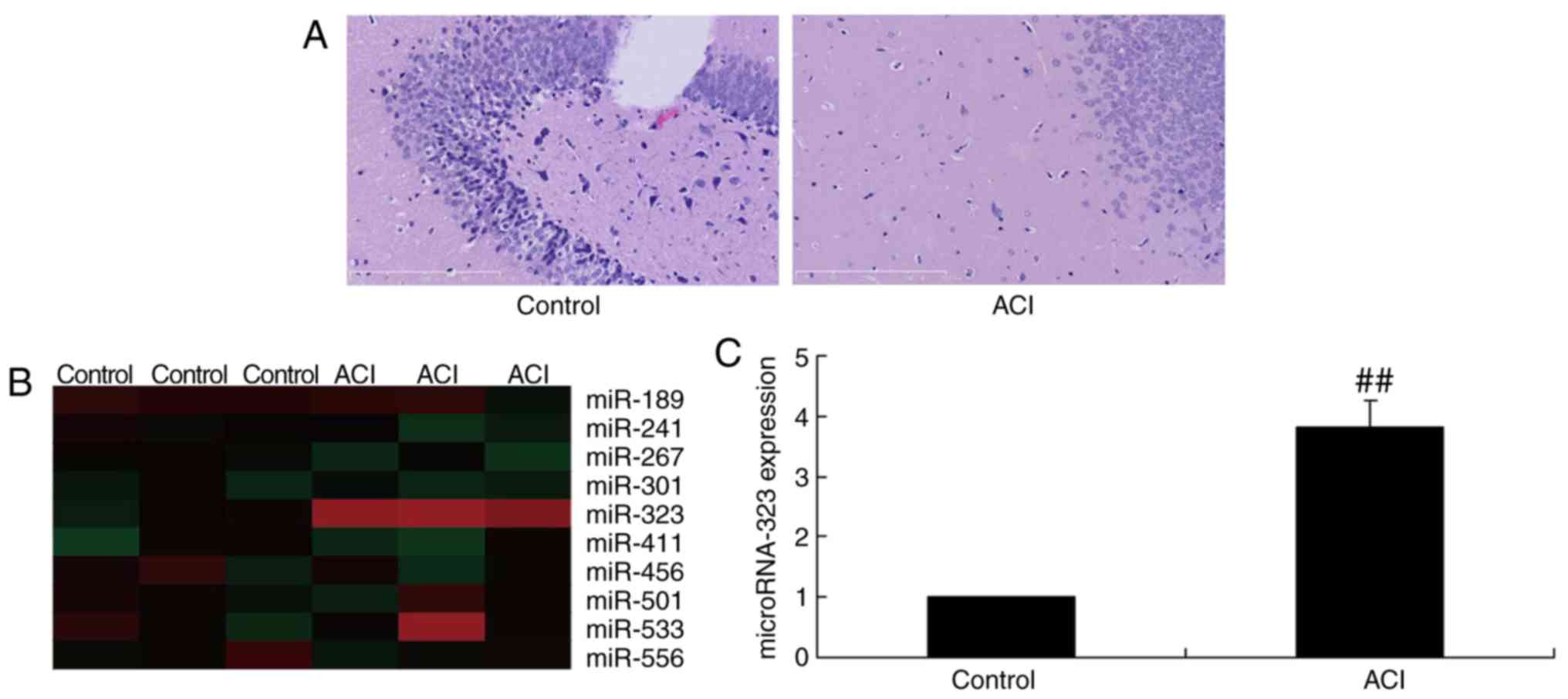
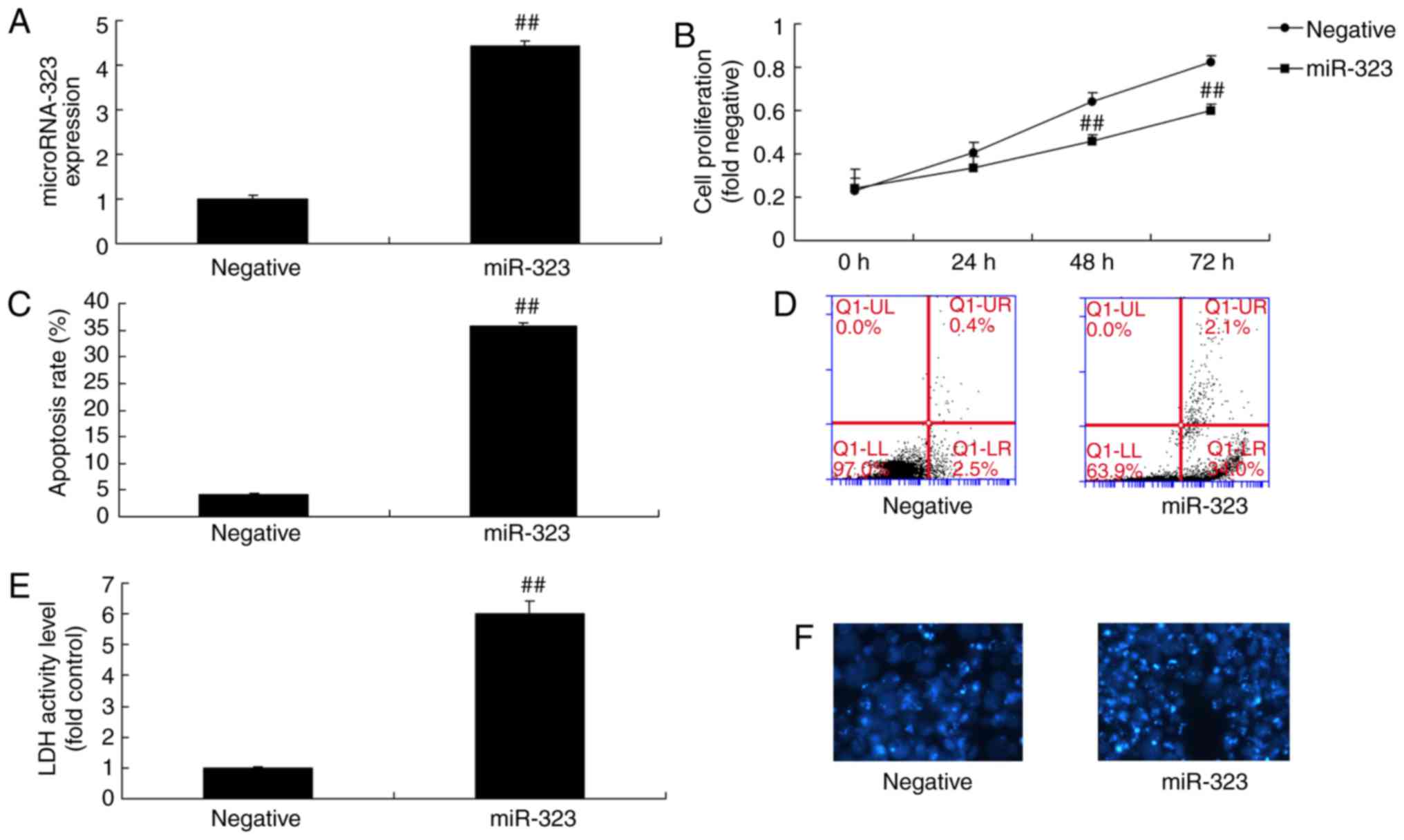
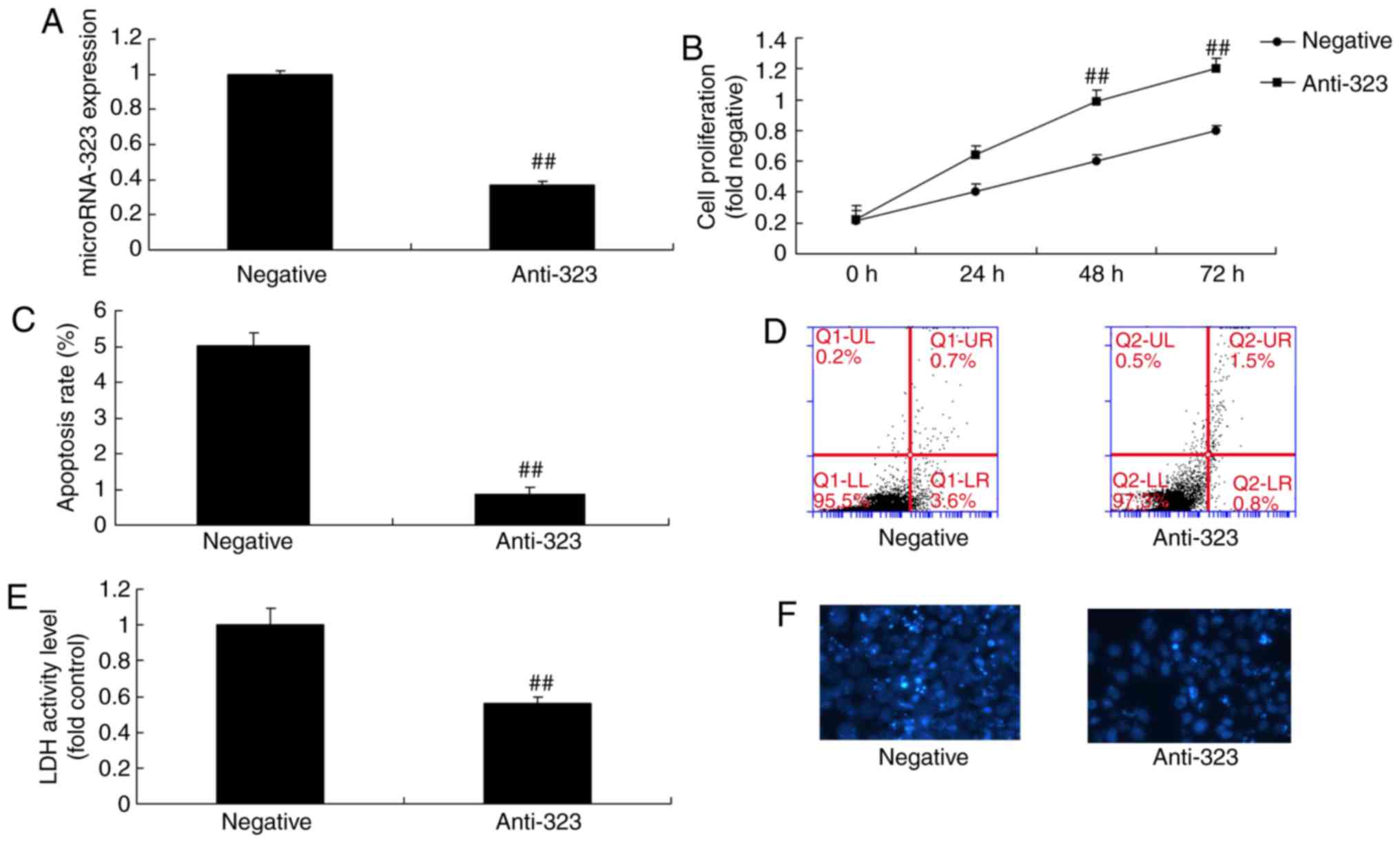
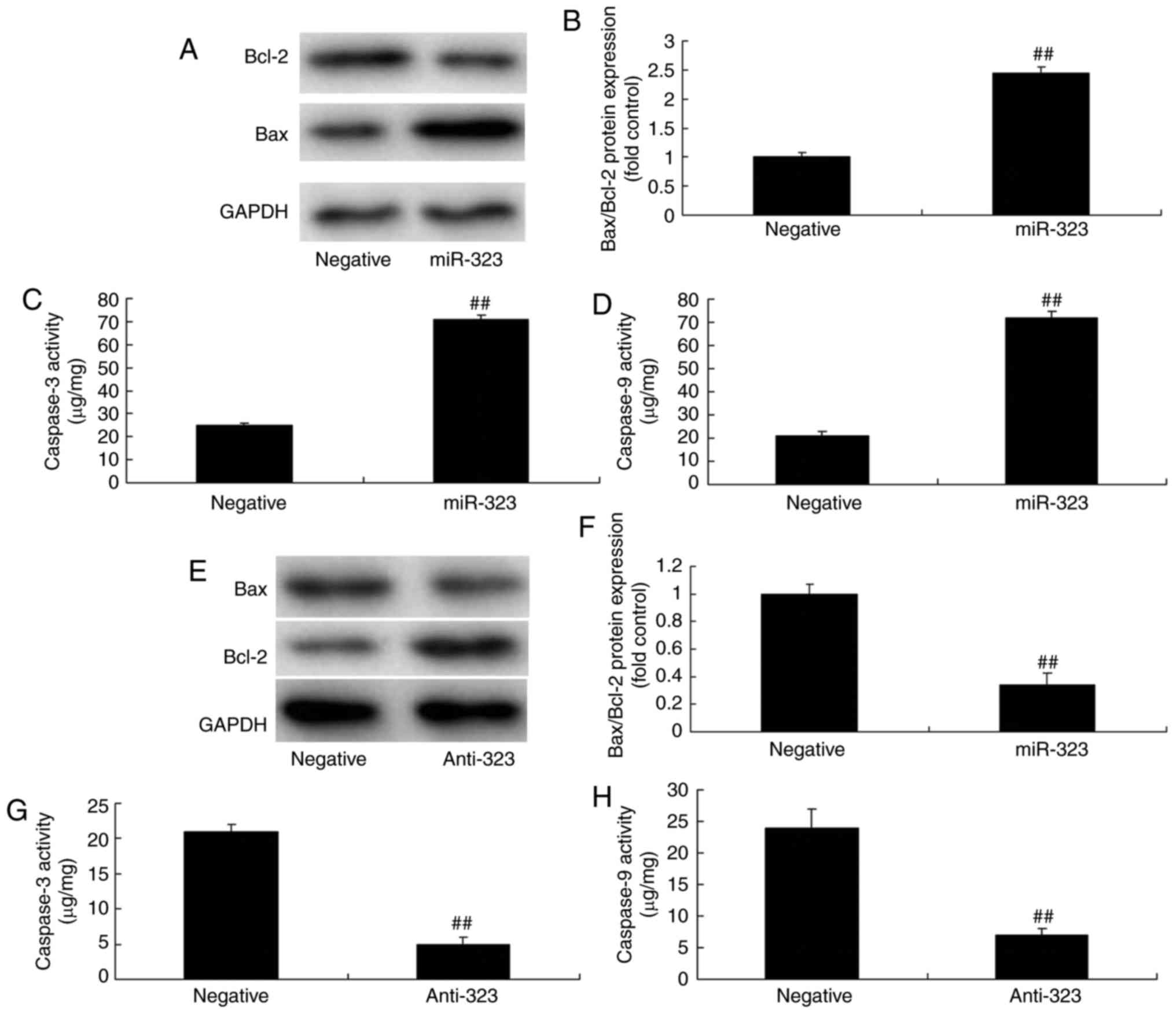
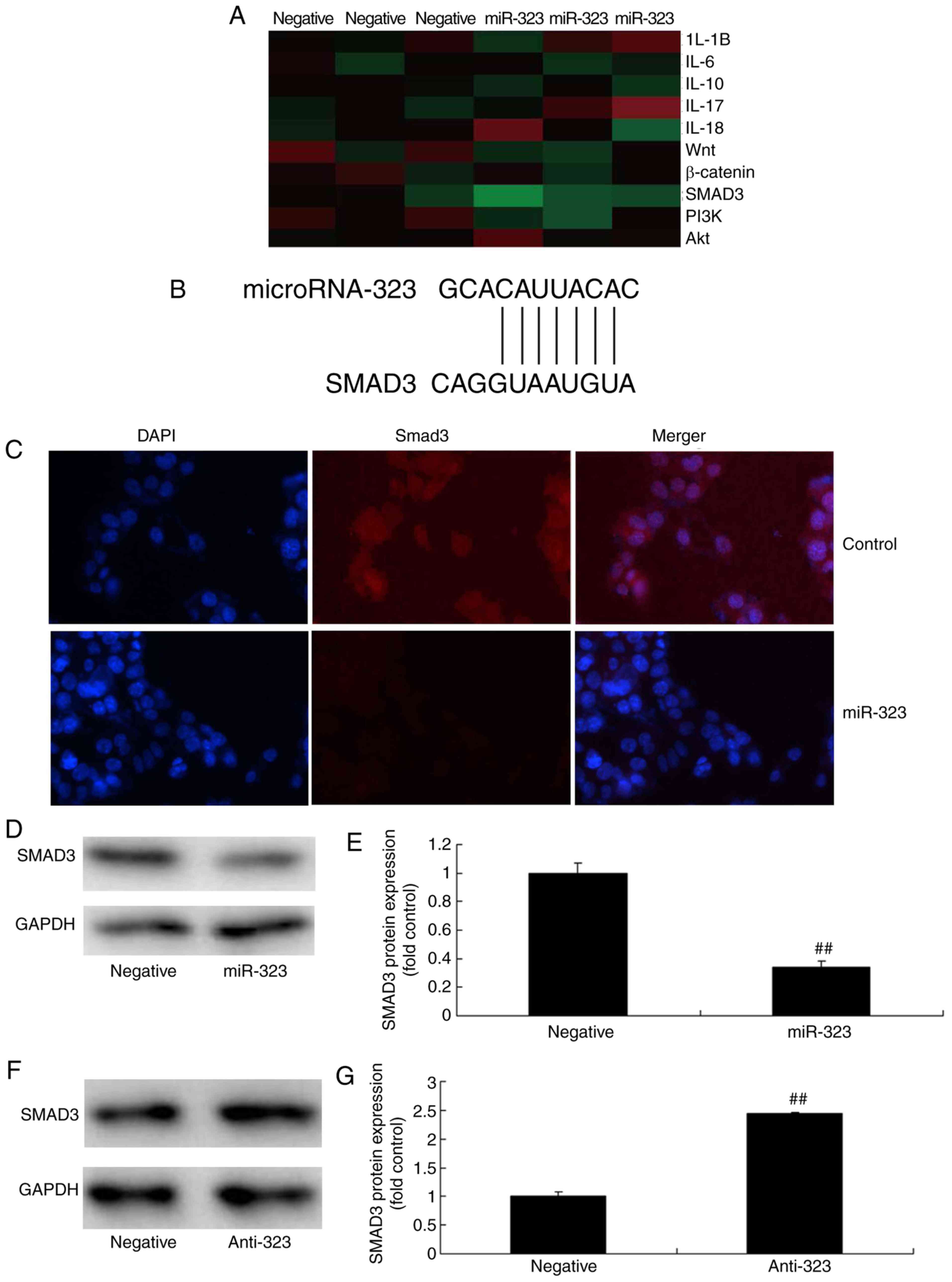
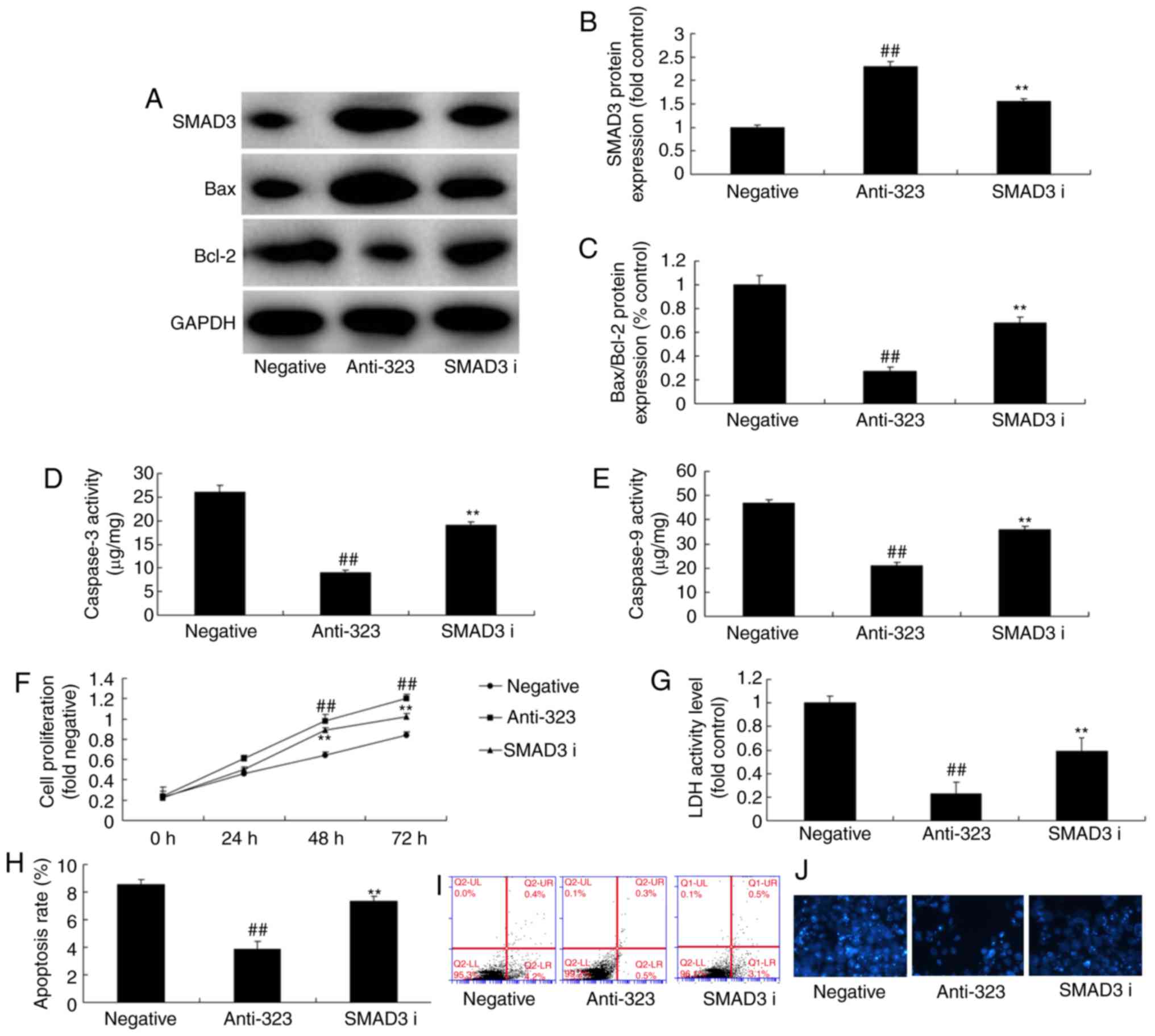
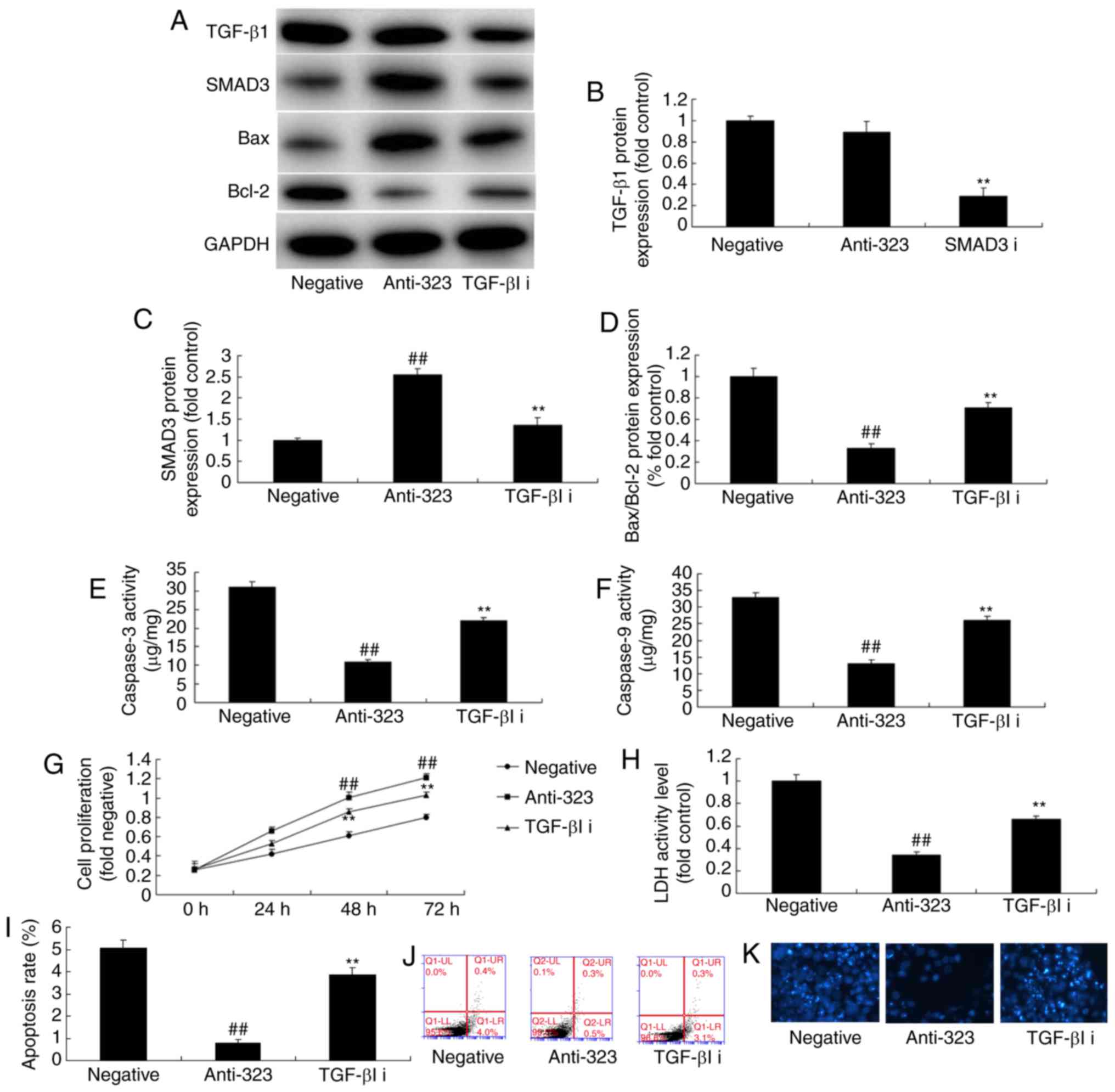
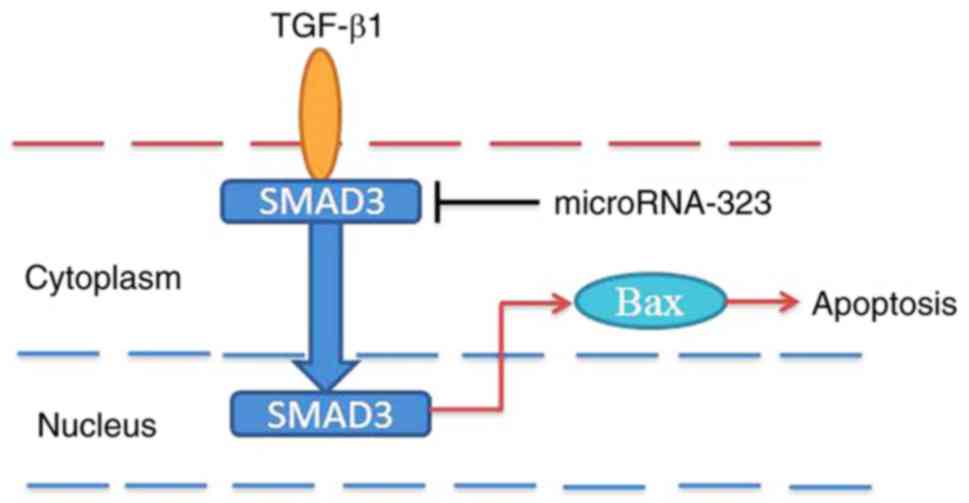
|
1
|
Al-Ali F, Berkhemer OA, Yousman WP, Elias
JJ, Bender EN, Lingsma HF, van der Lugt A, Dippel DW, Roos YB, van
Oostenbrugge RJ, et al: The capillary index score as a marker of
viable cerebral tissue: Proof of concept-the capillary index score
in the MR CLEAN (multicenter randomized clinical trial of
endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke in the
Netherlands) trial. Stroke. 47:2286–2291. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maeshima S, Okamoto S, Okazaki H, Mizuno
S, Asano N, Tsunoda T, Maeda H, Masaki M and Sonoda S: Hemorrhagic
transformation in patients with cerebral infarction referred to a
rehabilitation hospital. Interv Neurol. 4:69–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kim DH, Kim SU, Sung JH, Lee DH, Yi HJ and
Lee SW: Significances and outcomes of mechanical thrombectomy for
acute infarction in very elderly patients: A single center
experience. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 60:654–660. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fasanaro P, Greco S, Ivan M, Capogrossi MC
and Martelli F: microRNA: Emerging therapeutic targets in acute
ischemic diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 125:92–104. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Khanna S, Rink C, Ghoorkhanian R, Gnyawali
S, Heigel M, Wijesinghe DS, Chalfant CE, Chan YC, Banerjee J, Huang
Y, et al: Loss of miR-29b following acute ischemic stroke
contributes to neural cell death and infarct size. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 33:1197–1206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kim JM, Jung KH, Chu K, Lee ST, Ban J,
Moon J, Kim M, Lee SK and Roh JK: Atherosclerosis-related
circulating MicroRNAs as a predictor of stroke recurrence. Transl
Stroke Res. 6:191–197. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Selvamani A, Williams MH, Miranda RC and
Sohrabji F: Circulating miRNA profiles provide a biomarker for
severity of stroke outcomes associated with age and sex in a rat
model. Clin Sci (Lond). 127:77–89. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Slevin M, Krupinski J, Slowik A, Kumar P,
Szczudlik A and Gaffney J: Serial measurement of vascular
endothelial growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta1 in
serum of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 31:1863–1870.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dowling MM, Quinn CT, Plumb P, Rogers ZR,
Rollins NK, Koral K and Buchanan GR: Acute silent cerebral ischemia
and infarction during acute anemia in children with and without
sickle cell disease. Blood. 120:3891–3897. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang L, Xiong Y, Hu XF and Du YH:
MicroRNA-323 regulates ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced neuronal
cell death by targeting BRI3. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:10725–10733.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dewdney B, Trollope A, Moxon J, Thomas
Manapurathe D, Biros E and Golledge J: Circulating MicroRNAs as
biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke: A Systematic review. J Stroke
Cerebrovasc Dis. 27:522–530. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhou J and Zhang J: Identification of
miRNA-21 and miRNA-24 in plasma as potential early stage markers of
acute cerebral infarction. Mol Med Rep. 10:971–976. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim JS, Yoon SS, Kim YH and Ryu JS: Serial
measurement of interleukin-6, transforming growth factor-beta, and
S-100 protein in patients with acute stroke. Stroke. 27:1553–1557.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ata KA, Lennmyr F, Funa K, Olsson Y and
Terent A: Expression of transforming growth factor-beta1, 2, 3
isoforms and type I and II receptors in acute focal cerebral
ischemia: An immunohistochemical study in rat after transient and
permanent occlusion of middle cerebral artery. Acta Neuropathol.
97:447–455. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang C, Liu P, Wu H, Cui P, Li Y, Liu Y,
Liu Z and Gou S: MicroRNA-323-3p inhibits cell invasion and
metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via direct
suppression of SMAD2 and SMAD3. Oncotarget. 7:14912–14924.
2016.
|
|
16
|
Ronaldson PT, Demarco KM,
Sanchez-Covarrubias L, Solinsky CM and Davis TP: Transforming
growth factor-beta signaling alters substrate permeability and
tight junction protein expression at the blood-brain barrier during
inflammatory pain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:1084–1098. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lan W, Yang F, Li Z, Liu L, Sang H, Jiang
Y, Xiong Y and Zhang R: Human urine kininogenase attenuates
balloon-induced intimal hyperplasia in rabbit carotid artery
through transforming growth factor β1/SMAD2/3 signaling pathway. J
Vasc Surg. 64:1074–1083. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tinoco-Veras CM, Santos AAQA, Stipursky J,
Meloni M, Araujo APB, Foschetti DA, López-Ureña D, Quesada-Gómez C,
Leitão RFC, Gomes FCA and Brito GAC: Transforming growth factor
β1/SMAD signaling pathway activation protects the intestinal
epithelium from clostridium difficile toxin a-induced damage.
Infect Immun. 85:e00430–17. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Grand Moursel L, Munting LP, van der Graaf
LM, van Duinen SG, Goumans MTH, Ueberham U, Natté R, van Buchem MA,
van Roon-Mom WMC and van der Weerd L: TGFβ pathway deregulation and
abnormal phospho-SMAD2/3 staining in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage
with amyloidosis-Dutch type. Brain Pathol. 28:495–506. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kärner J, Wawrzyniak M, Tankov S, Runnel
T, Aints A, Kisand K, Altraja A, Kingo K, Akdis CA, Akdis M and
Rebane A: Increased microRNA-323-3p in IL-22/IL-17-producing T
cells and asthma: A role in the regulation of the TGF-β pathway and
IL-22 production. Allergy. 72:55–65. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|