Spandidos Publications style
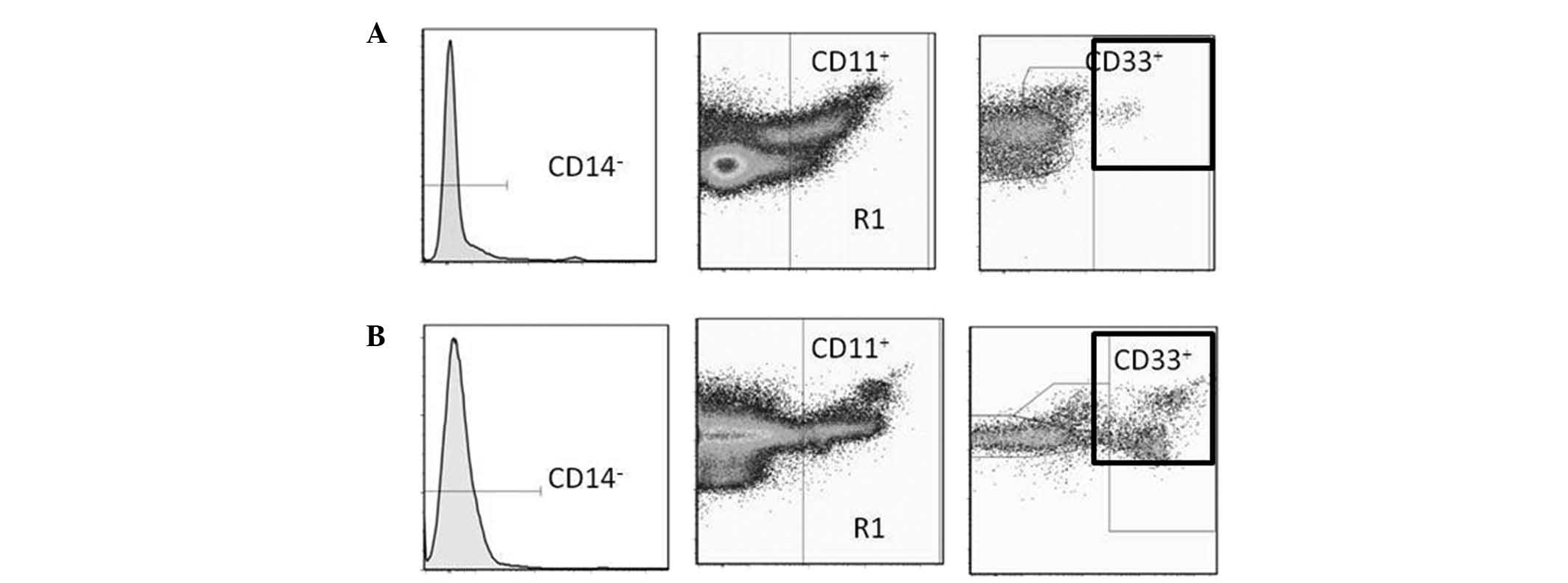
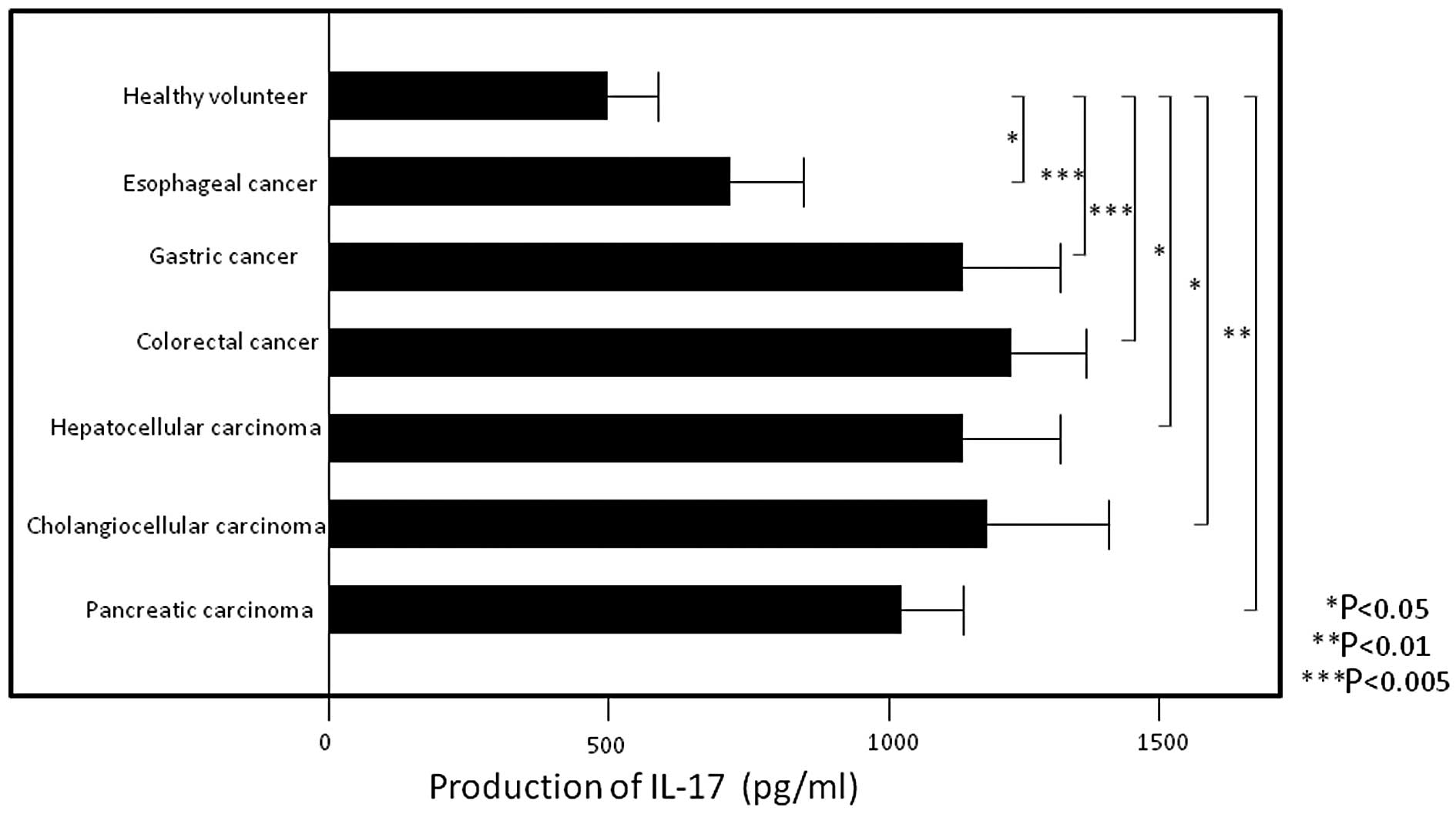
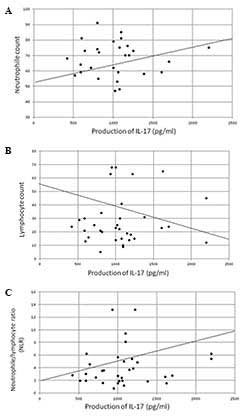
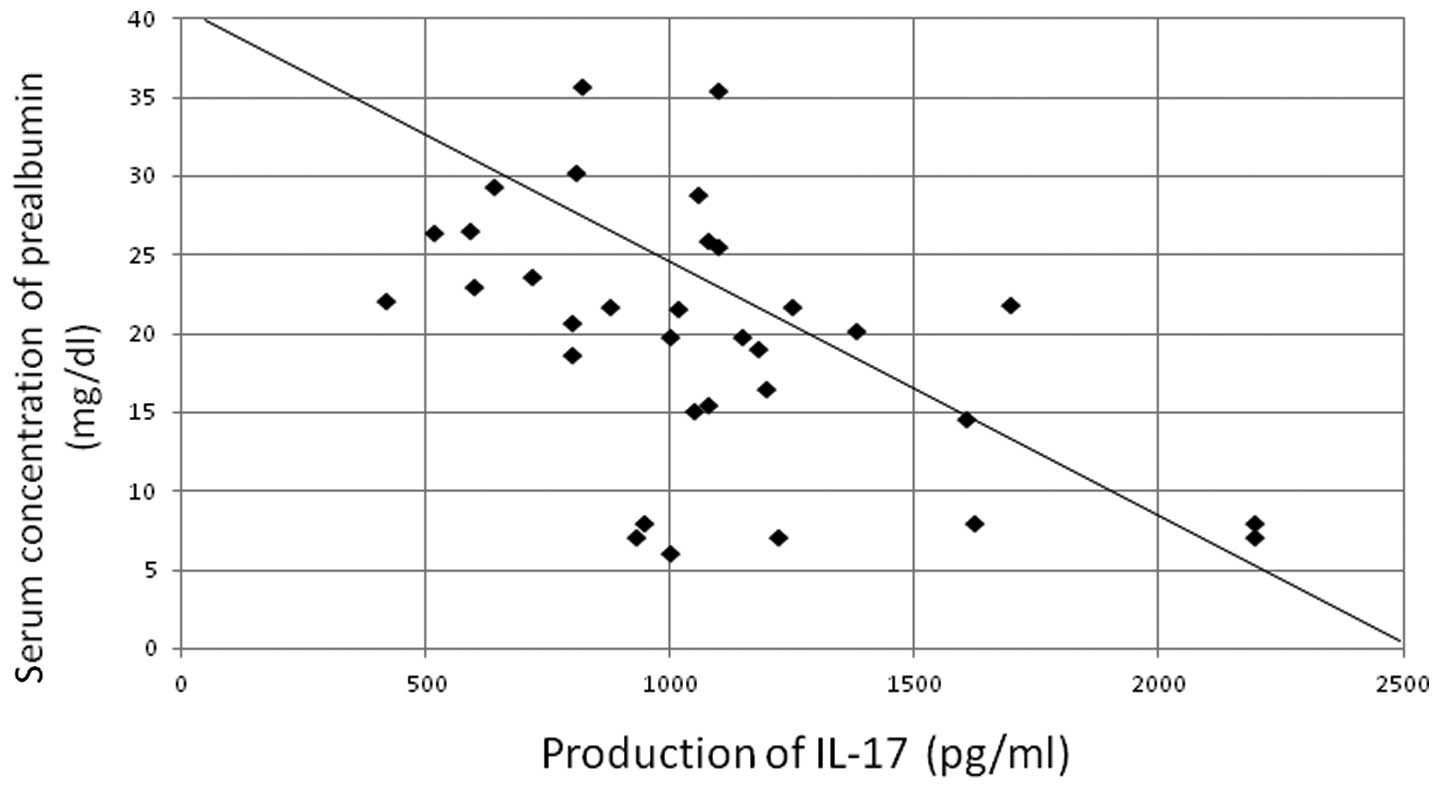
Yazawa T, Shibata M, Gonda K, Machida T, Suzuki S, Kenjo A, Nakamura I, Tsuchiya T, Koyama Y, Sakurai K, Sakurai K, et al: Increased IL‑17 production correlates with immunosuppression involving myeloid-derived suppressor cells and nutritional impairment in patients with various gastrointestinal cancers. Mol Clin Oncol 1: 675-679, 2013.
APA
Yazawa, T., Shibata, M., Gonda, K., Machida, T., Suzuki, S., Kenjo, A. ... Takenoshita, S. (2013). Increased IL‑17 production correlates with immunosuppression involving myeloid-derived suppressor cells and nutritional impairment in patients with various gastrointestinal cancers. Molecular and Clinical Oncology, 1, 675-679. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2013.134
MLA
Yazawa, T., Shibata, M., Gonda, K., Machida, T., Suzuki, S., Kenjo, A., Nakamura, I., Tsuchiya, T., Koyama, Y., Sakurai, K., Shimura, T., Tomita, R., Ohto, H., Gotoh, M., Takenoshita, S."Increased IL‑17 production correlates with immunosuppression involving myeloid-derived suppressor cells and nutritional impairment in patients with various gastrointestinal cancers". Molecular and Clinical Oncology 1.4 (2013): 675-679.
Chicago
Yazawa, T., Shibata, M., Gonda, K., Machida, T., Suzuki, S., Kenjo, A., Nakamura, I., Tsuchiya, T., Koyama, Y., Sakurai, K., Shimura, T., Tomita, R., Ohto, H., Gotoh, M., Takenoshita, S."Increased IL‑17 production correlates with immunosuppression involving myeloid-derived suppressor cells and nutritional impairment in patients with various gastrointestinal cancers". Molecular and Clinical Oncology 1, no. 4 (2013): 675-679. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2013.134