Introduction
The prognosis of gallbladder cancer (GBC) with lymph
node metastases is poor. The 5-year survival rate following
surgical resection has been reported to be 65% for patients with no
lymph node metastases and <30% for those with regional lymph
node metastases (pN1) (1). In the
pN1 group, lymph node metastases characteristically arise in the
pericholedochal area or the posterosuperior pancreaticoduodenal
region, rather than around the hepatic artery (2,3).
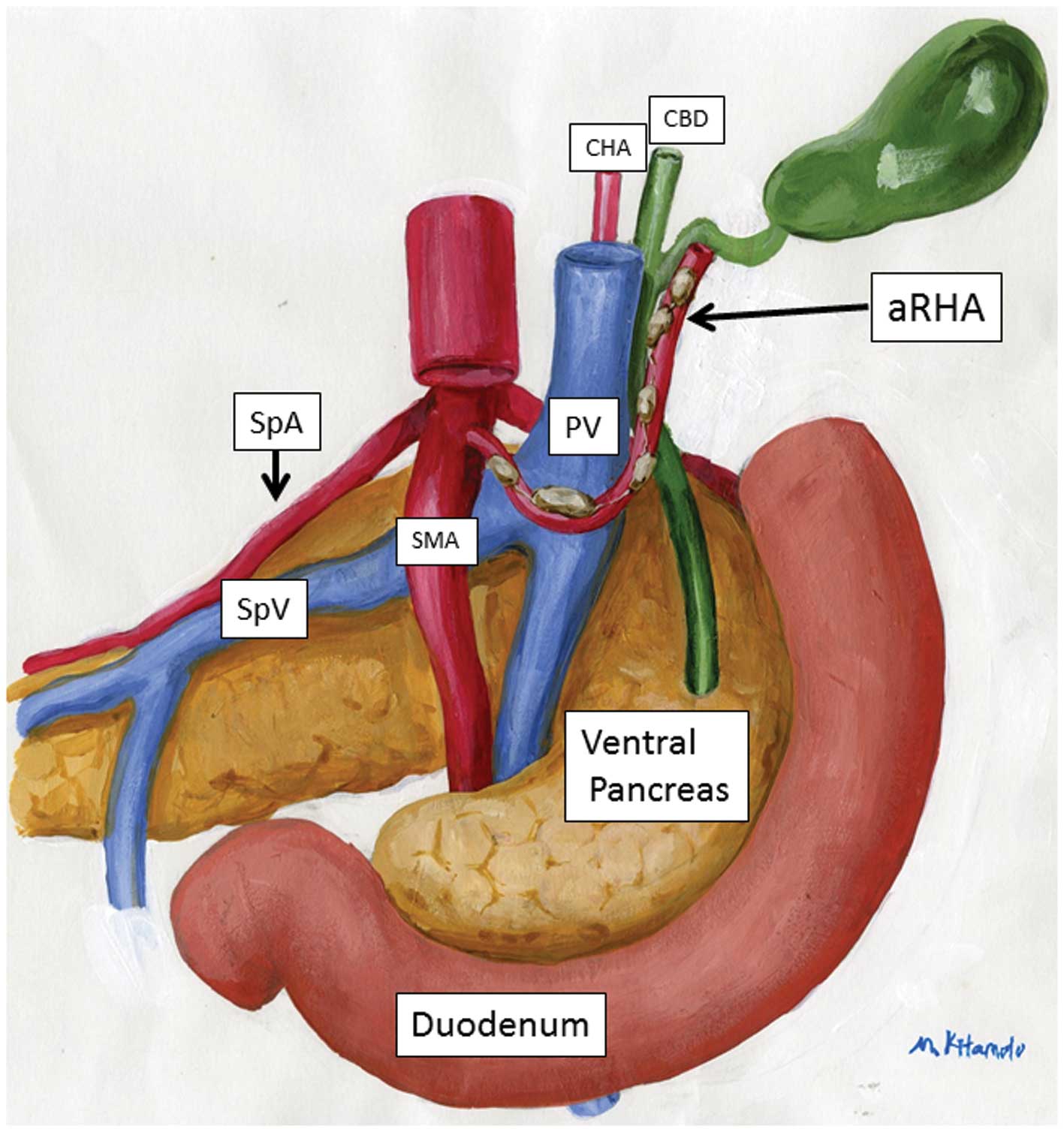
However, no feeding arteries are present around the pericholedochal
lymph nodes and posterosuperior pancreaticoduodenal lymph nodes
(PPLNs), although lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels generally exist
along a feeding artery (4–7).
We previously performed pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD)
for pancreatic cancer in patients with an aberrant right hepatic
artery (aRHA). In such cases, PPLNs were distributed along the
aRHA. This artery is considered to represent an embryonic right
hepatic artery (eRHA) that has not regressed. We hypothesized that
the artery responsible for PPLNs would be the eRHA. If this
hypothesis is accurate, lymphadenectomy for GBC should be performed
based on the course of the eRHA (8). The aim of this study was to determine
the artery supplying the PPLNs.
Materials and methods
Patients
Between 1997 and 2005, a total of 58 patients
underwent PD for invasive pancreatic ductal cancer in the
Department of Gastroenterologic Surgery at Kanazawa University.
Among these cases, radical PD with major vessel resection [superior
mesenteric artery (SMA) and superior mesenteric vein (SMV)
resection] was performed in 18 patients for complete clearance of
the soft tissues around these arteries (9). This study was approved by the Ethics
Committee at our institution and was conducted in accordance with
the Declaration of Helsinki.
Specimens
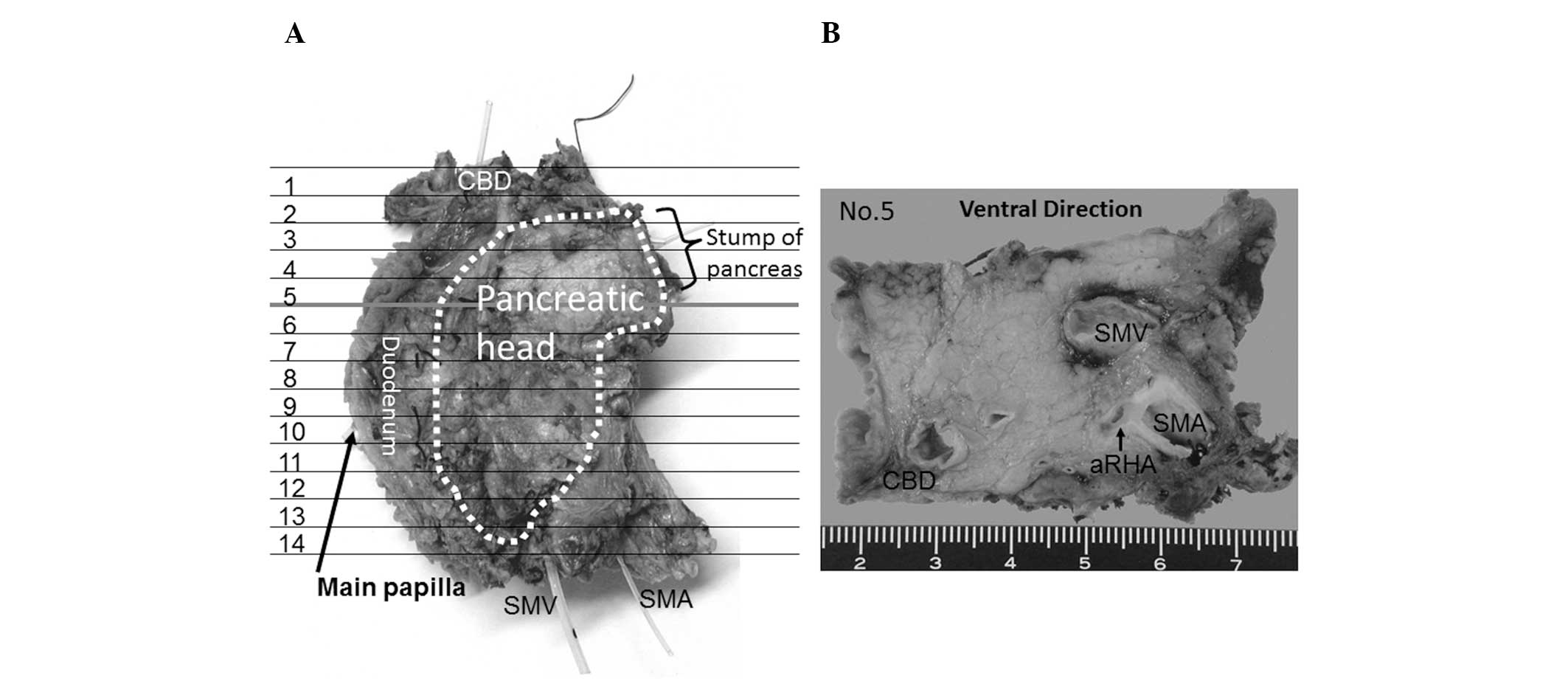
The resected specimens were immediately fixed in 10%
neutral-buffered formaldehyde solution, then cut horizontally into
5-mm tissue blocks corresponding to computed tomography images,
dehydrated and fixed in paraffin (Fig.
1). Finally, the specimens were cut into 5-μm sections and
stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Eight cases in which evaluation
of the lymphatic route was difficult, due to failed fixation of
specimens or development of pancreatic cancer lesions, were
excluded from our study. For the evaluation, the patients were
divided into 2 groups, those with an aRHA and those with a normal
hepatic artery and no aRHA. Each section was carefully examined
under a light microscope to determine the presence of lymph nodes
around the blood vessels and their distribution (Fig. 2).
Results
Cases
Among the 18 cases, 10 met the inclusion criteria
and were examined for the pattern of lymphatic spread. Among these,
2 patients had an aRHA and 8 exhibited normal arterial branching.
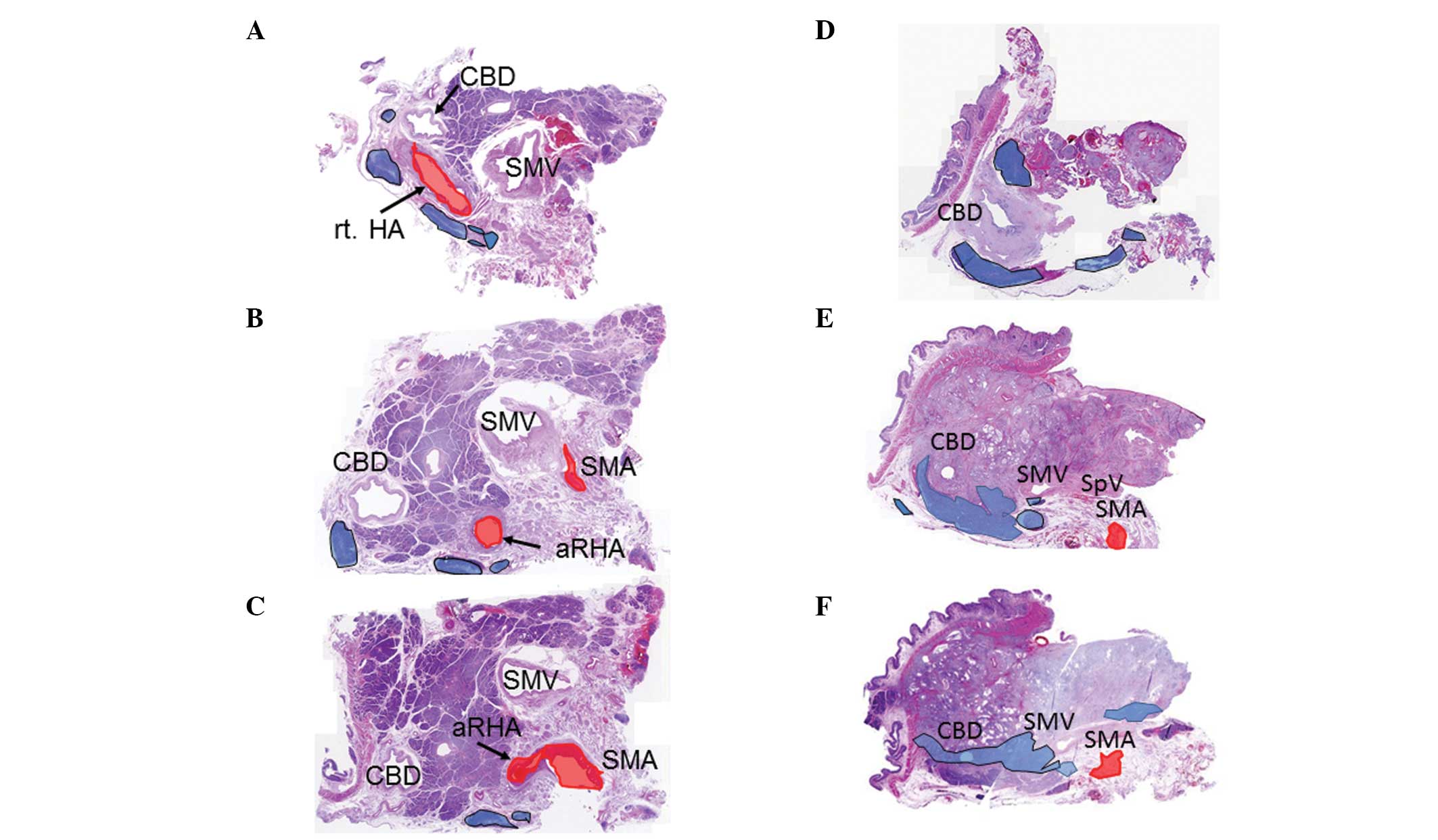
Representative examples of cases with typical distribution of lymph
nodes are shown in Fig. 2. In
these specimens, removal of the duodenum, pancreatic head, bile
duct, SMV, SMA and surrounding connective tissue by en bloc
resection allowed for the determination of the lymphatic route
between the area surrounding the SMA and the pericholedochal area
(9).
Arterial pattern
Examination of the course of the arteries in the 2
cases with an aRHA revealed that the vessel branched from the right
side of the SMA (Fig. 2C) and
crossed dorsal to the SMV and pancreatic head (Fig. 2B), then proceeded to the right side
of the bile duct (Fig. 2A).
Observation of the lymph node distribution revealed enlarged PPLNs
along the aRHA in both patients (Fig.
3). In the 8 patients with normal hepatic artery branching,
enlarged lymph nodes were observed in the pericholedochal area,
dorsal to the pancreatic head, in the retroportal area and on the
right side of the SMA (Fig. 3).
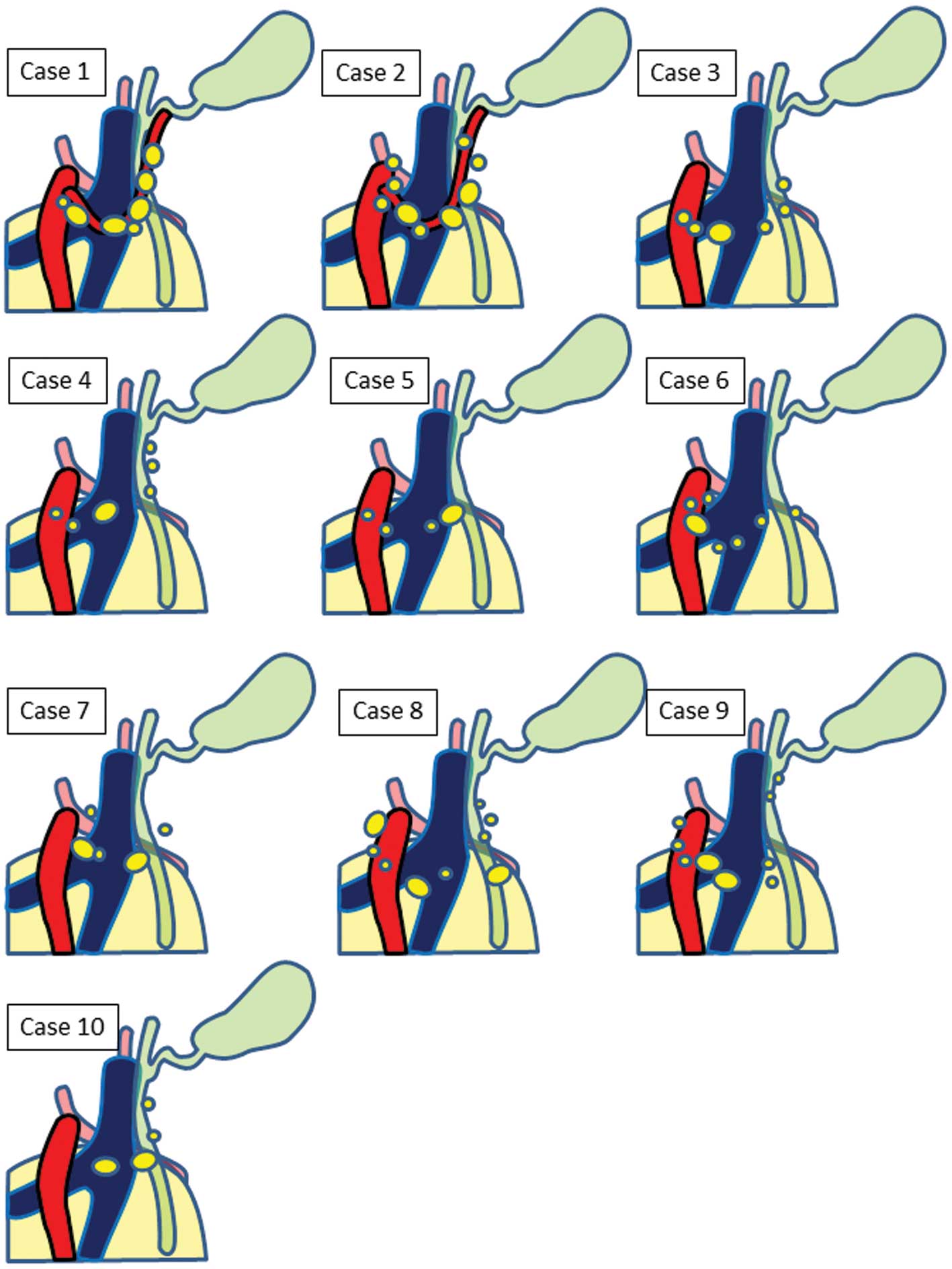
Interestingly, the lymph node distribution closely resembled that
of cases with an aRHA, appearing with a similar distribution, but
where a regressed eRHA would have passed (Fig. 4).
Discussion
Radical lymph node dissection for GBC is crucial
(10) and understanding the
pattern of lymph node metastatic spread from GBC is mandatory for
surgeons (11,12). This study demonstrated that PPLNs
were distributed along the aRHA. In patients with a normal right
hepatic artery, these lymph nodes were also distributed in a
similar manner, suggesting distribution along the regressed
eRHA.
During early human fetal life, 3 vessels exist, the
embryonic left, middle and right hepatic arteries (13). During the developmental process,
the embryonic left and right hepatic arteries regress and the
middle hepatic artery persists. By adulthood, the embryonic middle
hepatic artery has differentiated into the right, middle and left
hepatic arteries. However, in some cases the eRHA persists without
regression, representing an aRHA. The lymphatics travel primarily
with blood vessels (6,7). Even if the artery completely
regresses, the accompanying lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes and
nerves presumably remain (4). We
therefore considered that the enlarged lymph nodes observed in
cases with normal hepatic arterial branching were compatible with
lymph nodes along a regressed eRHA.
An understanding of this concept may contribute to
lymphadenectomy for GBC. As the standard surgical treatment in
colorectal cancer, intestinal resection and regional
lymphadenectomy, including feeding arteries, is considered
essential (13,14). In GBC up to stage IIa, the
frequency of lymph node metastasis in the pericholedochal area has
been reported to be higher compared to that of lymph node
metastasis around the hepatic artery (2,3). The
lymphatic pathway of PPLNs has been called ‘the right route of
lymphatic drainage of the gallbladder’ in Japan and has been
considered as the main lymphatic route requiring resection in the
treatment of GBC (12,15,16).
From the present study, the right route is considered part of the
route of the eRHA. To completely remove the lymphatic basin in the
eRHA route, resection of the nodes in the pericholedochal area,
posterosuperior pancreaticoduodenal area and retroportal area
should also be performed (14).
This consideration is undoubtedly a key reason as to why the
addition of PD is associated with improved prognosis for patients
with GBC (17–19). We hypothesize that PD allows en
bloc resection of the lymphatic basin along the eRHA. However,
performing the surgery with awareness of the fetal pathway of
lymphatic vessels may enable surgery with appropriate
lymphadenectomy, without PD, for GBC.
Clearly, this hypothesis requires confirmation by
further embryological studies; however, we suggest that surgery
with an awareness of lymph node metastasis along the eRHA may lead
to improved prognosis for patients with GBC and we suggest that the
feeding artery for PPLNs is either the regressed eRHA or an aRHA
persisting without regression.
References
|
1
|
Miyakawa S, Ishihara S, Horiguchi A,
Takada T, Miyazaki M and Nagakawa T: Biliary tract cancer
treatment: 5,584 results from the Biliary Tract Cancer Statistics
Registry from 1998 to 2004 in Japan. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
16:1–7. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsukada K, Kurosaki I, Uchida K, et al:
Lymph node spread from carcinoma of the gallbladder. Cancer.
80:661–667. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nagakawa T, Kayahara M, Ikeda S, et al:
Biliary tract cancer treatment: results from the Biliary Tract
Cancer Statistics Registry in Japan. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
9:569–575. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yi SQ, Shimokawa T, Akita K, Ohta T,
Kayahara M, Miwa K and Tanaka S: Anatomical study of the pancreas
in the house musk shrew (Suncus murinus), with special
reference to the blood supply and innervation. Anat Rec A Discov
Mol Cell Evol Biol. 273:630–635. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cha YR, Fujita M, Butler M, Isogai S,
Kochhan E, Siekmann AF and Weinstein BM: Chemokine signaling
directs trunk lymphatic network formation along the preexisting
blood vasculature. Dev Cell. 22:824–836. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Geudens I, Herpers R, Hermans K, et al:
Role of delta-like-4/Notch in the formation and wiring of the
lymphatic network in zebrafish. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
30:1695–1702. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liao S, Padera TP and Jain RK: Notch leads
lymphatics and links them to blood vessels. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 30:1682–1683. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miwa K, Kinami S, Taniguchi K, Fushida S,
Fujimura T and Nonomura A: Mapping sentinel nodes in patients with
early-stage gastric carcinoma. Br J Surg. 90:178–182. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kitagawa H, Ohta T, Makino I, et al:
Carcinomas of the ventral and dorsal pancreas exhibit different
patterns of lymphatic spread. Front Biosci. 13:2728–2735. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang JD, Liu YB, Quan ZW, Li SG, Wang XF
and Shen J: Role of regional lymphadenectomy in different stage of
gallbladder carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 56:593–596.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Uesaka K, Yasui K, Morimoto T, et al:
Visualization of routes of lymphatic drainage of the gallbladder
with a carbon particle suspension. J Am Coll Surg. 183:345–350.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shirai Y, Yoshida K, Tsukada K, Ohtani T
and Muto T: Identification of the regional lymphatic system of the
gallbladder by vital staining. Br J Surg. 79:659–662. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen SL and Bilchik AJ: Resecting lymph
nodes in colon cancer: more than a staging operation? Ann Surg
Oncol. 14:2175–2176. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takeuchi H and Kitagawa Y: Sentinel node
navigation surgery in patients with early gastric cancer. Dig Surg.
30:104–111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ito M, Mishima Y and Sato T: An anatomical
study of the lymphatic drainage of the gallbladder. Surg Radiol
Anat. 13:89–104. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deki H and Sato T: An anatomic study of
the peripancreatic lymphatics. Surg Radiol Anat. 10:121–135. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shirai Y, Ohtani T, Tsukada K and
Hatakeyama K: Pancreaticoduodenectomy for gallbladder cancer with
peripancreatic nodal metastases. Hepatogastroenterology.
44:376–377. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Doty JR, Cameron JL, Yeo CJ, Campbell K,
Coleman J and Hruban RH: Cholecystectomy, liver resection, and
pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy for gallbladder cancer:
report of five cases. J Gastrointest Surg. 6:776–780. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shirai Y, Wakai T and Hatakeyama K:
Radical lymph node dissection for gallbladder cancer: indications
and limitations. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 16:221–232. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|