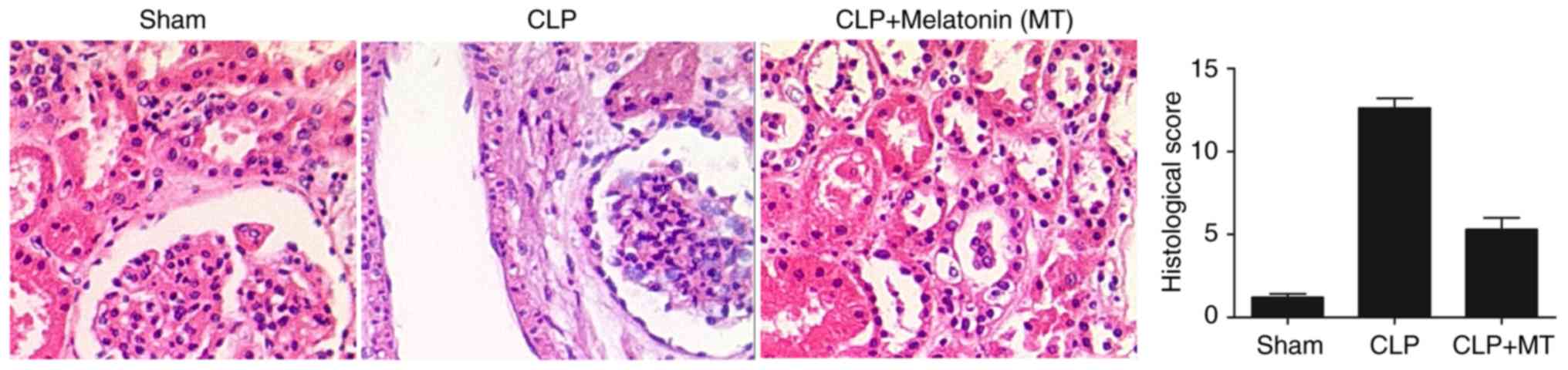
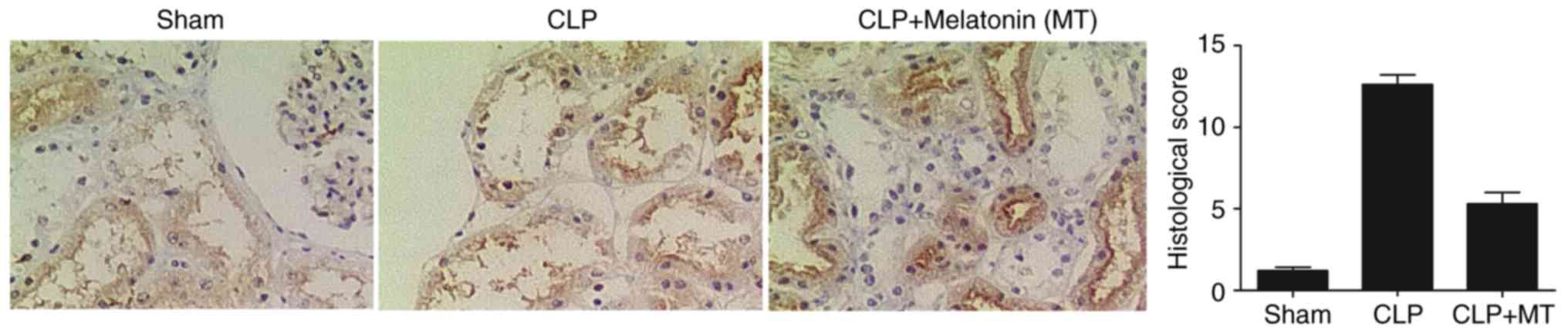
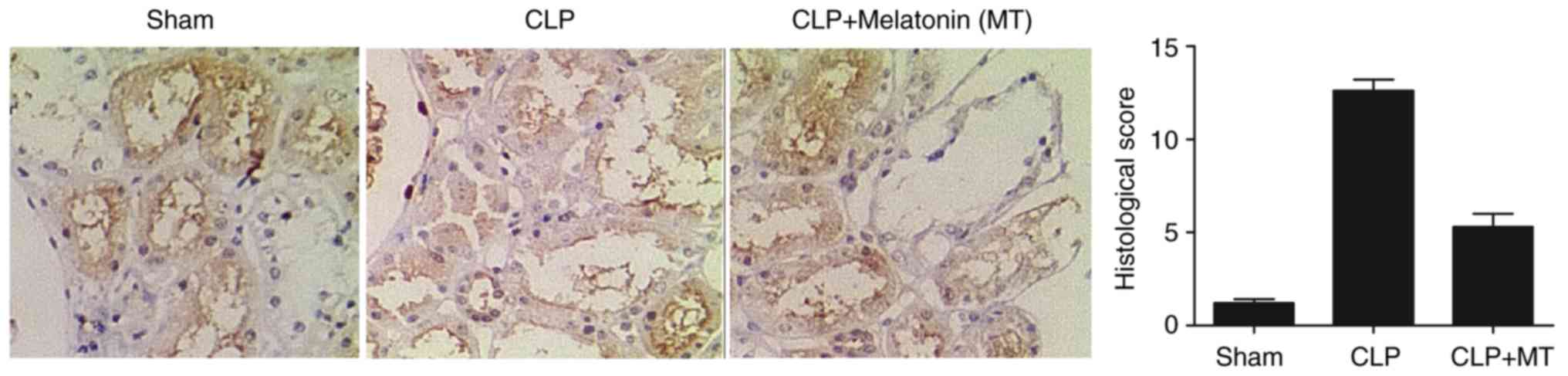
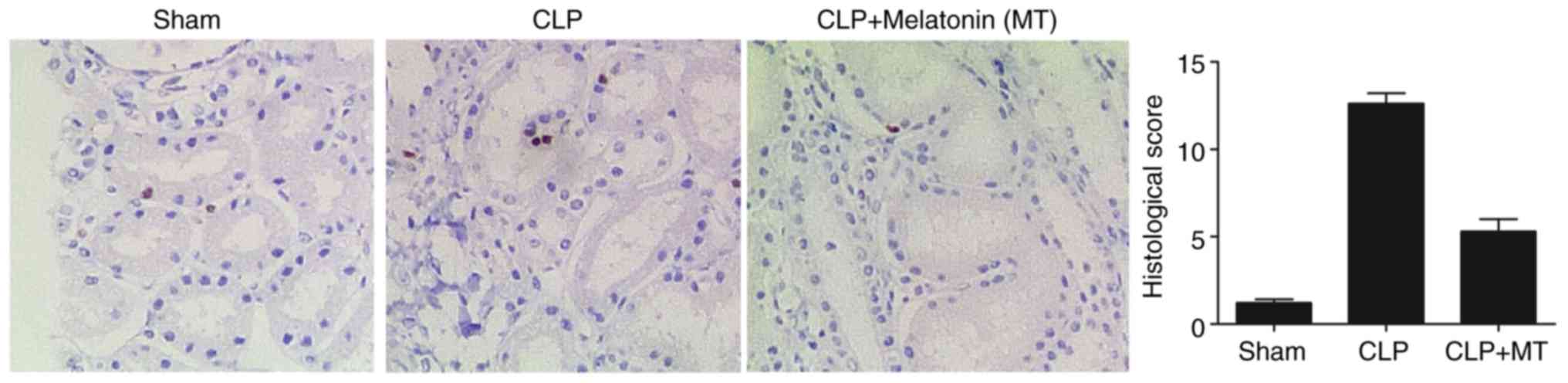
|
1
|
Hotchkiss RS and Karl IE: The
pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 348:138–150.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Davis BK, Wen H and Ting JP: The
inflammasome NLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated
diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 29:707–735. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lamkanfi M: Emerging inflammasome effector
mechanisms. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:213–220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Edelstein CL, Hoke TS, Somerset H, Fang W,
Klein CL, Dinarello CA and Faubel S: Proximal tubules from
caspase-1-deficient mice are protected against hypoxia-induced
membrane injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 22:1052–1061. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vilaysane A, Chun J, Seamone ME, Wang W,
Chin R, Hirota S, Li Y, Clark SA, Tschopp J, Trpkov K, et al: The
NLRP3 inflammasome promotes renal inflammation and contributes to
CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:1732–1744. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Granfeldt A, Ebdrup L, Tønnesen E and
Wogensen L: Renal cytokine profile in an endotoxemic porcine model.
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 52:614–620. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen A, Sheu LF, Chou WY, Tsai SC, Chang
DM, Liang SC, Lin FG and Lee WH: Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist
modulates the progression of a spontaneously occurring IgA
nephropathy in rats. Am J Kidney Dis. 30:693–702. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Furuichi K, Wada T, Iwata Y, Kokubo S,
Hara A, Yamahana J, Sugaya T, Iwakura Y, Matsushima K, Asano M, et
al: Interleukin-1- dependent sequential chemokine expression and
inflammatory cell infiltration in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Crit
Care Med. 34:2447–2455. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bani-Hani AH, Leslie JA, Asanuma H,
Dinarello CA, Campbell MT, Meldrum DR, Zhang H, Hile K and Meldrum
KK: IL-18 neutralization ameliorates obstruction-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis. Kidney Int.
76:500–511. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mulay SR, Kulkarni OP, Rupanagudi KV,
Migliorini A, Darisipudi MN, Vilaysane A, Muruve D, Shi Y, Munro F,
Liapis H and Anders HJ: Calcium oxalate crystals induce renal
inflammation by NLRP3-mediated IL-1β secretion. J Clin Invest.
123:236–246. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Homsi E, Janino P and de Faria JB: Role of
caspases on cell death, inflammation, and cell cycle in
glycerol-induced acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 69:1385–1392.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Allam R, Lawlor KE, Yu EC, Mildenhall AL,
Moujalled DM, Lewis RS, Ke F, Mason KD, White MJ, Stacey KJ, et al:
Mitochondrial apoptosis is dispensable for NLRP3 inflamma-some
activation but non-apoptotic caspase-8 is required for inflammasome
priming. EMBO Rep. 15:982–990. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Galano A, Tan DX and Reiter RJ: On the
free radical scavenging activities of melatonin's metabolites, AFMK
and AMK. J Pineal Res. 54:245–257. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
López A, García JA, Escames G, Venegas C,
Ortiz F, López LC and Acuña-Castroviejo D: Melatonin protects the
mitochondria from oxidative damage reducing oxygen consumption,
membrane potential, and superoxide anion production. J Pineal Res.
46:188–198. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Acuña Castroviejo D, López LC, Escames G,
López A, García JA and Reiter RJ: Melatonin-mitochondria interplay
in health and disease. Curr Top Med Chem. 11:221–240. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Crespo E, Macías M, Pozo D, Escames G,
Martin M, Vives F, Guerrero JM and Acuña Castroviejo D: Melatonin
inhibits expression of the inducible NO synthase II in liver and
lung and prevents endotoxemia in lipopolysaccharide-induced
multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in rats. FASEB J. 13:1537–1546.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Escames G, López LC, Tapias V, Utrilla P,
Reiter RJ, Hitos AB, León J, Rodríguez MI and Acuña Castroviejo D:
Melatonin counteracts inducible mitochondrial nitric oxide
synthase-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle of
septic rats. J Pineal Res. 40:71–78. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
García JA, Volt H, Venegas C, Doerrier C,
Escames G, López LC and Acuña Castroviejo D: Disruption of the
NF-κB/NLRP3 connection by melatonin requires retinoid-related
orphan receptor-α and blocks the septic response in rats. FASEB J.
29:3863–3875. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rahim I, Djerdjouri B, Sayed RK,
Fernández-Ortiz M, Fernández-Gil B, Hidalgo-Gutiérrez A, López LC,
Escames G, Reiter RJ and Acuña-Castroviejo D: Melatonin
administration to wild-type rats and nontreated NLRP3 mutant rats
share similar inhibition of the inflammatory response during
sepsis. J Pineal Res. 63:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Patiutko IuI, Khubiev AI, Poliakov MI,
Kirsanov MI and Sorokin AI: Functional results of gastrectomy in
cancer in relation to the surgical method and creation of
esophago-intestinal anastomosis. Vestn Khir Im I I Grek. 143:23–26.
1989.In Russian. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Schrier RW and Wang W: Acute renal failure
and sepsis. N Engl J Med. 351:159–169. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Melnikov VY, Ecder T, Fantuzzi G, Siegmund
B, Lucia MS, Dinarello CA, Schrier RW and Edelstein CL: Impaired
IL-18 processing protects caspase-1-deficient rats from ischemic
acute renal failure. J Clin Invest. 107:1145–1152. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jimenez MF, Watson RW, Parodo J, Evans D,
Foster D, Steinberg M, Rotstein OD and Marshall JC: Dysregulated
expression of neutrophil apoptosis in the systemic inflammatory
response syndrome. Arch Surg. 132:1263–1269. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mangan DF, Mergenhagen SE and Wahl SM:
Apoptosis in human monocytes: Possible role in chronic inflammatory
diseases. J Periodontol. 64:461–466. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schroder K and Tschopp J: The
inflammasomes. Cell. 140:821–832. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bergsbaken T, Fink SL and Cookson BT:
Pyroptosis: Host cell death and inflammation. Nat Rev Microbiol.
7:99–109. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I and
Tschopp J: Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress
to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol. 11:136–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gringhuis SI, Kaptein TM, Wevers BA,
Theelen B, van der Vlist M, Boekhout T and Geijtenbeek TB: Dectin-1
is an extracellular pathogen sensor for the induction and
processing of IL-1β via a noncanonical caspase-8 inflammasome. Nat
Immunol. 13:246–254. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tamura H, Nakamura Y, Korkmaz A,
Manchester LC, Tan DX, Sugino N and Reiter RJ: Melatonin and the
ovary: Physiological and pathophysiological implications. Fertil
Steril. 92:328–343. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Reiter RJ, Rosales-Corral SA, Manchester
LC and Tan DX: Peripheral reproductive organ health and melatonin:
Ready for prime time. Int J Mol Sci. 14:7231–7272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Siah KT, Wong RK and Ho KY: Melatonin for
the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol.
20:2492–2498. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schwertner A, Conceição Dos Santos CC,
Costa GD, Deitos A, de Souza A, de Souza IC, Torres IL, da Cunha
Filho JS and Caumo W: Efficacy of melatonin in the treatment of
endometriosis: A phase II, randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Pain. 154:874–881. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
de Matos Cavalcante AG, de Bruin PF, de
Bruin VM, Nunes DM, Pereira ED, Cavalcante MM and Andrade GM:
Melatonin reduces lung oxidative stress in patients with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled study. J Pineal Res. 53:238–244. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bai XZ, He T, Gao JX, Liu Y, Liu JQ, Han
SC, Li Y, Shi JH, Han JT, Tao K, et al: Melatonin prevents acute
kidney injury in severely burned rats via the activation of SIRT1.
Sci Rep. 6:321992016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yildirim ME, Badem H, Cakmak M, Yilmaz H,
Kosem B, Karatas OF, Bayrak R and Cimentepe E: Melatonin protects
kidney against apoptosis induced by acute unilateral ureteral
obstruction in rats. Cent European J Urol. 69:225–230.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang YC, Hsu SY, Yang CC, Sung PH, Chen
YL, Huang TH, Kao GS, Chen SY, Chen KH, Chiang HJ, et al: Enhanced
protection against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury with combined
melatonin and exendin-4 in a rodent model. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
241:1588–1602. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhu F, Chong Lee, Shin OL, Xu H, Zhao Z,
Pei G, Hu Z, Yang J, Guo Y, Mou J, Sun J, et al: Melatonin promoted
renal regeneration in folic acid-induced acute kidney injury via
inhibiting nucleocytoplasmic translocation of HMGB1 in tubular
epithelial cells. Am J Transl Res. 9:1694–1707. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Greene JC, Whitworth AJ, Kuo I, Andrews
LA, Feany MB and Pallanck LJ: Mitochondrial pathology and apoptotic
muscle degeneration in Drosophila parkin mutants. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 100:4078–4083. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen DF and Youle
RJ: Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and
promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol. 183:795–803. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang X, Winter D, Ashrafi G, Schlehe J,
Wong YL, Selkoe D, Rice S, Steen J, LaVoie MJ and Schwarz TL: PINK1
and Parkin target Miro for phosphorylation and degradation to
arrest mitochondrial motility. Cell. 147:893–906. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yan Y, Jiang W, Liu L, Wang X, Ding C,
Tian Z and Zhou R: Dopamine controls systemic inflammation through
inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell. 160:62–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|