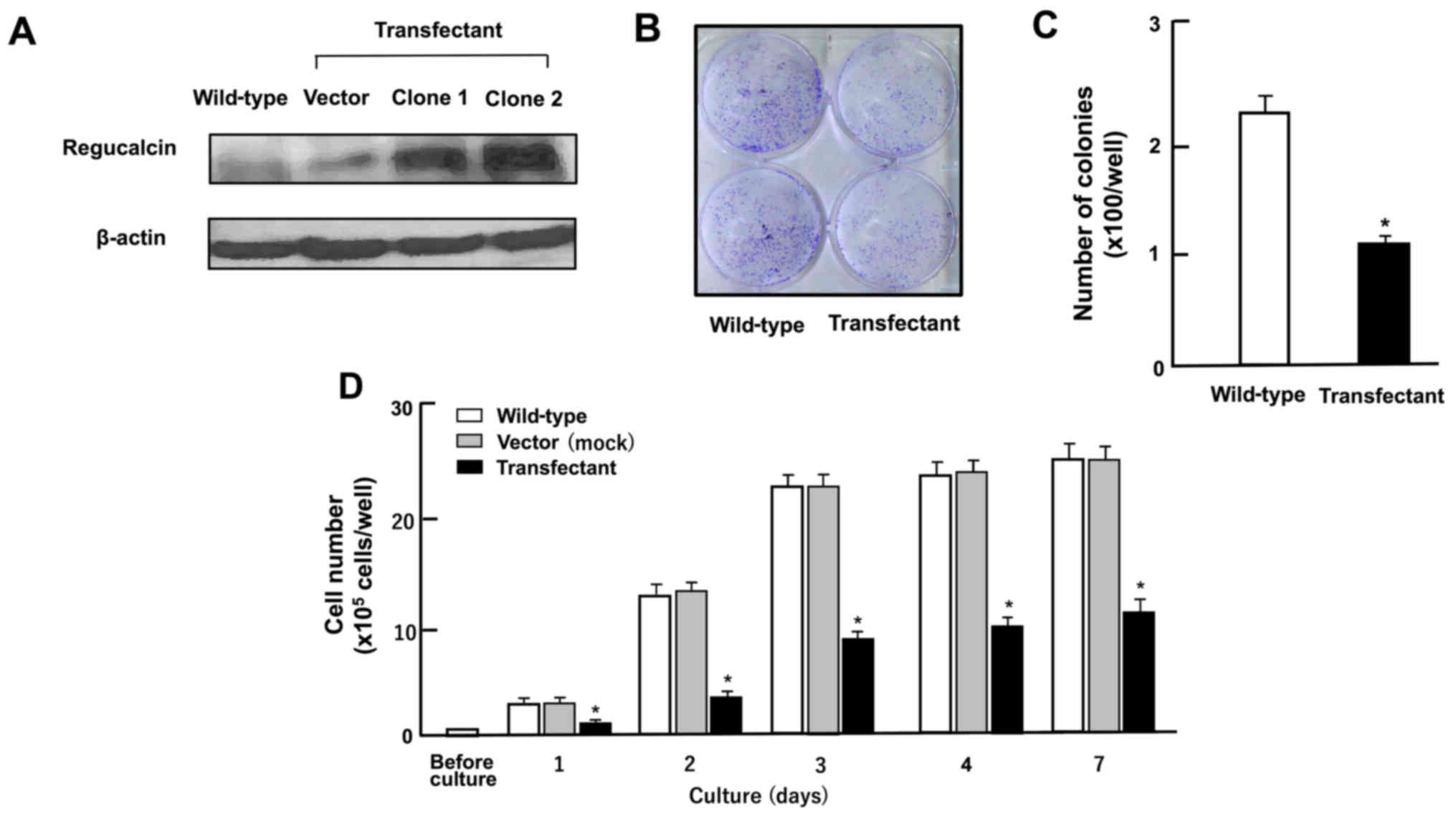
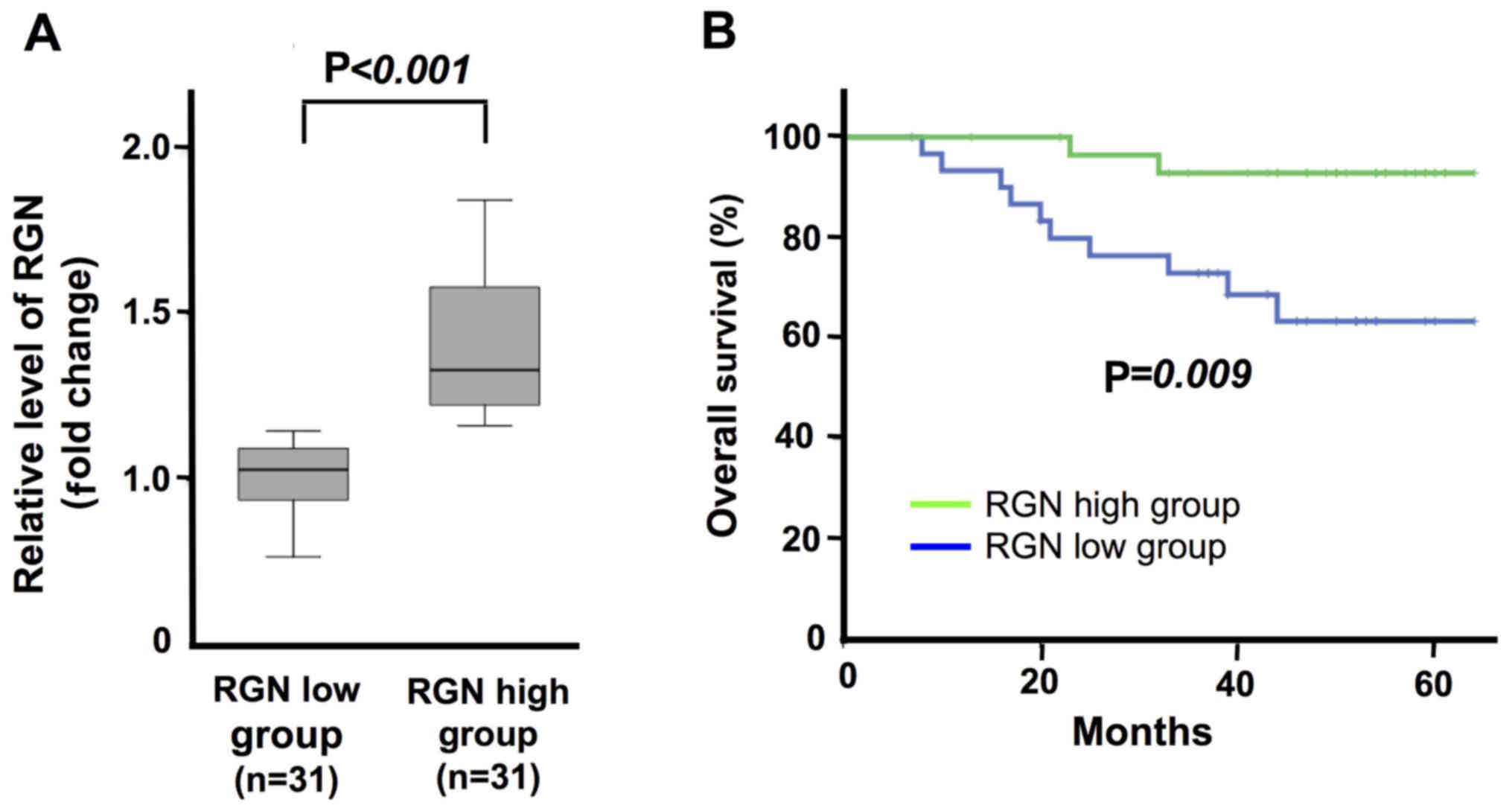
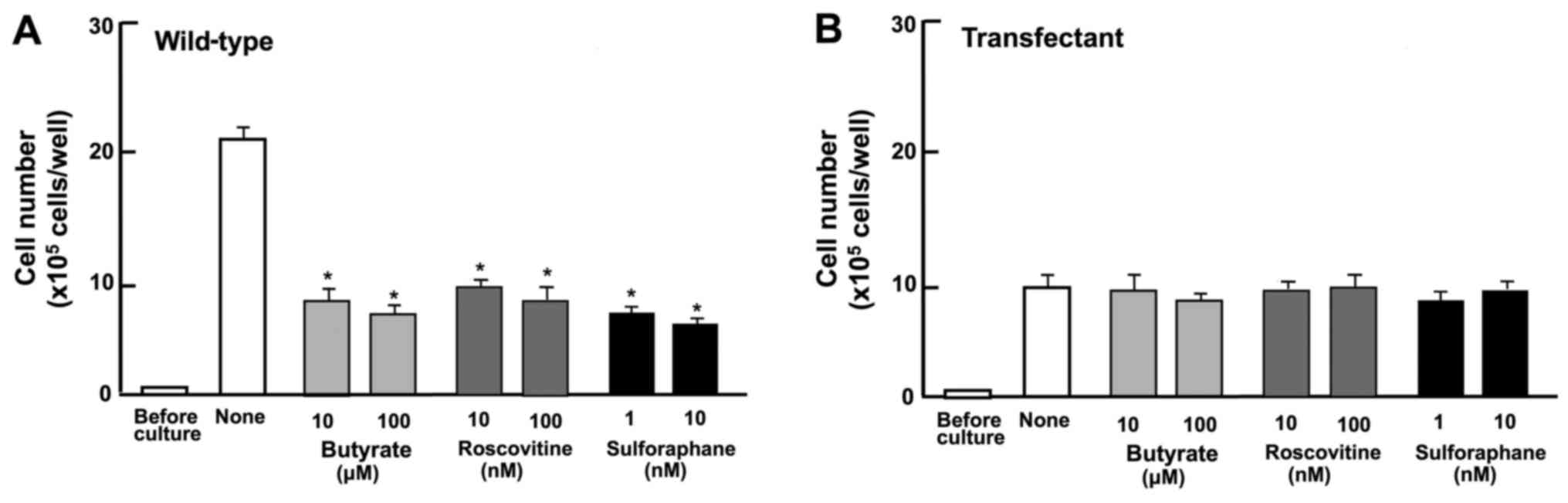
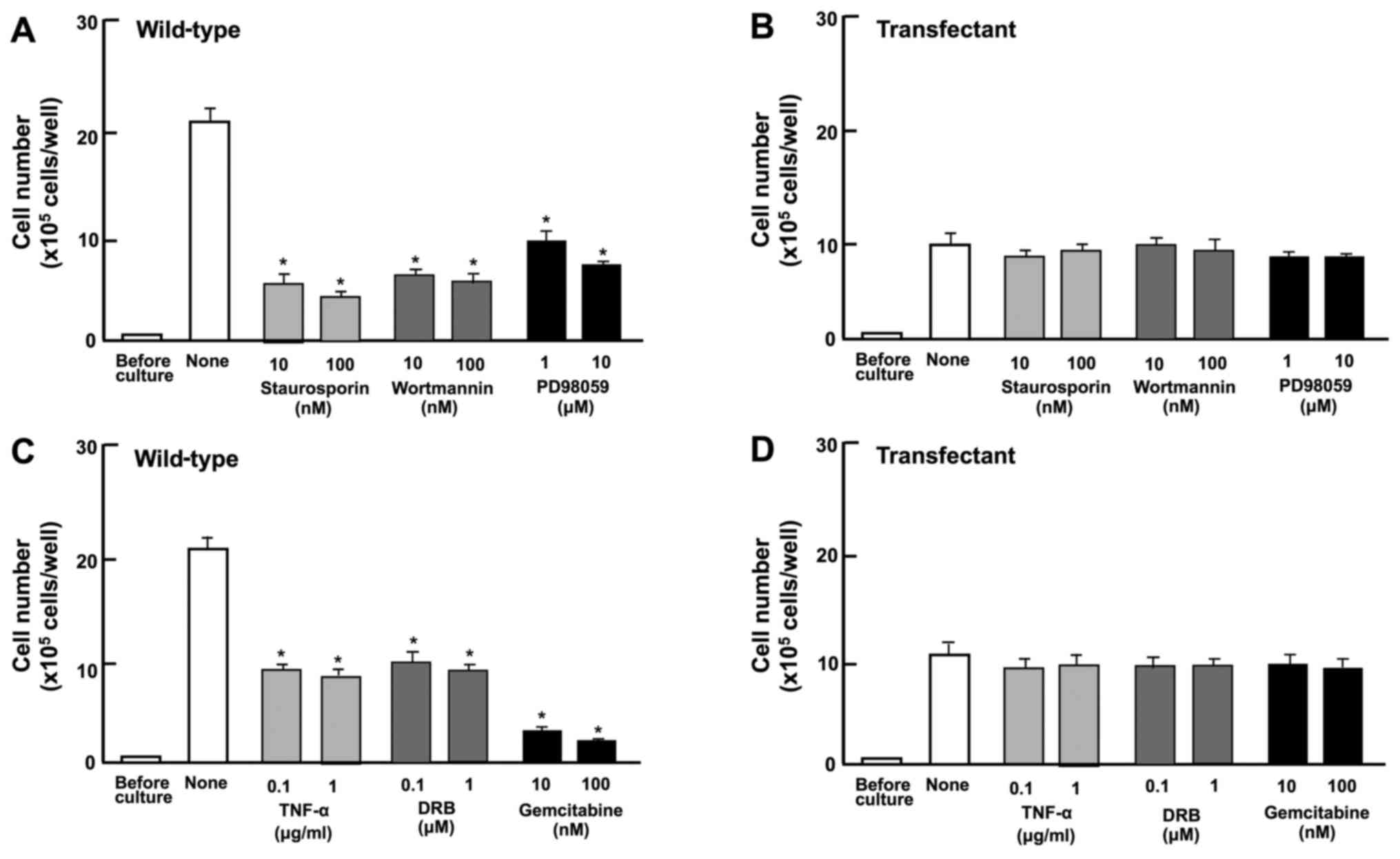
|
1
|
Porter MG and Stoeger SM: Atypical
colorectal neoplasms. Surg Clin North Am. 97:641–656. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
American Society Cancer: Cancer facts
& figures. 2016, https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2016.html.
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Alnabulsi A and Murray GI: Integrative
analysis of the colorectal cancer proteome: Potential clinical
impact. Expert Rev Proteomics. 13:1–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Alnabulsi A, Swan R, Cash B, Alnabulsi A
and Murray GI: The differential expression of omega-3 and omega-6
fatty acid metabolising enzymes in colorectal cancer and its
prognostic significance. Br J Cancer. 116:1612–1620. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carini F, Mazzola M, Rappa F, Jurjus A,
Geagea AG, Al Kattar S, Bou-Assi T, Jurjus R, Damiani P, Leone A,
et al: Colorectal carcinogenesis: Role of oxidative stress and
antioxidants. Anticancer Res. 37:4759–4766. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Colussi D, Brandi G, Bazzoli F and
Ricciardiello L: Molecular pathways involved in colorectal cancer:
Implications for disease behavior and prevention. Int J Mol Sci.
14:16365–16385. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kudryavtseva AV, Lipatova AV, Zaretsky AR,
Moskalev AA, Fedorova MS, Rasskazova AS, Shibukhova GA, Snezhkina
AV, Kaprin AD, Alekseev BY, et al: Important molecular genetic
markers of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 7:53959–53983. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jones RP, Sutton PA, Evans JP, Clifford R,
McAvoy A, Lewis J, Rousseau A, Mountford R, McWhirter D and Malik
HZ: Specific mutations in KRAS codon 12 are associated with worse
overall survival in patients with advanced and recurrent colorectal
cancer. Br J Cancer. 116:923–929. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Downward J: Targeting RAS signalling
pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:11–22. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shimokawa N and Yamaguchi M: Molecular
cloning and sequencing of the cDNA coding for a calcium-binding
protein regucalcin from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 327:251–255. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shimokawa N, Matsuda Y and Yamaguchi M:
Genomic cloning and chromosomal assignment of rat regucalcin gene.
Mol Cell Biochem. 151:157–163. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thiselton DL, McDowall J, Brandau O,
Ramser J, d'Esposito F, Bhattacharya SS, Ross MT, Hardcastle AJ and
Meindl A: An integrated, functionally annotated gene map of the
DXS8026-ELK1 interval on human Xp11.3-Xp11.23: Potential hotspot
for neuro-genetic disorders. Genomics. 79:560–572. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yamaguchi M: Suppressive role of
regucalcin in liver cell proliferation: Involvement in
carcinogenesis. Cell Prolif. 46:243–253. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yamaguchi M: Involvement of regucalcin as
a suppressor protein in human carcinogenesis: Insight into the gene
therapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:1333–1341. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yamaguchi M: Role of regucalcin in
maintaining cell homeostasis and function (review). Int J Mol Med.
15:371–389. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamaguchi M: Regucalcin and cell
regulation: Role as a suppressor protein in signal transduction.
Mol Cell Biochem. 353:101–137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamaguchi M: Role of regucalcin in cell
nuclear regulation: Involvement as a transcription factor. Cell
Tissue Res. 354:331–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamaguchi M: The anti-apoptotic effect of
regucalcin is mediated through multisignaling pathways. Apoptosis.
18:1145–1153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamaguchi M: The Role of Regucalcin in
Cell Homeostasis and Disorder. Nova Science Publishers, Inc; New
York, NY: 2017
|
|
22
|
Murata T and Yamaguchi M: Alternatively
spliced variants of the regucalcin gene in various human normal and
tumor tissues. Int J Mol Med. 34:1141–1146. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yamaguchi M, Osuka S, Weitzmann MN,
El-Rayes BF, Shoji M and Murata T: Prolonged survival in pancreatic
cancer patients with increased regucalcin gene expression:
Overexpression of regucalcin suppresses the proliferation in human
pancreatic cancer MIA PaCa-2 cells in vitro. Int J Oncol.
48:1955–1964. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yamaguchi M, Osuka S, Weitzmann MN, Shoji
M and Murata T: Increased regucalcin gene expression extends
survival in breast cancer patients: Overexpression of regucalcin
suppresses the proliferation and metastatic bone activity in
MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells in vitro. Int J Oncol.
49:812–822. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yamaguchi M, Osuka S, Weitzmann MN,
El-Rayes BF, Shoji M and Murata T: Prolonged survival in
hepatocarcinoma patients with increased regucalcin gene expression:
HepG2 cell proliferation is suppressed by overexpression of
regucalcin in vitro. Int J Oncol. 49:1686–1694. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamaguchi M, Osuka S, Shoji M, Weitzmann
MN and Murata T: Survival of lung cancer patients is prolonged with
higher regucalcin gene expression: Suppressed proliferation of lung
adenocarcinoma A549 cells in vitro. Mol Cell Biochem. 430:37–46.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Staub E, Groene J, Heinze M, Mennerich D,
Roepcke S, Klaman I, Hinzmann B, Castanos-Velez E, Pilarsky C, Mann
B, et al: An expression module of WIPF1-coexpressed genes
identifies patients with favorable prognosis in three tumor types.
J Mol Med (Berl). 87:633–644. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Misawa H, Inagaki S and Yamaguchi M:
Suppression of cell proliferation and deoxyribonucleic acid
synthesis in the cloned rat hepatoma H4-II-E cells overexpressing
regucalcin. J Cell Biochem. 84:143–149. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fang Z, Tang Y, Fang J, Zhou Z, Xing Z,
Guo Z, Guo X, Wang W, Jiao W, Xu Z, et al: Simvastatin inhibits
renal cancer cell growth and metastasis via AKT/mTOR, ERK and
JAK2/STAT3 pathway. PLoS One. 17:e628232013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yamaguchi M and Daimon Y: Overexpression
of regucalcin suppresses cell proliferation in cloned rat hepatoma
H4-II-E cells: Involvement of intracellular signaling factors and
cell cycle-related genes. J Cell Biochem. 95:1169–1177. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Izumi T and Yamaguchi M: Overexpression of
regucalcin suppresses cell death in cloned rat hepatoma H4-II-E
cells induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha or thapsigargin. J
Cell Biochem. 92:296–306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yamaguchi M and Isogai M: Tissue
concentration of calcium-binding protein regucalcin in rats by
enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay. Mol Cell Biochem. 122:65–68.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Charollais RH, Buquet C and Mester J:
Butyrate blocks the accumulation of CDC2 mRNA in late G1 phase but
inhibits both the early and late G1 progression in chemically
transformed mouse fibroblasts BP-A31. J Cell Physiol. 145:46–52.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meijer L, Borgne A, Mulner O, Chong JP,
Blow JJ, Inagaki N, Inagaki M, Delcros JG and Moulinoux JP:
Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and
selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and
cdk5. Eur J Biochem. 243:527–536. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Singh SV, Herman-Antosiewicz A, Singh AV,
Lew KL, Srivastava SK, Kamath R, Brown KD, Zhang L and Baskaran R:
Sulforaphane-induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest involves
checkpoint kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of cell division cycle
25C. J Biol Chem. 279:25813–25822. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nakagawa T, Sawada N and Yamaguchi M:
Overexpression of regucalcin suppresses cell proliferation of
cloned normal rat kidney proximal tubular epithelial NRK52E cells.
Int J Mol Med. 16:637–643. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tamaoki T, Nomoto H, Takahashi I, Kato Y,
Morimoto M and Tomita F: Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of
phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 135:397–402. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Serrano-Nascimento C, da Silva Teixeira S,
Nicola JP, Nachbar RT, Masini-Repiso AM and Nunes MT: The acute
inhibitory effect of iodide excess on sodium/iodide symporter
expression and activity involves the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Endocrinology. 155:1145–1156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pelech SL, Charest DL, Mordret GP, Siow
YL, Palaty C, Campbell D, Charlton L, Samiei M and Sanghera JS:
Networking with mitogen-activated protein kinases. Mol Cell
Biochem. 127–128:157–169. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Palangat M, Grass JA, Langelier MF,
Coulombe B and Landick R: The RPB2 flap loop of human RNA
polymerase II is dispensable for transcription initiation and
elongation. Mol Cell Biol. 31:3312–3325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tang SC and Chen YC: Novel therapeutic
targets for pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
20:10825–10844. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tsurusaki Y and Yamaguchi M: Role of
regucalcin in liver nuclear function: Binding of regucalcin to
nuclear protein or DNA and modulation of tumor-related gene
expression. Int J Mol Med. 14:277–281. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|