|
1
|
Waldmann T and Schneider R: Targeting
histone modifications - epigenetics in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
25:184–189. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dawson MA, Kouzarides T and Huntly BJ:
Targeting epigenetic readers in cancer. N Engl J Med. 367:647–657.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dawson MA and Kouzarides T: Cancer
epigenetics: From mechanism to therapy. Cell. 150:12–27. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
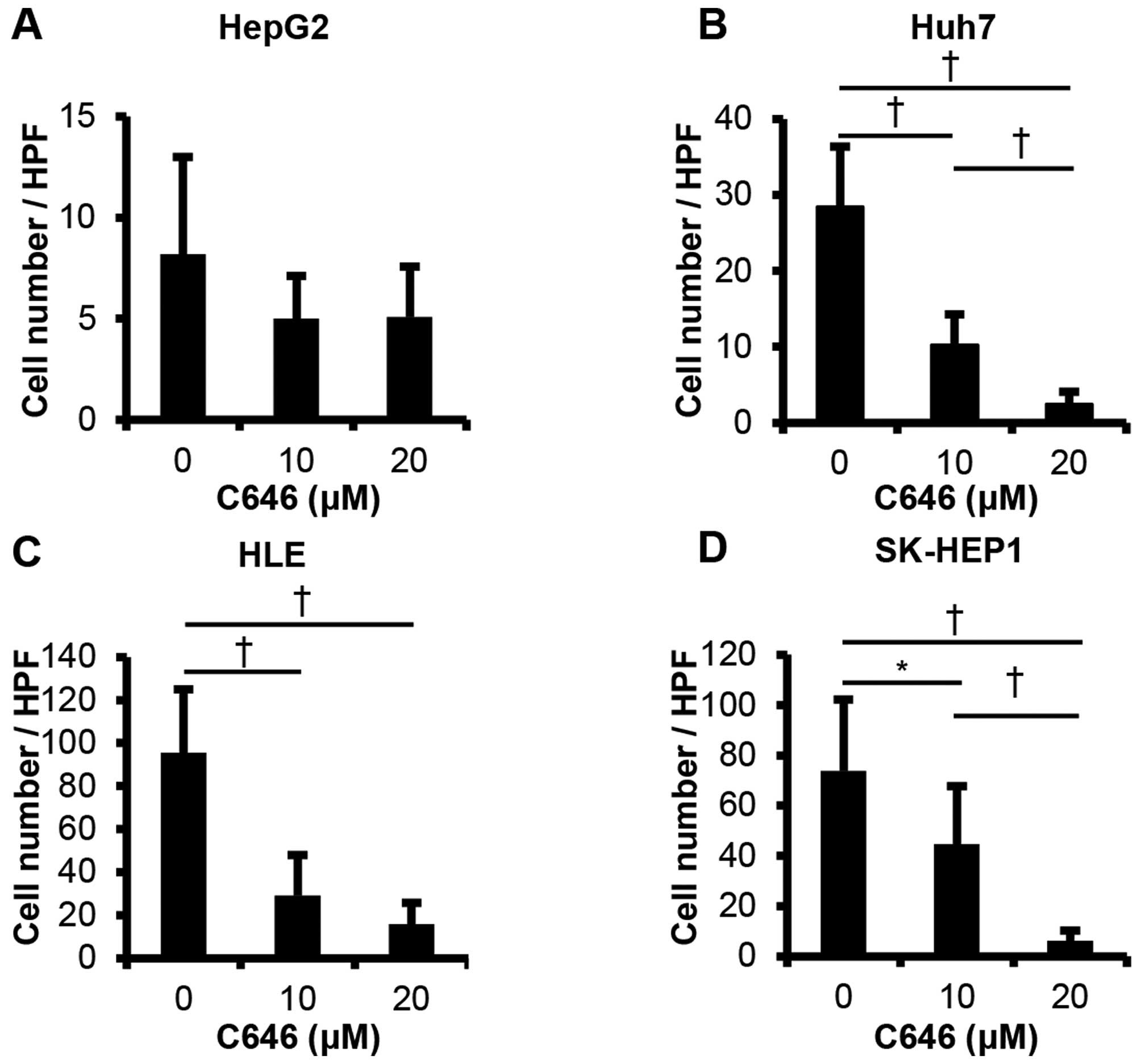
4
|
Wang F, Marshall CB and Ikura M:
Transcriptional/epigenetic regulator CBP/p300 in tumorigenesis:
Structural and functional versatility in target recognition. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 70:3989–4008. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
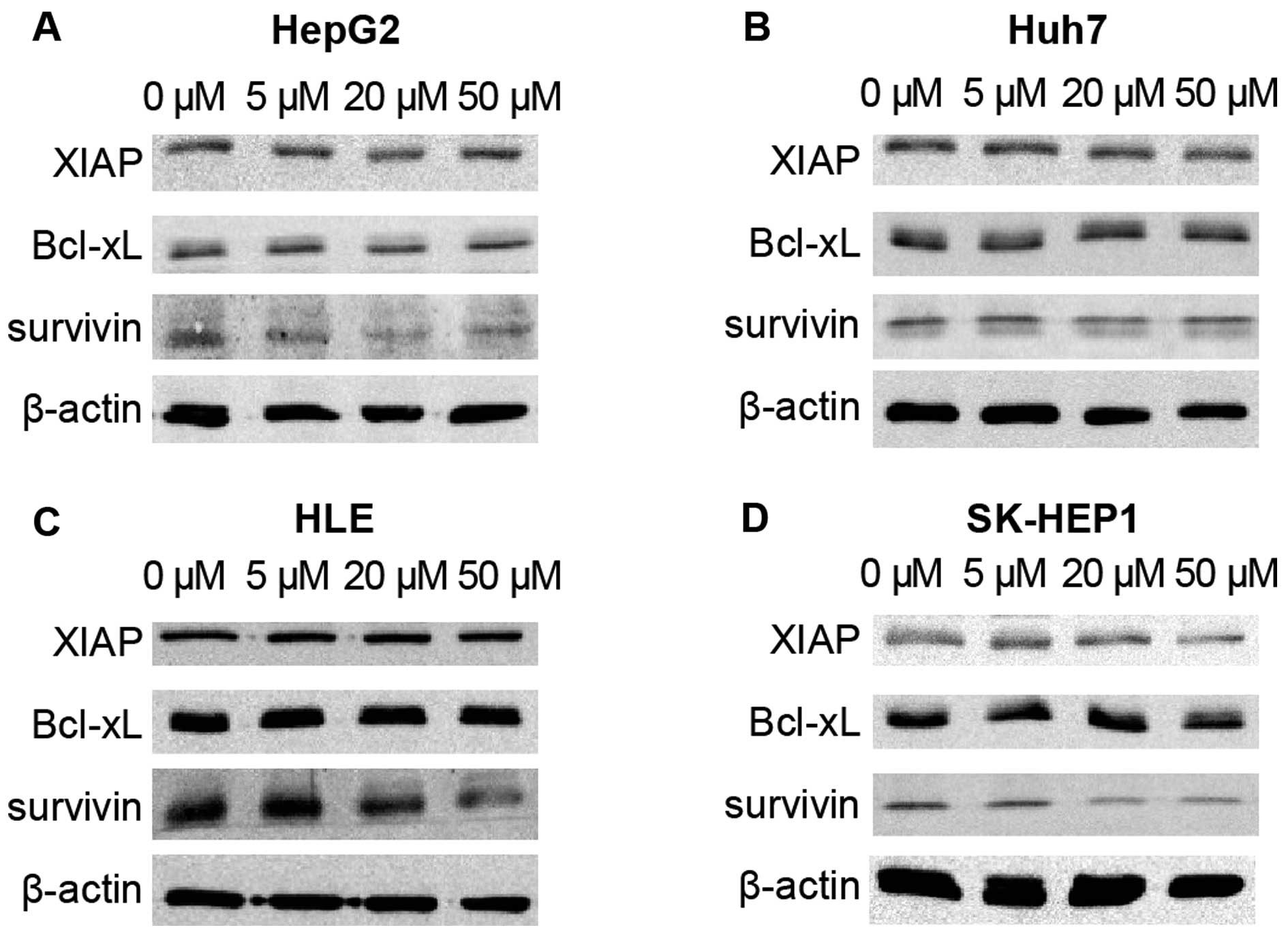
|
5
|
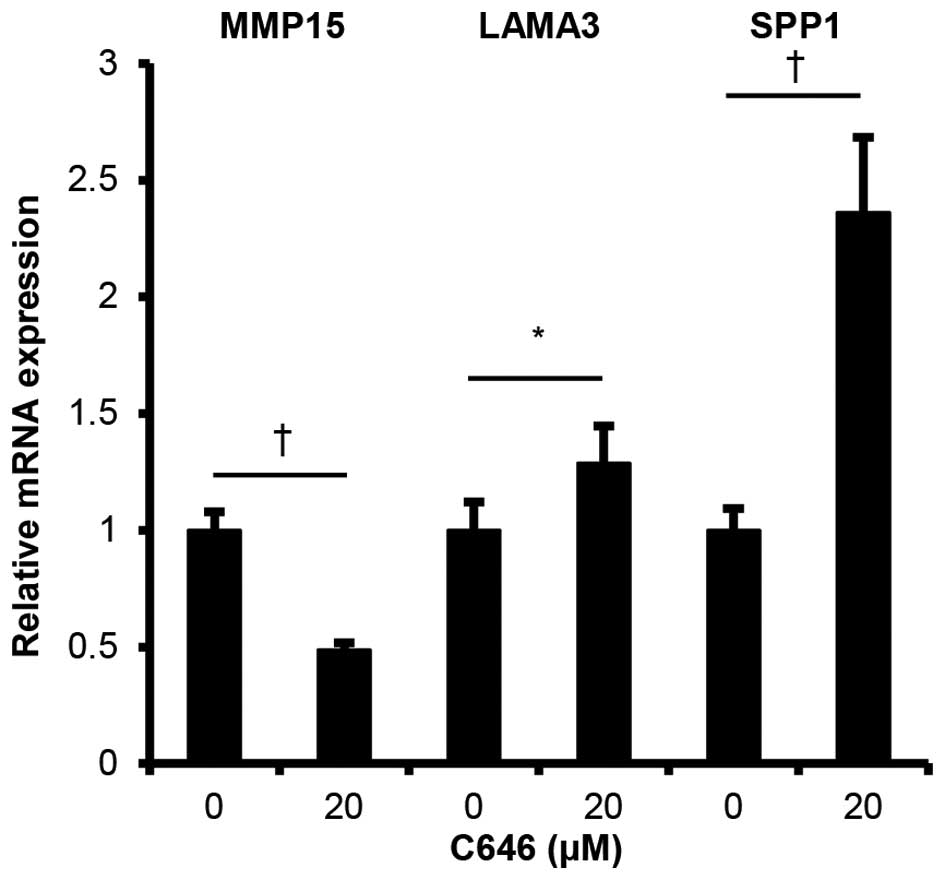
Bedford DC, Kasper LH, Fukuyama T and
Brindle PK: Target gene context influences the transcriptional
requirement for the KAT3 family of CBP and p300 histone
acetyltransferases. Epigenetics. 5:9–15. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kalkhoven E: CBP and p300: HATs for
different occasions. Biochem Pharmacol. 68:1145–1155. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Borrow J, Stanton VP Jr, Andresen JM,
Becher R, Behm FG, Chaganti RS, Civin CI, Disteche C, Dubé I,
Frischauf AM, et al: The translocation t(8;16)(p11;p13) of acute
myeloid leukaemia fuses a putative acetyltransferase to the
CREB-binding protein. Nat Genet. 14:33–41. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chaffanet M, Gressin L, Preudhomme C,
Soenen-Cornu V, Birnbaum D and Pébusque MJ: MOZ is fused to p300 in
an acute monocytic leukemia with t(8;22). Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
28:138–144. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Muraoka M, Konishi M, Kikuchi-Yanoshita R,
Tanaka K, Shitara N, Chong JM, Iwama T and Miyaki M: p300 gene
alterations in colorectal and gastric carcinomas. Oncogene.
12:1565–1569. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gayther SA, Batley SJ, Linger L, Bannister
A, Thorpe K, Chin SF, Daigo Y, Russell P, Wilson A, Sowter HM, et
al: Mutations truncating the EP300 acetylase in human cancers. Nat
Genet. 24:300–303. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kung AL, Rebel VI, Bronson RT, Ch'ng LE,
Sieff CA, Livingston DM and Yao TP: Gene dose-dependent control of
hematopoiesis and hematologic tumor suppression by CBP. Genes Dev.
14:272–277. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rebel VI, Kung AL, Tanner EA, Yang H,
Bronson RT and Livingston DM: Distinct roles for CREB-binding
protein and p300 in hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 99:14789–14794. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ionov Y, Matsui S and Cowell JK: A role
for p300/CREB binding protein genes in promoting cancer progression
in colon cancer cell lines with microsatellite instability. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:1273–1278. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Iyer NG, Chin SF, Ozdag H, Daigo Y, Hu DE,
Cariati M, Brindle K, Aparicio S and Caldas C: p300 regulates
p53-dependent apoptosis after DNA damage in colorectal cancer cells
by modulation of PUMA/p21 levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:7386–7391. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Krubasik D, Iyer NG, English WR, Ahmed AA,
Vias M, Roskelley C, Brenton JD, Caldas C and Murphy G: Absence of
p300 induces cellular phenotypic changes characteristic of
epithelial to mesenchyme transition. Br J Cancer. 94:1326–1332.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ozen C, Yildiz G, Dagcan AT, Cevik D, Ors
A, Keles U, Topel H and Ozturk M: Genetics and epigenetics of liver
cancer. N Biotechnol. 30:381–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pogribny IP and Rusyn I: Role of
epigenetic aberrations in the development and progression of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 342:223–230. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Ma L, Chua MS, Andrisani O and So S:
Epigenetics in hepatocellular carcinoma: An update and future
therapy perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 20:333–345. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bowers EM, Yan G, Mukherjee C, Orry A,
Wang L, Holbert MA, Crump NT, Hazzalin CA, Liszczak G, Yuan H, et
al: Virtual ligand screening of the p300/CBP histone
acetyltransferase: Identification of a selective small molecule
inhibitor. Chem Biol. 17:471–482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Santer FR, Höschele PP, Oh SJ, Erb HH,
Bouchal J, Cavarretta IT, Parson W, Meyers DJ, Cole PA and Culig Z:
Inhibition of the acetyltransferases p300 and CBP reveals a
targetable function for p300 in the survival and invasion pathways
of prostate cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:1644–1655. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan G, Eller MS, Elm C, Larocca CA, Ryu B,
Panova IP, Dancy BM, Bowers EM, Meyers D, Lareau L, et al:
Selective inhibition of p300 HAT blocks cell cycle progression,
induces cellular senescence, and inhibits the DNA damage response
in melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 133:2444–2452. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Oike T, Komachi M, Ogiwara H, Amornwichet
N, Saitoh Y, Torikai K, Kubo N, Nakano T and Kohno T: C646, a
selective small molecule inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase
p300, radio-sensitizes lung cancer cells by enhancing mitotic
catastrophe. Radiother Oncol. 111:222–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao XN, Lin J, Ning QY, Gao L, Yao YS,
Zhou JH, Li YH, Wang LL and Yu L: A histone acetyltransferase p300
inhibitor C646 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis selectively
in AML1-ETO-positive AML cells. PLoS One. 8:e554812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fuke H, Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Tanaka J,
Beppu T, Yoneda K, Yamamoto N, Ito K, Masuya M and Takei Y: Jak
inhibitor induces S phase cell-cycle arrest and augments
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 363:738–744. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Isharwal S, Miller MC, Marlow C, Makarov
DV, Partin AW and Veltri RW: p300 (histone acetyltransferase)
biomarker predicts prostate cancer biochemical recurrence and
correlates with changes in epithelia nuclear size and shape.
Prostate. 68:1097–1104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ishihama K, Yamakawa M, Semba S, Takeda H,
Kawata S, Kimura S and Kimura W: Expression of HDAC1 and CBP/p300
in human colorectal carcinomas. J Clin Pathol. 60:1205–1210. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liao ZW, Zhou TC, Tan XJ, Song XL, Liu Y,
Shi XY, Huang WJ, Du LL, Tu BJ and Lin XD: High expression of p300
is linked to aggressive features and poor prognosis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Transl Med. 10:1102012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li M, Luo RZ, Chen JW, Cao Y, Lu JB, He
JH, Wu QL and Cai MY: High expression of transcriptional
coactivator p300 correlates with aggressive features and poor
prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med. 9:52011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ito T, Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Yamanaka T,
Fujikawa K, Ito M, Takase K, Moriyama M, Kawano H, Hayashida M, et
al: Survivin promotes cell proliferation in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 31:1080–1085. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Takehara T, Liu X, Fujimoto J, Friedman SL
and Takahashi H: Expression and role of Bcl-xL in human
hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology. 34:55–61. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Yamanaka Y,
Yamaguchi Y, Saitou Y, Ito K, Yamamoto N, Yamanaka T, Fujikawa K,
Murata K, et al: Overexpression of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis
in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 12:705–708.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ito E, Yana I, Fujita C, Irifune A, Takeda
M, Madachi A, Mori S, Hamada Y, Kawaguchi N and Matsuura N: The
role of MT2-MMP in cancer progression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
393:222–227. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen L, Zhou Q, Xu B, Liu J, Shi L, Zhu D,
Wu C and Jiang J: MT2-MMP expression associates with tumor
progression and angiogenesis in human lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:3469–3477. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ii M, Yamamoto H, Taniguchi H, Adachi Y,
Nakazawa M, Ohashi H, Tanuma T, Sukawa Y, Suzuki H, Sasaki S, et
al: Co-expression of laminin β3 and γ2 chains and epigenetic
inactivation of laminin α3 chain in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol.
39:593–599. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Miller KA, Chung J, Lo D, Jones JC,
Thimmapaya B and Weitzman SA: Inhibition of laminin-5 production in
breast epithelial cells by overexpression of p300. J Biol Chem.
275:8176–8182. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shevde LA and Samant RS: Role of
osteopontin in the pathophysiology of cancer. Matrix Biol.
37:131–141. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|