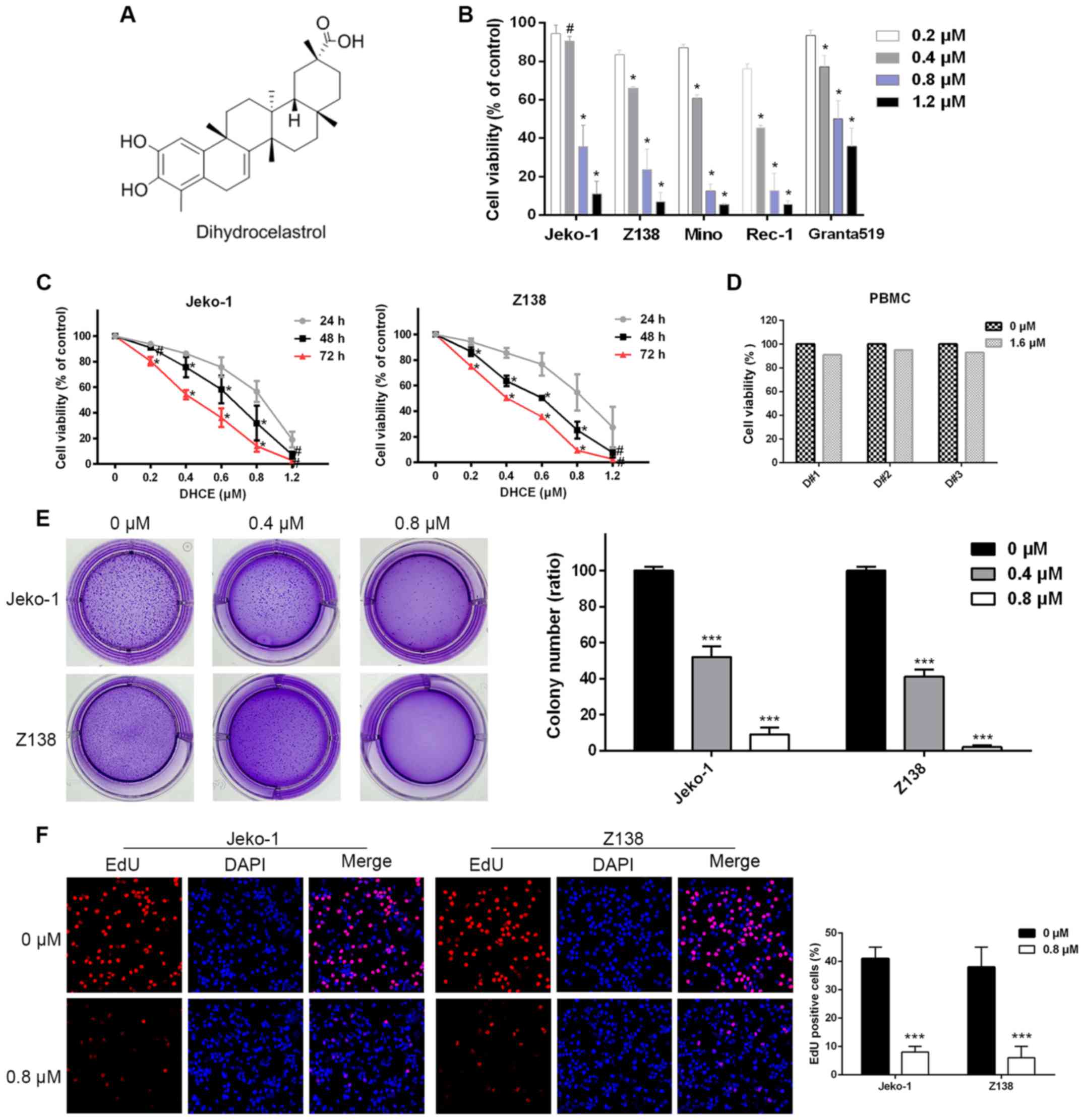
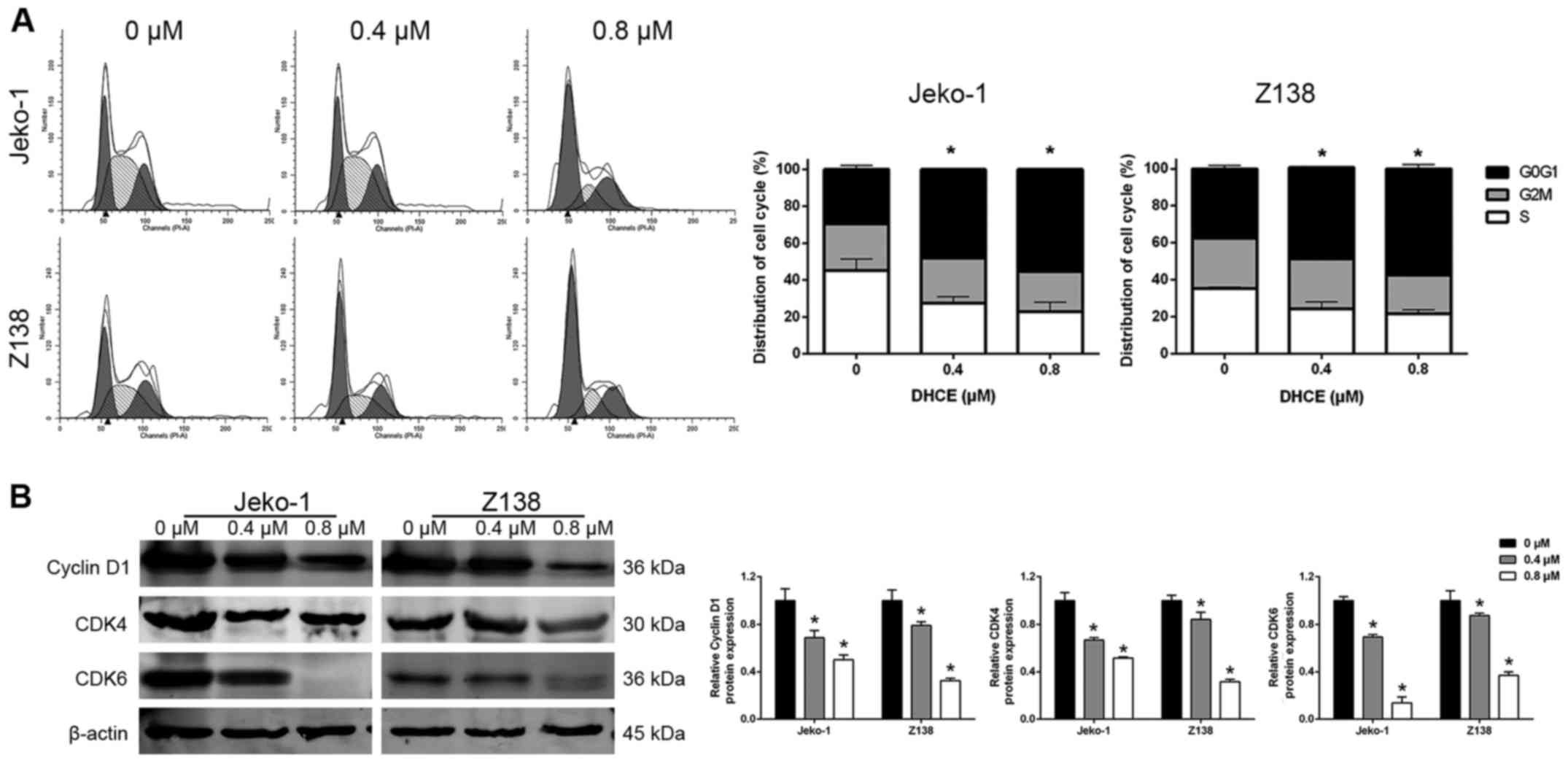
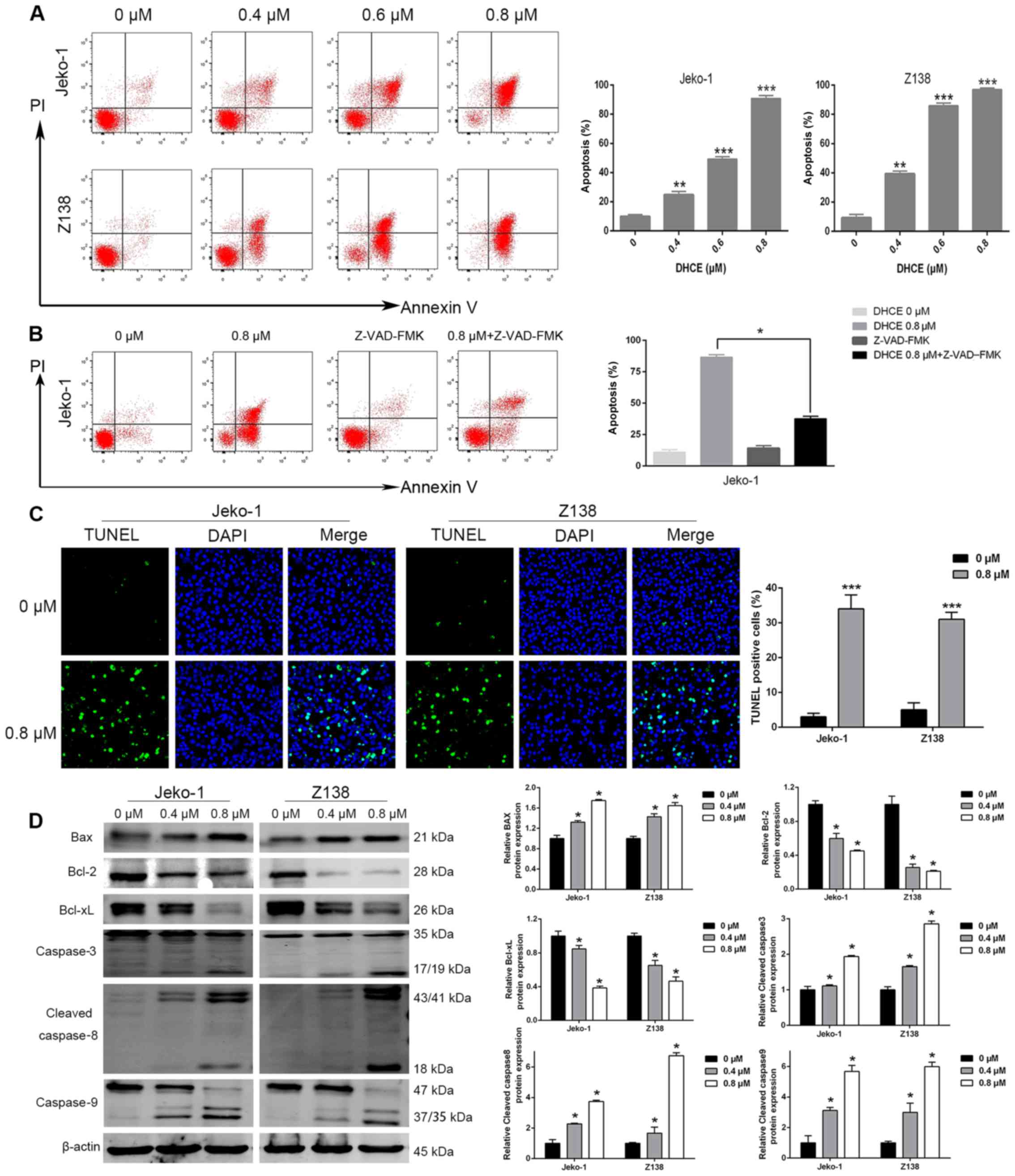
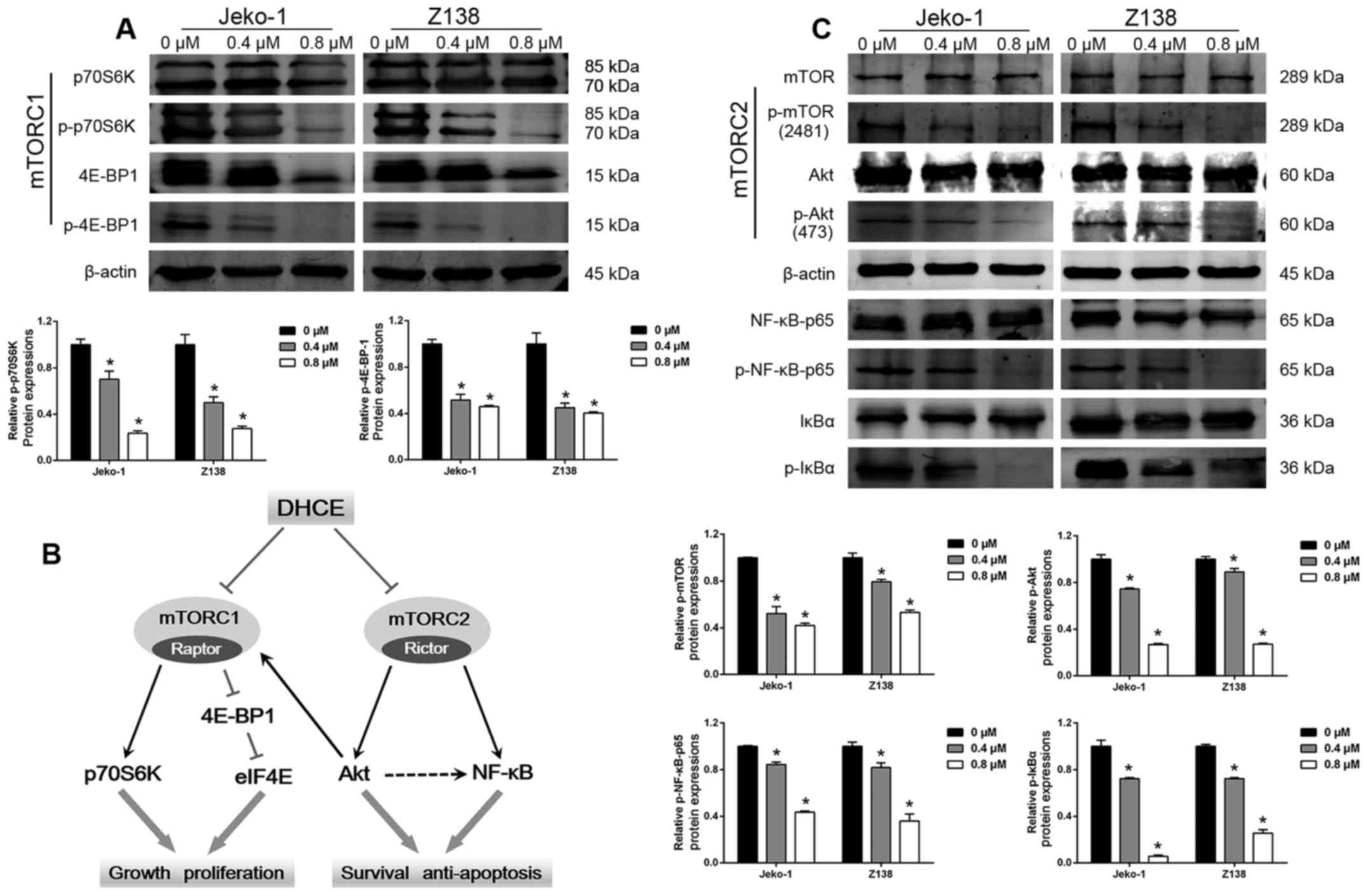
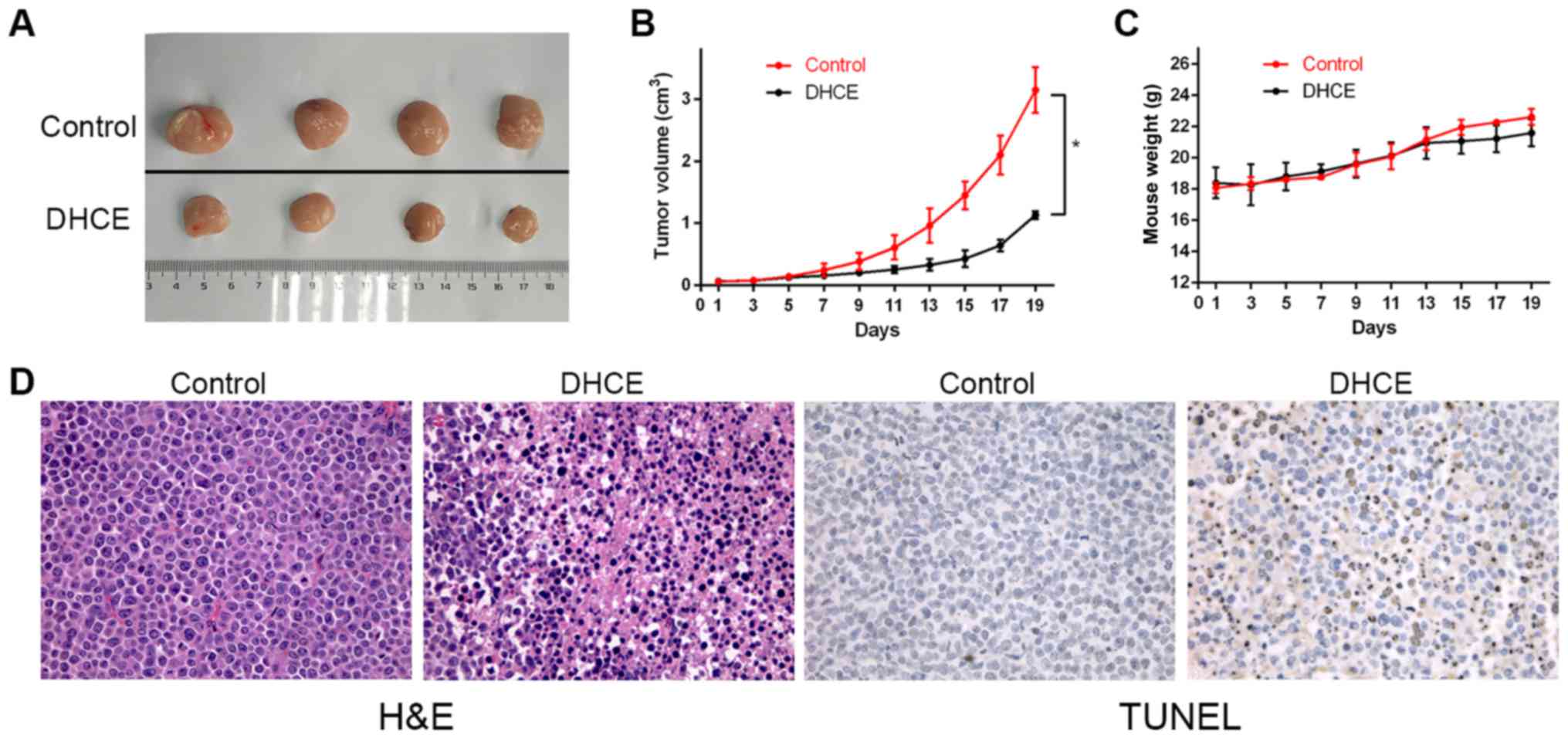
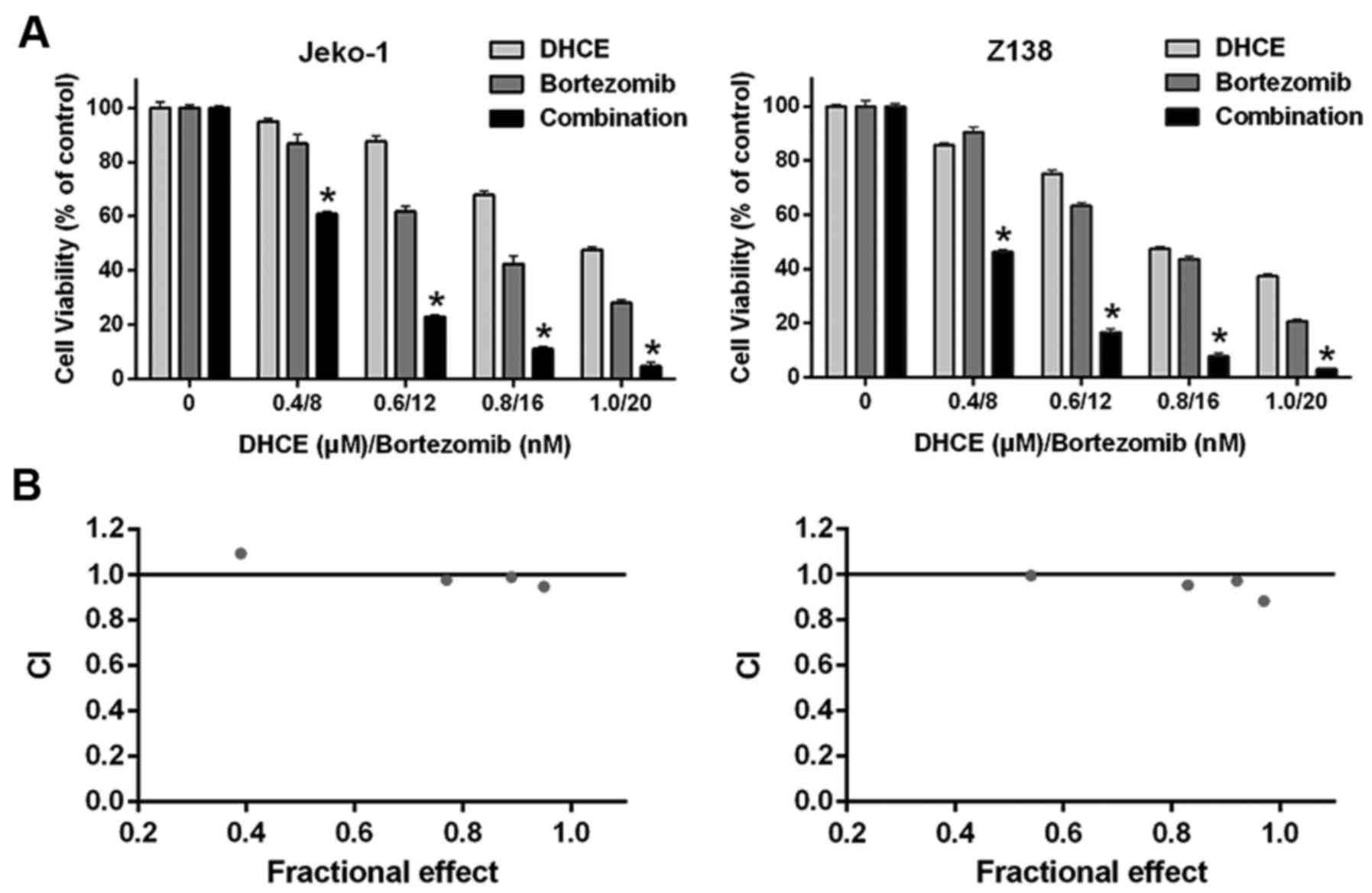
|
1
|
Spurgeon SE, Till BG, Martin P, Goy AH,
Dreyling MP, Gopal AK, LeBlanc M, Leonard JP, Friedberg JW, Baizer
L, et al: Recommendations for clinical trial development in mantle
cell lymphoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 109:1092016.
|
|
2
|
Zhou Y, Wang H, Fang W, Romaguer JE, Zhang
Y, Delasalle KB, Kwak L, Yi Q, Du XL and Wang M: Incidence trends
of mantle cell lymphoma in the United States between 1992 and 2004.
Cancer. 113:791–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bosch F, Jares P, Campo E, Lopez-Guillermo
A, Piris MA, Villamor N, Tassies D, Jaffe ES, Montserrat E, Rozman
C, et al: PRAD-1/cyclin D1 gene overexpression in chronic
lymphoproliferative disorders: A highly specific marker of mantle
cell lymphoma. Blood. 84:2726–2732. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheah CY, Seymour JF and Wang ML: Mantle
cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 34:1256–1269. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hamad N, Armytage T, McIlroy K, Singh N
and Ward C: Primary cutaneous mantle-cell lymphoma: A case report
and literature review. J Clin Oncol. 33:e104–e108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Campo E and Rule S: Mantle cell lymphoma:
Evolving management strategies. Blood. 125:48–55. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lee JS, Vo TT and Fruman DA: Targeting
mTOR for the treatment of B cell malignancies. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
82:1213–1228. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Strimpakos AS, Karapanagiotou EM, Saif MW
and Syrigos KN: The role of mTOR in the management of solid tumors:
An overview. Cancer Treat Rev. 35:148–159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Baldo P, Cecco S, Giacomin E, Lazzarini R,
Ros B and Marastoni S: mTOR pathway and mTOR inhibitors as agents
for cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:647–665. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Inoki K, Corradetti MN and Guan KL:
Dysregulation of the TSC-mTOR pathway in human disease. Nat Genet.
37:19–24. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lee DF, Kuo HP, Chen CT, Hsu JM, Chou CK,
Wei Y, Sun HL, Li LY, Ping B, Huang WC, et al: IKK beta suppression
of TSC1 links inflammation and tumor angiogenesis via the mTOR
pathway. Cell. 130:440–455. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eyre TA, Collins GP, Goldstone AH and
Cwynarski K: Time now to TORC the TORC? New developments in mTOR
pathway inhibition in lymphoid malignancies. Br J Haematol.
166:336–351. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peponi E, Drakos E, Reyes G, Leventaki V,
Rassidakis GZ and Medeiros LJ: Activation of mammalian target of
rapamycin signaling promotes cell cycle progression and protects
cells from apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma. Am J Pathol.
169:2171–2180. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saxton RA and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell. 168:960–976. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dancey J: mTOR signaling and drug
development in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 7:209–219. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM and
Sabatini DM: Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the
rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 307:1098–1101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gupta M, Hendrickson AE, Yun SS, Han JJ,
Schneider PA, Koh BD, Stenson MJ, Wellik LE, Shing JC, Peterson KL,
et al: Dual mTORC1/mTORC2 inhibition diminishes Akt activation and
induces Puma-dependent apoptosis in lymphoid malignancies. Blood.
119:476–487. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Witzig TE, Geyer SM, Ghobrial I, Inwards
DJ, Fonseca R, Kurtin P, Ansell SM, Luyun R, Flynn PJ, Morton RF,
et al: Phase II trial of single-agent temsirolimus (CCI-779) for
relapsed mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 23:5347–5356. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ansell SM, Inwards DJ, Rowland KM Jr,
Flynn PJ, Morton RF, Moore DF Jr, Kaufmann SH, Ghobrial I, Kurtin
PJ, Maurer M, et al: Low-dose, single-agent temsirolimus for
relapsed mantle cell lymphoma: A phase 2 trial in the North Central
Cancer Treatment Group. Cancer. 113:508–514. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu J, Lee J, Salazar Hernandez MA,
Mazitschek R and Ozcan U: Treatment of obesity with celastrol.
Cell. 161:999–1011. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kannaiyan R, Shanmugam MK and Sethi G:
Molecular targets of celastrol derived from Thunder of God Vine:
Potential role in the treatment of inflammatory disorders and
cancer. Cancer Lett. 303:9–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sethi G, Ahn KS, Pandey MK and Aggarwal
BB: Celastrol, a novel triterpene, potentiates TNF-induced
apoptosis and suppresses invasion of tumor cells by inhibiting
NF-kappaB-regulated gene products and TAK1-mediated NF-kappaB
activation. Blood. 109:2727–2735. 2007.
|
|
23
|
Jang SY, Jang SW and Ko J: Celastrol
inhibits the growth of estrogen positive human breast cancer cells
through modulation of estrogen receptor α. Cancer Lett. 300:57–65.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fribley AM, Miller JR, Brownell AL,
Garshott DM, Zeng Q, Reist TE, Narula N, Cai P, Xi Y, Callaghan MU,
et al: Celastrol induces unfolded protein response-dependent cell
death in head and neck cancer. Exp Cell Res. 330:412–422. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Klaić L, Trippier PC, Mishra RK, Morimoto
RI and Silverman RB: Remarkable stereospecific conjugate additions
to the Hsp90 inhibitor celastrol. J Am Chem Soc. 133:19634–19637.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hu L, Wu H, Li B, Song D, Yang G, Chen G,
Xie B, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Yu D, et al: Dihydrocelastrol inhibits
multiple myeloma cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis through
ERK1/2 and IL-6/STAT3 pathways in vitro and in vivo. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 49:420–427. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ashton JC: Drug combination studies and
their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method -
letter. Cancer Res. 75:24002015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rudelius M, Rosenfeldt MT, Leich E,
Rauert-Wunderlich H, Solimando AG, Beilhack A, Ott G and Rosenwald
A: Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase overcomes resistance of
mantle cell lymphoma to ibrutinib in the bone marrow
microenvironment. Haematologica. 103:116–125. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Zhou J, Tiemann K, Chomchan P, Alluin J,
Swiderski P, Burnett J, Zhang X, Forman S, Chen R and Rossi J: Dual
functional BAFF receptor aptamers inhibit ligand-induced
proliferation and deliver siRNAs to NHL cells. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:4266–4283. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: CDK inhibitors:
Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes
Dev. 13:1501–1512. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. BioMed Res Int. 2014:1508452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Taylor RC, Cullen SP and Martin SJ:
Apoptosis: Controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:231–241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Davids MS: Targeting BCL-2 in B-cell
lymphomas. Blood. 130:1081–1088. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dal Col J, Zancai P, Terrin L, Guidoboni
M, Ponzoni M, Pavan A, Spina M, Bergamin S, Rizzo S, Tirelli U, et
al: Distinct functional significance of Akt and mTOR constitutive
activation in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood. 111:5142–5151. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Madrid LV, Mayo MW, Reuther JY and Baldwin
AS Jr: Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65
Subunit of NF-kappa B through utilization of the Ikappa B kinase
and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. J Biol
Chem. 276:18934–18940. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ahmad A, Biersack B, Li Y, Kong D, Bao B,
Schobert R, Padhye SB and Sarkar FH: Targeted regulation of
PI3K/Akt/mTOR/NF-κB signaling by indole compounds and their
derivatives: Mechanistic details and biological implications for
cancer therapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 13:1002–1013. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tanaka K, Babic I, Nathanson D, Akhavan D,
Guo D, Gini B, Dang J, Zhu S, Yang H, De Jesus J, et al: Oncogenic
EGFR signaling activates an mTORC2-NF-κB pathway that promotes
chemotherapy resistance. Cancer Discov. 1:524–538. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee K, Gudapati P, Dragovic S, Spencer C,
Joyce S, Killeen N, Magnuson MA and Boothby M: Mammalian target of
rapamycin protein complex 2 regulates differentiation of Th1 and
Th2 cell subsets via distinct signaling pathways. Immunity.
32:743–753. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Stewart ZA, Westfall MD and Pietenpol JA:
Cell-cycle dysregulation and anticancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 24:139–145. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Halazonetis TD, Gorgoulis VG and Bartek J:
An oncogene-induced DNA damage model for cancer development.
Science. 319:1352–1355. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Riedl SJ and Salvesen GS: The apoptosome:
Signalling platform of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
8:405–413. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
LoPiccolo J, Blumenthal GM, Bernstein WB
and Dennis PA: Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: Effective
combinations and clinical considerations. Drug Resist Updat.
11:32–50. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sabatini DM: mTOR and cancer: Insights
into a complex relationship. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:729–734. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gingras AC, Gygi SP, Raught B, Polakiewicz
RD, Abraham RT, Hoekstra MF, Aebersold R and Sonenberg N:
Regulation of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation: A novel two-step mechanism.
Genes Dev. 13:1422–1437. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hsu PP, Kang SA, Rameseder J, Zhang Y,
Ottina KA, Lim D, Peterson TR, Choi Y, Gray NS, Yaffe MB, et al:
The mTOR-regulated phosphoproteome reveals a mechanism of
mTORC1-mediated inhibition of growth factor signaling. Science.
332:1317–1322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang HT, Wang WW, Ren LH, Zhao XX, Wang
ZH, Zhuang DL and Bai YN: The mTORC2/Akt/NFκB pathway-mediated
activation of TRPC6 participates in adriamycin-induced podocyte
apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:1079–1093. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lee K, Nam KT, Cho SH, Gudapati P, Hwang
Y, Park DS, Potter R, Chen J, Volanakis E and Boothby M: Vital
roles of mTOR complex 2 in Notch-driven thymocyte differentiation
and leukemia. J Exp Med. 209:713–728. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bassères DS and Baldwin AS: Nuclear
factor-kappaB and inhibitor of kappaB kinase pathways in oncogenic
initiation and progression. Oncogene. 25:6817–6830. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Karin M: Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer
development and progression. Nature. 441:431–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yun S, Vincelette ND, Knorr KL, Almada LL,
Schneider PA, Peterson KL, Flatten KS, Dai H, Pratz KW, Hess AD, et
al: 4EBP1/c-MYC/PUMA and NF-κB/EGR1/BIM pathways underlie
cytotoxicity of mTOR dual inhibitors in malignant lymphoid cells.
Blood. 127:2711–2722. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|