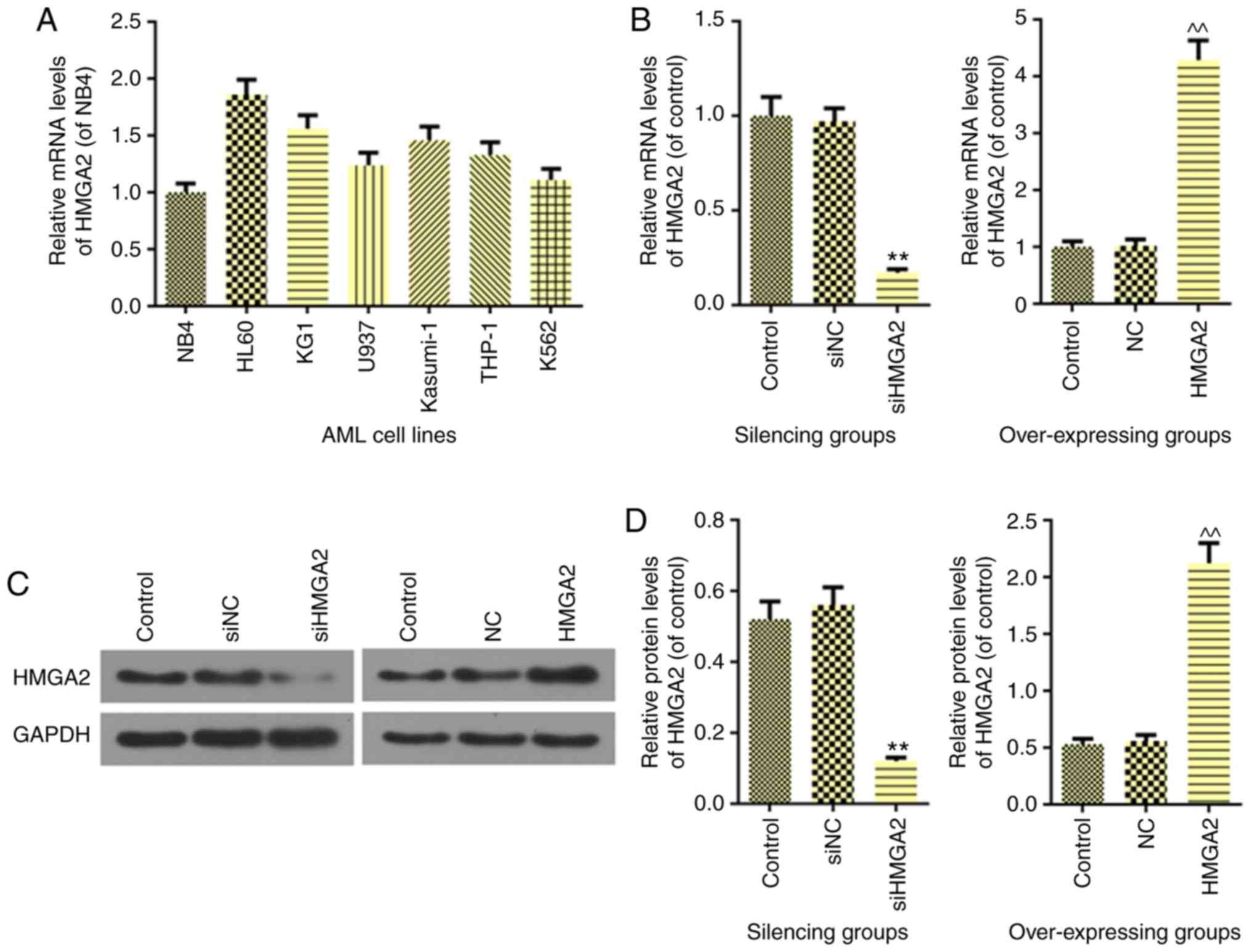
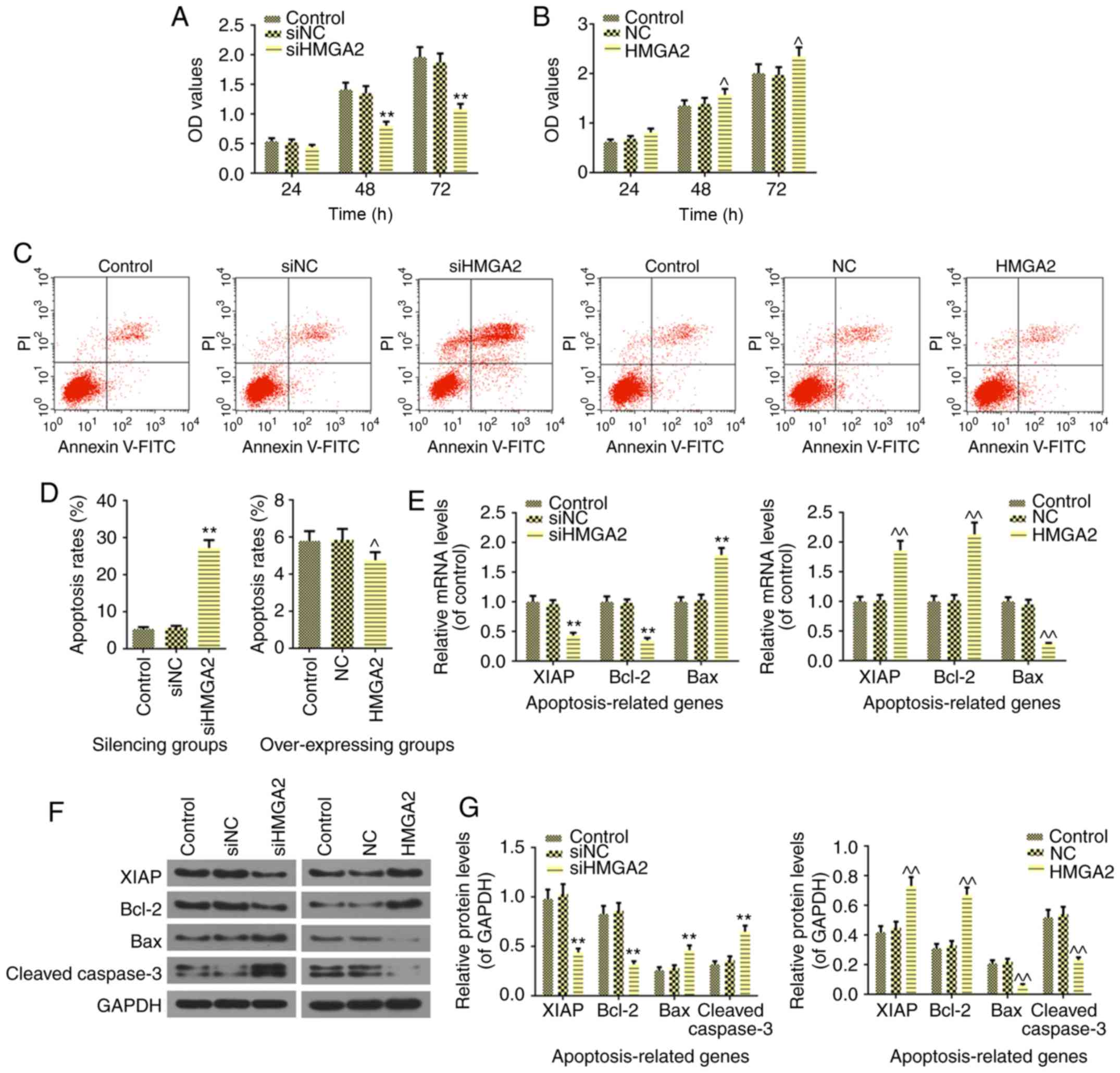
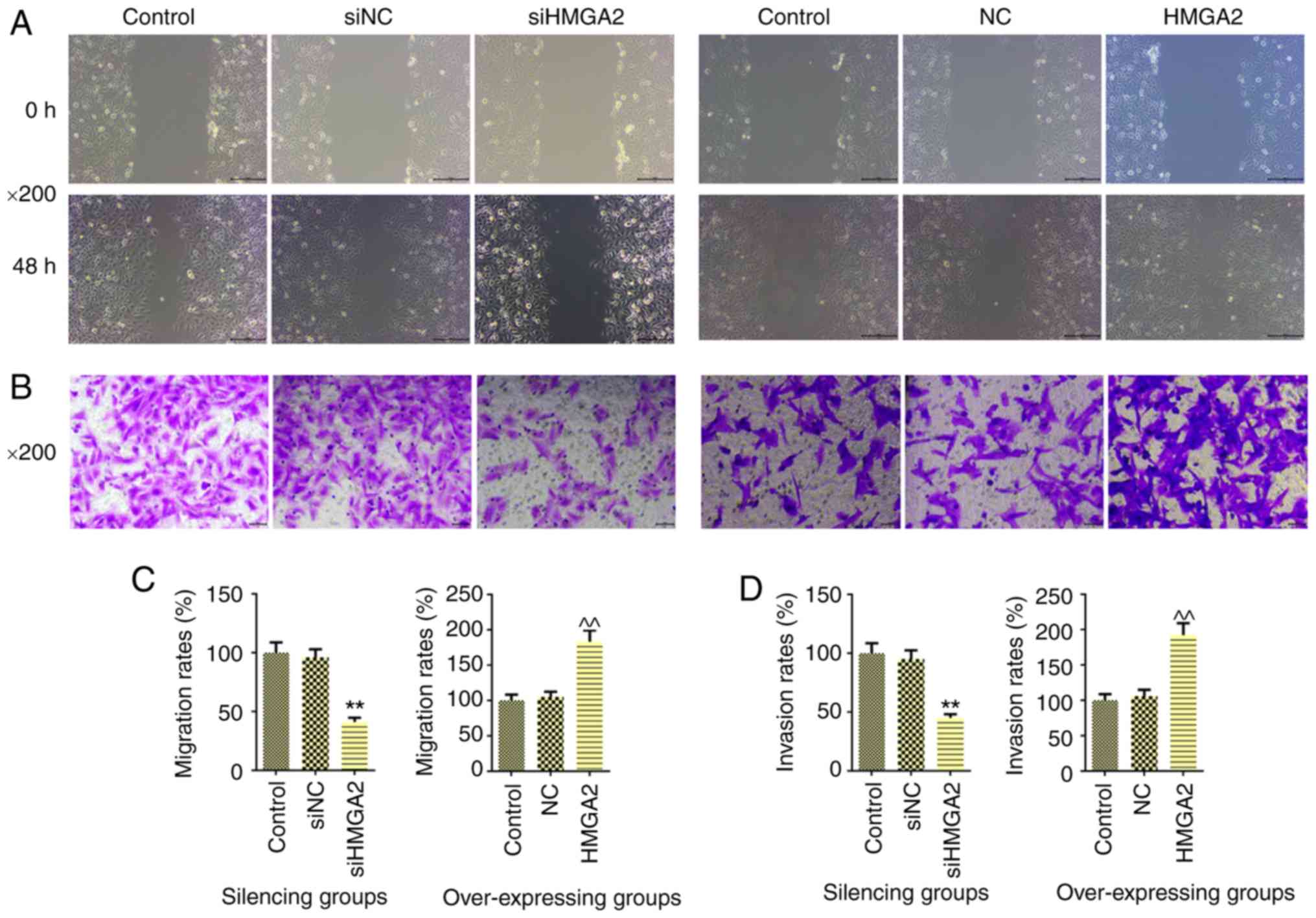
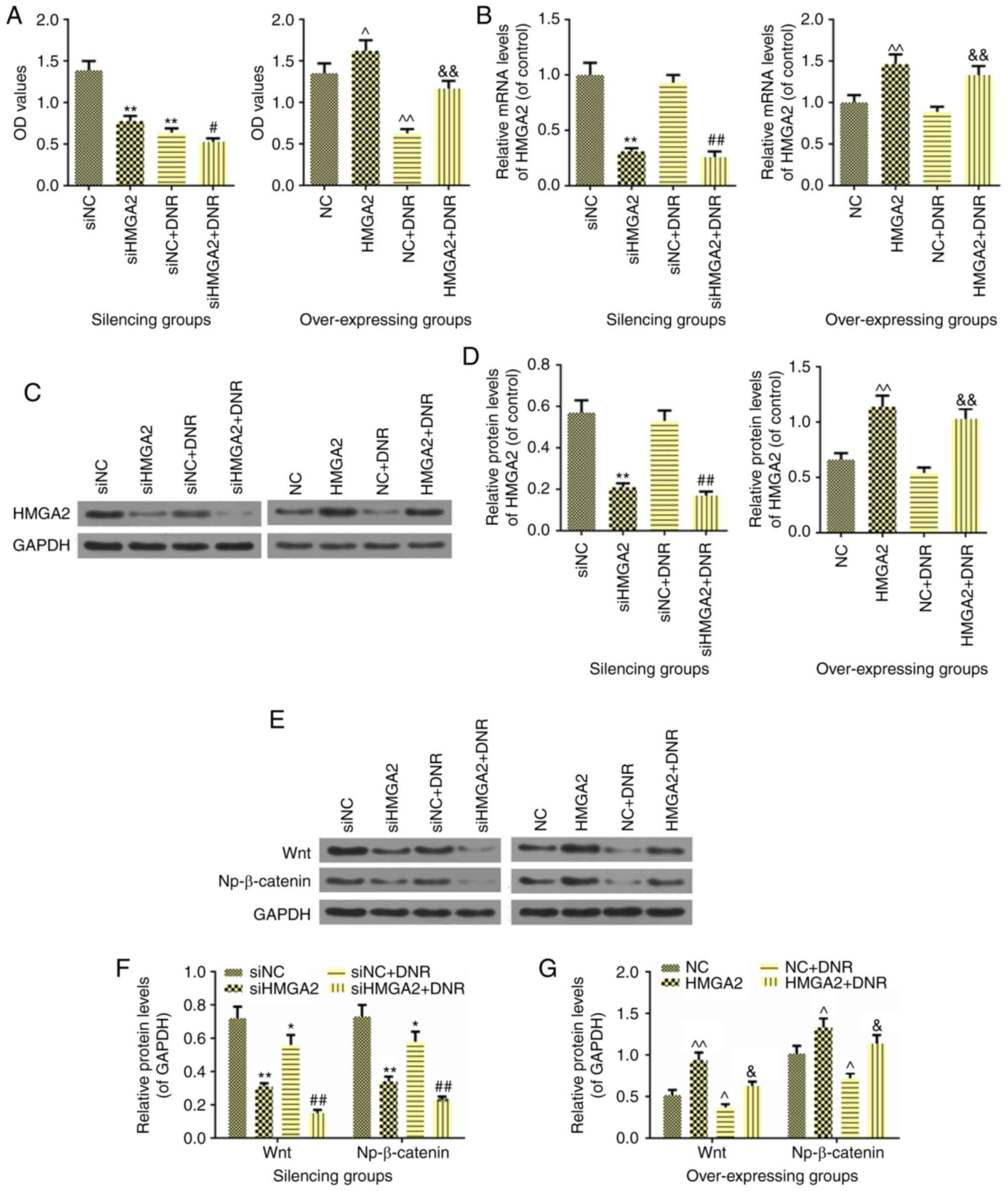
|
1
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Döhner H, Weisdorf DJ and Bloomfield CD:
Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 373:1136–1152. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee SC and Abdel-Wahab O: Therapeutic
targeting of splicing in cancer. Nat Med. 22:976–986. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Buchner M and Müschen M: Targeting the
B-cell receptor signaling pathway in B lymphoid malignancies. Curr
Opin Hematol. 21:341–349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Piemontese S, Ciceri F, Labopin M,
Bacigalupo A, Huang H, Santarone S, Gorin NC, Koc Y, Wu D, Beelen
D, et al: A survey on unmanipulated haploidentical hematopoietic
stem cell transplantation in adults with acute leukemia. Leukemia.
29:1069–1075. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Herbaux C, Genet P, Bouabdallah K, Pignon
JM, Debarri H, Guidez S, Betrian S, Leleu X, Facon T, Morschhauser
F, et al: Bendamustine is effective in T-cell prolymphocytic
leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 168:916–919. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Döhner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, Appelbaum
FR, Büchner T, Burnett AK, Dombret H, Fenaux P, Grimwade D, Larson
RA, et al: Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in
adults: Recommendations from an international expert panel, on
behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 115:453–474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Walter RB, Othus M, Burnett AK, Löwenberg
B, Kantarjian HM, Ossenkoppele GJ, Hills RK, Ravandi F, Pabst T,
Evans A, et al: Resistance prediction in AML: Analysis of 4601
patients from MRC/NCRI, HOVON/SAKK, SWOG and MD Anderson cancer
center. Leukemia. 29:312–320. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ramos NR, Mo CC, Karp JE and Hourigan CS:
Current approaches in the treatment of relapsed and refractory
acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Med. 4:665–695. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mrózek K, Heerema NA and Bloomfield CD:
Cytogenetics in acute leukemia. Blood Rev. 18:115–136. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rowley JD: Chromosomal translocations:
Revisited yet again. Blood. 112:2183–2189. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jin J, Yu M, Hu C, Ye L, Xie L, Jin J,
Chen F and Tong H: Pesticide exposure as a risk factor for
myelodysplastic syndromes: A meta-analysis based on 1,942 cases and
5,359 controls. PLoS One. 9:e1108502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu J, Liu Z, Shao C, Gong Y, Hernando E,
Lee P, Narita M, Muller W, Liu J and Wei JJ: HMGA2
overexpression-induced ovarian surface epithelial transformation is
mediated through regulation of EMT genes. Cancer Res. 71:349–359.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Young AR and Narita M: Oncogenic HMGA2:
Short or small? Genes Dev. 21:1005–1009. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fedele M and Fusco A: HMGA and cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1799:48–54. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morishita A, Zaidi MR, Mitoro A,
Sankarasharma D, Szabolcs M, Okada Y, D'Armiento J and Chada K:
HMGA2 is a driver of tumor metastasis. Cancer Res. 73:4289–4299.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Natarajan S, Hombach-Klonisch S, Dröge P
and Klonisch T: HMGA2 inhibits apoptosis through interaction with
ATR-CHK1 signaling complex in human cancer cells. Neoplasia.
15:263–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li O, Li J and Dröge P: DNA architectural
factor and proto-oncogene HMGA2 regulates key developmental genes
in pluripotent human embryonic stem cells. FEBS Lett.
581:3533–3537. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meyer B, Krisponeit D, Junghanss C, Murua
Escobar H and Bullerdiek J: Quantitative expression analysis in
peripheral blood of patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia:
Correlation between HMGA2 expression and white blood cell count.
Leuk Lymphoma. 48:2008–2013. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wei J, Li H, Wang S, Li T, Fan J, Liang X,
Li J, Han Q, Zhu L, Fan L and Zhao RC: let-7 enhances osteogenesis
and bone formation while repressing adipogenesis of human
stromal/mesenchymal stem cells by regulating HMGA2. Stem Cells Dev.
23:1452–1463. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fusco A and Fedele M: Roles of HMGA
proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:899–910. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma S, Yang LL, Niu T, Cheng C, Zhong L,
Zheng MW, Xiong Y, Li LL, Xiang R, Chen LJ, et al: SKLB-677, an
FLT3 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibitor, displays potent
activity in models of FLT3-driven AML. Sci Rep. 5:156462015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sokolowski KM, Koprowski S, Kunnimalaiyaan
S, Balamurugan M, Gamblin TC and Kunnimalaiyaan M: Potential
molecular targeted therapeutics: Role of PI3-K/Akt/mTOR inhibition
in cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 16:29–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li J, Volk A, Zhang J, Cannova J, Dai S,
Hao C, Hu C, Sun J, Xu Y, Wei W, et al: Sensitizing leukemia stem
cells to NF-κB inhibitor treatment in vivo by inactivation of both
TNF and IL-1 signaling. Oncotarget. 8:8420–8435. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cook AM, Li L, Ho Y, Lin A, Li L, Stein A,
Forman S, Perrotti D, Jove R and Bhatia R: Role of altered growth
factor receptor-mediated JAK2 signaling in growth and maintenance
of human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Blood. 123:2826–2837.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lin TL and Levy MY: Acute myeloid
leukemia: Focus on novel therapeutic strategies. Clin Med Insights
Oncol. 6:205–217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Masaoka T, Ogawa M, Yamada K, Kimura K and
Ohashi Y: A phase II comparative study of idarubicin plus
cytarabine versus daunorubicin plus cytarabine in adult acute
myeloid leukemia. Semin Hematol. 33(Suppl 3): S12–S17. 1996.
|
|
29
|
Shi S, Chen X, Liu H, Yu K, Bao Y, Chai J,
Gao H and Zou L: LGR5 acts as a target of miR-340 5p in the
suppression of cell progression and drug resistance in breast
cancer via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Gene. 683:47–53. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang J, Mook RA Jr, Ren XR, Zhang Q, Jing
G, Lu M, Spasojevic I, Lyerly HK, Hsu D and Chen W: Identification
of DK419, a potent inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and
colorectal cancer growth. Bioorg Med Chem. 26:5435–5442. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu P, Chen B, Gu Y and Liu Q: PNMA1,
regulated by miR-33a 5p promotes proliferation and EMT in
hepatocellular carcinoma by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 108:492–499. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jin L, Lloyd RV, Henry MR, Erickson LA,
Sebo TJ, Rumilla KM and Zhang J: The diagnostic utility of
combination of HMGA2 and IMP3 qRT-PCR testing in thyroid neoplasms.
Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 23:36–43. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhu C, Li J, Cheng G, Zhou H, Tao L, Cai
H, Li P, Cao Q, Ju X, Meng X, et al: miR-154 inhibits EMT by
targeting HMGA2 in prostate cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
379:69–75. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ding X, Wang Y, Ma X, Guo H, Yan X, Chi Q,
Li J, Hou Y and Wang C: Expression of HMGA2 in bladder cancer and
its association with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell
Prolif. 47:146–151. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kong D, Su G, Zha L, Zhang H, Xiang J, Xu
W, Tang Y and Wang Z: Coexpression of HMGA2 and Oct4 predicts an
unfavorable prognosis in human gastric cancer. Med Oncol.
31:1302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pierantoni GM, Santulli B, Caliendo I,
Pentimalli F, Chiappetta G, Zanesi N, Santoro M, Bulrich F and
Fusco A: HMGA2 locus rearrangement in a case of acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Int J Oncol. 23:363–367. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Marquis M, Beaubois C, Lavallée VP,
Abrahamowicz M, Danieli C, Lemieux S, Ahmad I, Wei A, Ting SB,
Fleming S, et al: High expression of HMGA2 independently predicts
poor clinical outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J.
8:682018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tan L, Wei X, Zheng L, Zeng J, Liu H, Yang
S and Tan H: Amplified HMGA2 promotes cell growth by regulating Akt
pathway in AML. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:389–399. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nyquist KB, Panagopoulos I, Thorsen J,
Roberto R, Wik HS, Tierens A, Heim S and Micci F: t(12;13)(q14;q31)
leading to HMGA2 upregulation in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J
Haematol. 157:769–771. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fulda S and Vucic D: Targeting IAP
proteins for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 11:109–124. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dean EJ, Ranson M, Blackhall F and Dive C:
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein as a therapeutic target.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 11:1459–1471. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mastrangelo E, Vachette P, Cossu F,
Malvezzi F, Bolognesi M and Milani M: The activator of apoptosis
Smac-DIABLO acts as a tetramer in solution. Biophys J. 108:714–723.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Saraei R, Soleimani M, Movassaghpour
Akbari AA, Farshdousti Hagh M, Hassanzadeh A and Solali S: The role
of XIAP in resistance to TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
(TRAIL) in Leukemia. Biomed Pharmacother. 107:1010–1019. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
O'Donnell MR, Abboud CN, Altman J,
Appelbaum FR, Arber DA, Attar E, Borate U, Coutre SE, Damon LE,
Goorha S, et al: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines Acute myeloid
leukemia. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 10:984–1021. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Quiney C, Billard C, Faussat AM,
Salanoubat C and Kolb JP: Hyperforin inhibits P-gp and BCRP
activities in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells and myeloid
cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 48:1587–1599. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xu X, Wang Y, Deng H, Liu C, Wu J and Lai
M: HMGA2 enhances 5-fluorouracil chemoresistance in colorectal
cancer via the Dvl2/Wnt pathway. Oncotarget. 9:9963–9974. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tan L, Xu H, Chen G, Wei X, Yu B, Ye J, Xu
L and Tan H: Silencing of HMGA2 reverses retardance of cell
differentiation in human myeloid leukaemia. Br J Cancer.
118:405–415. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ohshima K, Inoue K, Fujiwara A, Hatakeyama
K, Kanto K, Watanabe Y, Muramatsu K, Fukuda Y, Ogura S, Yamaguchi K
and Mochizuki T: Let-7 microRNA family is selectively secreted into
the extracellular environment via exosomes in a metastatic gastric
cancer cell line. PLoS One. 5:e132472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Watanabe S, Ueda Y, Akaboshi S, Hino Y,
Sekita Y and Nakao M: HMGA2 maintains oncogenic RAS-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Am J Pathol. 174:854–868. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lin Y, Meng F, Lu Z, Chen K, Tao Y, Ouyang
Y and Cao X: Knockdown of PKM2 suppresses tumor progression in
human cervical cancer by modulating epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cancer Manag Res.
10:4191–4202. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Yang F, Xiao Z and Zhang S: Knockdown of
miR-194 5p inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in
breast cancer by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Int J Mol Med. 42:3355–3363. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao C, Qiao C, Zong L and Chen Y: Long
non-coding RNA-CCAT2 promotes the occurrence of non-small cell lung
cancer by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol
Lett. 16:4600–4606. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu L, Jiang H, Zhao J and Wen H: MiRNA-16
inhibited oral squamous carcinoma tumor growth in vitro and in vivo
via suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther.
11:5111–5119. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
Kumar R, Kotapalli V, Naz A, Gowrishankar
S, Rao S, Pollack JR and Bashyam MD: XPNPEP3 is a novel
transcriptional target of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 57:304–310. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Qiu F, Shin Y, Chen D, Cheng R, Chen Q,
Zhou K, Larrick JW, Mendelson AR and Ma JX: Anti-angiogenic effect
of a humanized antibody blocking the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Microvasc Res. 119:29–37. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zha L, Zhang J, Tang W, Zhang N, He M, Guo
Y and Wang Z: HMGA2 elicits EMT by activating the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 58:724–733. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Wend P, Runke S, Wend K, Anchondo B,
Yesayan M, Jardon M, Hardie N, Loddenkemper C, Ulasov I, Lesniak
MS, et al: WNT10B/β-catenin signalling induces HMGA2 and
proliferation in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. EMBO Mol
Med. 5:264–279. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|