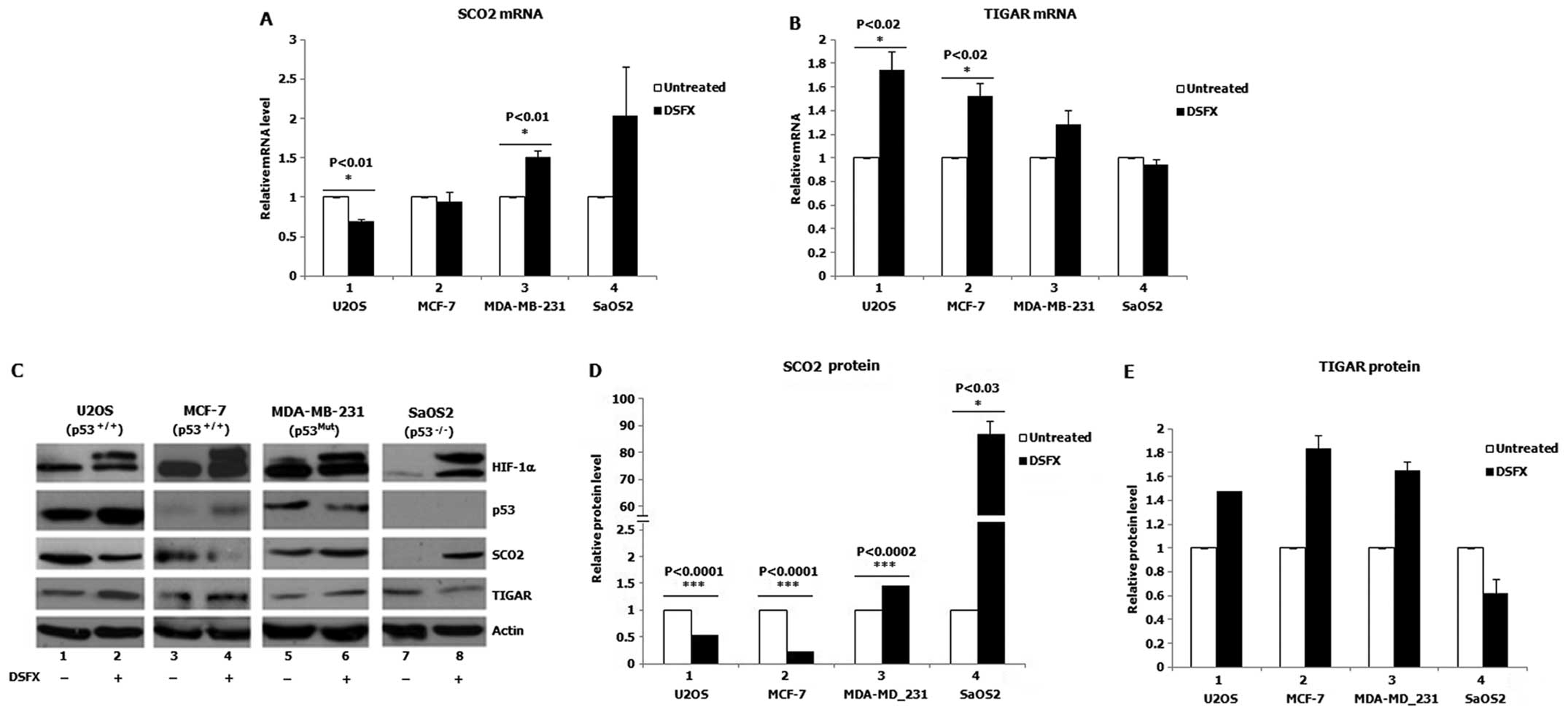
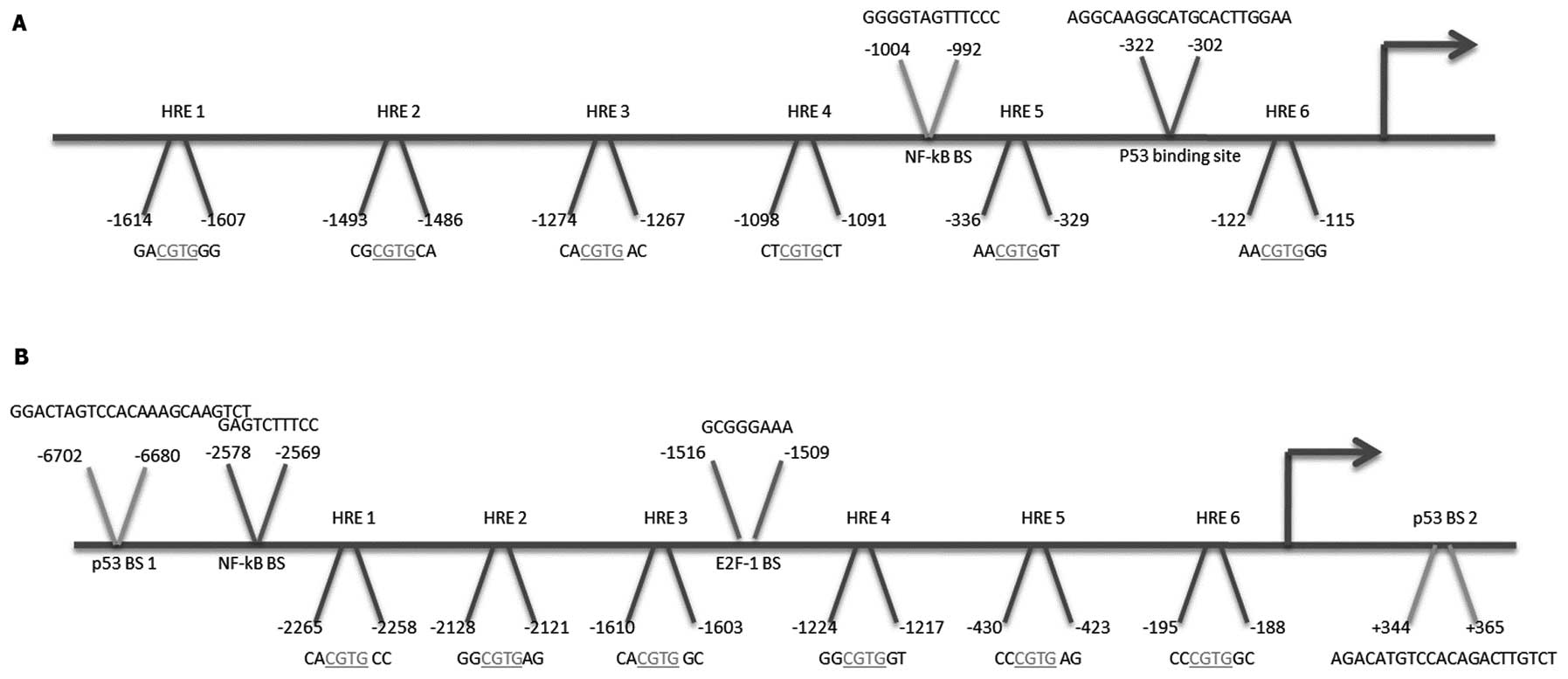
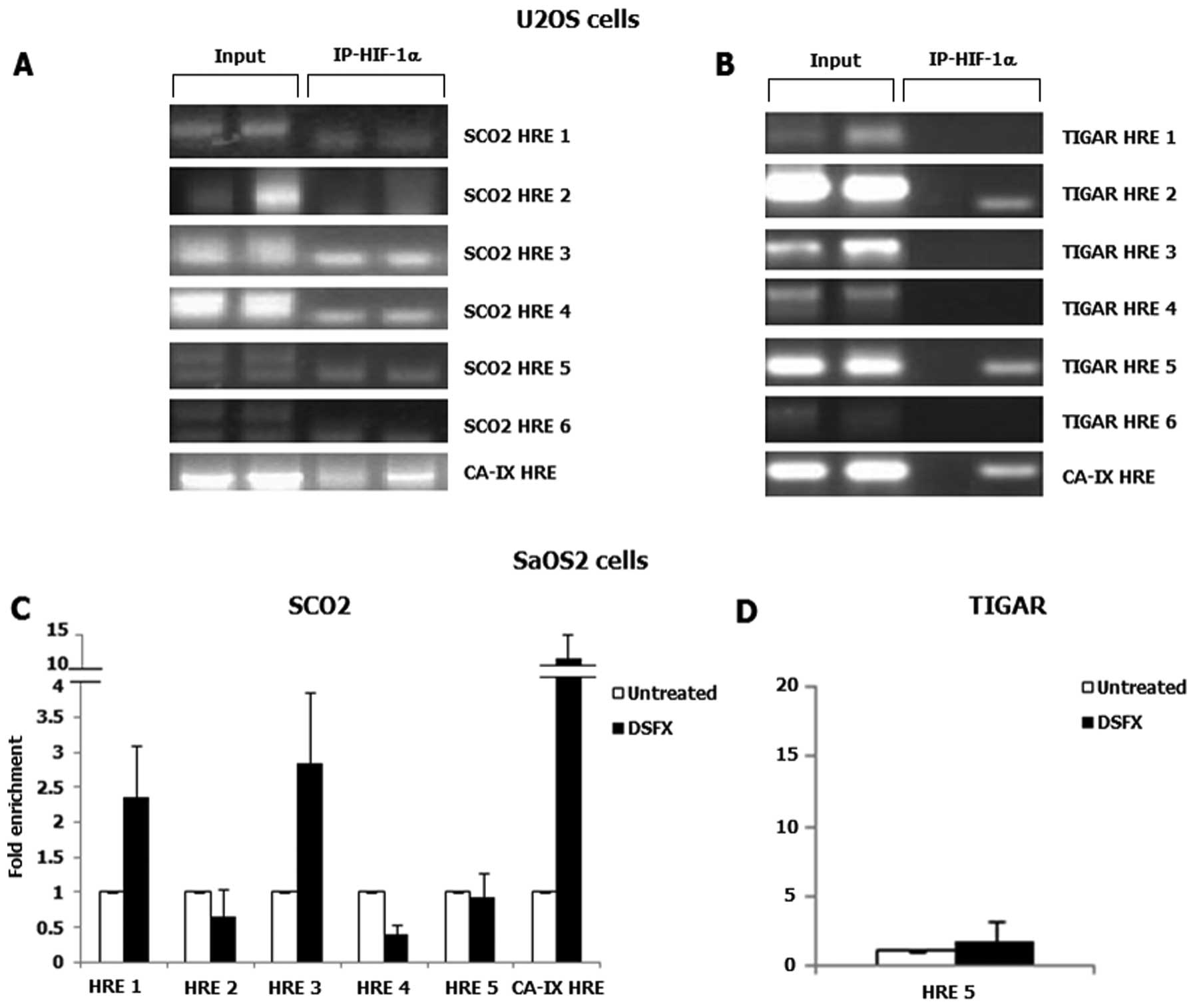
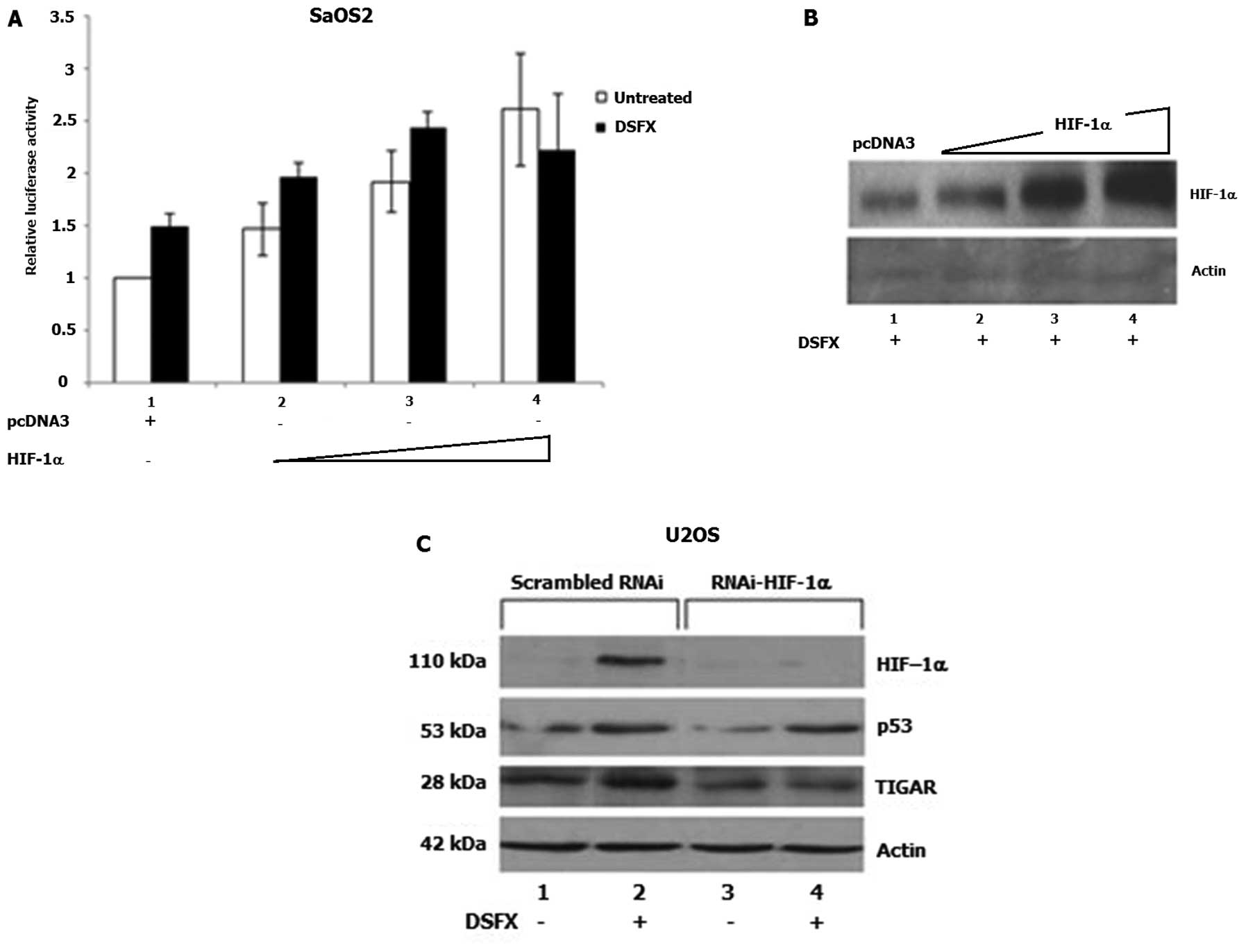
|
1
|
Fantin VR, St-Pierre J and Leder P:
Attenuation of LDH-A expression uncovers a link between glycolysis,
mitochondrial physiology, and tumor maintenance. Cancer Cell.
9:425–434. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vander Heiden MG, Plas DR, Rathmell JC,
Fox CJ, Harris MH and Thompson CB: Growth factors can influence
cell growth and survival through effects on glucose metabolism. Mol
Cell Biol. 21:5899–5912. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Olovnikov IA, Kravchenko JE and Chumakov
PM: Homeostatic functions of the p53 tumor suppressor: Regulation
of energy metabolism and antioxidant defense. Semin Cancer Biol.
19:32–41. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sonveaux P, Végran F, Schroeder T, et al:
Targeting lactate-fueled respiration selectively kills hypoxic
tumor cells in mice. J Clin Invest. 118:3930–3942. 2008.
|
|
5
|
Kroemer G and Pouyssegur J: Tumor cell
metabolism: cancer’s Achilles’ heel. Cancer Cell. 13:472–482.
2008.
|
|
6
|
Papandreou I, Cairns RA, Fontana L, Lim AL
and Denko NC: HIF-1 mediates adaptation to hypoxia by actively
downregulating mitochondrial oxygen consumption. Cell Metab.
3:187–197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Semenza G: HIF-1 mediates the Warburg
effect in clear cell renal carcinoma. J Bioenerg Biomembr.
39:231–234. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tennant DA, Duran RV, Boulahbel H and
Gottlieb E: Metabolic transformation in cancer. Carcinogenesis.
30:1269–1280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vousden KH and Ryan KM: p53 and
metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:691–700. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shen L, Sun X, Fu Z, Yang G, Li J and Yao
L: The fundamental role of the p53 pathway in tumor metabolism and
its implication in tumor therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1561–1567.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Matoba S, Kang J-G, Patino WD, et al: p53
regulates mitochondrial respiration. Science. 312:1650–1653. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bensaad K, Cheung EC and Vousden KH:
Modulation of intracellular ROS levels by TIGAR controls autophagy.
EMBO J. 28:3015–3026. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stiburek L and Zeman J: Assembly factors
and ATP-dependent proteases in cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1797:1149–1158. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jaksch M, Ogilvie I, Yao J, et al:
Mutations in SCO2 are associated with a distinct form of
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and cytochrome c oxidase deficiency.
Hum Mol Genet. 9:795–801. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li H and Jogl G: Structural and
biochemical studies of TIGAR (Tp53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis
regulator). J Biol Chem. 284:1748–1754. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bensaad K, Tsuruta A, Selak MA, et al:
TIGAR, a p53-inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis. Cell.
126:107–120. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xenaki G, Ontikatze T, Rajendran R, et al:
PCAF is an HIF-1[alpha] co-factor that regulates p53
transcriptional activity in hypoxia. Oncogene. 27:5785–5796.
2008.
|
|
18
|
Lim J-H, Lee Y-M, Chun Y-S, Chen J, Kim
J-E and Park J-W: Sirtuin 1 modulates cellular responses to hypoxia
by deacetylating hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Mol Cell. 38:864–878.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fulco M, Schiltz RL, Iezzi S, et al: Sir2
regulates skeletal muscle differentiation as a potential sensor of
the redox state. Mol Cell. 12:51–62. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Motta MC, Divecha N, Lemieux M, et al:
Mammalian SIRT1 represses forkhead transcription factors. Cell.
116:551–563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haigis MC and Sinclair DA: Mammalian
sirtuins: biological insights and disease relevance. Annu Rev
Pathol. 5:253–295. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sohda M, Ishikawa H, Masuda N, et al:
Pretreatment evaluation of combined HIF-1α, p53 and p21 expression
is a useful and sensitive indicator of response to radiation and
chemotherapy in esophageal cancer. Int J Cancer. 110:838–844.
2004.
|
|
23
|
Fritz V and Fajas L: Metabolism and
proliferation share common regulatory pathways in cancer cells.
Oncogene. 29:4369–4377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Soutoglou E, Katrakili N and Talianidis I:
Acetylation regulates transcription factor activity at multiple
levels. Mol Cell. 5:745–751. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Demonacos C, Krstic-Demonacos M and La
Thangue NB: A TPR motif co-factor contributes to p300 activity in
the p53 response. Mol Cell. 8:71–84. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wallace DC: Bioenergetics, the origins of
complexity, and the ascent of man. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:8947–8953. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bensaad K and Vousden KH: p53: new roles
in metabolism. Trends Cell Biol. 17:286–291. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou S, Kachhap S and Singh KK:
Mitochondrial impairment in p53-deficient human cancer cells.
Mutagenesis. 18:287–292. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schwartzenberg-Bar-Yoseph F, Armoni M and
Karnieli E: The tumor suppressor p53 down-regulates glucose
transporters GLUT1 and GLUT4 gene expression. Cancer Res.
64:2627–2633. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Formenti F, Constantin-Teodosiu D,
Emmanuel Y, et al: Regulation of human metabolism by
hypoxia-inducible factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:12722–12727.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yalcin A, Telang S, Clem B and Chesney J:
Regulation of glucose metabolism by
6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatases in cancer.
Exp Mol Pathol. 86:174–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chesney J:
6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase and tumor cell
glycolysis. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 9:535–539. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Seyfried T and Shelton L: Cancer as a
metabolic disease. Nutr Metab. 7:72010. View Article : Google Scholar
|