious effect of oltipraz on
extrahepatic cholestasis in bile duct-ligated mice. J Hepatol.
60:160–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Beuers U, Rauner M, Jansen P and Poupon R:
New paradigms in the treatment of hepatic cholestasis: From UDCA to
FXR, PXR and beyond. J Hepatol. 62(Suppl 1): S25–S37. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kaplan MM and Gershwin ME: Primary biliary
cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 353:1261–1273. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McKiernan PJ: Neonatal cholestasis. Semin
Neonatol. 7:153–165. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ghonem NS, Assis DN and Boyer JL: Fibrates
and cholestasis. Hepatology. 62:635–643. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Acuña-Castroviejo D, Escames G, Venegas C,
Díaz-Casado ME, Lima-Cabello E, López LC, Rosales-Corral S, Tan DX
and Reiter RJ: Extrapineal melatonin: Sources, regulation, and
potential functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 71:2997–3025. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pääkkönen T, Mäkinen TM, Leppäluoto J,
Vakkuri O, Rintamäki H, Palinkas LA and Hassi J: Urinary melatonin:
A noninvasive method to follow human pineal function as studied in
three experimental conditions. J Pineal Res. 40:110–115. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Claustrat B and Leston J: Melatonin:
Physiological effects in humans. Neurochirurgie. 61:77–84. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Calvo JR, González-Yanes C and Maldonado
MD: The role of melatonin in the cells of the innate immunity: A
review. J Pineal Res. 55:103–120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lotufo CM, Lopes C, Dubocovich ML, Farsky
SH and Markus RP: Melatonin and N-acetylserotonin inhibit leukocyte
rolling and adhesion to rat microcirculation. Eur J Pharmacol.
430:351–357. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Allegra M, Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Gentile C,
Tesoriere L and Livrea MA: The chemistry of melatonin's interaction
with reactive species. J Pineal Res. 34:1–10. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jaworek J, Leja-Szpak A, Kot M, Jaworek A,
Nawrot-Porbka K, Bonior J and Szklarczyk J: The role of melatonin
in pancreatic protection: Could melatonin be used in the treatment
of acute pancreatitis? Curr Pharm Des. 20:4834–4840. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ohta Y, Kongo-Nishimura M, Imai Y and
Kitagawa A: Melatonin attenuates disruption of serum cholesterol
status in rats with a single alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate
treatment. J Pineal Res. 42:159–165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang JB, Zhao HP, Zhao YL, Jin C, Liu DJ,
Kong WJ, Fang F, Zhang L, Wang HJ and Xiao XH: Hepatotoxicity or
hepatoprotection? Pattern recognition for the paradoxical effect of
the Chinese herb Rheum palmatum L. in treating rat liver injury.
PLoS One. 6:e244982011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X, Zhang A, Han Y, Wang P, Sun H,
Song G, Dong T, Yuan Y, Yuan X, Zhang M, et al: Urine metabolomics
analysis for biomarker discovery and detection of jaundice syndrome
in patients with liver disease. Mol Cell Proteomics. 11:370–380.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma X, Chi YH, Niu M, Zhu Y, Zhao YL, Chen
Z, Wang JB, Zhang CE, Li JY, Wang LF, et al: Metabolomics coupled
with multivariate data and pathway analysis on potential biomarkers
in cholestasis and intervention effect of Paeonia lactiflora Pall.
Front Pharmacol. 7:142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun H, Zhang AH, Zou DX, Sun WJ, Wu XH and
Wang XJ: Metabolomics coupled with pattern recognition and pathway
analysis on potential biomarkers in liver injury and
hepatoprotective effects of yinchenhao. Appl Biochem Biotechnol.
173:857–869. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang CE, Niu M, Li RY, Feng WW, Ma X,
Dong Q, Ma ZJ, Li GQ, Meng YK, Wang Y, et al: Untargeted
metabolomics reveals dose-response characteristics for effect of
rhubarb in a rat model of cholestasis. Front Pharmacol. 7:852016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hill DA and Roth RA:
Alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate causes neutrophils to release factors
that are cytotoxic to hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
148:169–175. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hill DA, Jean PA and Roth RA: Bile duct
epithelial cells exposed to alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate produces a
factor that causes neutrophil-dependent hepatocellular injury in
vitro. Toxicol Sci. 47:118–125. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cullen JM, Faiola B, Melich DH, Peterson
RA, Jordan HL, Kimbrough CL and Miller RT: Acute
alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced liver toxicity in germfree and
conventional male rats. Toxicol Pathol. 44:987–997. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li X, Liu R, Yu L, Yuan Z, Sun R, Yang H,
Zhang L and Jiang Z: Alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate impairs bile acid
homeostasis through AMPK-FXR pathways in rat primary hepatocytes.
Toxicology. 370:106–115. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Golbar HM, Izawa T, Wijesundera KK, Bondoc
A, Tennakoon AH, Kuwamura M and Yamate J: Depletion of hepatic
macrophages aggravates liver lesion induced in rats by
thioacetamide (TAA). Toxicol Pathol. 44:246–258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Capizzo F and Roberts RJ:
α-Naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT)-induced hepatotoxicity and
disposition in various species. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 19:176–187.
1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Plaa GL and Priestly BG: Intrahepatic
cholestasis induced by drugs and chemicals. Pharmacol Rev.
28:207–273. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cruz A, Padillo FJ, Torres E, Navarrete
CM, Muñoz-Castañeda JR, Caballero FJ, Briceño J, Marchal T, Túnez
I, Montilla P, et al: Melatonin prevents experimental liver
cirrhosis induced by thio-acetamide in rats. J Pineal Res.
39:143–150. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bothe MK, Meyer C, Mueller U, Queudot JC,
Roger V, Harleman J and Westphal M: Characterization of a rat model
of moderate liver dysfunction based on
alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestasis. J Toxicol Sci.
42:715–721. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou HQ, Liu W, Wang J, Huang YQ, Li PY,
Zhu Y, Wang JB, Ma X, Li RS, Wei SZ, et al: Paeoniflorin attenuates
ANIT-induced cholestasis by inhibiting apoptosis in vivo via
mitochondria-dependent pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 89:696–704.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yuan B, Xu C, Liu L, Zhang Q, Ji S, Pi L,
Zhang D and Huo Q: Cu2O/NiOx/graphene oxide
modified glassy carbon electrode for the enhanced electrochemical
oxidation of reduced glutathione and nonenzyme glucose sensor.
Electrochimica Acta. 104:78–83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jaeschke H: The role of reactive oxygen
species in hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury and
preconditioning. J Inv Surg. 16:127–140. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Carbonell LF, Nadal JA, Llanos MC,
Hernández I, Nava E and Díaz J: Depletion of liver glutathione
potentiates the oxidative stress and decreases nitric oxide
synthesis in a rat endotoxin shock model. Crit Care Med.
28:2002–2006. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee SJ and Boyer TD: The effect of hepatic
regeneration on the expression of the glutathione S-transferases.
Biochem J. 293:137–142. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang ZZ, Li H, Cai J, Kuhlenkamp J,
Kaplowitz N and Lu SC: Changes in glutathione homeostasis during
liver regeneration in the rat. Hepatology. 27:147–153. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Grace MS, Cahill GM and Besharse JC:
Melatonin deacetylation: Retinal vertebrate class distribution and
Xenopus laevis tissue distribution. Brain Res. 559:56–63. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rogawski MA, Roth RH and Aghajanian GK:
Melatonin: Deacetylation to 5-methoxytryptamine by liver but not
brain aryl acylamidase. J Neurorhem. 32:1219–1226. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Jean M and DeMoss RD: Indolelactate
dehydrogenase from Clostridium sporogenes. Can J Microbiol.
14:429–435. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Reiter RJ, Qi W,
Karbownik M and Calvo JR: Significance of melatonin in
antioxidative defense: Reactions and products. Biol Signals Recept.
9:137–159. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Karbownik M, Reiter RJ, Garcia JJ, Cabrera
J, Burkhardt S, Osuna C and Lewiński A: Indole-3-propionic acid, a
melatonin-related molecule, protects hepatic microsomal membranes
from ironinduced oxidative damage: Relevance to cancer reduction. J
Cell Biochem. 81:507–513. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Drüppel K, Hensler M, Trautwein K,
Kozzmehl S, Wöhlbrand L, Schmidt-Hohagen K, Ulbrich M, Bergen N,
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Göker M, et al: Pathways and substrate-specific
regulation of amino acid degradation in Phaeobacter inhibens DSM
17395 (archetype of the marine Roseobacter clade). Environ
Microbiol. 16:218–238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lee Y, Khan A, Hong S, Jee SH and Park YH:
A metabolomic study on high-risk stroke patients determines low
levels of serum lysine metabolites: A retrospective cohort study.
Mol Biosyst. 1109–1120. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Young SN: The effect of raising and
lowering tryptophan levels on human mood and social behaviour.
Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 368:201103752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Anderson G, Maes M and Berk M:
Schizophrenia is primed for an increased expression of depression
through activation of immuno-inflammatory, oxidative and
nitrosative stress, and tryptophan catabolite pathways. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 42:101–114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Anderson G, Maes M and Berk M:
Inflammation-related disorders in the tryptophan catabolite pathway
in depression and somatization. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol.
88:27–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hogewind-Schoonenboom JE, Huang L, de
Groof F, Zhu L, Voortman GJ, Schierbeek H, Vermes A, Chen C, Huang
Y and van Goudoever JB: Threonine requirement of the enterally fed
term infant in the first month of life. J Pediatr Gastroenterol
Nutr. 61:373–379. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kilberg MS, Handlogten ME and Christensen
HN: Characteristics of system ASC for transport of neutral amino
acids in the isolated rat hepatocyte. J Biol Chem. 256:3304–3312.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Floc'h NL, Obled C and Sève B: In vivo
threonine oxidation in growing pigs fed on diets with graded levels
of threonine. Br J Nutr. 75:825–837. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Le Floc'h N, Thibault JN and Sève B:
Tissue localization of threonine oxidation in pigs. Br J Nutr.
77:593–603. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Lu SC, Mato JM, Espinosa-Diez C and Lamas
S: MicroRNA-mediated regulation of glutathione and methionine
metabolism and its relevance for liver disease. Free Radic Biol
Med. 100:66–72. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bouzouf M, Martinez-Cruz F, Molinero P,
Guerrero JM and Osuna C: Melatonin prevents hyperhomocysteinemia
and neural lipid peroxidation induced by methionine intake. Curr
Neurovasc Res. 2:175–178. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|