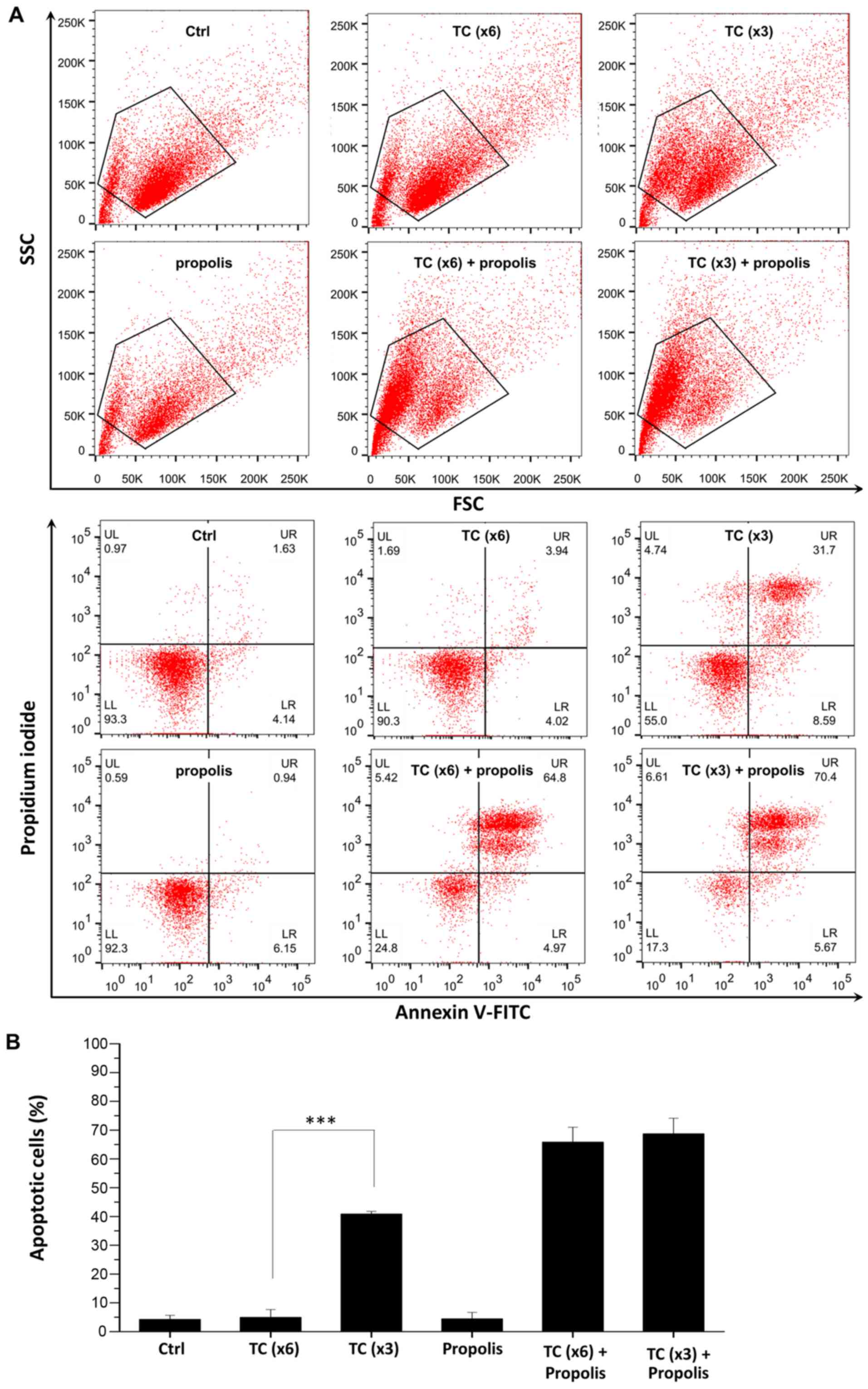
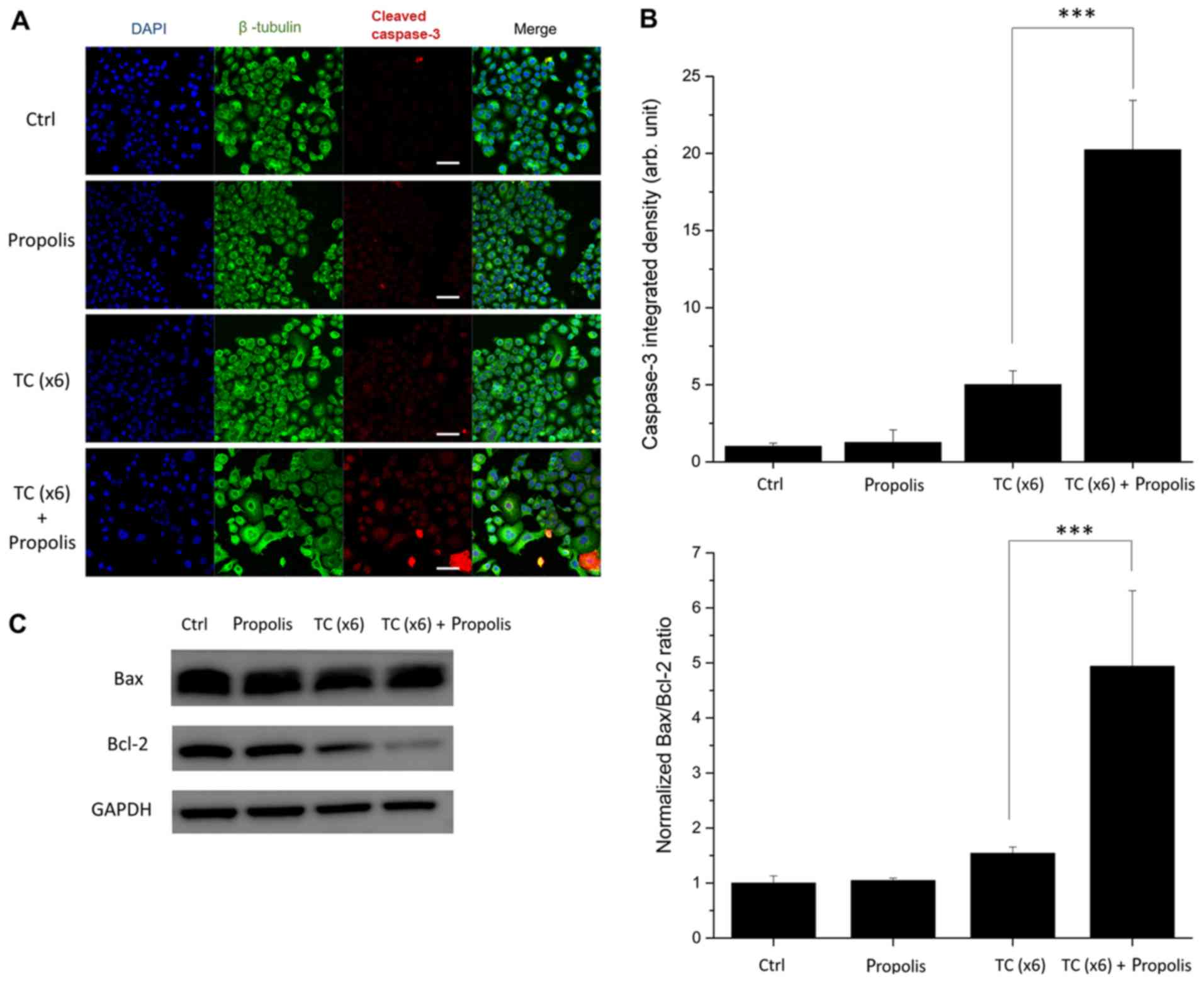
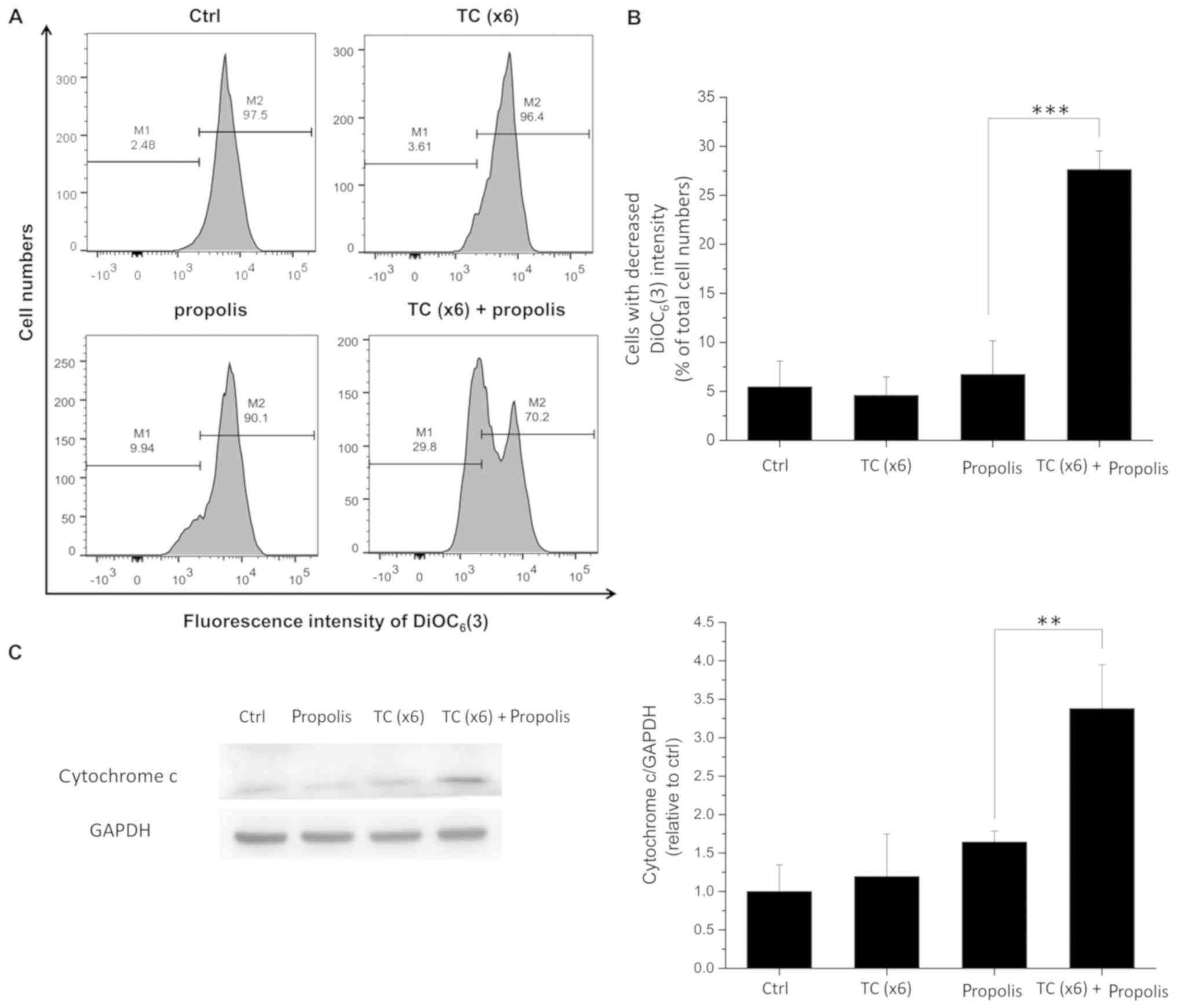
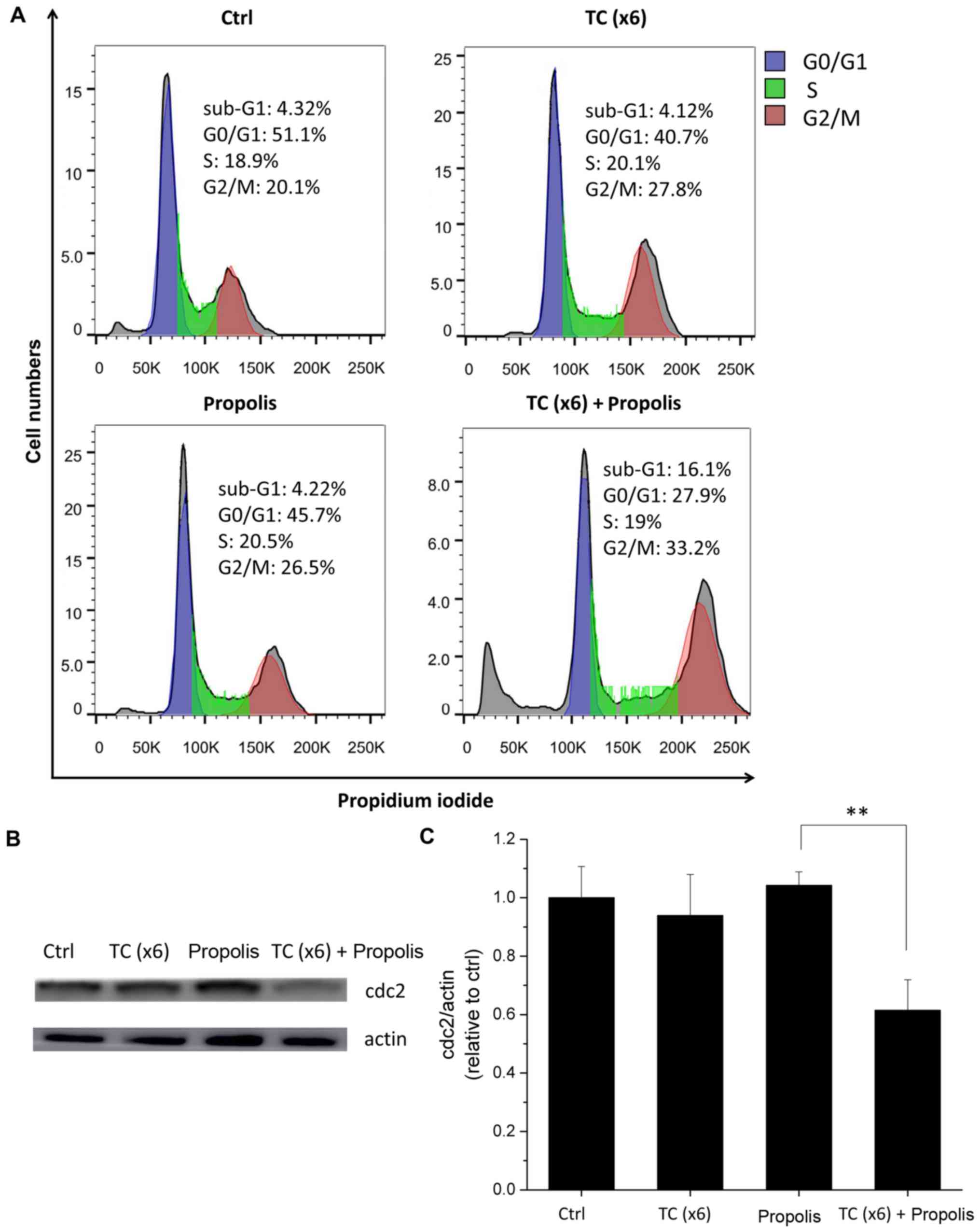
|
1
|
van den Tempel N, Horsman MR and Kanaar R:
Improving efficacy of hyperthermia in oncology by exploiting
biological mechanisms. Int J Hyperthermia. 32:446–454. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mantso T, Goussetis G, Franco R, Botaitis
S, Pappa A and Panayiotidis M: Effects of hyperthermia as a
mitigation strategy in DNA damage-based cancer therapies. Semin
Cancer Biol. 37-38:96–105. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chu KF and Dupuy DE: Thermal ablation of
tumours: Biological mechanisms and advances in therapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 14:199–208. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Paulson JR, Kresch AK and Mesner PW:
Moderate hyperthermia induces apoptosis in metaphase-arrested cells
but not in interphase Hela cells. Adv Biol Chem. 6:126–139. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lim CU, Zhang Y and Fox MH: Cell cycle
dependent apoptosis and cell cycle blocks induced by hyperthermia
in HL-60 cells. Int J Hyperthermia. 22:77–91. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bhowmick S, Coad JE, Swanlund DJ and
Bischof JC: In vitro thermal therapy of AT-1 Dunning prostate
tumours. Int J Hyperthermia. 20:73–92. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sminia P, van der Zee J, Wondergem J and
Haveman J: Effect of hyperthermia on the central nervous system: A
review. Int J Hyperthermia. 10:1–30. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schaaf L, Schwab M, Ulmer C, Heine S,
Mürdter TE, Schmid JO, Sauer G, Aulitzky WE and van der Kuip H:
Hyperthermia synergizes with chemotherapy by inhibiting
PARP1-dependent DNA replication arrest. Cancer Res. 76:2868–2875.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miyamoto R, Oda T, Hashimoto S, Kurokawa
T, Inagaki Y, Shimomura O, Ohara Y, Yamada K, Akashi Y, Enomoto T,
et al: Cetuximab delivery and antitumor effects are enhanced by
mild hyperthermia in a xenograft mouse model of pancreatic cancer.
Cancer Sci. 107:514–520. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Man J, Shoemake JD, Ma T, Rizzo AE, Godley
AR, Wu Q, Mohammadi AM, Bao S, Rich JN and Yu JS: Hyperthermia
sensitizes glioma stem-like cells to radiation by inhibiting AKT
signaling. Cancer Res. 75:1760–1769. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schaaf L, van der Kuip H, Zopf W, Winter
S, Münch M, Mürdter TE, Thon KP, Steurer W, Aulitzky WE and Ulmer
C: A temperature of 40°C appears to be a critical threshold for
potentiating cytotoxic chemotherapy in vitro and in peritoneal
carcinomatosis patients undergoing HIPEC. Ann Surg Oncol. 22(Suppl
3): S758–S765. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Krawczyk PM, Eppink B, Essers J, Stap J,
Rodermond H, Odijk H, Zelensky A, van Bree C, Stalpers LJ, Buist
MR, et al: Mild hyperthermia inhibits homologous recombination,
induces BRCA2 degradation, and sensitizes cancer cells to poly
(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:9851–9856. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dewey WC: Arrhenius relationships from the
molecule and cell to the clinic. Int J Hyperthermia. 10:457–483.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ishiai S, Tahara W, Yamamoto E, Yamamoto R
and Nagai K: Histone deacetylase inhibitory effect of Brazilian
propolis and its association with the antitumor effect in Neuro2a
cells. Food Sci Nutr. 2:565–570. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Taira N, Nguyen BCQ, Be Tu PT and Tawata
S: Effect of Okinawa propolis on PAK1 activity, Caenorhabditis
elegans longevity, melanogenesis, and growth of cancer cells. J
Agric Food Chem. 64:5484–5489. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang S, Zhang C-P, Wang K, Li GQ and Hu
F-L: Recent advances in the chemical composition of propolis.
Molecules. 19:19610–19632. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Seydi E, Hosseini SA, Salimi A and
Pourahmad J: Propolis induce cytotoxicity on cancerous hepatocytes
isolated from rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma: Involvement of
ROS-mediated mitochondrial targeting. Pharma Nutrition. 4:143–150.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Seda Vatansever H, Sorkun K, Ismet
Deliloğlu Gurhan S, Ozdal-Kurt F, Turkoz E, Gencay O and Salih B:
Propolis from Turkey induces apoptosis through activating caspases
in human breast carcinoma cell lines. Acta Histochem. 112:546–556.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kouidhi B, Zmantar T and Bakhrouf A:
Anti-cariogenic and anti-biofilms activity of Tunisian propolis
extract and its potential protective effect against cancer cells
proliferation. Anaerobe. 16:566–571. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Frión-Herrera Y, Díaz-García A,
Ruiz-Fuentes J, Rodríguez-Sánchez H and Sforcin JM: Brazilian green
propolis induced apoptosis in human lung cancer A549 cells through
mitochondrial-mediated pathway. J Pharm Pharmacol. 67:1448–1456.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Demir S, Aliyazicioglu Y, Turan I, Misir
S, Mentese A, Yaman SO, Akbulut K, Kilinc K and Deger O:
Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity of Turkish propolis on
human lung cancer cell line. Nutr Cancer. 68:165–172. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Guzmán C, Bagga M, Kaur A, Westermarck J
and Abankwa D: ColonyArea: An ImageJ plugin to automatically
quantify colony formation in clonogenic assays. PLoS One.
9:e924442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Korchak HM, Rich AM, Wilkenfeld C,
Rutherford LE and Weissmann G: A carbocyanine dye,
DiOC6(3), acts as a mitochondrial probe in human
neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 108:1495–1501. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Suzuki K, Bose P, Leong-Quong RY, Fujita
DJ and Riabowol K: REAP: A two minute cell fractionation method.
BMC Res Notes. 3:294. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vaity C, Al-Subaie N and Cecconi M:
Cooling techniques for targeted temperature management post-cardiac
arrest. Crit Care. 19:1032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cai J, Yang J and Jones D: Mitochondrial
control of apoptosis: The role of cytochrome c. Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta (BBA). Bioenergetics. 1366:139–149. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Park M, Chae H-D, Yun J, Jung M, Kim YS,
Kim SH, Han MH and Shin DY: Constitutive activation of cyclin
B1-associated cdc2 kinase overrides p53-mediated G2-M arrest.
Cancer Res. 60:542–545. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kampinga HH: Cell biological effects of
hyperthermia alone or combined with radiation or drugs: A short
introduction to newcomers in the field. Int J Hyperthermia.
22:191–196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu X, Akutsu Y, Suganami A, Qin W, Hanari
N, Murakam K, Kano M, Usui A, Suito H, Takahashi M, et al: Low-dose
hyperthermia enhances the antitumor effects of chemotherapy in
squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 30:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Christophi C, Winkworth A, Muralihdaran V
and Evans P: The treatment of malignancy by hyperthermia. Surg
Oncol. 7:83–90. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Dewey WC: Arrhenius relationships from the
molecule and cell to the clinic. Int J Hyperthermia. 25:3–20. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Overgaard K and Overgaard J:
Investigations on the possibility of a thermic tumour therapy. I.
Short-wave treatment of a transplanted isologous mouse mammary
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 8:65–78. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dewey WC, Hopwood LE, Sapareto SA and
Gerweck LE: Cellular responses to combinations of hyperthermia and
radiation. Radiology. 123:463–474. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ishikawa T, Kokura S, Sakamoto N, Ando T,
Imamoto E, Hattori T, Oyamada H, Yoshinami N, Sakamoto M, Kitagawa
K, et al: Phase II trial of combined regional hyperthermia and
gemcitabine for locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer.
Int J Hyperthermia. 28:597–604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ishii H, Okada S, Tokuuye K, Nose H,
Okusaka T, Yoshimori M, Nagahama H, Sumi M, Kagami Y and Ikeda H:
Protracted 5-fluorouracil infusion with concurrent radiotherapy as
a treatment for locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer.
79:1516–1520. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Robins HI, Cohen JD, Schmitt CL, Tutsch
KD, Feierabend C, Arzoomanian RZ, Alberti D, d'Oleire F, Longo W
and Heiss C: Phase I clinical trial of carboplatin and 41.8 degrees
C whole-body hyperthermia in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol.
11:1787–1794. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stephens AD, Alderman R, Chang D, Edwards
GD, Esquivel J, Sebbag G, Steves MA and Sugarbaker PH: Morbidity
and mortality analysis of 200 treatments with cytoreductive surgery
and hyperthermic intraoperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy using
the coliseum technique. Ann Surg Oncol. 6:790–796. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Adachi S, Kokura S, Okayama T, Ishikawa T,
Takagi T, Handa O, Naito Y and Yoshikawa T: Effect of hyperthermia
combined with gemcitabine on apoptotic cell death in cultured human
pancreatic cancer cell lines. Int J Hyperthermia. 25:210–219. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Basel MT, Balivada S, Wang H, Shrestha TB,
Seo GM, Pyle M, Abayaweera G, Dani R, Koper OB, Tamura M, et al:
Cell-delivered magnetic nanoparticles caused hyperthermia-mediated
increased survival in a murine pancreatic cancer model. Int J
Nanomedicine. 7:297–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang L, Dong J, Ouyang W, Wang X and Tang
J: Anticancer effect and feasibility study of hyperthermia
treatment of pancreatic cancer using magnetic nanoparticles. Oncol
Rep. 27:719–726. 2012.
|
|
41
|
Partanen A, Tillander M, Yarmolenko PS,
Wood BJ, Dreher MR and Köhler MO: Reduction of peak acoustic
pressure and shaping of heated region by use of multifoci
sonications in MR-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound mediated
mild hyperthermia. Med Phys. 40:0133012013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Frazier N, Payne A, de Bever J, Dillon C,
Panda A, Subrahmanyam N and Ghandehari H: High intensity focused
ultrasound hyperthermia for enhanced macromolecular delivery. J
Control Release. 241:186–193. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Partanen A, Yarmolenko PS, Viitala A,
Appanaboyina S, Haemmerich D, Ranjan A, Jacobs G, Woods D, Enholm
J, Wood BJ, et al: Mild hyperthermia with magnetic resonance-guided
high-intensity focused ultrasound for applications in drug
delivery. Int J Hyperthermia. 28:320–336. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|