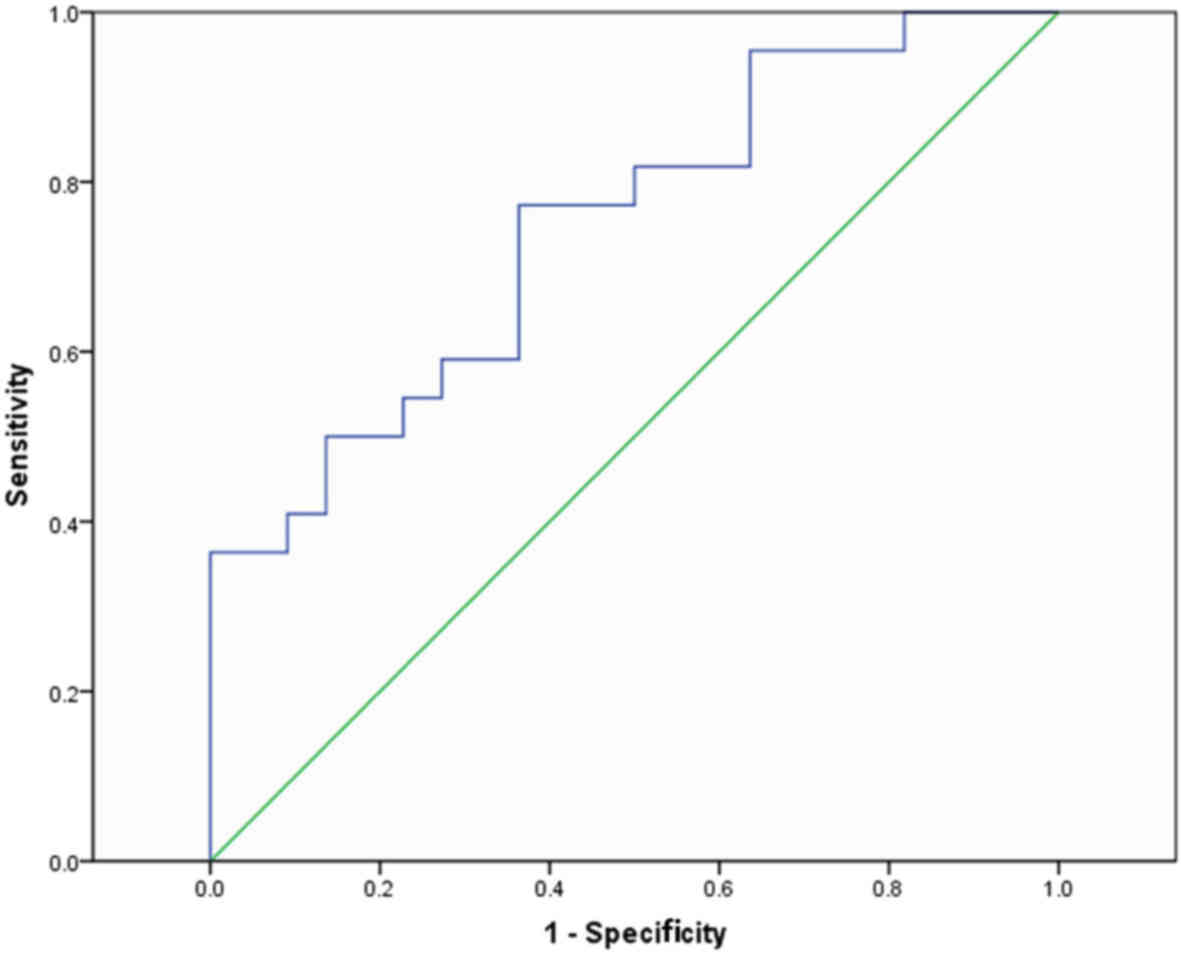
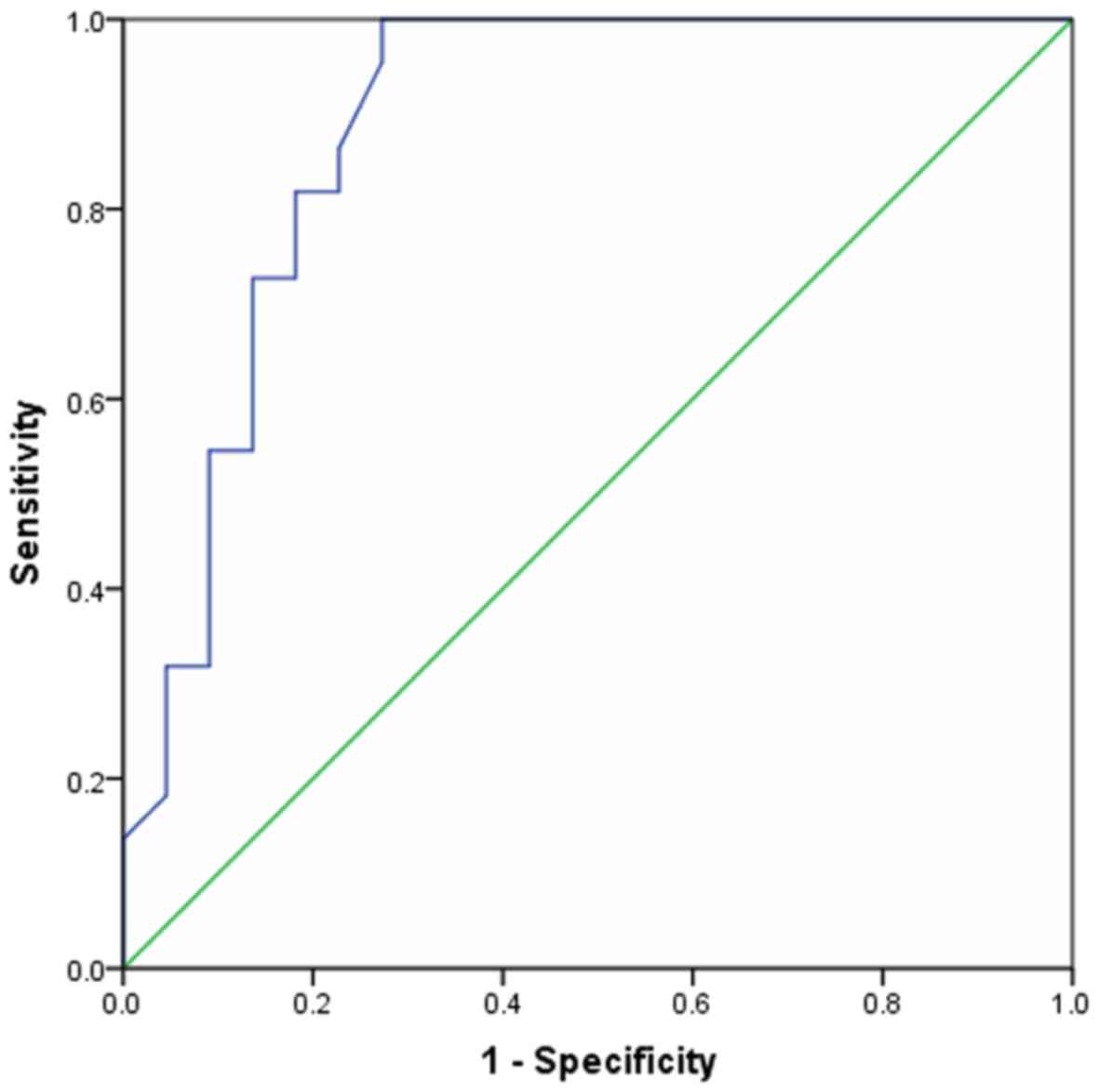
|
1
|
Freelove R and Walling AD: Pancreatic
cancer: Diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 73:485–492.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Balcom JH IV, Rattner DW, Warshaw AL,
Chang Y and Fernandez-del Castillo C: Ten-year experience with 733
pancreatic resections: Changing indications, older patients, and
decreasing length of hospitalization. Arch Surg. 136:391–398. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gouma DJ, van Geenen RC, van Gulik TM, de
Haan RJ, de Wit LT, Busch OR and Obertop H: Rates of complications
and death after pancreaticoduodenectomy: Risk factors and the
impact of hospital volume. Ann Surg. 232:786–795. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cameron JL, Pitt HA, Yeo CJ, Lillemoe KD,
Kaufman HS and Coleman J: One hundred and forty-five consecutive
pancreaticoduodenectomies without mortality. Ann Surg. 217:430–438.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aranha GV, Aaron JM, Shoup M and Pickleman
J: Current management of pancreatic fistula after
pancreaticoduodenectomy. Surgery. 140:561–569. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bassi C, Butturini G, Molinari E, Mascetta
G, Salvia R, Falconi M, Gumbs A and Pederzoli P: Pancreatic fistula
rate after pancreatic resection. The importance of definitions. Dig
Surg. 21:54–59. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mathur A, Pitt HA, Marine M, Saxena R,
Schmidt CM, Howard TJ, Nakeeb A, Zyromski NJ and Lillemoe KD: Fatty
pancreas: A factor in postoperative pancreatic fistula. Ann Surg.
246:1058–1064. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Lee KB, Kim SW, Kang MJ,
Jang JY, Kannengiesser S, Han JK and Choi BI: Pancreatic steatosis
and fibrosis: Quantitative assessment with preoperative
multiparametric MR imaging. Radiology. 279:140–150. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim Z, Kim MJ, Kim JH, Jin SY, Kim YB, Seo
D, Choi D, Hur KY, Kim JJ, Lee MH and Moon C: Prediction of
post-operative pancreatic fistula in pancreaticoduodenectomy
patients using pre-operative MRI: A pilot study. HPB (Oxford).
11:215–221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Scialpi M, Cagini L, Pierotti L, De Santis
F, Pusiol T, Piscioli I, Magli M, D'Andrea A, Brunese L and Rotondo
A: Detection of small (≤2 cm) pancreatic adenocarcinoma and
surrounding parenchyma: correlations between enhancement patterns
at triphasic MDCT and histologic features. BMC Gastroenterol.
14:162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fukumura Y, Kumasaka T, Mitani K, Karita K
and Suda K: Expression of transforming growth factor beta1, beta2,
and beta3 in chronic, cancer-associated, obstructive pancreatitis.
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 130:356–361. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kamisawa T, Takuma K, Anjiki H, Egawa N,
Hata T, Kurata M, Honda G, Tsuruta K, Suzuki M, Kamata N and Sasaki
T: Differentiation of autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic
cancer by diffusion-weighted MRI. Am J Gastroenterol.
105:1870–1875. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Muraoka N, Uematsu H, Kimura H, Imamura Y,
Fujiwara Y, Murakami M, Yamaguchi A and Itoh H: Apparent diffusion
coefficient in pancreatic cancer: Characterization and
histopathological correlations. J Magn Reson Imaging. 27:1302–1308.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rosso E, Casnedi S, Pessaux P,
Oussoultzoglou E, Panaro F, Mahfud M, Jaeck D and Bachellier P: The
role of ‘fatty pancreas’ and of BMI in the occurrence of pancreatic
fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Gastrointest Surg.
13:1845–1851. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee SE, Jang JY, Lim CS, Kang MJ, Kim SH,
Kim MA and Kim SW: Measurement of pancreatic fat by magnetic
resonance imaging: Predicting the occurrence of pancreatic fistula
after pancreatoduodenectomy. Ann Surg. 251:932–936. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Molinari E, Bassi C, Salvia R, Butturini
G, Crippa S, Talamini G, Falconi M and Pederzoli P: Amylase value
in drains after pancreatic resection as predictive factor of
postoperative pancreatic fistula: Results of a prospective study in
137 patients. Ann Surg. 246:281–287. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bassi C, Dervenis C, Butturini G,
Fingerhut A, Yeo C, Izbicki J, Neoptolemos J, Sarr M, Traverso W
and Buchler M: International Study Group on Pancreatic Fistula
Definition: Postoperative pancreatic fistula: An international
study group (ISGPF) definition. Surgery. 138:8–13. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Puig-Diví V, Molero X, Vaquero E, Salas A,
Guarner F and Malagelada J: Ethanol feeding aggravates
morphological and biochemical parameters in experimental chronic
pancreatitis. Digestion. 60:166–174. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Puig-Diví V, Molero X, Salas A, Guarner F,
Guarner L and Malagelada JR: Induction of chronic pancreatic
disease by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid infusion into rat
pancreatic ducts. Pancreas. 13:417–424. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Butturini G, Marcucci S, Molinari E,
Mascetta G, Landoni L, Crippa S and Bassi C: Complications after
pancreaticoduodenectomy: The problem of current definitions. J
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 13:207–211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tajima Y, Kuroki T, Tsuneoka N, Adachi T,
Kosaka T, Okamoto T, Takatsuki M, Eguchi S and Kanematsu T:
Anatomy-specific pancreatic stump management to reduce the risk of
pancreatic fistula after pancreatic head resection. World J Surg.
33:2166–2176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sanjay P, Fawzi A, Fulke JL, Kulli C, Tait
IS, Zealley IA and Polignano FM: Late post pancreatectomy
haemorrhage. Risk factors and modern management. JOP. 11:220–225.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yencilek E, Telli S, Tekesin K, Ozgür A,
Cakır O, Türkoğlu O, Meriç K and Simşek M: The efficacy of
diffusion weighted imaging for detection of acute pancreatitis and
comparison of subgroups according to Balthazar classification. Turk
J Gastroenterol. 25:553–557. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Akisik MF, Aisen AM, Sandrasegaran K,
Jennings SG, Lin C, Sherman S, Lin JA and Rydberg M: Assessment of
chronic pancreatitis: Utility of diffusion-weighted MR imaging with
secretin enhancement. Radiology. 250:103–109. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shinya S, Sasaki T, Nakagawa Y, Guiquing
Z, Yamamoto F and Yamashita Y: Acute pancreatitis successfully
diagnosed by diffusion-weighted imaging: A case report. World J
Gastroenterol. 14:5478–5480. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Frozanpor F, Loizou L, Ansorge C,
Segersvärd R, Lundell L and Albiin N: Preoperative pancreas CT/MRI
characteristics predict fistula rate after pancreaticoduodenectomy.
World J Surg. 36:1858–1865. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lewin M, Poujol-Robert A, Boëlle PY,
Wendum D, Lasnier E, Viallon M, Guéchot J, Hoeffel C, Arrivé L,
Tubiana JM and Poupon R: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance
imaging for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C.
Hepatology. 46:658–665. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yoshikawa T, Kawamitsu H, Mitchell DG,
Ohno Y, Ku Y, Seo Y, Fujii M and Sugimura K: ADC measurement of
abdominal organs and lesions using parallel imaging technique. AJR
Am J Roentgenol. 187:1521–1530. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Patel J, Sigmund EE, Rusinek H, Oei M,
Babb JS and Taouli B: Diagnosis of cirrhosis with intravoxel
incoherent motion diffusion MRI and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI
alone and in combination: Preliminary experience. J Magn Reson
Imaging. 31:589–600. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kah Heng CA, Salleh I, San TS, Ying F and
Su-Ming T: Pancreatic fistula after distal pancreatectomy:
Incidence, risk factors and management. ANZ J Surg. 80:619–623.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Watanabe H, Kanematsu M, Tanaka K, Osada
S, Tomita H, Hara A, Goshima S, Kondo H, Kawada H, Noda Y, et al:
Fibrosis and postoperative fistula of the pancreas: Correlation
with MR imaging findings-preliminary results. Radiology.
270:791–799. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jimenez RE and Hawkins WG: Emerging
strategies to prevent the development of pancreatic fistula after
distal pancreatectomy. Surgery. 152 (3 Suppl 1):S64–S70. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Harada N, Ishizawa T, Inoue Y, Aoki T,
Sakamoto Y, Hasegawa K, Sugawara Y, Tanaka M, Fukayama M and Kokudo
N: Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging of the pancreas for
estimation of pathologic fibrosis and risk of postoperative
pancreatic fistula. J Am Coll Surg. 219:887–894.e5. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chang YR, Kang JS, Jang JY, Jung WH, Kang
MJ, Lee KB and Kim SW: Prediction of pancreatic fistula after
distal pancreatectomy based on cross-sectional images. World J
Surg. 41:1610–1617. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wiggermann P, Grützmann R, Weissenböck A,
Kamusella P, Dittert DD and Stroszczynski C: Apparent diffusion
coefficient measurements of the pancreas, pancreas carcinoma, and
mass-forming focal pancreatitis. Acta Radiol. 53:135–139. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gallix BP, Bret PM, Atri M, Lecesne R and
Reinhold C: Comparison of qualitative and quantitative measurements
on unenhanced T1-weighted fat saturation MR images in predicting
pancreatic pathology. J Magn Reson Imaging. 21:583–589. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Barral M, Sebbag-Sfez D, Hoeffel C, Chaput
U, Dohan A, Eveno C, Boudiaf M and Soyer P: Characterization of
focal pancreatic lesions using normalized apparent diffusion
coefficient at 1.5-Tesla: Preliminary experience. Diagn Interv
Imaging. 94:619–627. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|