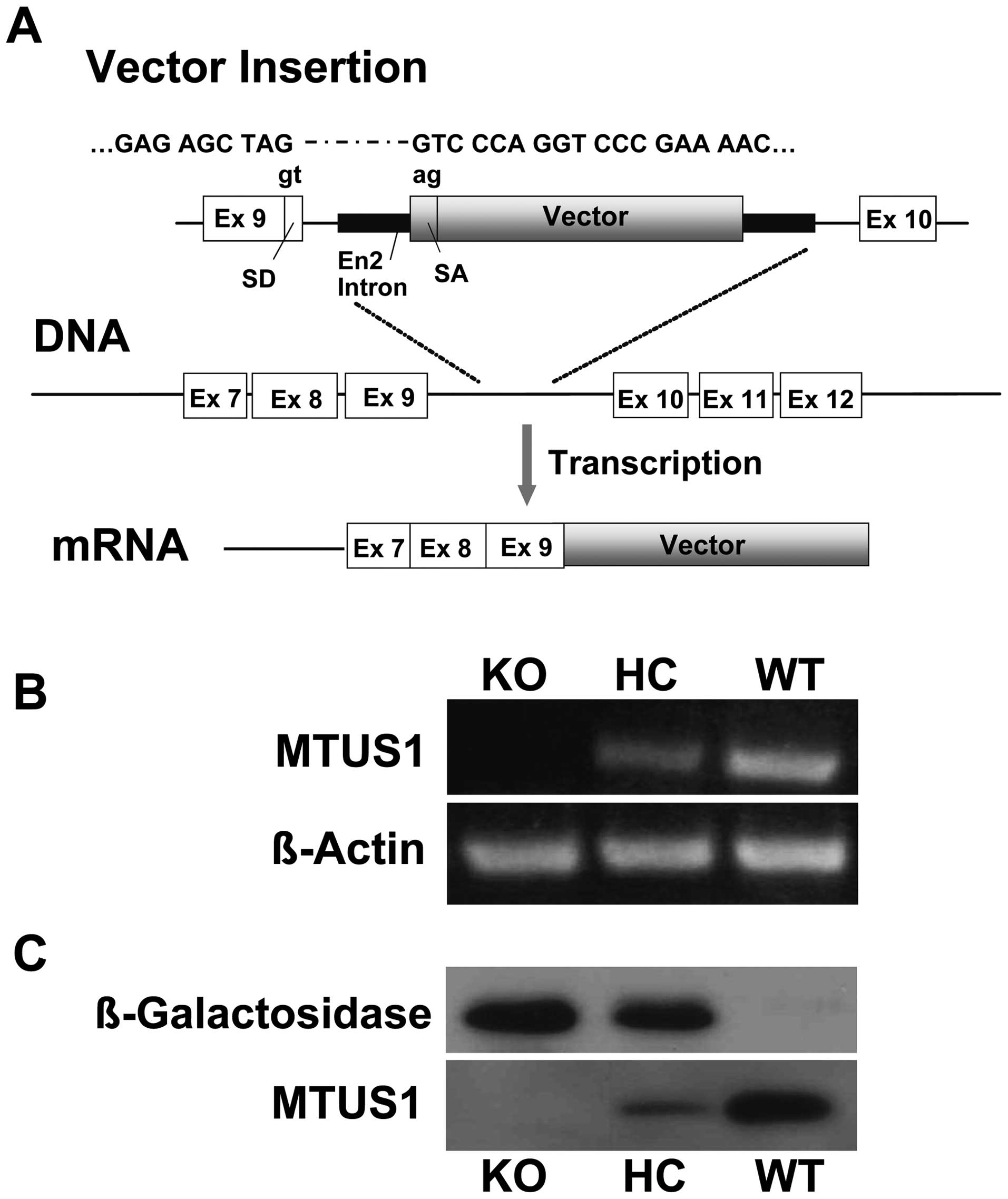
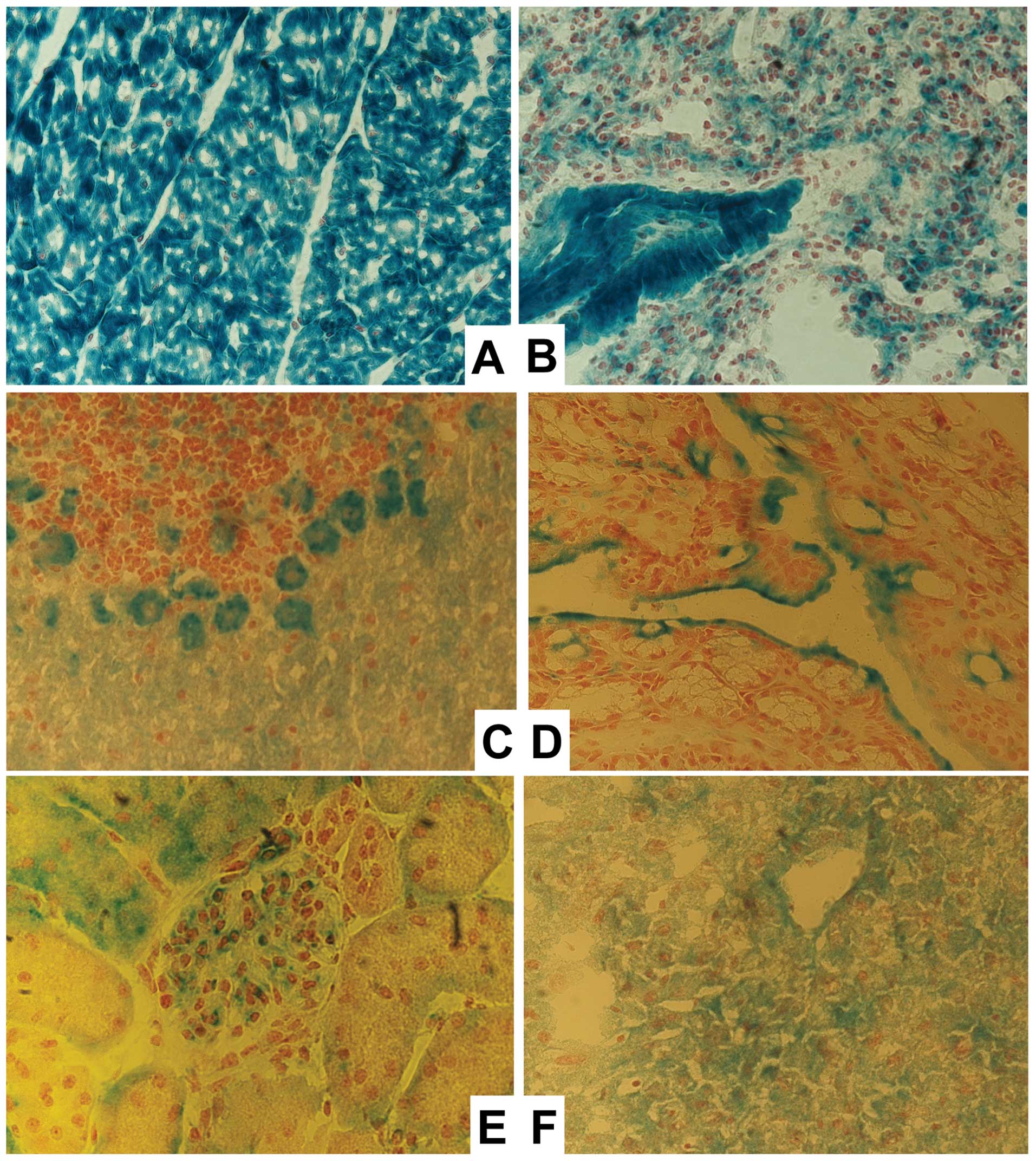
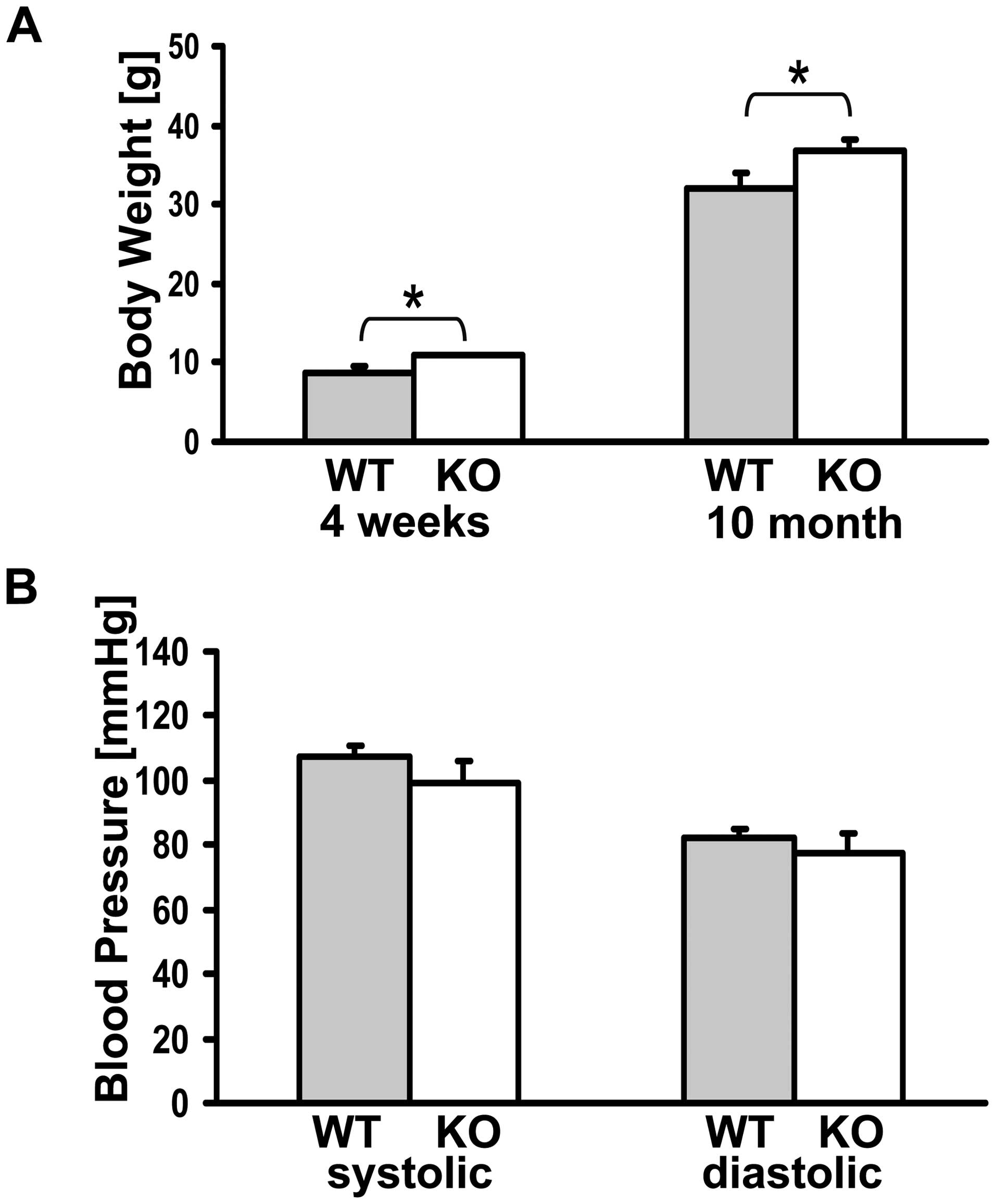
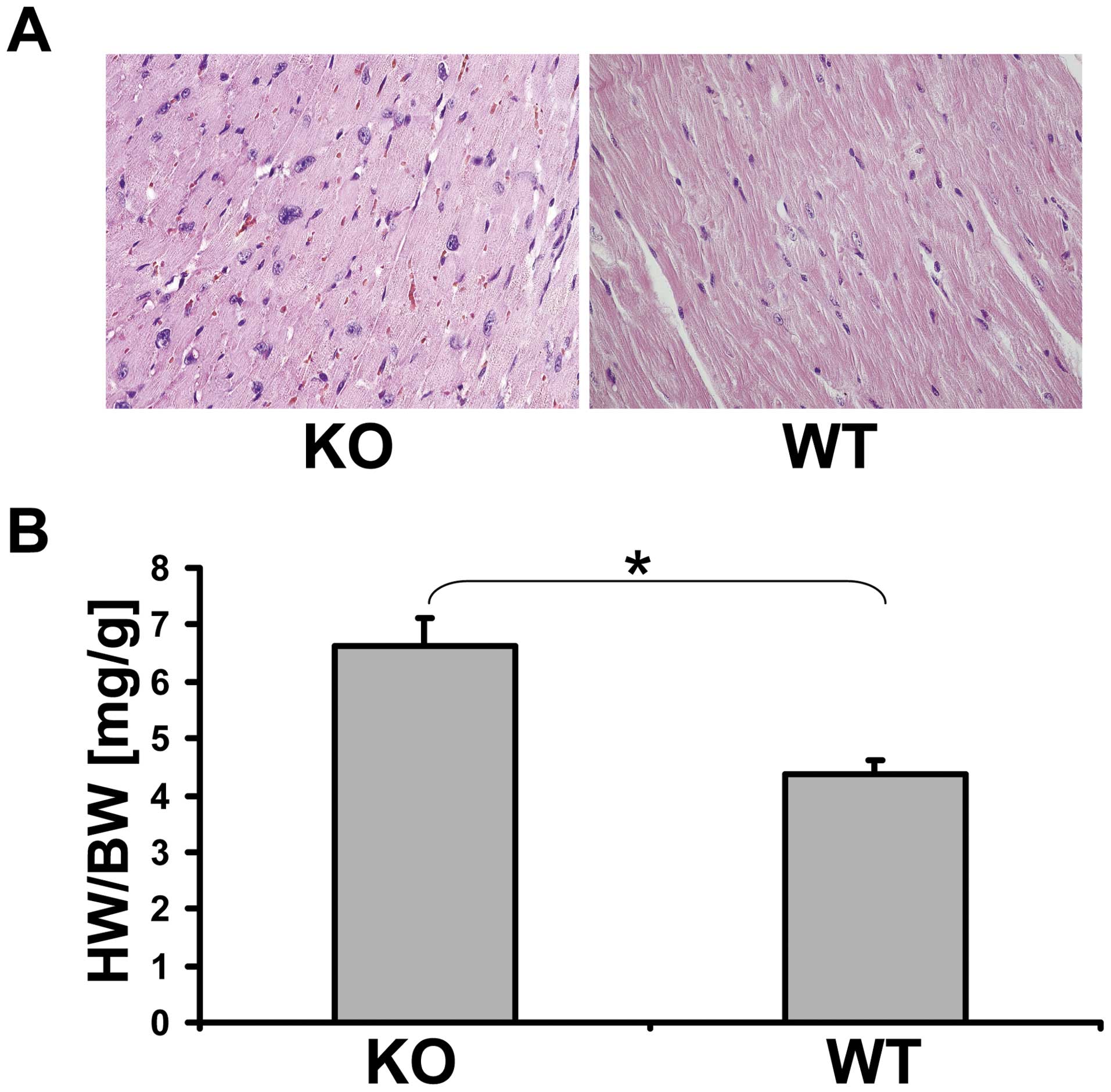
|
1
|
Deshayes F and Nahmias C: Angiotensin
receptors: a new role in cancer? Trends Endocrinol Metab.
16:293–299. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Egami K, Murohara T, Shimada T, et al:
Role of host angiotensin II type 1 receptor in tumor angiogenesis
and growth. J Clin Invest. 112:67–75. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Seibold S, Rudroff C, Weber M, Galle J,
Wanner C and Marx M: Identification of a new tumor suppressor gene
located at chromosome 8p21.3-22. FASEB J. 02-0934fje2003.
|
|
4
|
Mogi M, Iwai M and Horiuchi M: Emerging
concepts of regulation of angiotensin II receptors: new players and
targets for traditional receptors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
27:2532–2539. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Frank B, Bermejo JL, Hemminki K, et al:
Copy number variant in the candidate tumor suppressor gene MTUS1
and familial breast cancer risk. Carcinogenesis. 28:1442–1445.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee S, Bang S, Song K and Lee I:
Differential expression in normal-adenoma-carcinoma sequence
suggests complex molecular carcinogenesis in colon. Oncol Rep.
16:747–754. 2006.
|
|
7
|
Tchatchou S and Burwinkel B: Chromosome
copy number variation and breast cancer risk. Cytogenet Genome Res.
123:183–187. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ye HP, Huang N, Muzio BL, et al: Genomic
assessments of the frequent loss of heterozygosity region on
8p21.3-p22 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Genet
Cytogenet. 176:100–106. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Simon NSL, Laurie C, Linda R, et al:
Expression and function of ATIP/MTUS1 in human prostate cancer cell
lines. Prostate. 70:1563–1574. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rodrigues-Ferreira S, Di Tommaso A,
Dimitrov A, et al: 8p22 MTUS1 gene product ATIP3 is a novel
anti-mitotic protein underexpressed in invasive breast carcinoma of
poor prognosis. PLoS One. 4:E72392009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zuern C, Heimrich J, Kaufmann R, et al:
Down-regulation of MTUS1 in human colon tumors. Oncol Rep.
23:183–189. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nouet S, Amzallag N, Li JM, et al:
Trans-inactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases by novel
angiotensin II AT2 receptor-interacting protein, ATIP. J Biol Chem.
279:28989–28997. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wruck CJ, Funke-Kaiser H, Pufe T, et al:
Regulation of transport of the angiotensin AT2 receptor by a novel
membrane-associated golgi protein. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
25:57–64. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Di Benedetto M, Bièche I, Deshayes F, et
al: Structural organization and expression of human MTUS1, a
candidate 8p22 tumor suppressor gene encoding a family of
angiotensin II AT2 receptor-interacting proteins, ATIP. Gene.
380:127–136. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Reinemund J, Seidel K, Steckelings UM, et
al: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) transcriptionally
regulates angiotensin AT2 receptor (AT2R) and AT2R binding protein
(ATBP) genes. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:1795–1805. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pillai JB, Gupta M, Rajamohan SB, Lang R,
Raman J and Gupta MP: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-deficient mice
are protected from angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 291:H1545–H1553. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li JM, Mogi M, Tsukuda K, et al:
Angiotensin II-induced neural differentiation via angiotensin II
type 2 (AT2) receptor-MMS2 cascade involving interaction between
AT2 receptor-interacting protein and Src homology 2
domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1. Mol Endocrinol.
21:499–511. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fujita T, Mogi M, Min LJ, et al:
Attenuation of cuff-induced neointimal formation by overexpression
of angiotensin II type 2 receptor-interacting protein 1.
Hypertension. 53:688–693. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bundschu K, Knobeloch KP, Ullrich M, et
al: Gene disruption of Spred-2 causes dwarfism. J Biol Chem.
280:28572–28580. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wollert KC and Drexler H: The
renin-angiotensin system and experimental heart failure. Cardiovasc
Res. 43:838–849. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Senbonmatsu T, Ichihara S, Price E Jr,
Gaffney FA and Inagami T: Evidence for angiotensin II type 2
receptor-mediated cardiac myocyte enlargement during in vivo
pressure overload. J Clin Invest. 106:R1–R5. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Senbonmatsu T, Saito T, Landon EJ, et al:
A novel angiotensin II type 2 receptor signaling pathway: possible
role in cardiac hypertrophy. EMBO J. 22:6471–6482. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Landon EJ and Inagami T: Beyond the G
protein: the saga of the type 2 angiotensin II receptor.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:15–16. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park TS and Zambidis ET: A role for the
renin-angiotensin system in hematopoiesis. Haematologica.
94:745–747. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wuthrich RP: RAS meets SLE. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 24:2634–2636. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Herlitz H, Tarkowski A, Svalander C,
Volkmann R and Westberg G: Beneficial effect of captopril on
systemic lupus erythematosus-like disease in MRL lpr/lpr mice. Int
Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 85:272–277. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Di Benedetto M, Pineau P, Nouet S, et al:
Mutation analysis of the 8p22 candidate tumor suppressor gene
ATIP/MTUS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
252:207–215. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Garcia M, Konoplev S, Morosan C, Abruzzo
LV, Bueso-Ramos CE and Medeiros LJ: MALT lymphoma involving the
kidney: a report of 10 cases and review of the literature. Am J
Clin Pathol. 128:464–473. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Smedby KE, Baecklund E and Askling J:
Malignant lymphomas in autoimmunity and inflammation: a review of
risks, risk factors, and lymphoma characteristics. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 15:2069–2077. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Isaacson PG and Du MQ: MALT lymphoma: from
morphology to molecules. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:644–653. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Suzuki Y, Ruiz-Ortega M, Lorenzo O,
Ruperez M, Esteban V and Egido J: Inflammation and angiotensin II.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 35:881–900. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wu L, Iwai M, Li Z, et al: Regulation of
inhibitory protein-kappaB and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 by
angiotensin II type 2 receptor-activated Src homology protein
tyrosine phosphatase-1 in fetal vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol
Endocrinol. 18:666–678. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Okamoto T: NF-kappaB and rheumatic
diseases. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 6:359–372. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Newton CR, Curran B and Victorino GP:
Angiotensin II type 2 receptor effect on microvascular hydraulic
permeability. J Surg Res. 120:83–88. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang ZQ, Moore AF, Ozono R, Siragy HM and
Carey RM: Immunolocalization of subtype 2 angiotensin II (AT2)
receptor protein in rat heart. Hypertension. 32:78–83. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cao Z, Kelly DJ, Cox A, et al: Angiotensin
type 2 receptor is expressed in the adult rat kidney and promotes
cellular proliferation and apoptosis. Kidney Int. 58:2437–2451.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lenkei Z, Palkovits M, Corvol P and
Llorens-Cortes C: Distribution of angiotensin II type-2 receptor
(AT2) mRNA expression in the adult rat brain. J Comp Neurol.
373:322–339. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
De Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright
JW and Unger T: International union of pharmacology. XXIII. The
angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 52:415–472.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|