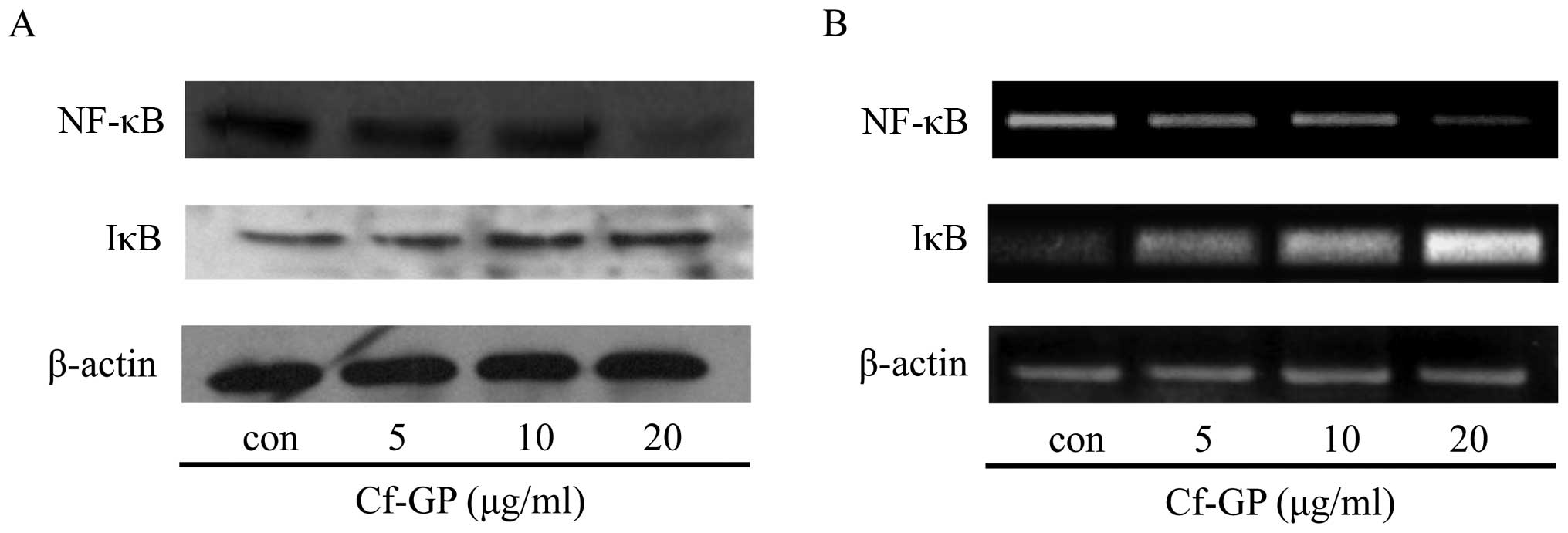
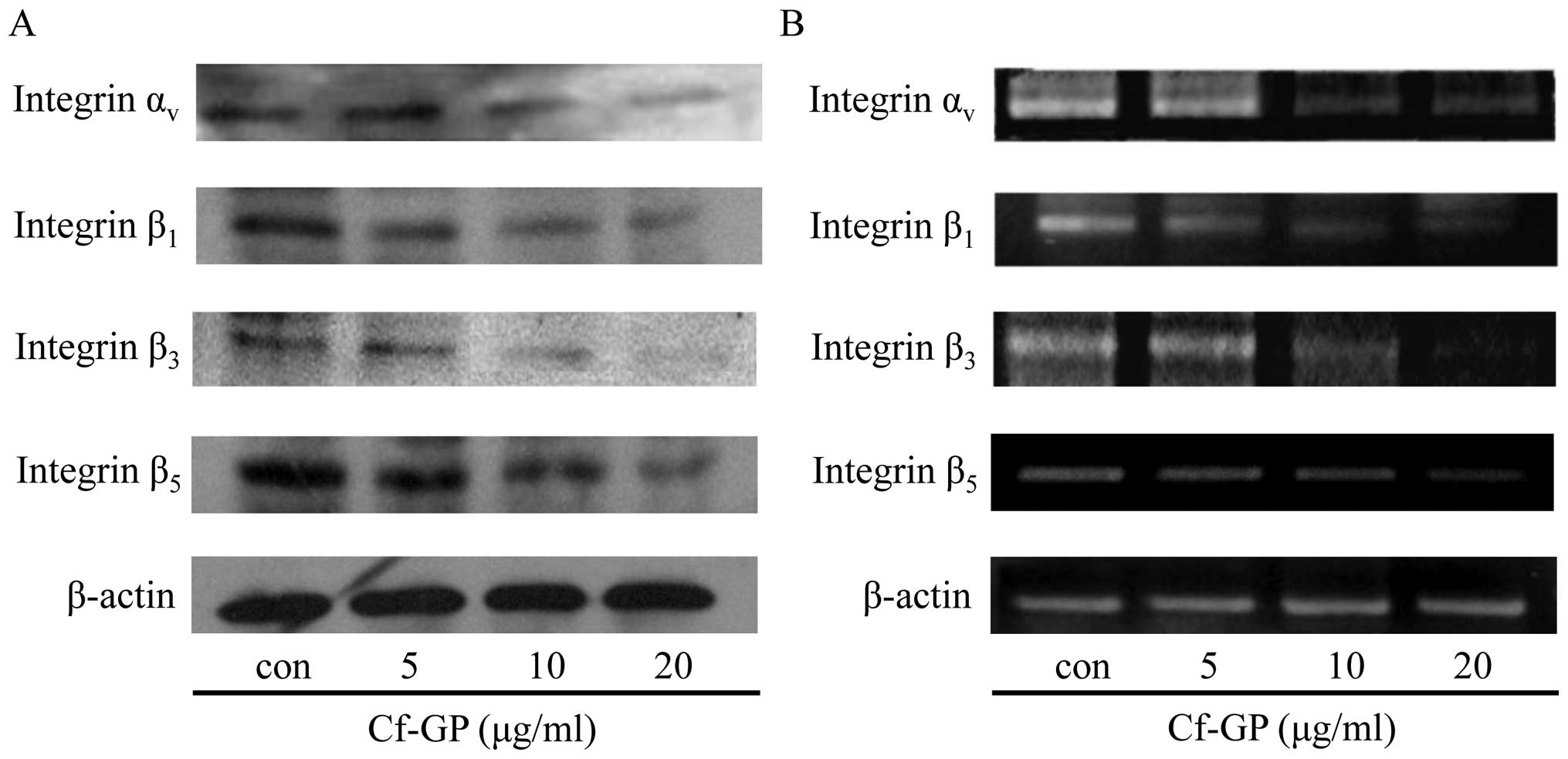
|
1.
|
Park HY, Lim CW, Kim YK, Yoon HD and Lee
KJ: Immunostimulating and anticancer activities of hot water
extract from Capsosiphon fulvescens. J Korean Soc Appl Biol
Chem. 49:343–348. 2006.
|
|
2.
|
Jung KJ, Jung CH, Pyeun JH and Choi YJ:
Changes of food components in Mesangi (Capsosiphon
fulvescens), Gashiparae (Enteromorpha prolifera), and
Cheonggak (Codium fragile) depending on harvest times. J
Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 34:687–693. 2005.
|
|
3.
|
Na YS, Kim WJ, Kim SM, Park JK, Lee MS,
Kim SO, Synytsya A and Park YI: Purification, characterization and
immunostimulating activity of water-soluble polysaccharide isolated
from Capsosiphon fulvescens. Int Immunopharmacol.
10:364–370. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Karnjanapratum S, Tabarsa M, Cho M and You
S: Characterization and immunomodulatory activities of sulfated
polysaccharides from Capsosiphon fulvescens. Int J Biol
Macromol. 51:720–729. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Hwang HJ, Kwon MJ, Kim IH and Nam TJ: The
effect of polysaccharide extracted from the marine alga
Capsosiphon fulvescens on ethanol administration. Food Chem
Toxicol. 46:2653–2657. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kim YM, Kim IH and Nam TJ: Induction of
apoptosis signaling by a glycoprotein of Capsosiphon
fulvescens in AGS cell. Kor J Fish Aquat Sci. 44:216–224.
2011.
|
|
7.
|
Kim YM, Kim IH and Nam TJ: Induction of
apoptosis signaling by glycoprotein of Capsosiphon
fulvescens in human gastric cancer (AGS) cells. Nutr Cancer.
64:761–769. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Kim YM, Kim IH and Nam TJ: Inhibition of
AGS human gastric cancer cell invasion and proliferation by
Capsosiphon fulvescens glycoprotein. Mol Med Rep. 8:11–16.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Levy L and Hill CS: Alterations in
components of the TGF-beta superfamily signaling pathways in human
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:41–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Serra R and Crowley MR: Mouse models of
transforming growth factor beta impact in breast development and
cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 12:749–760. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Hua F, Zhongliang H, Jifang W, Kuansong W
and Ying L: TGF-beta promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric
cancer cells by increasing fascin1 expression via ERK and JNK
signal pathways. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 41:648–656.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Roarty K, Baxley SE, Crowley MR, Frost AR
and Serra R: Loss of TGF-β or Wnt5a results in an increase in
Wnt/β-catenin activity and redirects mammary tumor phenotype.
Breast Cancer Res. 11:R192009.
|
|
13.
|
Lee YC, Cheng TH, Lee JS, Chen JH, Liao
YC, Fong Y, Wu CH and Shih YW: Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid,
suppresses invasion and migration involving FAK/PI3K/Akt and small
GTPase signals in human gastric adenocarcinoma AGS cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 347:103–115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Humphries MJ: Integrin structure. Biochem
Soc Trans. 28:311–339. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Fong YC, Hsu SF, Wu CL, Li TM, Kao ST,
Tsai FJ, Chen WC, Liu SC, Wu CM and Tang CH: Transforming growth
factor-β1 increases cell migration and β1 integrin up-regulation in
human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 64:13–21. 2009.
|
|
16.
|
Woodhouse EC, Chuaqui RF and Liotta LA:
General mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer. 80:1529–1537. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Krysho DV, Vanden BT, D’Herde K and
Vandenabeele P: Apoptosis and necrosis: detection, discrimination
and phagocytosis. Methods. 44:205–221. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Sahai E and Marshall CJ: Rho-GTPases and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:133–142. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Fritz G, Just I and Kaina B: Rho GTPases
are over-expressed in human tumors. Int J Cancer. 81:682–687. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Leivonen SK and Kähäri VM: Transforming
growth factor-beta signaling in cancer invasion and metastasis. Int
J Cancer. 121:2119–2124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Boukerche H, Su ZZ, Emdad L, Sarkar D and
Fisher PB: mda-9/Syntenin regulates the metastatic phenotype in
human melanoma cells by activating nuclear factor-kappaB. Cancer
Res. 67:1812–1822. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Peng C, Liu X, Liu E, Xu K, Niu W, Chen R,
Wang J, Zhang Z, Lin P, Wang J, Agrez M and Niu J: Norcantharidin
induces HT-29 colon cancer cell apoptosis through the
ανβ6-extracellular signal-related kinase
signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 100:2302–2308. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Zhang ZY, Xu KS, Wang JS, Yang GY, Wang W,
Wang JY, Niu WB, Liu EY, Mi YT and Niu J: Integrin
ανβ6 acts as a prognostic indicator in
gastric carcinoma. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 20:61–66. 2008.
|
|
24.
|
Go H, Hwang HJ and Nam TJ: A glycoprotein
from Laminaria japonica induces apoptosis in HT-29 colon
cancer cells. Toxicology In Vitro. 24:1546–1553. 2010.
|
|
25.
|
Hwang HJ, Kim IH and Nam TJ: Effect of a
glycoprotein from Hizikia fusiformis on
acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Food Chem Toxicol.
46:3475–3481. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Cho EK, Yoo SK and Choi YJ: Inhibitory
effects of maesaengi (Capsosiphon fulvescens) extracts on
angiotensin converting enzyme and α-glucosidase. Korea J Life Sci.
21:811–818. 2011.
|
|
27.
|
Kown MJ and Nam TJ: A polysaccharide of
the marine alga Capsosiphon fulvescens induces apoptosis in
AGS gastric cancer cells via an IGF-IR-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway.
Cell Biol Int. 31:768–775. 2007.
|
|
28.
|
Wei YY, Chen YJ, Hsiao YC, Huang YC, Lai
TH and Tang CH: Osteoblasts-derived TGF-β1 enhance motility and
integrin upregulation through Akt, ERK, and NF-κB-dependent pathway
in human breast cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 47:526–537. 2008.
|
|
29.
|
Cooper CR, Chay CH and Pienta KJ: The role
of ανβ3 in prostate cancer progression.
Neoplasia. 4:191–194. 2002.
|
|
30.
|
Kumar CC: Integrin
ανβ3 as a therapeutic target for blocking
tumor-induced angiogenesis. Curr Drug Targets. 4:123–131. 2003.
|
|
31.
|
Helbig G, Christopherson KW II,
Bhat-Nakshatri P, Kumar S, Kishimoto H, Miller KD, Broxmeyer HE and
Naksharti H: NF-κB promotes breast cancer cell migration and
metastasis by inducing the expression of the chemokine receptor
CXCR4. J Biol Chem. 278:21631–21638. 2003.
|