|
1
|
Gupta R, Seethalakshmi V, Jambhekar NA, et
al: Clinico-pathologic profile of 470 giant cell tumors of bone
from a cancer hospital in western India. Ann Diagn Pathol.
12:239–248. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
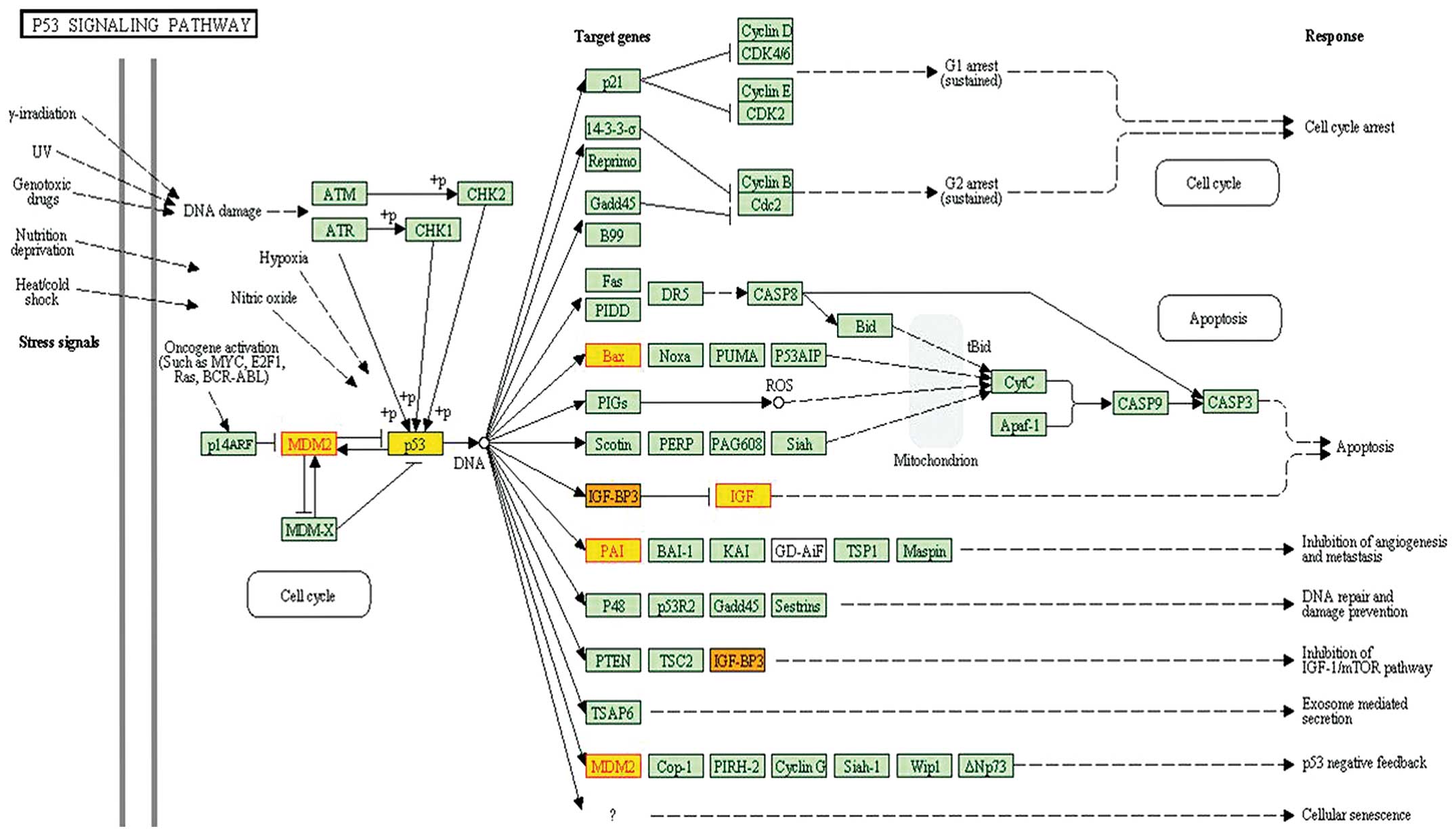
|
Gamberi G, Serra M, Ragazzini P, et al:
Identification of markers of possible prognostic value in 57 giant
cell tumors of bone. Oncol Rep. 10:351–356. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
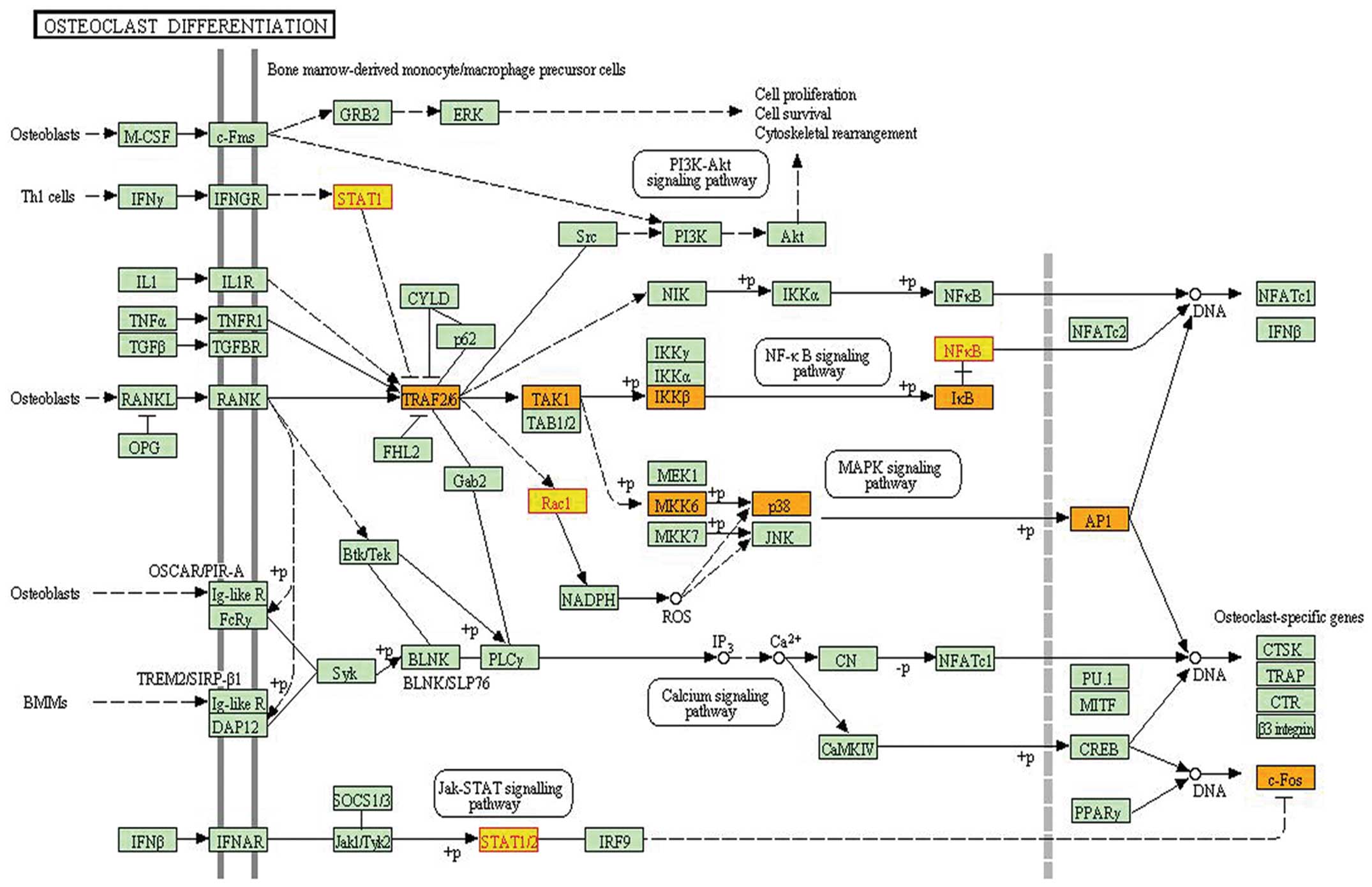
Szendröi M: Giant cell tumor of bone. J
Bone Joint Surg Br. 86:5–12. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thomas DM and Skubitz KM: Giant cell
tumour of bone. Curr Opin Oncol. 21:338–344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mendenhall WM, Zlotecki RA, Scarborough
MT, Gibbs CP and Mendenhall NP: Giant cell tumour of bone. Am J
Clin Oncol. 29:96–99. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eckardt JJ and Grogan TJ: Giant cell tumor
of bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 204:45–58. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
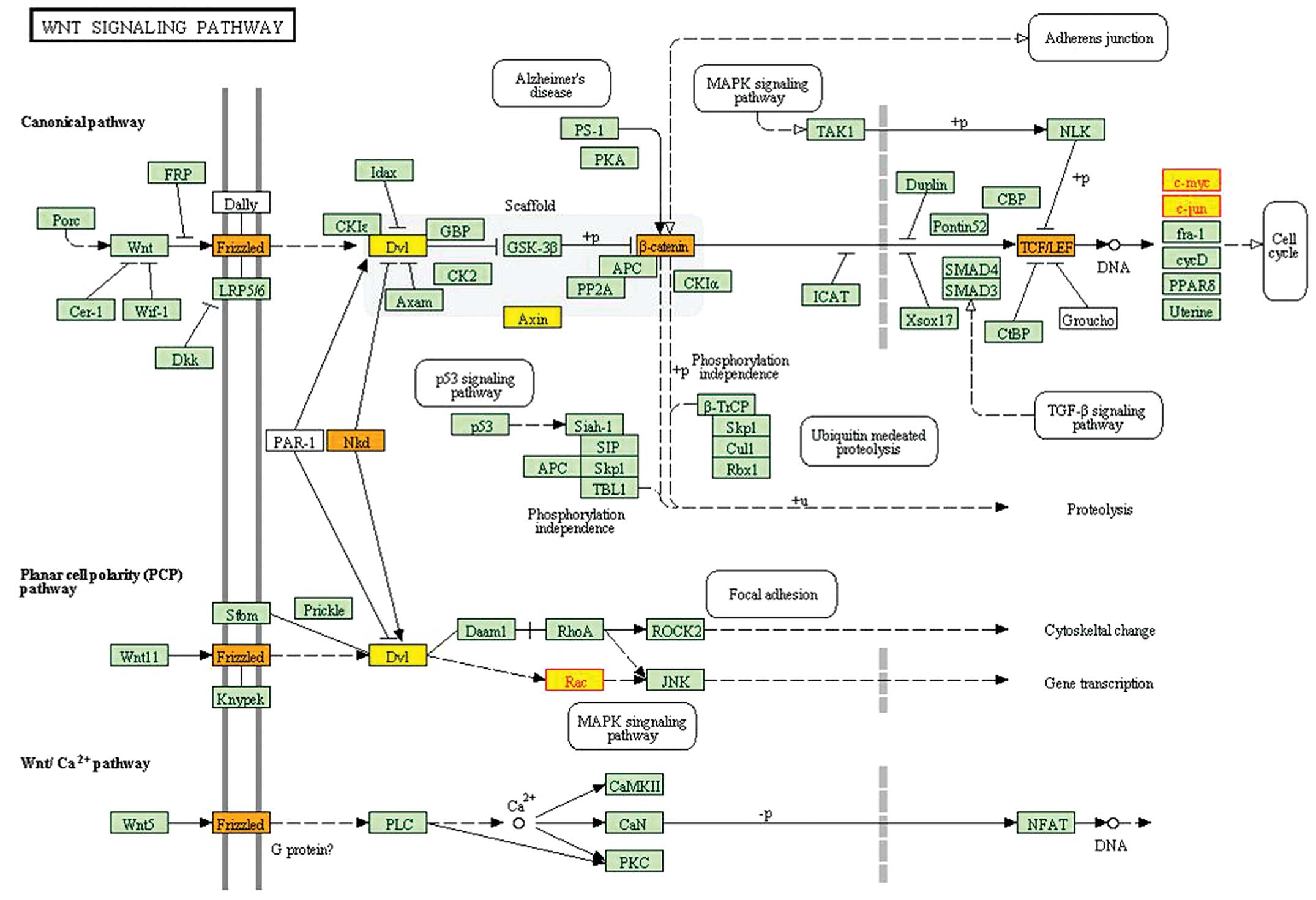
|
|
7
|
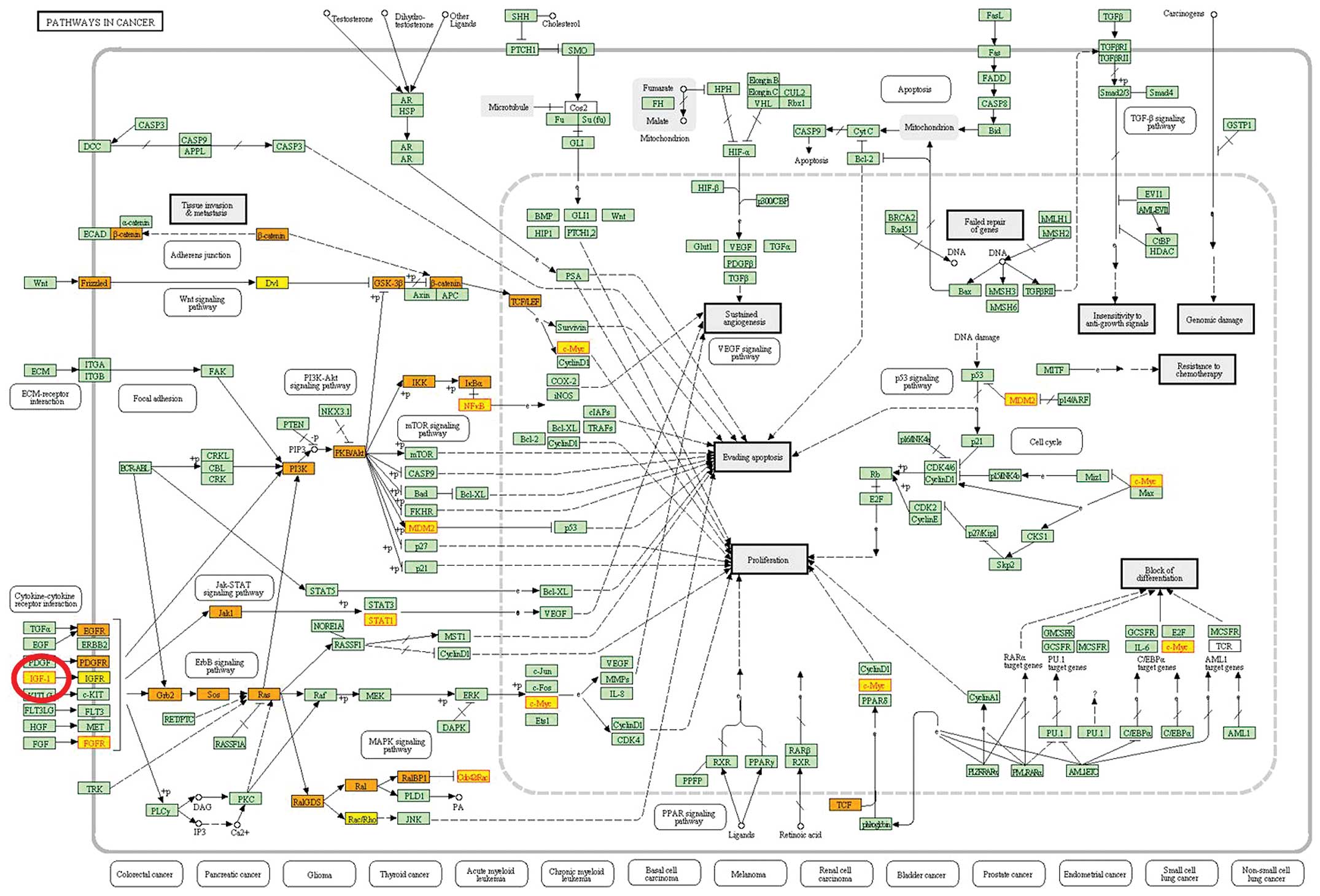
Khatri P, Sellamuthu S, Malhotra P, et al:
Recent additions and improvements to the Onto-Tools. Nucleic Acids
Res. 33:W762–W765. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang K, Li M and Hakonarson H: Analysing
biological pathways in genomewide association studies. Nat Rev
Genet. 11:843–854. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Becker KG, Barnes KC, Bright TJ and Wang
SA: The genetic association database. Nat Genet. 36:431–432. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Papanastassiou I, Ioannou M,
Papagelopoulos PJ, et al: P53 expression as a prognostic marker in
giant cell tumor of bone: a pilot study. Orthopedics.
33:3072010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wülling M, Delling G and Kaiser E: The
origin of the neoplastic stromal cell in giant cell tumor of bone.
Hum Pathol. 34:983–993. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li C, Li X, Miao Y, et al:
SubpathwayMiner: a software package for flexible identification of
pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:e1312009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li X, Li C, Shang D, et al: The
implications of relationships between human diseases and metabolic
subpathways. PLoS One. 6:e211312011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M
and Tanabe M: KEGG for integration and interpretation of
large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40(Database
issue): D109–D114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Oda Y, Sakamoto A, Saito T, et al:
Secondary malignant giant- cell tumor of bone: molecular
abnormalities of p53 and H-ras gene correlated with malignant
transformation. Histopathology. 39:6292001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Masui F, Ushigome S and Fujii K: Giant
cell tumor of bone: a clinicopathologic study of prognostic
factors. Pathol Int. 48:7231998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gong L, Liu W, Sun X, et al: Histological
and clinical characteristics of malignant giant cell tumor of bone.
Virchows Arch. 460:327–334. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet SW and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Murata A, Fujita T, Kawahara N, Tsuchiya H
and Tomita K: Osteoblast lineage properties in giant cell tumors of
bone. J Orthop Sci. 10:581–588. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guenther R, Krenn V, Morawietz L, et al:
Giant cell tumors of bone: molecular profiling and expression
analysis of Ephrin A receptor, Claudin 7, CD52, FGFR3 and AMFR.
Pathol Res Pract. 201:649–663. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Skubitz KM, Cheng EY, Clohisy DR, Thompson
RC and Skubitz AP: Gene expression in giant cell tumors. J Lab Clin
Med. 144:193–200. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kappel CC, Velez-Yanguas MC, Hirschfeld S
and Helman LJ: Human osteosarcoma cell lines are dependent on
insulin-like growth factor I for in vitro growth. Cancer Res.
54:2803–2807. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bonjour JP, Schurch MA, Chevalley T,
Ammann P and Rizolli R: Protein intake. IGF-1 and osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis Int. 7:36–42. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
de Souza PE, Paim JF, Carvalhais JN and
Gomez RS: Immunohistochemical expression of p53, MDM2, Ki-67 and
PCNA in central giant cell granuloma and giant cell tumor. J Oral
Pathol Med. 28:54–58. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mak IW, Turcotte RE, Popovic S, Singh G
and Ghert M: AP-1 as a regulator of MMP-13 in the stromal cell of
giant cell tumor of bone. Biochem Res Int.
2011:1641972011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rao VH, Singh RK, Delimont DC, et al:
Interleukin-1beta upregulates MMP-9 expression in stromal cells of
human giant cell tumor of bone. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
19:1207–1217. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Teti A, Farina AR, Villanova I, et al:
Activation of MMP-2 by human GCT23 giant cell tumor cells induced
by osteopontin, bone sialoprotein and GRGDSP peptides is RGD and
cell shape change dependent. Int J Cancer. 77:82–93. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mak IW, Seidlitz EP, Cowan RW, et al:
Evidence for the role of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in bone
resorption by giant cell tumor of bone. Hum Pathol. 41:1320–1329.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoon SO, Park SJ, Yun CH and Chung AS:
Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in tumor metastasis and
angiogenesis. J Biochem Mol Biol. 36:128–137. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karin M: Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer
development and progression. Nature. 441:431–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dougall WC, Glaccum M, Charrier K, et al:
RANK is essential for osteoclast and lymph node development. Genes
Dev. 13:2412–2424. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, et al:
Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the
regulation of bone density. Cell. 89:309–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Morgan T, Atkins GJ, Trivett MK, et al:
Molecular profiling of giant cell tumor of bone and the
osteoclastic localization of ligand for receptor activator of
nuclear factor kappaB. Am J Pathol. 167:117–128. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Geldyyev A, Koleganova N, Piecha G, et al:
High expression level of bone degrading proteins as a possible
inducer of osteolytic features in pigmented villonodular synovitis.
Cancer Lett. 255:275–283. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Thomas D, Henshaw R, Skubitz K, et al:
Denosumab in patients with giant-cell tumor of bone: an open-label,
phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 11:275–280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J and Jove R:
STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene. 19:2474–2488. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Boudný V, Kocák I, Lauerová L and Kovarík
J: Interferon inducibility of STAT 1 activation and its prognostic
significance in melanoma patients. Folia Biol. 49:142–146.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sims NA, Jenkins BJ, Quinn JM, et al:
Glycoprotein 130 regulates bone turnover and bone size by distinct
downstream signaling pathways. J Clin Invest. 113:379–389. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Holmen SL, Zylstra CR, Mukherjee A, et al:
Essential role of beta-catenin in postnatal bone acquisition. J
Biol Chem. 280:21162–21168. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gaur T, Lengner CJ, Hovhannisyan H, et al:
Canonical WNT signaling promotes osteogenesis by directly
stimulating Runx2 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 280:33132–33140.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Goldring SR and Goldring MB: Eating bone
or adding it: the Wnt pathway decides. Nat Med. 13:133–134. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Matsubayashi S, Nakashima M, Kumagai K, et
al: Immunohistochemical analyses of beta-catenin and cyclin D1
expression in giant cell tumor of bone (GCTB): a possible role of
Wnt pathway in GCTB tumorigenesis. Pathol Res Pract. 205:626–633.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gamberi G, Benassi MS, Böhling T, et al:
Prognostic relevance of C-myc gene expression in giant-ceIl tmnor
of bone. J Orthop Res. 16:1–7. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ridley AJ: Rho GTPases and actin dynamics
in membrane protrusions and vesicle trafficking. Trends Cell Biol.
16:522–529. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Stallings-Mann ML, Waldmann J, Zhang Y,
Miller E and Gauthier ML: Matrix metalloproteinase induction of
Rac1b, a key effector of lung cancer progression. Sci Transl Med.
4:142ra952012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
McAllister SS: Got a light? Illuminating
lung cancer. Sci Transl Med. 4:142fs222012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang L, Kuang L, Pan X, et al: Isoalvaxant
hone inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation, migration and
invasion through inactivating Racl and AP-1. Int J Cancer.
127:1220–1229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fukuda A, Hikita A, Wakeyama H, et al:
Regulation of osteoclast apoptosis and motility by small GTPase
binding protein Rac1. J Bone Miner Res. 20:2245–2253. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|