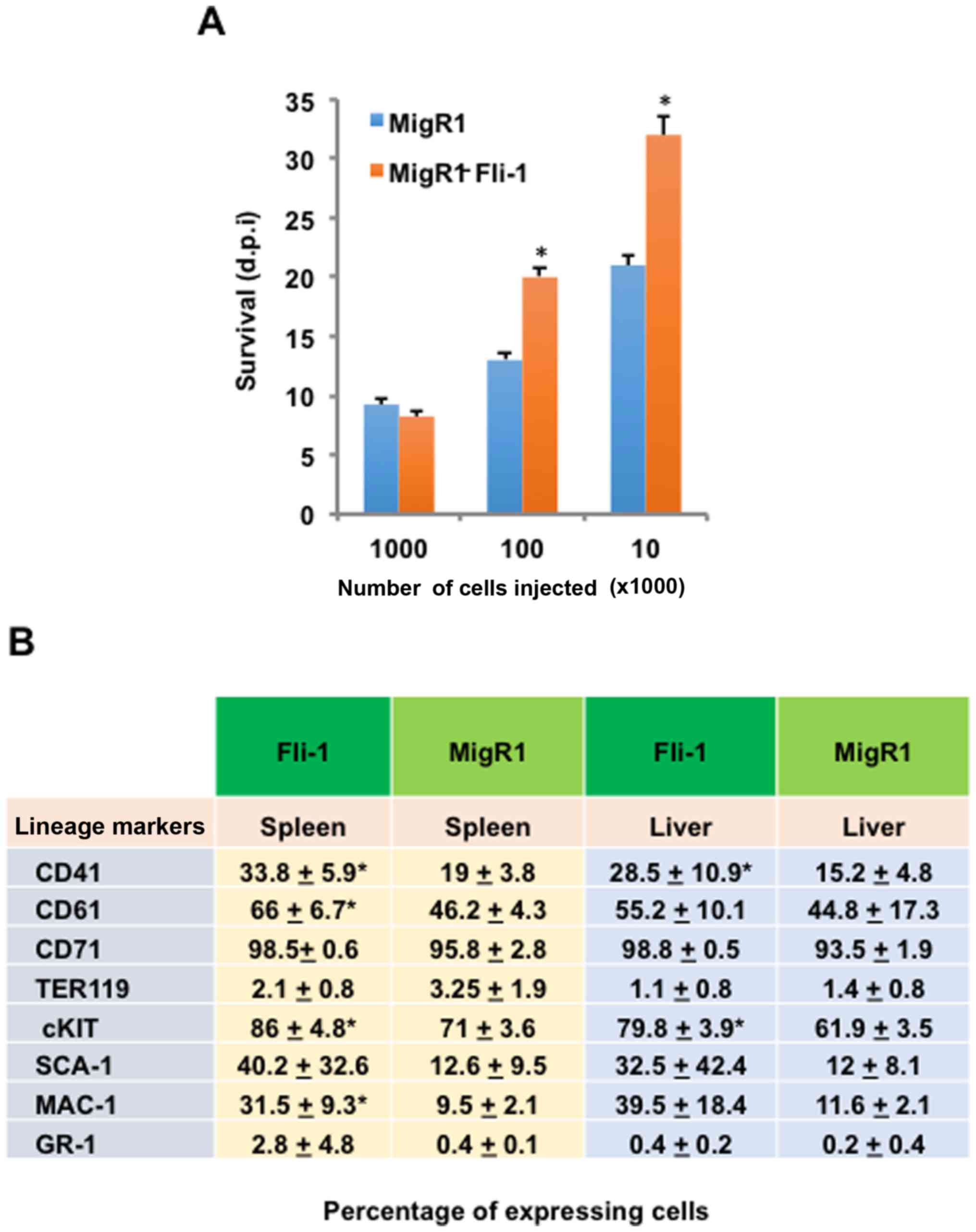
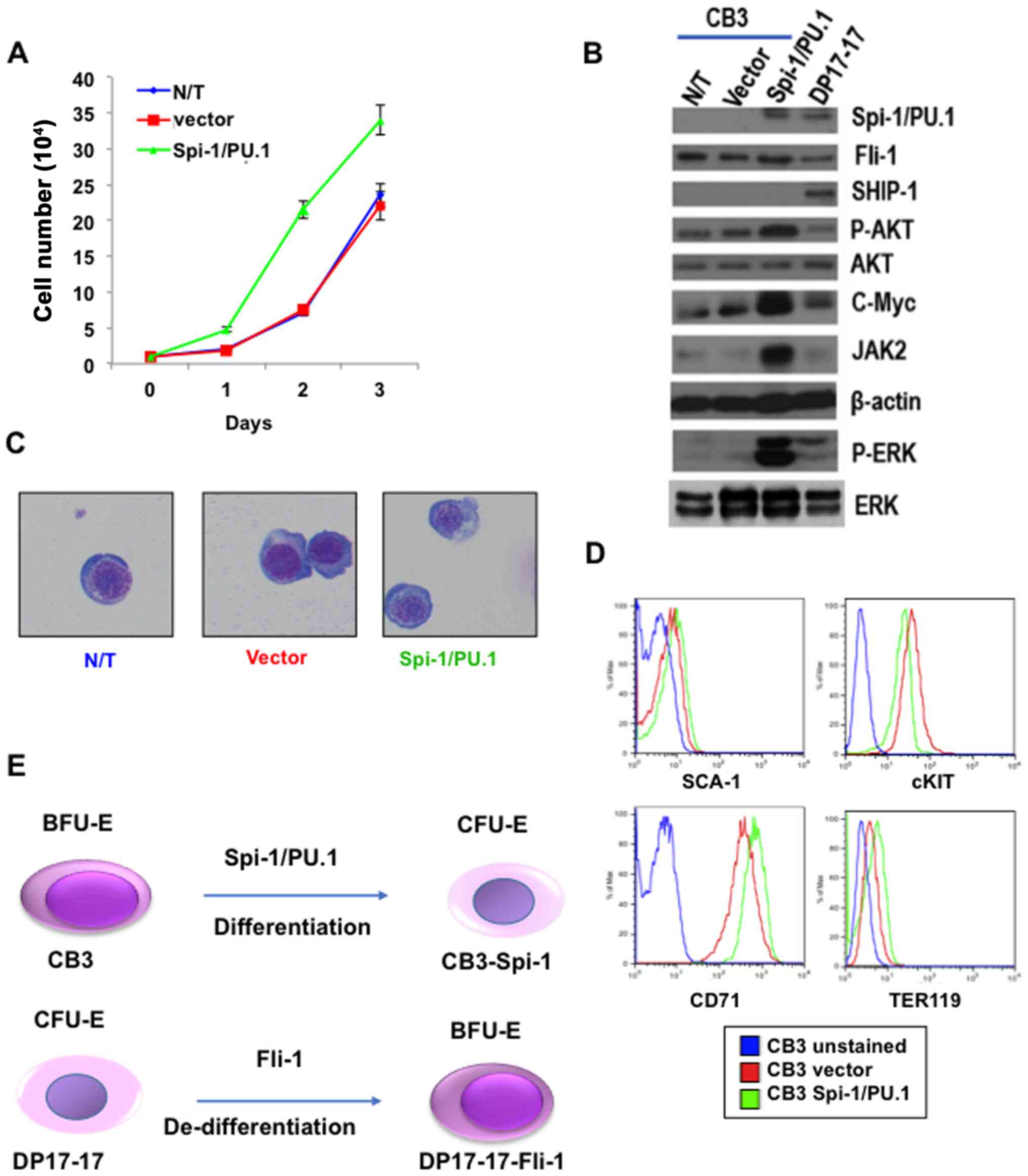
|
1
|
Göttgens B: Regulatory network control of
blood stem cells. Blood. 125:2614–2620. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li Y, Luo H, Liu T, Zacksenhaus E and
Ben-David Y: The ets transcription factor Fli-1 in development,
cancer and disease. Oncogene. 34:2022–2031. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ben-David Y and Bernstein A: Friend
virus-induced erythroleukemia and the multistage nature of cancer.
Cell. 66:831–834. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mager D, MacDonald ME, Robson IB, Mak TW
and Bernstein A: Clonal analysis of the late stages of
erythroleukemia induced by two distinct strains of Friend leukemia
virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1:721–730. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moreau-Gachelin F: Multi-stage Friend
murine erythroleukemia: Molecular insights into oncogenic
cooperation. Retrovirology. 5:992008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moreau-Gachelin F, Tavitian A and
Tambourin P: Spi-1 is a putative oncogene in virally induced murine
erythroleukaemias. Nature. 331:277–280. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ben-David Y, Giddens EB and Bernstein A:
Identification and mapping of a common proviral integration site
Fli-1 in erythroleukemia cells induced by Friend murine leukemia
virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:1332–1336. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ben-David Y, Giddens EB, Letwin K and
Bernstein A: Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia
virus: Insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene
family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. Genes Dev. 5:908–918.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shibuya T and Mak TW: Isolation and
induction of erythroleukemic cell lines with properties of
erythroid progenitor burst-forming cell (BFU-E) and erythroid
precursor cell (CFU-E). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 80:3721–3725. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cui JW, Vecchiarelli-Federico LM, Li YJ,
Wang GJ and Ben-David Y: Continuous Fli-1 expression plays an
essential role in the proliferation and survival of F-MuLV-induced
erythroleukemia and human erythroleukemia. Leukemia. 23:1311–1319.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Juban G, Giraud G, Guyot B, Belin S, Diaz
JJ, Starck J, Guillouf C, Moreau-Gachelin F and Morlé F: Spi-1 and
Fli-1 directly activate common target genes involved in ribosome
biogenesis in Friend erythroleukemic cells. Mol Cell Biol.
29:2852–2864. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Papetti M and Skoultchi AI: Reprogramming
leukemia cells to terminal differentiation and growth arrest by RNA
interference of PU.1. Mol Cancer Res. 5:1053–1062. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Delattre O, Zucman J, Plougastel B,
Desmaze C, Melot T, Peter M, Kovar H, Joubert I, de Jong P, Rouleau
G, et al: Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by
chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 359:162–165.
1992. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stockley J, Morgan NV, Bem D, Lowe GC,
Lordkipanidzé M, Dawood B, Simpson MA, Macfarlane K, Horner K, Leo
VC, et al: UK Genotyping and Phenotyping of Platelets Study Group:
Enrichment of FLI1 and RUNX1 mutations in families with excessive
bleeding and platelet dense granule secretion defects. Blood.
122:4090–4093. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tamir A, Howard J, Higgins RR, Li YJ,
Berger L, Zacksenhaus E, Reis M and Ben-David Y: Fli-1, an
Ets-related transcription factor, regulates erythropoietin-induced
erythroid proliferation and differentiation: Evidence for direct
transcriptional repression of the Rb gene during differentiation.
Mol Cell Biol. 19:4452–4464. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lesault I, Quang CT, Frampton J and
Ghysdael J: Direct regulation of BCL-2 by Fli-1 is involved in the
survival of FLI-1-transformed erythroblasts. EMBO J. 21:694–703.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Athanasiou M, Mavrothalassitis G,
Sun-Hoffman L and Blair DG: FLI-1 is a suppressor of erythroid
differentiation in human hematopoietic cells. Leukemia. 14:439–445.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lakhanpal GK, Vecchiarelli-Federico LM, Li
YJ, Cui JW, Bailey ML, Spaner DE, Dumont DJ, Barber DL and
Ben-David Y: The inositol phosphatase SHIP-1 is negatively
regulated by Fli-1 and its loss accelerates leukemogenesis. Blood.
116:428–436. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li YJ, Liu G, Xia L, Xiao X, Liu JC,
Menezes ME, Das SK, Emdad L, Sarkar D, Fisher PB, et al:
Suppression of Her2/Neu mammary tumor development in mda-7/IL-24
transgenic mice. Oncotarget. 6:36943–36954. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shimizu R, Engel JD and Yamamoto M:
GATA1-related leukaemias. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:279–287. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Blaybel R, Théoleyre O, Douablin A and
Baklouti F: Down-regulation of the Spi-1/PU.1 oncogene induces the
expression of TRIM10/HERF1, a key factor required for terminal
erythroid cell differentiation and survival. Cell Res. 18:834–845.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pereira R, Quang CT, Lesault I, Dolznig H,
Beug H and Ghysdael J: FLI-1 inhibits differentiation and induces
proliferation of primary erythroblasts. Oncogene. 18:1597–1608.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tijssen MR, Cvejic A, Joshi A, Hannah RL,
Ferreira R, Forrai A, Bellissimo DC, Oram SH, Smethurst PA, Wilson
NK, et al: Genome-wide analysis of simultaneous GATA1/2, RUNX1,
FLI1, and SCL binding in megakaryocytes identifies hematopoietic
regulators. Dev Cell. 20:597–609. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hart A, Melet F, Grossfeld P, Chien K,
Jones C, Tunnacliffe A, Favier R and Bernstein A: Fli-1 is required
for murine vascular and megakaryocytic development and is
hemizygously deleted in patients with thrombocytopenia. Immunity.
13:167–177. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Spyropoulos DD, Pharr PN, Lavenburg KR,
Jackers P, Papas TS, Ogawa M and Watson DK: Hemorrhage, impaired
hematopoiesis, and lethality in mouse embryos carrying a targeted
disruption of the Fli1 transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol.
20:5643–5652. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu F, Walmsley M, Rodaway A and Patient
R: Fli1 acts at the top of the transcriptional network driving
blood and endothelial development. Curr Biol. 18:1234–1240. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Göttgens B, Nastos A, Kinston S, Piltz S,
Delabesse EC, Stanley M, Sanchez MJ, Ciau-Uitz A, Patient R and
Green AR: Establishing the transcriptional programme for blood: The
SCL stem cell enhancer is regulated by a multiprotein complex
containing Ets and GATA factors. EMBO J. 21:3039–3050. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Akashi K, Traver D, Miyamoto T and
Weissman IL: A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise
to all myeloid lineages. Nature. 404:193–197. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ceredig R, Rolink AG and Brown G: Models
of haematopoiesis: Seeing the wood for the trees. Nat Rev Immunol.
9:293–300. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hassan HT and Freund M: Characteristic
biological features of human megakaryoblastic leukaemia cell lines.
Leuk Res. 19:589–594. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Drexler HG, Matsuo Y and MacLeod RA:
Malignant hematopoietic cell lines: In vitro models for the study
of erythroleukemia. Leuk Res. 28:1243–1251. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tallack MR and Perkins AC:
Megakaryocyte-erythroid lineage promiscuity in EKLF null mouse
blood. Haematologica. 95:144–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Yamada H, Sekikawa T, Iwase S, Arakawa Y,
Suzuki H, Agawa M, Akiyama M, Takeda N and Horiguchi-Yamada J:
Segregation of megakaryocytic or erythroid cells from a
megakaryocytic leukemia cell line (JAS-R) by adhesion during
culture. Leuk Res. 31:1537–1543. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jackers P, Szalai G, Moussa O and Watson
DK: Ets-dependent regulation of target gene expression during
megakaryopoiesis. J Biol Chem. 279:52183–52190. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Edvardsson L, Dykes J and Olofsson T:
Isolation and characterization of human myeloid progenitor
populations - TpoR as discriminator between common myeloid and
megakaryocyte/erythroid progenitors. Exp Hematol. 34:599–609. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun S, Zimmet JM, Toselli P, Thompson A,
Jackson CW and Ravid K: Overexpression of cyclin D1 moderately
increases ploidy in megakaryocytes. Haematologica. 86:17–23.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pang L, Xue HH, Szalai G, Wang X, Wang Y,
Watson DK, Leonard WJ, Blobel GA and Poncz M: Maturation
stage-specific regulation of megakaryopoiesis by pointed-domain Ets
proteins. Blood. 108:2198–2206. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu T, Yao Y, Zhang G, Wang Y, Deng B,
Song J, Li X, Han F, Xiao X, Yang J, et al: A screen for Fli-1
transcriptional modulators identifies PKC agonists that induce
erythroid to megakaryocytic differentiation and suppress
leukemogenesis. Oncotarget. 8:16728–16743. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ratajczak MZ, Perrotti D, Melotti P,
Powzaniuk M, Calabretta B, Onodera K, Kregenow DA, Machalinski B
and Gewirtz AM: Myb and ets proteins are candidate regulators of
c-kit expression in human hematopoietic cells. Blood. 91:1934–1946.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Akada H, Akada S, Gajra A, Bair A,
Graziano S, Hutchison RE and Mohi G: Efficacy of vorinostat in a
murine model of polycythemia vera. Blood. 119:3779–3789. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Signer RA, Magee JA, Salic A and Morrison
SJ: Haematopoietic stem cells require a highly regulated protein
synthesis rate. Nature. 509:49–54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang J, Socolovsky M, Gross AW and Lodish
HF: Role of Ras signaling in erythroid differentiation of mouse
fetal liver cells: Functional analysis by a flow cytometry-based
novel culture system. Blood. 102:3938–3946. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|