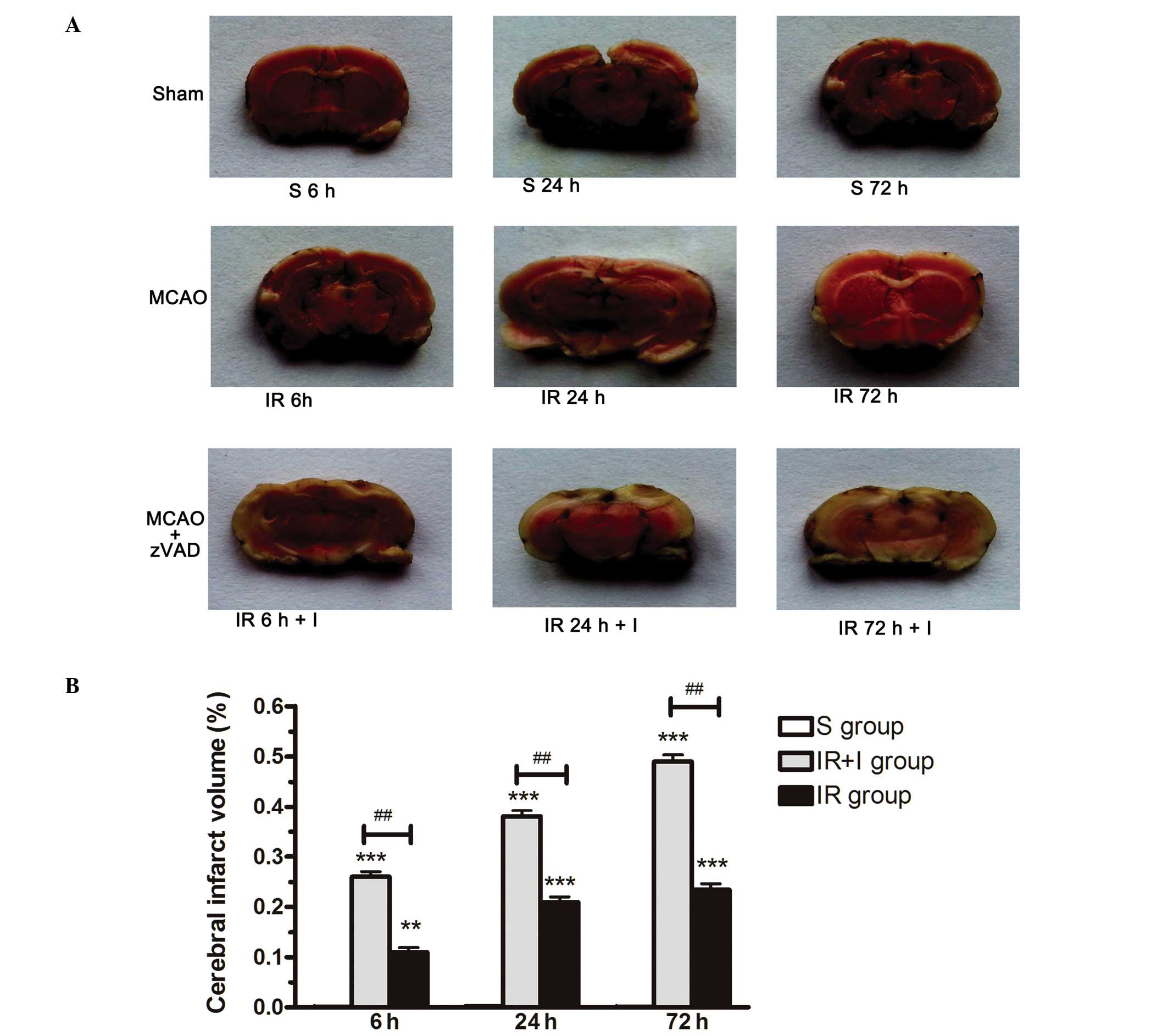
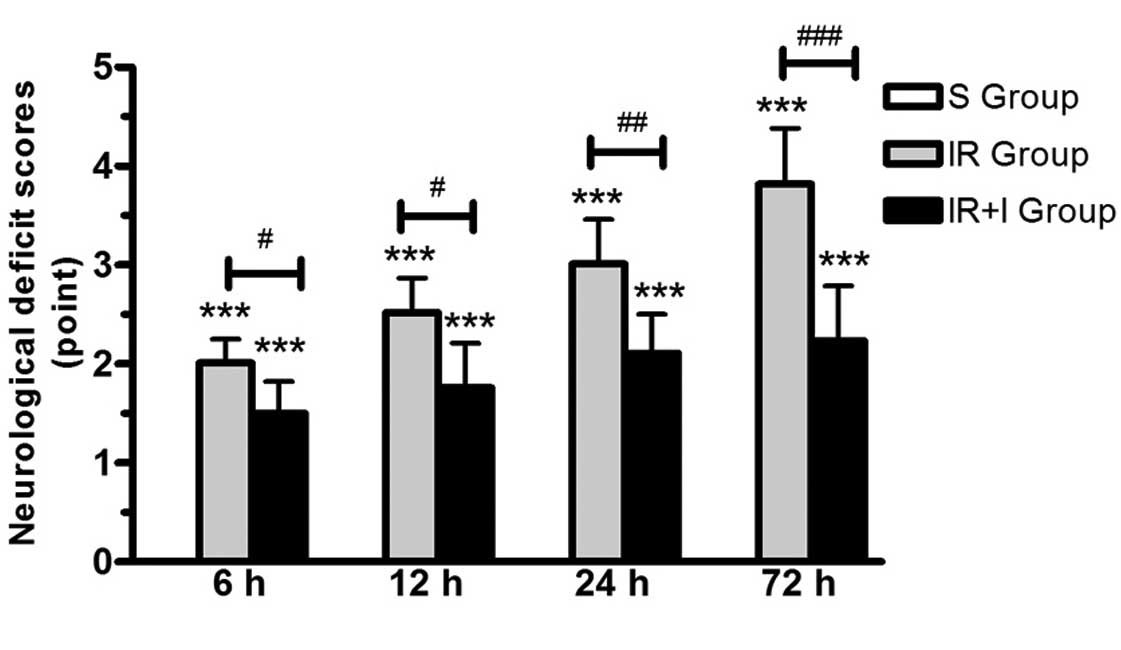
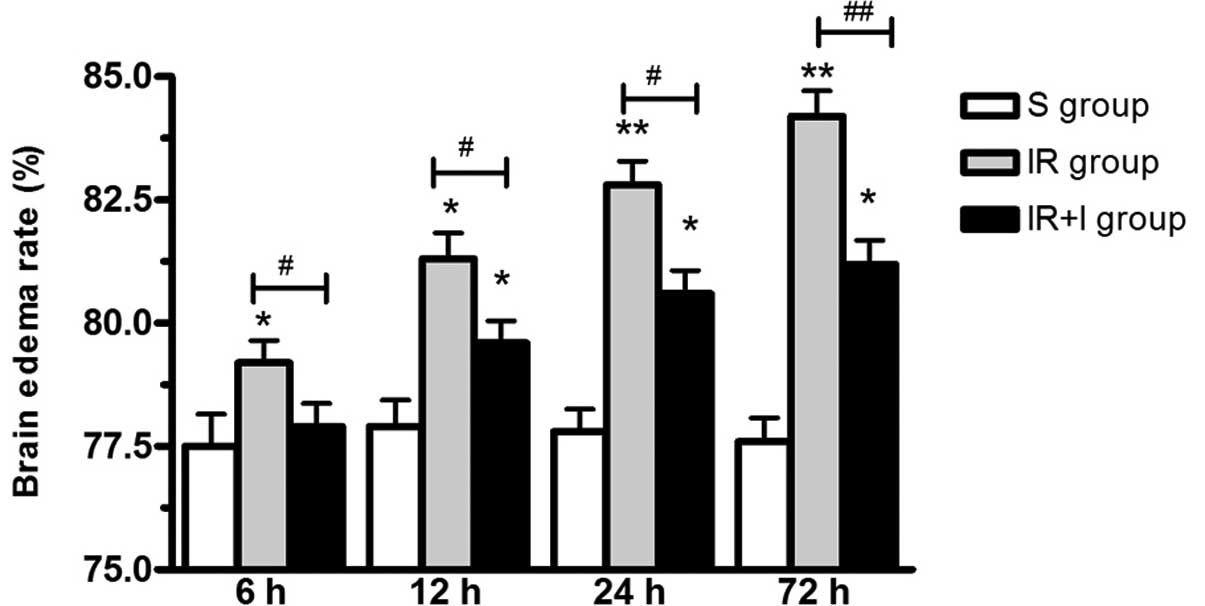
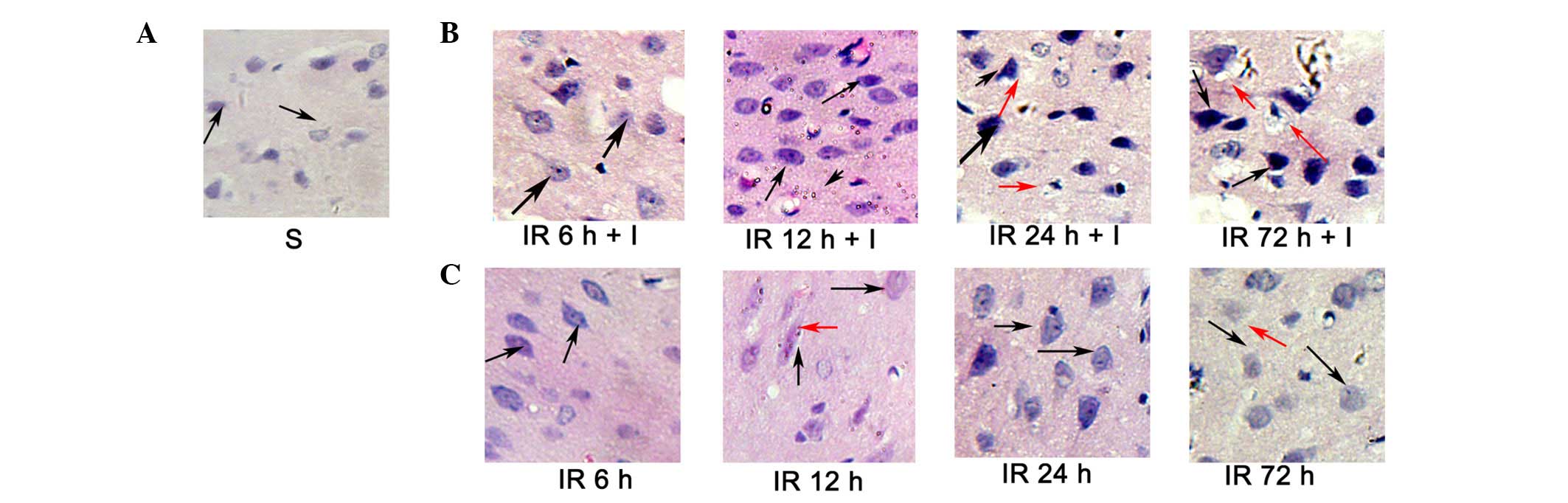
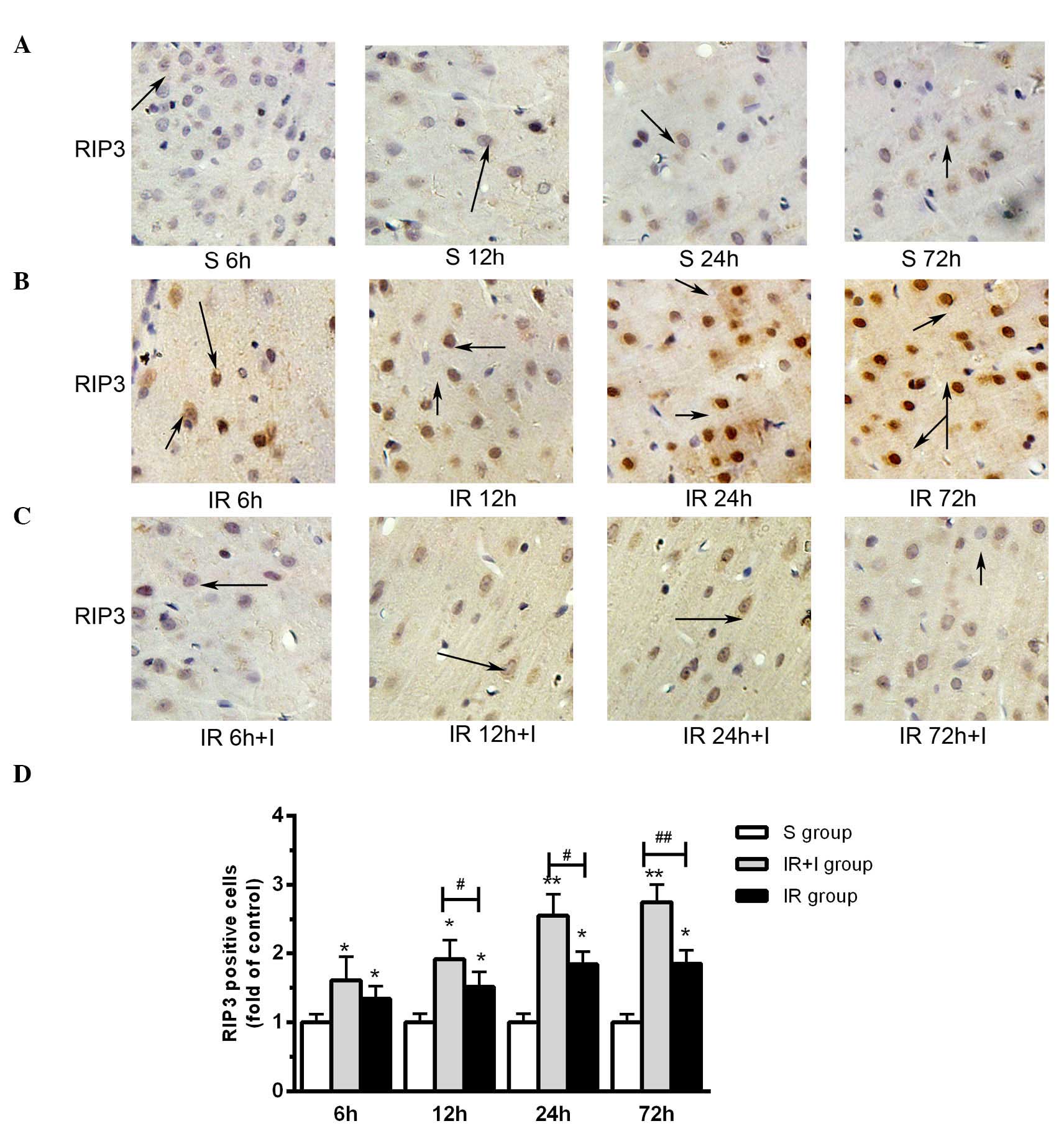
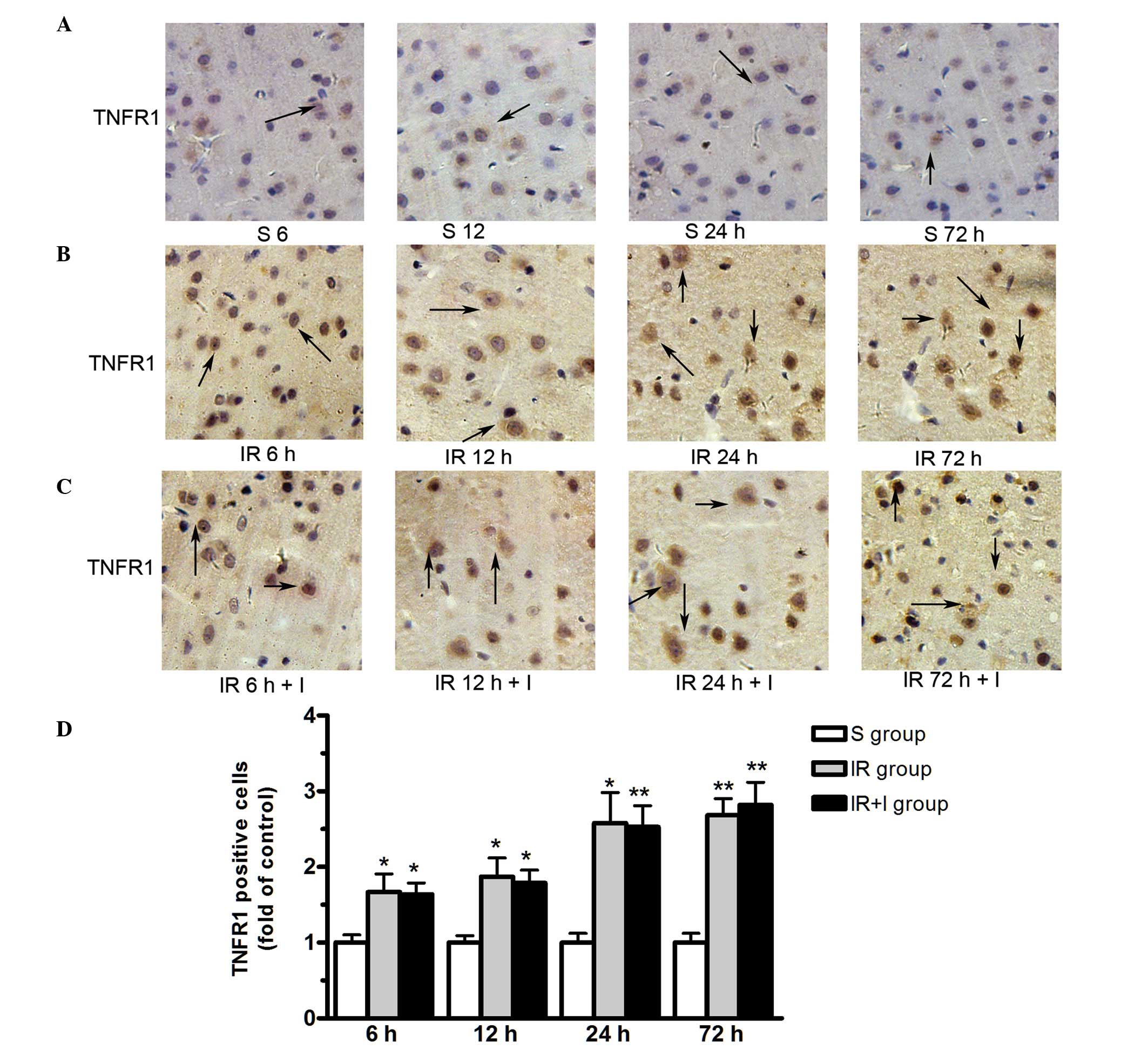
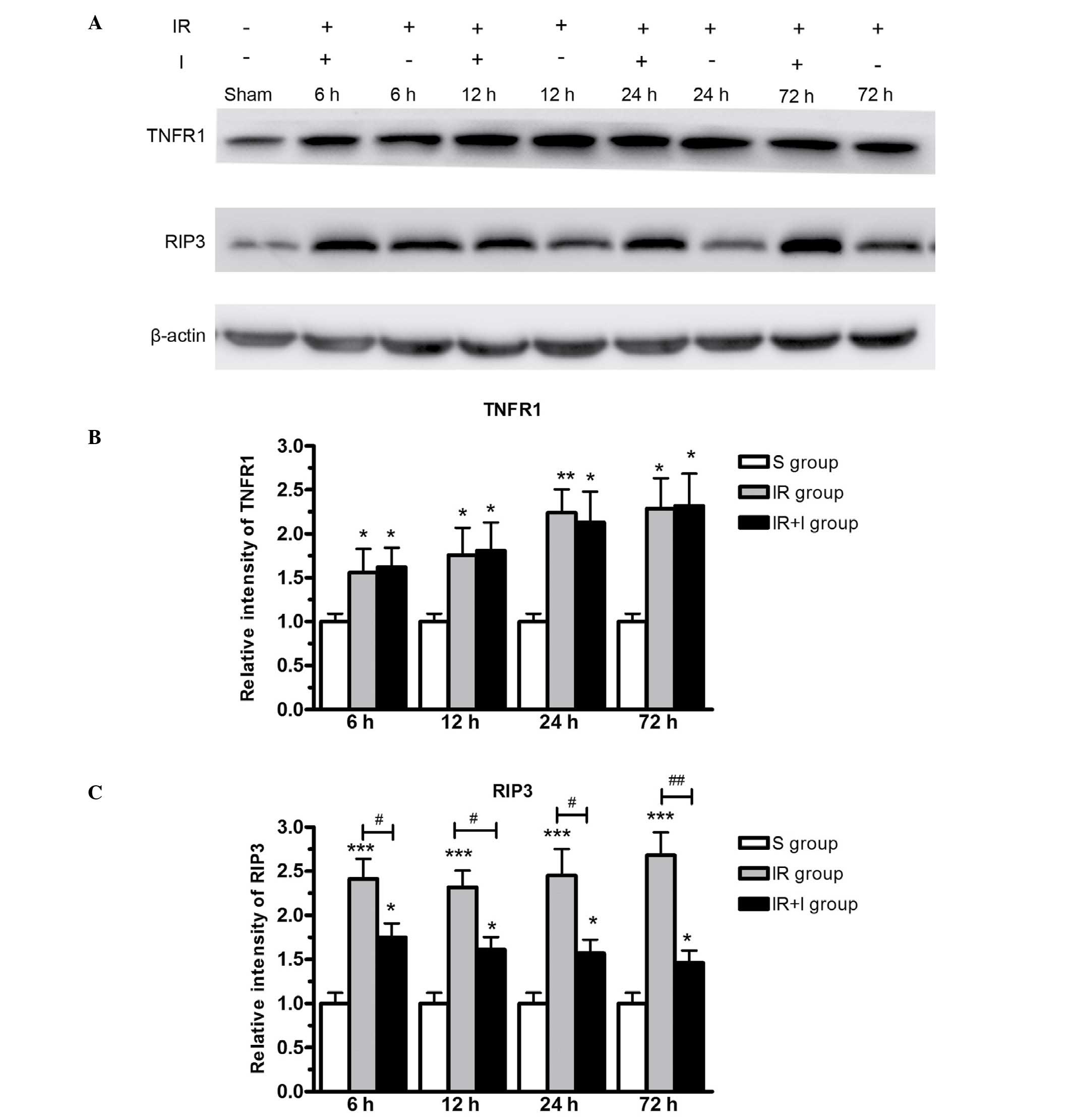
|
1
|
Cerqueira NF, Hussni CA and Yoshida WB:
Pathophysiology of mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion: A review. Acta
Cir Bras. 20:336–343. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Takahashi H, Xia P, Cui J, Talantova M,
Bodhinathan K, Li W, Holland EA, Tong G, Piña Crespo J, Zhang D, et
al: Pharmacologically targeted NMDA receptor antagonism by
NitroMemantine for cerebrovascular disease. Sci Rep. 5:147812015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Granger DN and Kvietys PR: Reperfusion
injury and reactive oxygen species: The evolution of a concept.
Redox Biol. 6:524–551. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu M, Chen X, Gu Y, Peng T, Yang D, Chang
RC, So KF, Liu K and Shen J: Baicalin can scavenge peroxynitrite
and ameliorate endogenous peroxynitrite-mediated neurotoxicity in
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Ethnopharmacol.
150:116–124. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang J, Wang P, Li S, Wang S, Li Y, Liang
N and Wang M: Mdivi-1 prevents apoptosis induced by
ischemia-reperfusion injury in primary hippocampal cells via
inhibition of reactive oxygen species-activated mitochondrial
pathway. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 23:1491–1499. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Van Herreweghe F, Festjens N, Declercq W
and Vandenabeele P: Tumor necrosis factor-mediated cell death: To
break or to burst, that's the question. Cell Mol Life Sci.
67:1567–1579. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xanthoulea S, Pasparakis M, Kousteni S,
Brakebusch C, Wallach D, Bauer J, Lassmann H and Kollias G: Tumor
necrosis factor (TNF) receptor shedding controls thresholds of
innate immune activation that balance opposing TNF functions in
infectious and inflammatory diseases. J Exp Med. 200:367–376. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L
and Wang X: Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines
cellular necrotic response to TNF-α. Cell. 137:1100–1111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, McQuade T, Siemer AB, Napetschnig J,
Moriwaki K, Hsiao YS, Damko E, Moquin D, Walz T, McDermott A, et
al: The RIP1/RIP3 necrosome forms a functional amyloid signaling
complex required for programmed necrosis. Cell. 150:339–350. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu W, Liu P and Li J: Necroptosis: An
emerging form of programmed cell death. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
82:249–258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray
TD, Guildford M and Chan FK: Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the
RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced
inflammation. Cell. 137:1112–1123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kaiser WJ, Upton JW, Long AB,
Livingston-Rosanoff D, Daley-Bauer LP, Hakem R, Caspary T and
Mocarski ES: RIP3 mediates the embryonic lethality of
caspase-8-deficient mice. Nature. 471:368–372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vandenabeele P, Declercq W, Van Herreweghe
F and Vanden Berghe T: The role of the kinases RIP1 and RIP3 in
TNF-induced necrosis. Sci Signal. 3:re42010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Moriwaki K and Chan FK: RIP3: A molecular
switch for necrosis and inflammation. Genes Dev. 27:1640–1649.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang DW, Zheng M, Zhao J, Li YY, Huang Z,
Li Z and Han J: Multiple death pathways in TNF-treated fibroblasts:
RIP3- and RIP1-dependent and independent routes. Cell Res.
21:368–371. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ,
Lin SC, Dong MQ and Han J: RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator
that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis.
Science. 325:332–336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
National Research Council (USA) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research: Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. 8th edition. National Academies Press (USA);
Washington, DC: 1996
|
|
18
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thored P, Wood J, Arvidsson A, Cammenga J,
Kokaia Z and Lindvall O: Long-term neuroblast migration along blood
vessels in an area with transient angiogenesis and increased
vascularization after stroke. Stroke. 38:3032–3039. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Swanson RA, Morton MT, Tsao-Wu G, Savalos
RA, Davidson C and Sharp FR: A semiautomated method for measuring
brain infarct volume. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 10:290–293. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim SJ and Li J: Caspase blockade induces
RIP3-mediated programmed necrosis in Toll-like receptor-activated
microglia. Cell Death Dis. 4:e7162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Durai Pandian J, Padma V, Vijaya P, Sylaja
PN and Murthy JM: Stroke and thrombolysis in developing countries.
Int J Stroke. 2:17–26. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xu D, Du W, Zhao L, Davey AK and Wang J:
The neuroprotective effects of isosteviol against focal cerebral
ischemia injury induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion in
rats. Planta Med. 74:816–821. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Budohoski KP, Guilfoyle M, Helmy A,
Huuskonen T, Czosnyka M, Kirollos R, Menon DK, Pickard JD and
Kirkpatrick PJ: The pathophysiology and treatment of delayed
cerebral ischaemia following subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurol
Neurosurg Psychiatry. 85:1343–1353. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu H, Zhang Y, Sun H, Chen S and Wang F:
Effects of acupuncture at GV20 and ST36 on the expression of matrix
metalloproteinase 2, aquaporin 4, and aquaporin 9 in rats subjected
to cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 9:e974882014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen HJ, Shen YC, Shiao YJ, Liou KT, Hsu
WH, Hsieh PH, Lee CY, Chen YR and Lin YL: Multiplex Brain Proteomic
Analysis Revealed the Molecular Therapeutic Effects of Buyang
Huanwu Decoction on Cerebral Ischemic Stroke Mice. PLoS One.
10:e01408232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li W, Tan C, Liu Y, Liu X, Wang X, Gui Y,
Qin L, Deng F, Yu Z, Hu C and Chen L: Resveratrol ameliorates
oxidative stress and inhibits aquaporin 4 expression following rat
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep. 12:7756–7762.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Saini MK, Sanyal SN and Vaiphei K:
Piroxicam and C-phycocyanin mediated apoptosis in
1,2-dimethylhydrazine dihydrochloride induced colon carcinogenesis:
Exploring the mitochondrial pathway. Nutr Cancer. 64:409–418. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Günther C, Martini E, Wittkopf N, Amann K,
Weigmann B, Neumann H, Waldner MJ, Hedrick SM, Tenzer S, Neurath MF
and Becker C: Caspase-8 regulates TNF-α-induced epithelial
necroptosis and terminal ileitis. Nature. 477:335–339. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bamias G, Jia LG and Cominelli F: The
tumor necrosis factor-like cytokine 1A/death receptor 3 cytokine
system in intestinal inflammation. Curr Opin Gastroenterol.
29:597–602. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma J, Endres M and Moskowitz MA:
Synergistic effects of caspase inhibitors and MK-801 in brain
injury after transient focal cerebral ischaemia in mice. Br J
Pharmacol. 124:756–762. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Madsen PM, Clausen BH, Degn M, Thyssen S,
Kristensen LK, Svensson M, Ditzel N, Finsen B, Deierborg T,
Brambilla R and Lambertsen KL: Genetic ablation of soluble tumor
necrosis factor with preservation of membrane tumor necrosis factor
is associated with neuroprotection after focal cerebral ischemia. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. Oct 19–2015.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu Y, Wang J, Song X, Wei R, He F, Peng G
and Luo B: Protective mechanisms of CA074-me (other than
cathepsin-B inhibition) against programmed necrosis induced by
global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Brain Res
Bull. 120:97–105. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Moulin M, Anderton H, Voss AK, Thomas T,
Wong WW, Bankovacki A, Feltham R, Chau D, Cook WD, Silke J and Vaux
DL: IAPs limit activation of RIP kinases by TNF receptor 1 during
development. EMBO J. 31:1679–1691. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap
P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA and Yuan J:
Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic
potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 1:112–119.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yeh WC, Itie A, Elia AJ, Ng M, Shu HB,
Wakeham A, Mirtsos C, Suzuki N, Bonnard M, Goeddel DV and Mak TW:
Requirement for Casper (c-FLIP) in regulation of death
receptor-induced apoptosis and embryonic development. Immunity.
12:633–642. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Boise LH, Minn AJ, Noel PJ, June CH,
Accavitti MA, Lindsten T and Thompson CB: CD28 costimulation can
promote T cell survival by enhancing the expression of Bcl-XL.
Immunity. 3:87–98. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Oberst A, Dillon CP, Weinlich R, McCormick
LL, Fitzgerald P, Pop C, Hakem R, Salvesen GS and Green DR:
Catalytic activity of the caspase-8-FLIP(L) complex inhibits
RIPK3-dependent necrosis. Nature. 471:363–367. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|