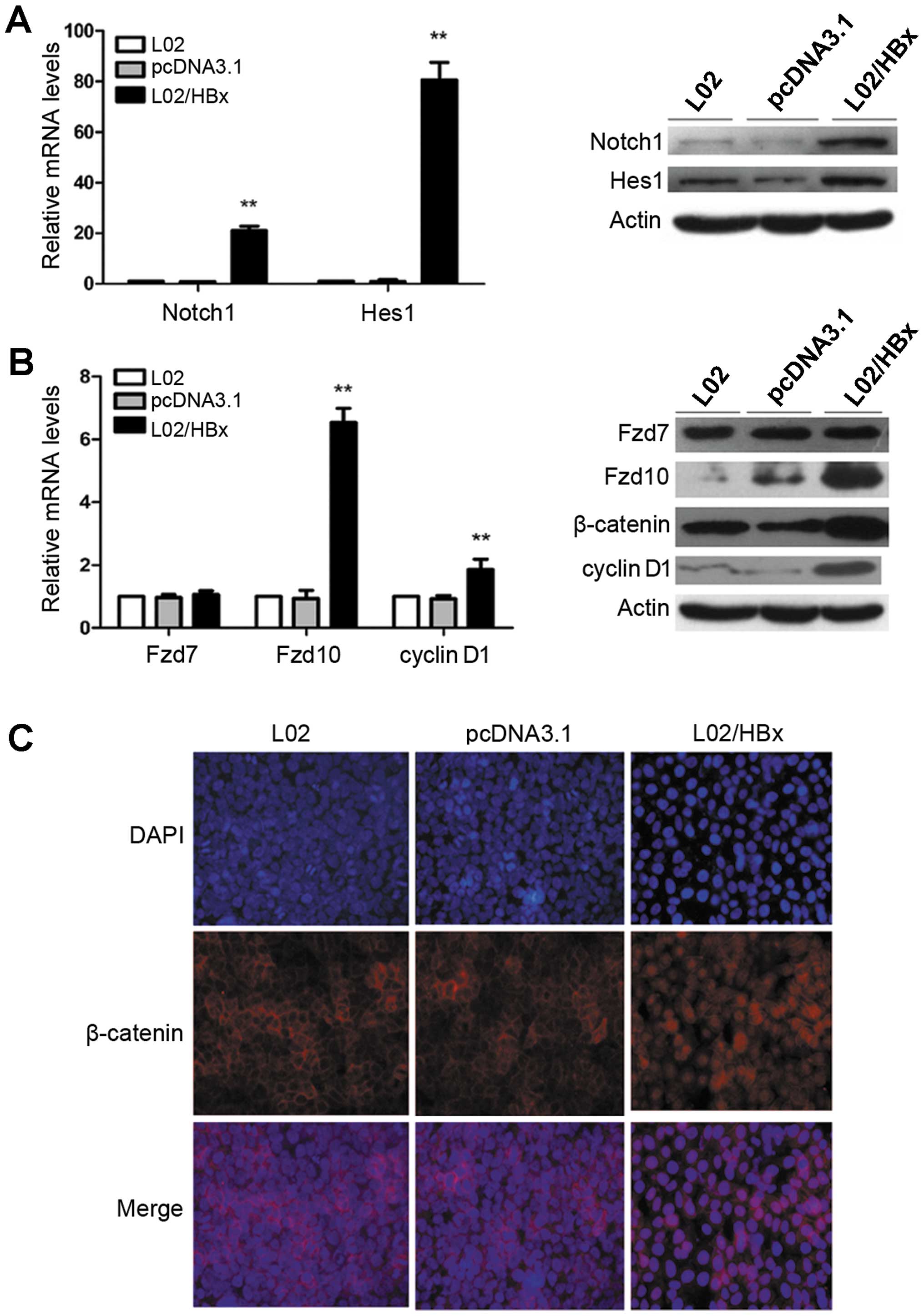
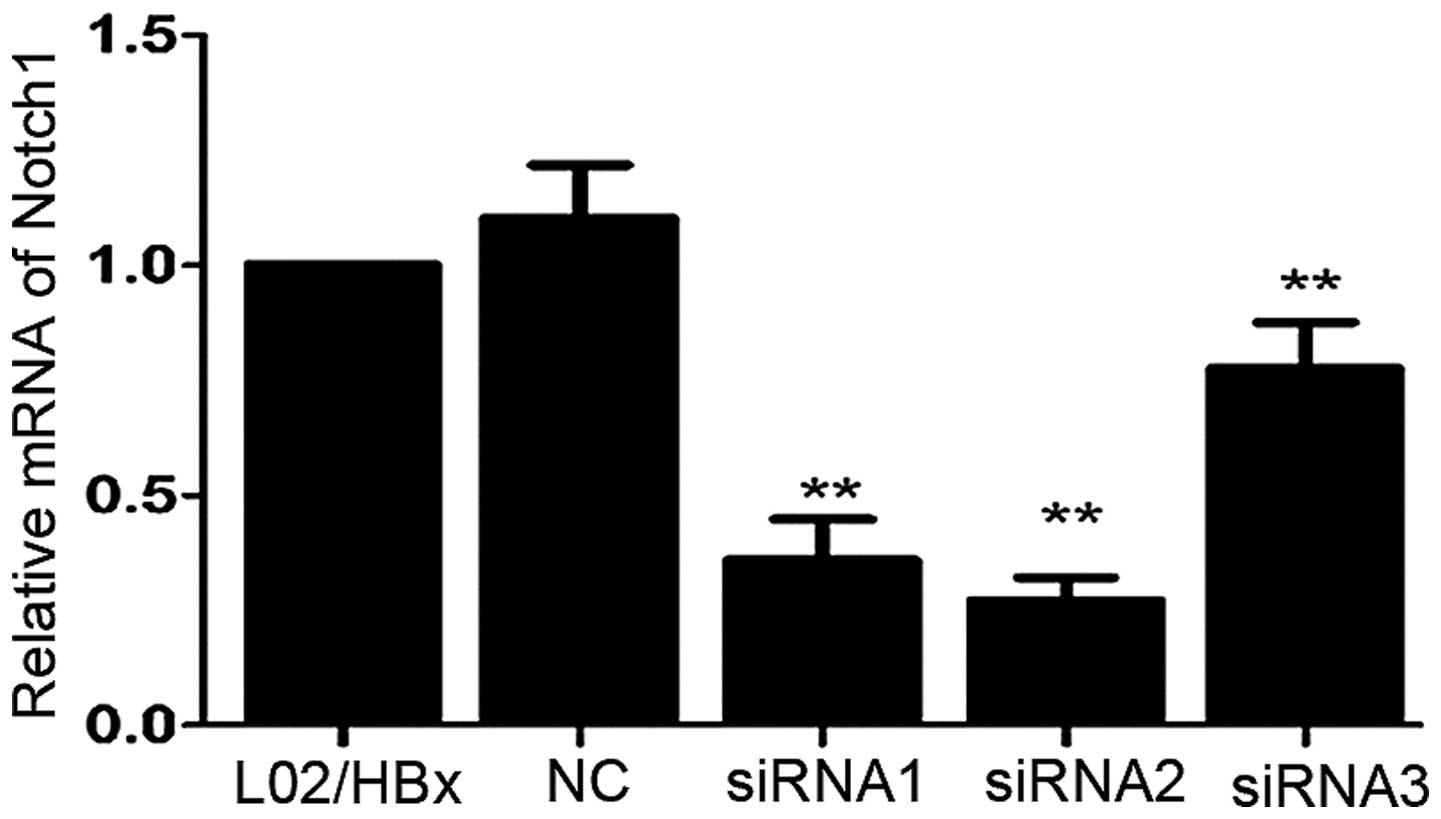
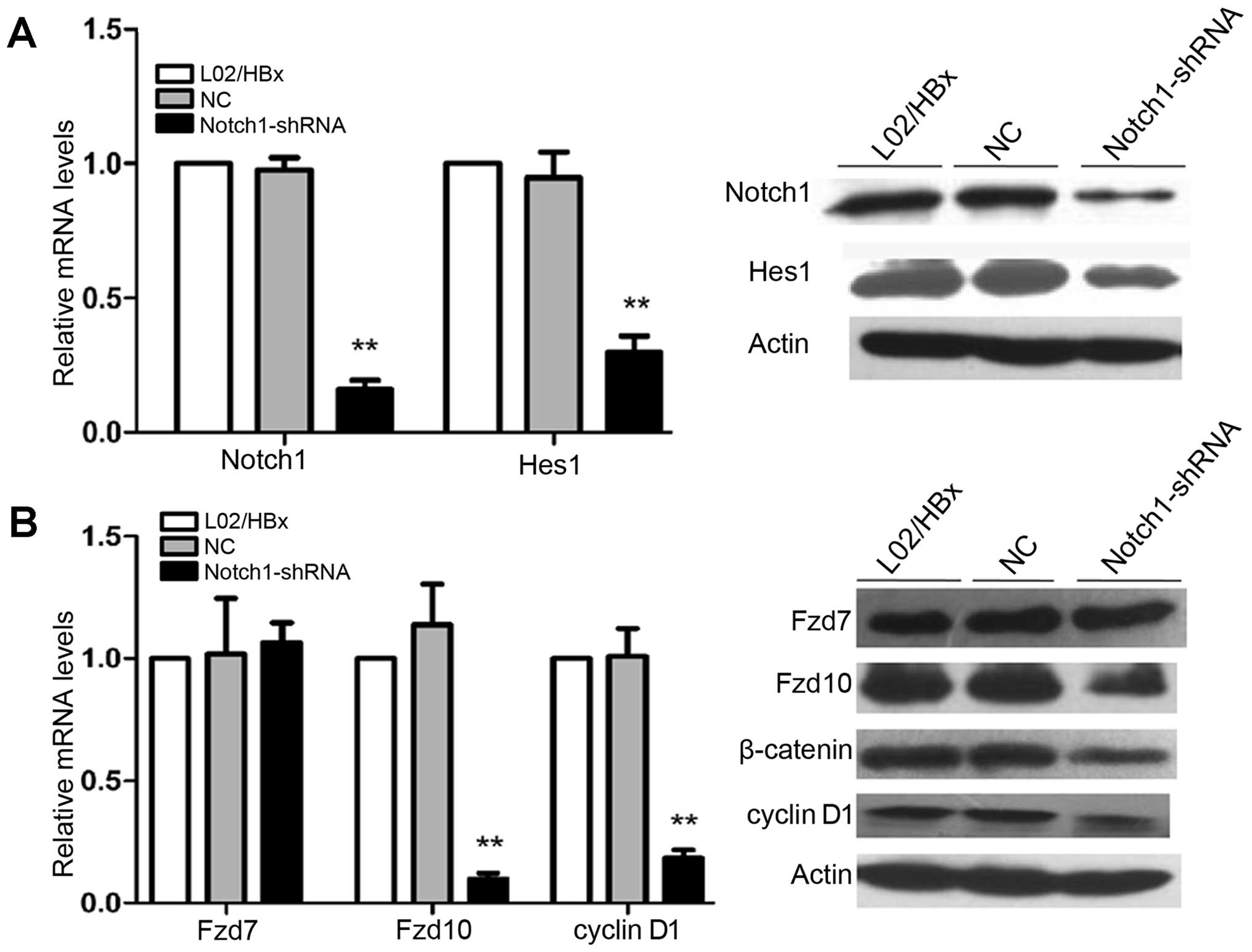
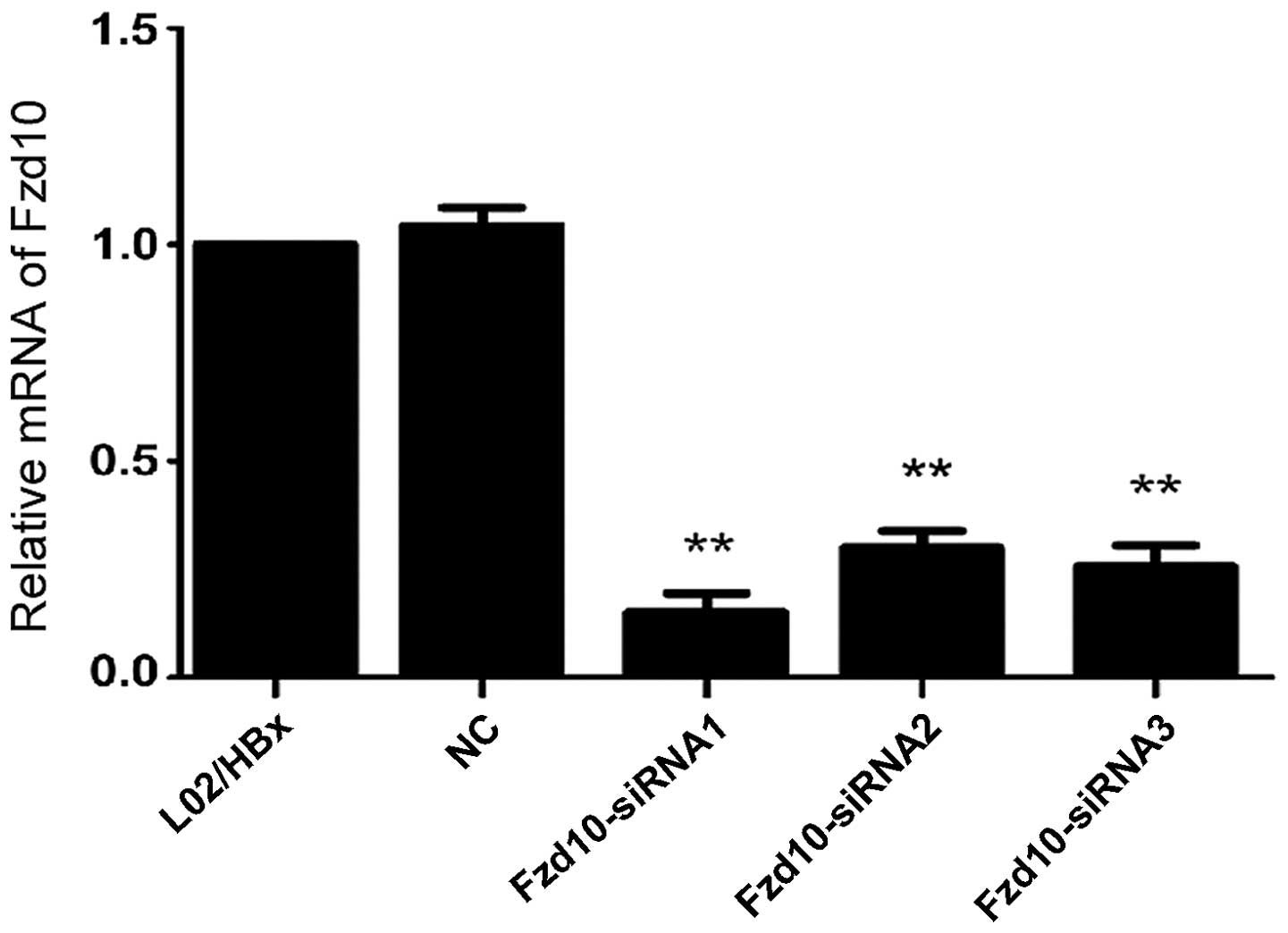
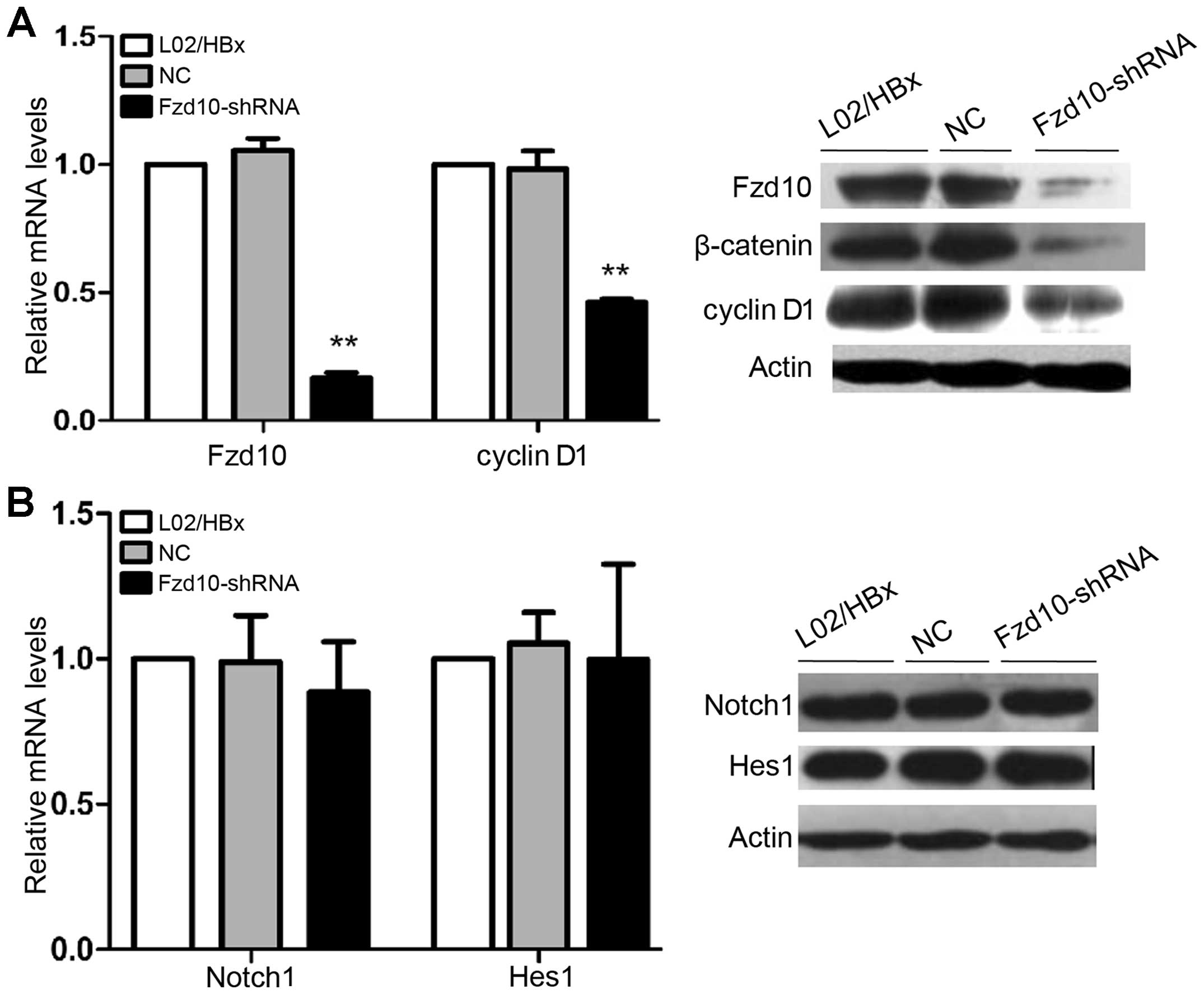
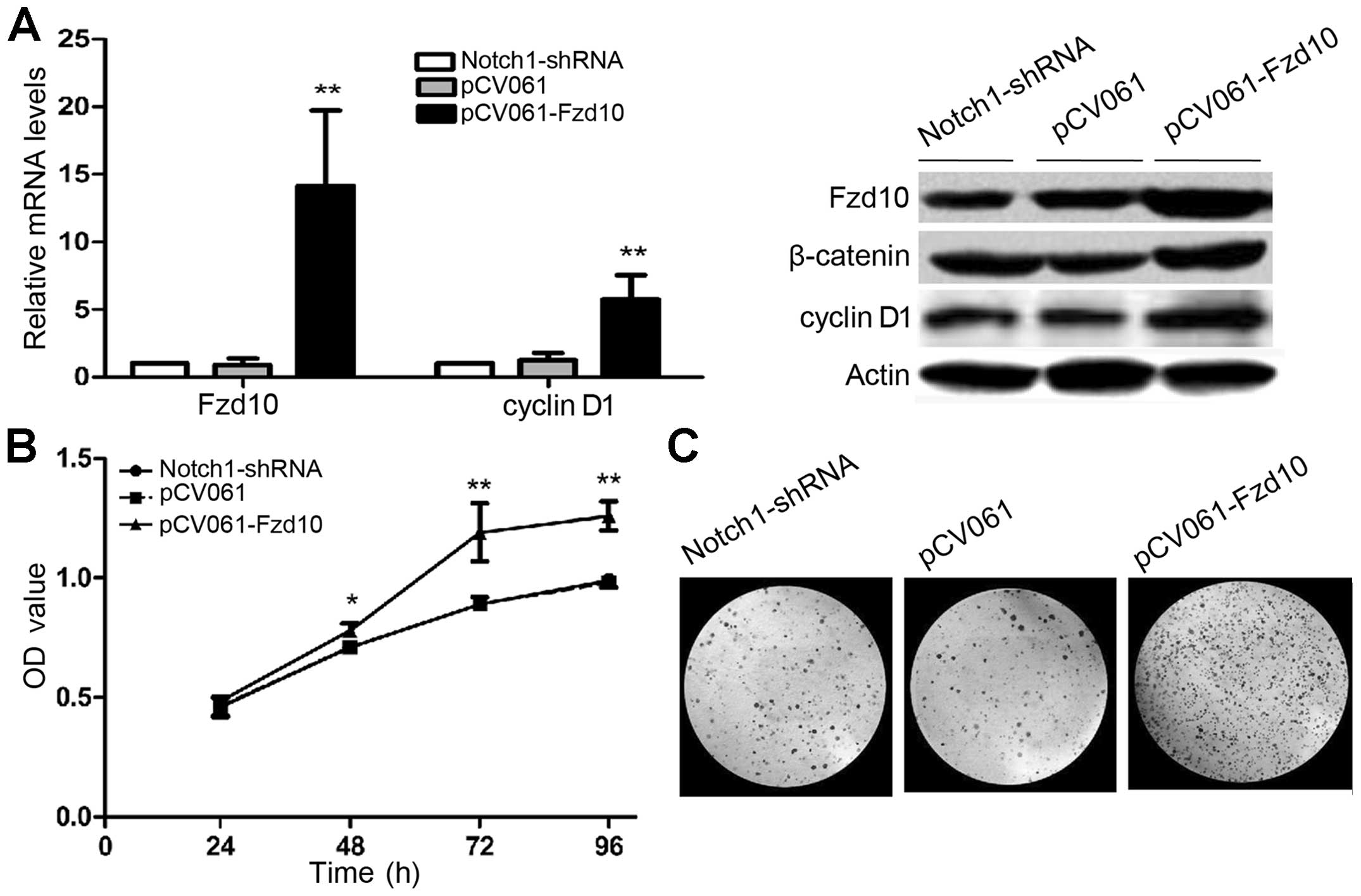
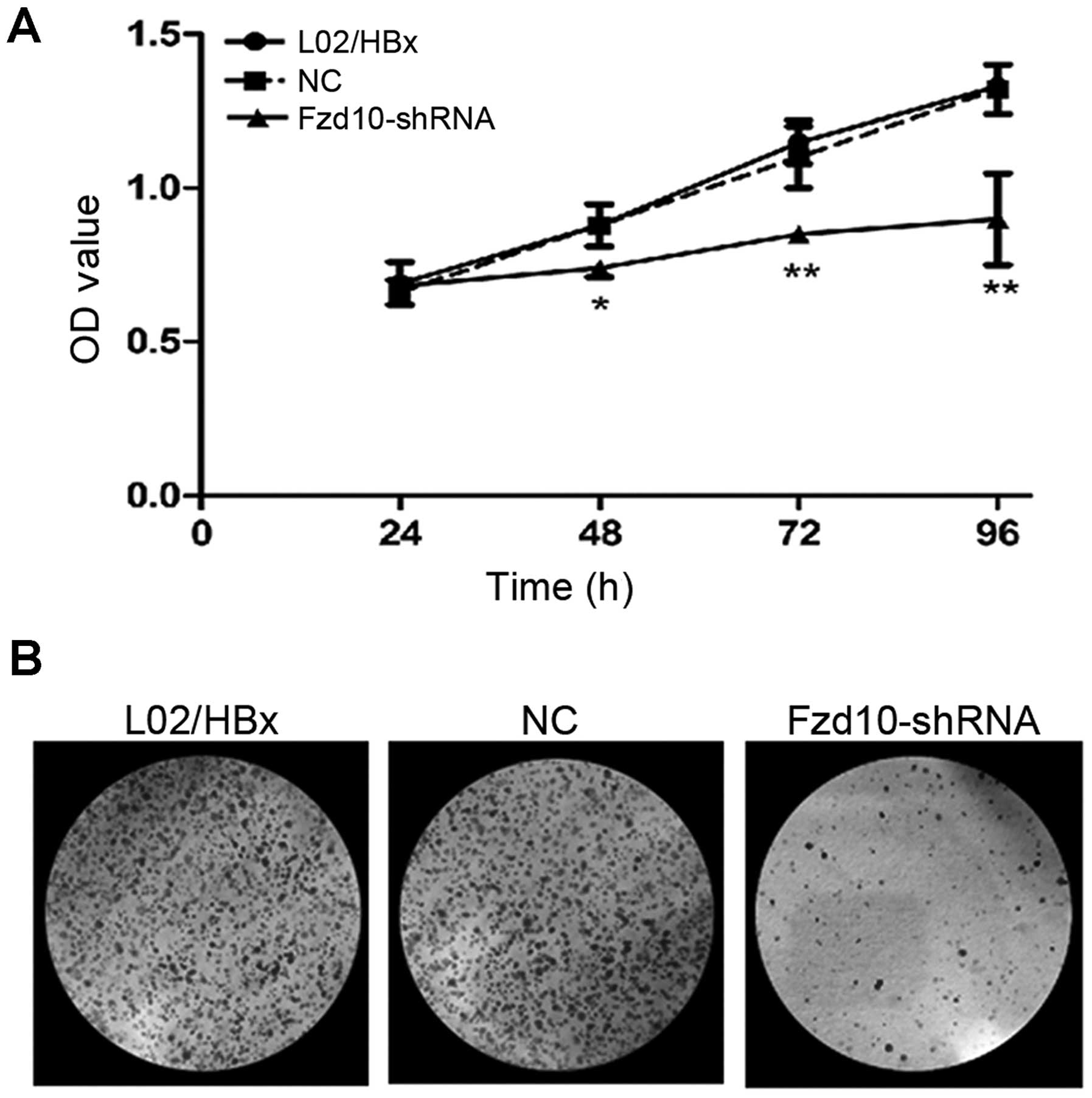
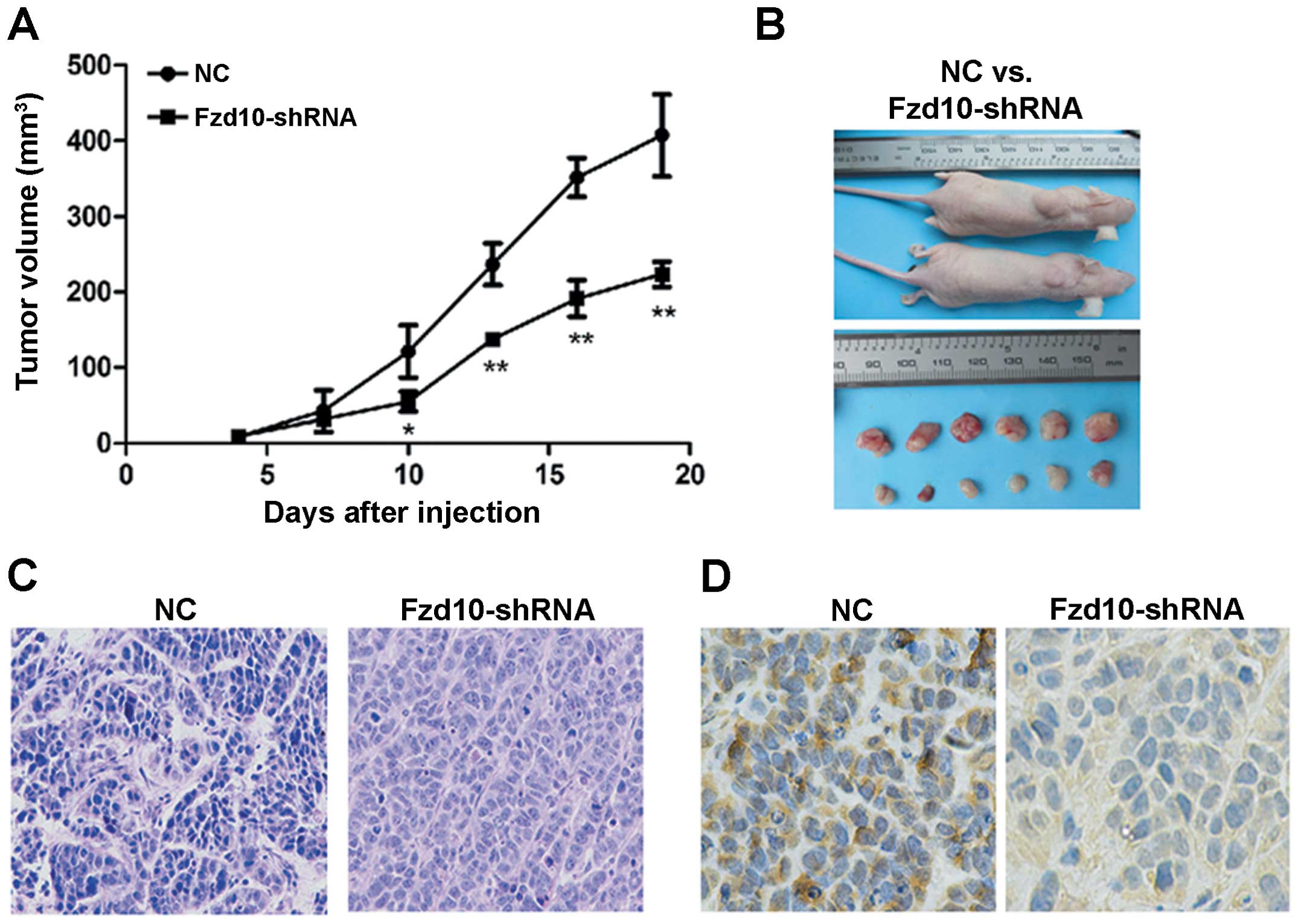
|
1
|
Block TM, Mehta AS, Fimmel CJ and Jordan
R: Molecular viral oncology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene.
22:5093–5107. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Martin-Vilchez S, Lara-Pezzi E,
Trapero-Marugan M, Moreno-Otero R and Sanz-Cameno P: The molecular
and pathophysiological implications of hepatitis B X antigen in
chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Rev Med Virol. 21:315–329.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Diao J, Garces R and Richardson CD: X
protein of hepatitis B virus modulates cytokine and growth factor
related signal transduction pathways during the course of viral
infections and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
12:189–205. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang F, Zhou H, Xia X, Sun Q, Wang Y and
Cheng B: Activated Notch signaling is required for hepatitis B
virus X protein to promote proliferation and survival of human
hepatic cells. Cancer Lett. 298:64–73. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang F, Zhou H, Yang Y, Xia X, Sun Q, Luo
J and Cheng B: Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes the growth of
hepatocellular carcinoma by modulation of the Notch signaling
pathway. Oncol Rep. 27:1170–1176. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Luo J, Zhou H, Wang F, Xia X, Sun Q, Wang
R and Cheng B: The hepatitis B virus X protein downregulates NF-κB
signaling pathways through decreasing the Notch signaling pathway
in HBx-transformed L02 cells. Int J Oncol. 42:1636–1643.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang F, Xia X, Wang J, Sun Q, Luo J and
Cheng B: Notch1 signaling contributes to the oncogenic effect of
HBx on human hepatic cells. Biotechnol Lett. 35:29–37. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun Q, Wang R, Wang Y, Luo J, Wang P and
Cheng B: Notch1 is a potential therapeutic target for the treatment
of human hepatitis B virus X protein-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 31:933–939. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kopan R and Ilagan MX: The canonical Notch
signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell.
137:216–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kopan R: Notch signaling. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 4:pii: a011213. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kalaitzidis D and Armstrong SA: Cancer:
the flipside of Notch. Nature. 473:159–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ranganathan P, Weaver KL and Capobianco
AJ: Notch signalling in solid tumours: a little bit of everything
but not all the time. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:338–351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Giovannini C, Gramantieri L, Chieco P, et
al: Selective ablation of Notch3 in HCC enhances doxorubicin’s
death promoting effect by a p53 dependent mechanism. J Hepatol.
50:969–979. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Villanueva A, Alsinet C, Yanger K, et al:
Notch signaling is activated in human hepatocellular carcinoma and
induces tumor formation in mice. Gastroenterology. 143:1660–1669.
e16672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qi R, An H, Yu Y, et al: Notch1 signaling
inhibits growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma through induction
of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 63:8323–8329.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang C, Qi R, Li N, et al: Notch1
signaling sensitizes tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by inhibiting Akt/Hdm2- mediated p53 degradation
and up-regulating p53-dependent DR5 expression. J Biol Chem.
284:16183–16190. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Viatour P, Ehmer U, Saddic LA, et al:
Notch signaling inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma following
inactivation of the RB pathway. J Exp Med. 208:1963–1976. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zimmerman ZF, Moon RT and Chien AJ:
Targeting Wnt pathways in disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
4:pii: a008086. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhou J, Cheng P, Youn JI, Cotter MJ and
Gabrilovich DI: Notch and wingless signaling cooperate in
regulation of dendritic cell differentiation. Immunity. 30:845–859.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Camps J, Pitt JJ, Emons G, et al: Genetic
amplification of the NOTCH modulator LNX2 upregulates the
WNT/beta-catenin pathway in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res.
73:2003–2013. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li C, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Cui Z, Yu M, Zhang S
and Xue X: Evidence of the cross talk between Wnt and Notch
signaling pathways in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC):
Notch3-siRNA weakens the effect of LiCl on the cell cycle of NSCLC
cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:771–778. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liao C, Zhao M, Song H, Uchida K, Yokoyama
KK and Li T: Identification of the gene for a novel liver-related
putative tumor suppressor at a high-frequency loss of
heterozygosity region of chromosome 8p23 in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 32:721–727. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cheng B, Zheng Y, Guo X, Wang Y and Liu C:
Hepatitis B viral X protein alters the biological features and
expressions of DNA repair enzymes in LO2 cells. Liver Int.
30:319–326. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ueno K, Hirata H, Hinoda Y and Dahiya R:
Frizzled homolog proteins, microRNAs and Wnt signaling in cancer.
Int J Cancer. 132:1731–1740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Terasaki H, Saitoh T, Shiokawa K and Katoh
M: Frizzled-10, up-regulated in primary colorectal cancer, is a
positive regulator of the WNT - beta-catenin - TCF signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 9:107–112. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nagayama S, Yamada E, Kohno Y, et al:
Inverse correlation of the up-regulation of FZD10 expression and
the activation of beta-catenin in synchronous colorectal tumors.
Cancer Sci. 100:405–412. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gugger M, White R, Song S, Waser B,
Cescato R, Riviere P and Reubi JC: GPR87 is an overexpressed
G-protein coupled receptor in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung.
Dis Markers. 24:41–50. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nagayama S, Fukukawa C, Katagiri T, et al:
Therapeutic potential of antibodies against FZD 10, a cell-surface
protein, for synovial sarcomas. Oncogene. 24:6201–6212. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fukukawa C, Hanaoka H, Nagayama S, et al:
Radioimmunotherapy of human synovial sarcoma using a monoclonal
antibody against FZD10. Cancer Sci. 99:432–440. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Merle P, de la Monte S, Kim M, et al:
Functional consequences of frizzled-7 receptor overexpression in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 127:1110–1122.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bengochea A, de Souza MM, Lefrancois L, et
al: Common dysregulation of Wnt/Frizzled receptor elements in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 99:143–150. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Merle P, Kim M, Herrmann M, et al:
Oncogenic role of the frizzled-7/beta-catenin pathway in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 43:854–862. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
King TD, Zhang W, Suto MJ and Li Y:
Frizzled7 as an emerging target for cancer therapy. Cell Signal.
24:846–851. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nambotin SB, Lefrancois L, Sainsily X, et
al: Pharmacological inhibition of Frizzled-7 displays anti-tumor
properties in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 54:288–299.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hsieh A, Kim HS, Lim SO, Yu DY and Jung G:
Hepatitis B viral X protein interacts with tumor suppressor
adenomatous polyposis coli to activate Wnt/beta-catenin signaling.
Cancer Lett. 300:162–172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cha MY, Kim CM, Park YM and Ryu WS:
Hepatitis B virus X protein is essential for the activation of
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in hepatoma cells. Hepatology.
39:1683–1693. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|