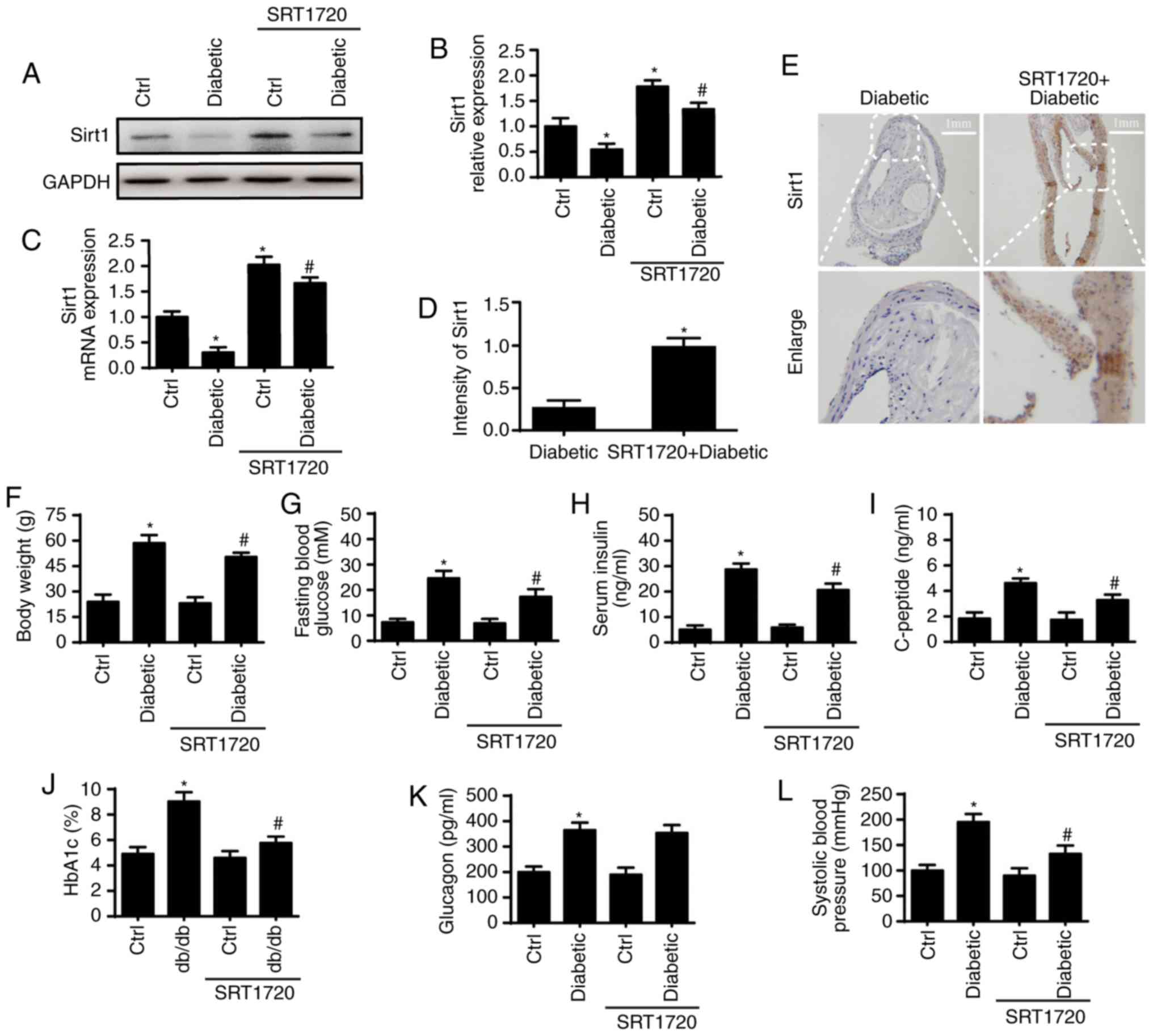
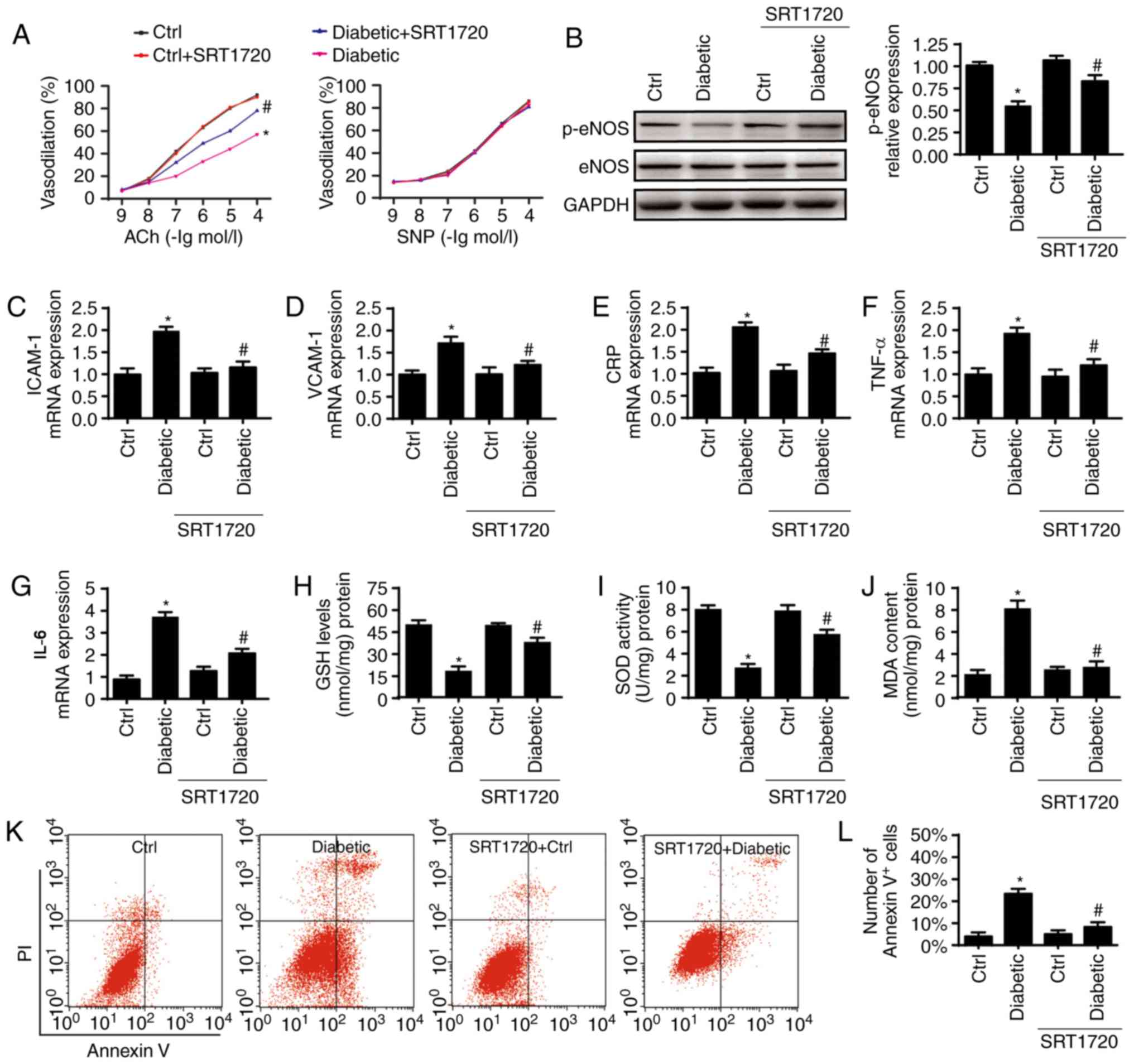
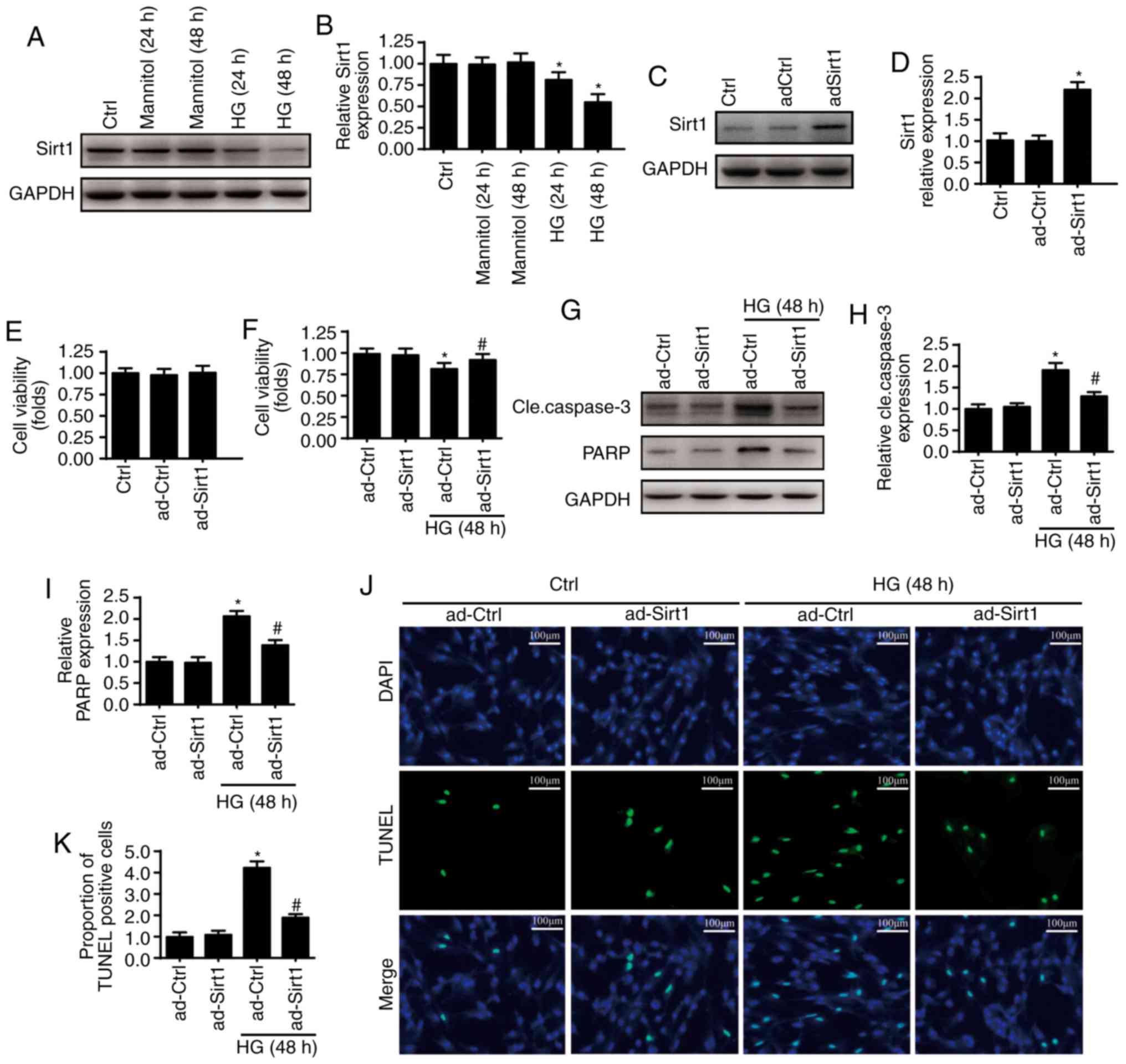
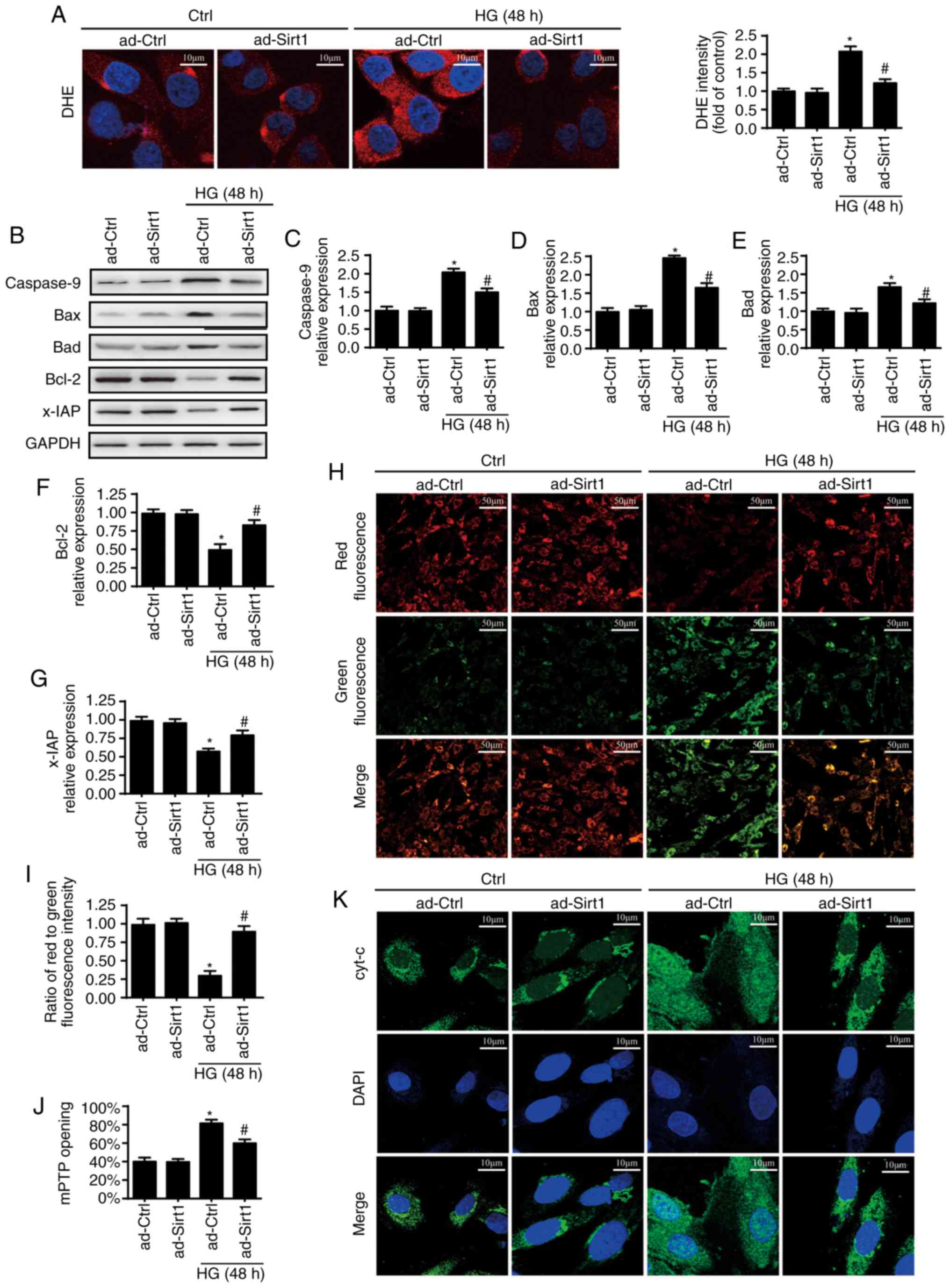
|
1
|
Booth GL, Kapral MK, Fung K and Tu JV:
Recent trends in cardiovascular complications among men and women
with and without diabetes. Diabetes Care. 29:32–37. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Brownlee M: The pathobiology of diabetic
complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 54:1615–1625. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lu J, Xiang G, Liu M, Mei W, Xiang L and
Dong J: Irisin protects against endothelial injury and ameliorates
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-Null diabetic mice.
Atherosclerosis. 243:438–448. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhou H, Wang S, Zhu P, Hu S, Chen Y and
Ren J: Empagliflozin rescues diabetic myocardial microvascular
injury via AMPK-mediated inhibition of mitochondrial fission. Redox
Biol. 15:335–346. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Bohuszewicz O and Low HH: Structure of a
mitochondrial fission dynamin in the closed conformation. Nat
Struct Mol Biol. 25:722–731. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mansouri A, Gattolliat CH and Asselah T:
Mitochondrial dysfunction and signaling in chronic liver diseases.
Gastroenterology. 155:629–647. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sheng J, Li H, Dai Q, Lu C, Xu M, Zhang J
and Feng J: NR4A1 promotes diabetic nephropathy by activating
mff-mediated mitochondrial fission and suppressing parkin-mediated
mitophagy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:1675–1693. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu WJ, Jiang HF, Rehman FU, Zhang JW,
Chang Y, Jing L and Zhang JZ: Lycium barbarum polysaccharides
decrease hyperglycemia-aggravated ischemic brain injury through
maintaining mitochondrial fission and fusion balance. Int J Biol
Sci. 13:901–910. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wils J, Favre J and Bellien J: Modulating
putative endothelial progenitor cells for the treatment of
endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular complications in
diabetes. Pharmacol Ther. 170:98–115. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fang WJ, Wang CJ, He Y, Zhou YL, Peng XD
and Liu SK: Resveratrol alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats
by improving mitochondrial function through PGC-1alpha
deacetylation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 39:59–73. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ding M, Feng N, Tang D, Feng J, Li Z, Jia
M, Liu Z, Gu X, Wang Y, Fu F and Pei J: Melatonin prevents
Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission in diabetic hearts through
SIRT1-PGC1alpha pathway. J Pineal Res. 65:e124912018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ou X, Lee MR, Huang X, Messina-Graham S
and Broxmeyer HE: Sirt1 positively regulates autophagy and
mitochondria function in embryonic stem cells under oxidative
stress. Stem Cells. 32:1183–1194. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi Y, Lv X, Liu Y, et al: Elevating
ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 improves re-endothelialization
function of endothelial progenitor cells via Lyn/Akt/eNOS in
diabetic mice. FASEB J. Jun 12–2018.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang W, Yang C, Wang XY, Zhou LY, Lao GJ,
Liu D, Wang C, Hu MD, Zeng TT, Yan L and Ren M: MicroRNA-129 and -
335 promote diabetic wound healing by inhibiting sp1-mediated mmp-9
expression. Diabetes. 67:1627–1638. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma TJ, Zhang ZW, Lu YL, Zhang YY, Tao DC,
Liu YQ and Ma YX: CLOCK and BMAL1 stabilize and activate RHOA to
promote F-actin formation in cancer cells. Exp Mol Med. 50:1302018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kilian P, Campbell S, Bilodeau L, Guimond
MO, Roberge C, Gallo-Payet N and Payet MD: Angiotensin II type 2
receptor stimulation increases the rate of NG10815 cell migration
via actin depolymerization. Endocrinology. 149:2923–2933. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang CH, Hsu CC, Lee AS, Wang SW, Lin KT,
Chang WL, Peng HC, Huang WC and Chung CH: 4-Acetylantroquinonol B
inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine release and alleviates
sepsis through of MAPK and NFkappaB suppression. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 18:1082018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Wang H, Zhang R, Zhang G, Yang Y and
Liu Z: Leukemia growth is inhibited by benzoxime without causing
any harmful effect in rats bearing RBL-1 xenotransplants. Oncol
Lett. 17:1934–1938. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cavariani MM, de Mello Santos T, Pereira
DN, de Almeida Chuffa LG, Felipe Pinheiro PF, Scarano WR and
Domeniconi RF: Maternal protein restriction differentially alters
the expression of AQP1, AQP9 and VEGFr-2 in the epididymis of rat
offspring. Int J Mol Sci. 20:E4692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu Y, Bai L, Chen X, Li Y, Qin Y, Meng X
and Zhang Q: 6-Shogaol ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through
anti-inflammatory, hyperlipidemic, anti-oxidative activity in db/db
mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 97:633–641. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu Y and Zheng Y: Bach1 siRNA attenuates
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by modulating oxidative stress
in mice. Int J Mol Med. 39:91–100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ekim Kocabey A, Kost L, Gehlhar M, Rodel G
and Gey U: Mitochondrial sco proteins are involved in oxidative
stress defense. Redox Biol. 21:1010792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu P, Hu S, Jin Q, Li D, Tian F, Toan S,
Li Y, Zhou H and Chen Y: Ripk3 promotes ER stress-induced
necroptosis in cardiac IR injury: A mechanism involving calcium
overload/XO/ROS/mPTP pathway. Redox Biol. 16:157–168. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang W, Buluc M, van Breemen C and Wang
X: Vectorial Ca2+ release via ryanodine receptors contributes to
Ca2+ extrusion from freshly isolated rabbit aortic endothelial
cells. Cell Calcium. 36:431–443. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pickart L and Thaler MM: Growth-modulating
human plasma tripeptide: Relationship between molecular structure
and DNA synthesis in hepatoma cells. FEBS Lett. 104:119–122. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shi C, Cai Y, Li Y, Li Y, Hu N, Ma S, Hu
S, Zhu P, Wang W and Zhou H: Yap promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
metastasis and mobilization via governing
cofilin/F-actin/lamellipodium axis by regulation of
JNK/Bnip3/SERCA/CaMKII pathways. Redox Biol. 14:59–71. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhou H, Zhu P, Guo J, Hu N, Wang S, Li D,
Hu S, Ren J, Cao F and Chen Y: Ripk3 induces mitochondrial
apoptosis via inhibition of FUNDC1 mitophagy in cardiac IR injury.
Redox Biol. 13:498–507. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jin Q, Li R, Hu N, Xin T, Zhu P, Hu S, Ma
S, Zhu H, Ren J and Zhou H: DUSP1 alleviates cardiac
ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing the Mff-required
mitochondrial fission and Bnip3-related mitophagy via the JNK
pathways. Redox Biol. 14:576–587. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shuang Y, Li C, Zhou X, Huang Y and Zhang
L: MicroRNA-195 inhibits growth and invasion of laryngeal carcinoma
cells by directly targeting DCUN1D1. Oncol Rep. 38:2155–2165. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ren Y, Du C, Shi Y, Wei J, Wu H and Cui H:
The Sirt1 activator, SRT1720, attenuates renal fibrosis by
inhibiting CTGF and oxidative stress. Int J Mol Med. 39:1317–1324.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhao WJ, Zhang HF and Su JY:
Downregulation of microRNA-195 promotes angiogenesis induced by
cerebral infarction via targeting VEGFA. Mol Med Rep. 16:5434–5440.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou H, Wang J, Zhu P, Hu S and Ren J:
Ripk3 regulates cardiac microvascular reperfusion injury: The role
of IP3R-dependent calcium overload, XO-mediated oxidative stress
and F-action/filopodia-based cellular migration. Cell Signal.
45:12–22. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dai Y, Zhang J, Xiang J, Li Y, Wu D and Xu
J: Calcitriol inhibits ROS-NLRP3-IL-1beta signaling axis via
activation of Nrf2-antioxidant signaling in hyperosmotic stress
stimulated human corneal epithelial cells. Redox Biol.
21:1010932018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Park SJ, Ahmad F, Um JH, Brown AL, Xu X,
Kang H, Ke H, Feng X, Ryall J, Philp A, et al: Specific Sirt1
activator-mediated improvement in glucose homeostasis requires
Sirt1-independent activation of AMPK. EBioMedicine. 18:128–138.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu J, Jiang C, Ma X and Wang J:
Notoginsenoside Fc attenuates high glucose-induced vascular
endothelial cell injury via upregulation of PPAR-gamma in diabetic
spraguedawley rats. Vascul Pharmacol. 109:27–35. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kojima H, Otani A, Oishi A, Makiyama Y,
Nakagawa S and Yoshimura N: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in vascular
endothelial cells and exhibits functional and morphologic
protective effect in oxygen-induced retinopathy. Blood.
117:1091–1100. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhou H, Hu S, Jin Q, Shi C, Zhang Y, Zhu
P, Ma Q, Tian F and Chen Y: Mff-dependent mitochondrial fission
contributes to the pathogenesis of cardiac microvasculature
ischemia/reperfusion injury via induction of mROS-mediated
cardiolipin oxidation and HK2/VDAC1 disassociation-involved mPTP
opening. J Am Heart Assoc. 6:e0053282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Y, Subramanian M, Yurdagul A Jr,
Barbosa-Lorenzi VC, Cai B, de Juan-Sanz J, Ryan TA, Nomura M,
Maxfield FR and Tabas I: Mitochondrial fission promotes the
continued clearance of apoptotic cells by macrophages. Cell.
171:331–345.e22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu P, Zhang G, Sha L and Hou S: DUSP1
alleviates cerebral ischaemia reperfusion injury via inactivating
JNK-Mff pathways and repressing mitochondrial fission. Life Sci.
210:251–262. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ji K, Lin K, Wang Y, Du L, Xu C, He N,
Wang J, Liu Y and Liu Q: TAZ inhibition promotes IL-2-induced
apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating the
JNK/F-actin/mitochondrial fission pathway. Cancer Cell Int.
18:1172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hubbard BP and Sinclair DA: Small molecule
SIRT1 activators for the treatment of aging and age-related
diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 35:146–154. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Q, Deng Q, Zhang J, Ke J, Zhu Y, Wen
RW, Ye Z, Peng H, Su ZZ, Wang C and Lou T: Activation of the
Nrf2-ARE pathway ameliorates hyperglycemia-mediated mitochondrial
dysfunction in podocytes partly through Sirt1. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 48:1–15. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mishra M, Duraisamy AJ and Kowluru RA:
Sirt1: A guardian of the development of diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetes. 67:745–754. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ayanga BA, Badal SS, Wang Y, Galvan DL,
Chang BH, Schumacker PT and Danesh FR: Dynamin-related protein 1
deficiency improves mitochondrial fitness and protects against
progression of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
27:2733–2747. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Galloway CA and Yoon Y: Mitochondrial
dynamics in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Antioxid Redox Signal.
22:1545–1562. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sheng J, Li H, Dai Q, Lu C, Xu M, Zhang J
and Feng J: DUSP1 recuses diabetic nephropathy via repressing
JNK-Mff-mitochondrial fission pathways. J Cell Physiol.
234:3043–3057. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Becatti M, Barygina V, Mannucci A, Emmi G,
Prisco D, Lotti T, Fiorillo C and Taddei N: Sirt1 protects against
oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in fibroblasts from psoriatic
patients: A new insight into the pathogenetic mechanisms of
psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 19:E15722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang L, Bao D, Li P, Lu Z, Pang L, Chen
Z, Guo H, Gao Z and Jin Q: Particle-induced SIRT1 downregulation
promotes osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis through ER stress
regulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 104:300–306. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Suzuki M, Bandoski C and Bartlett JD:
Fluoride induces oxidative damage and SIRT1/autophagy through
ROS-mediated JNK signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 89:369–378. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chae HD and Broxmeyer HE: SIRT1 deficiency
downregulates PTEN/JNK/FOXO1 pathway to block reactive oxygen
species-induced apoptosis in mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells
Dev. 20:1277–1285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Yamamoto K, Imamura H and Ando J: Shear
stress augments mitochondrial ATP generation that triggers ATP
release and Ca2+ signaling in vascular endothelial
cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 315:H1477–H1485. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Li X, Fang P, Li Y, Kuo YM, Andrews AJ,
Nanayakkara G, Johnson C, Fu H, Shan H, Du F, et al: Mitochondrial
reactive oxygen species mediate lysophosphatidylcholine-induced
endothelial cell activation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
36:1090–1100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Placido AI, Pereira CM, Correira SC,
Carvalho C, Oliveira CR and Moreira PI: Phosphatase 2a inhibition
affects endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria homeostasis via
cytoskeletal alterations in brain endothelial cells. Mol Neurobiol.
5:154–168. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Park SJ, Lee H, Jo DS, Jo YK, Shin JH, Kim
HB, Seo HM, Rubinsztein DC, Koh JY, Lee EK and Cho DH:
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 post-transcriptionally
regulates Drp1 expression in neuroblastoma cells. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1849:1423–1431. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kashatus DF: Restraining the divider: A
drp1-phospholipid interaction inhibits drp1 activity and shifts the
balance from mitochondrial fission to fusion. Mol Cell. 63:913–915.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zheng D, Yu Y, Li M, Wang G, Chen R, Fan
GC, Martin C, Xiong S and Peng T: Inhibition of MicroRNA 195
prevents apoptosis and multiple-organ injury in mouse models of
sepsis. J Infect Dis. 213:1661–1670. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Mortuza R, Feng B and Chakrabarti S:
miR-195 regulates sirt1-mediated changes in diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetologia. 57:1037–1046. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhu H, Yang Y, Wang Y, Li J, Schiller PW
and Peng T: MicroRNA- 195 p romotes palmitate-induced apoptosis in
cardiomyocytes by down-regulating sirt1. Cardiovasc Res. 92:75–84.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Khader A, Yang WL, Hansen LW, Rajayer SR,
Prince JM, Nicastro JM, Coppa GF and Wang P: SRT1720, a sirtuin 1
activator, attenuates organ injury and inflammation in sepsis. J
Surg Res. 219:288–295. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Guo S, Liao H, Liu J, Liu J, Tang F, He Z,
Li Y and Yang Q: Resveratrol activated sonic hedgehog signaling to
enhance viability of NIH3T3 cells in vitro via regulation of sirt1.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 50:1346–1360. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Pacholec M, Bleasdale JE, Chrunyk B,
Cunningham D, Flynn D, Garofalo RS, Griffith D, Griffor M, Loulakis
P, Pabst B, et al: SRT1720, SRT2183, SRT1460, and resveratrol are
not direct activators of SIRT1. J Biol Chem. 285:8340–8351. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|