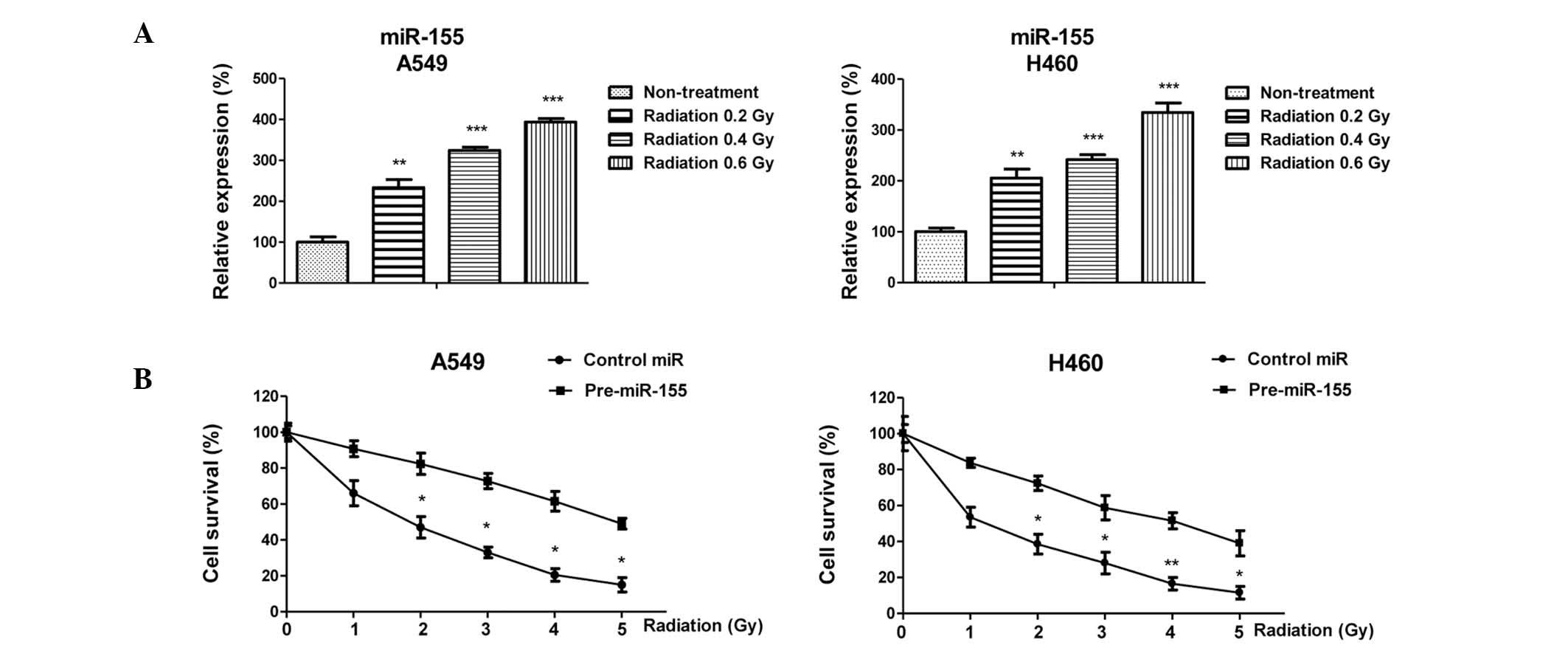
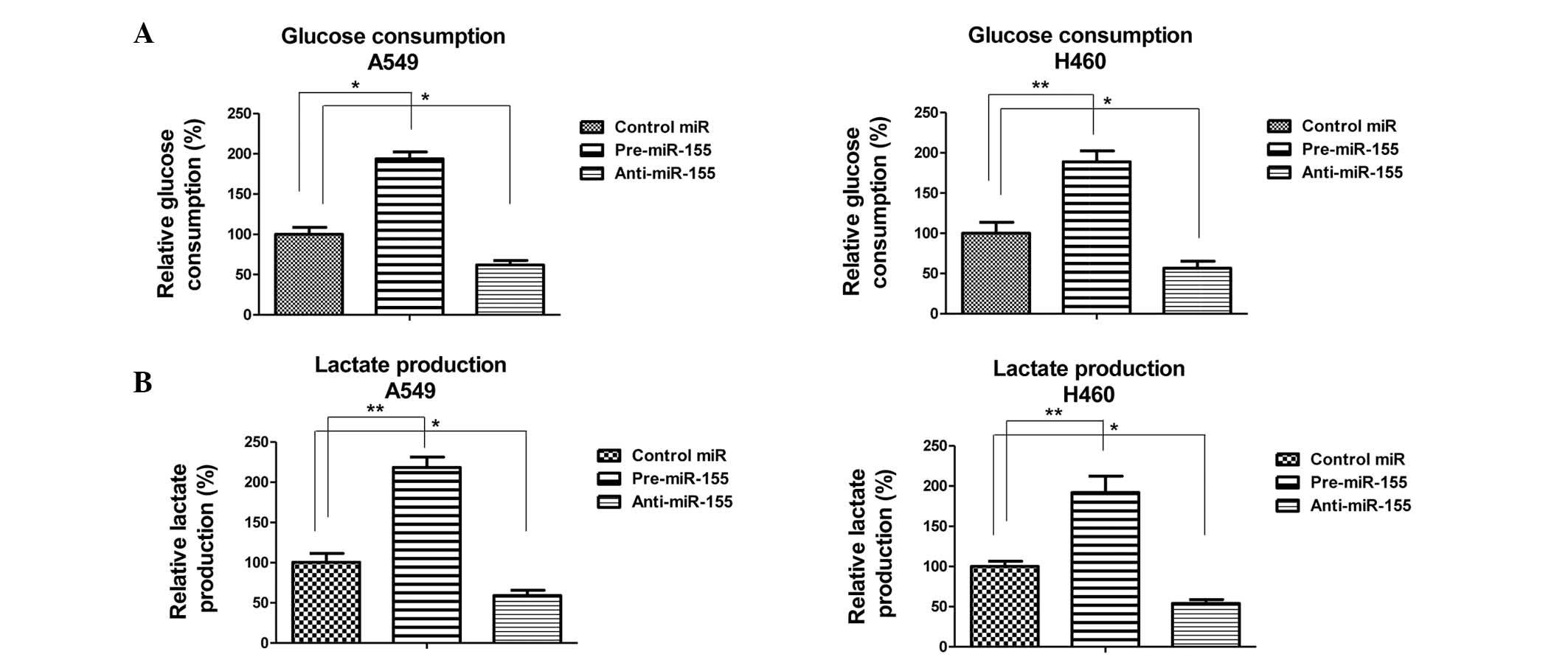
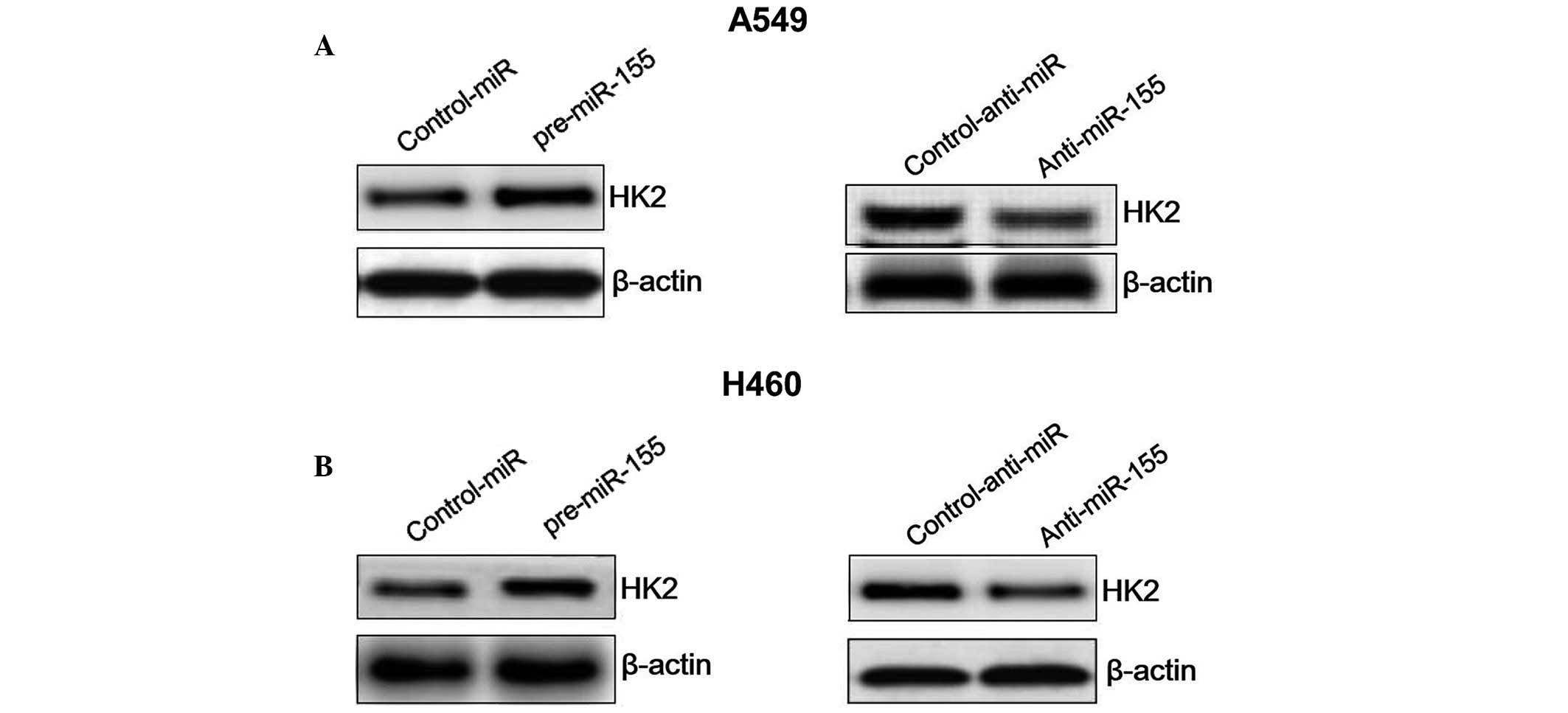
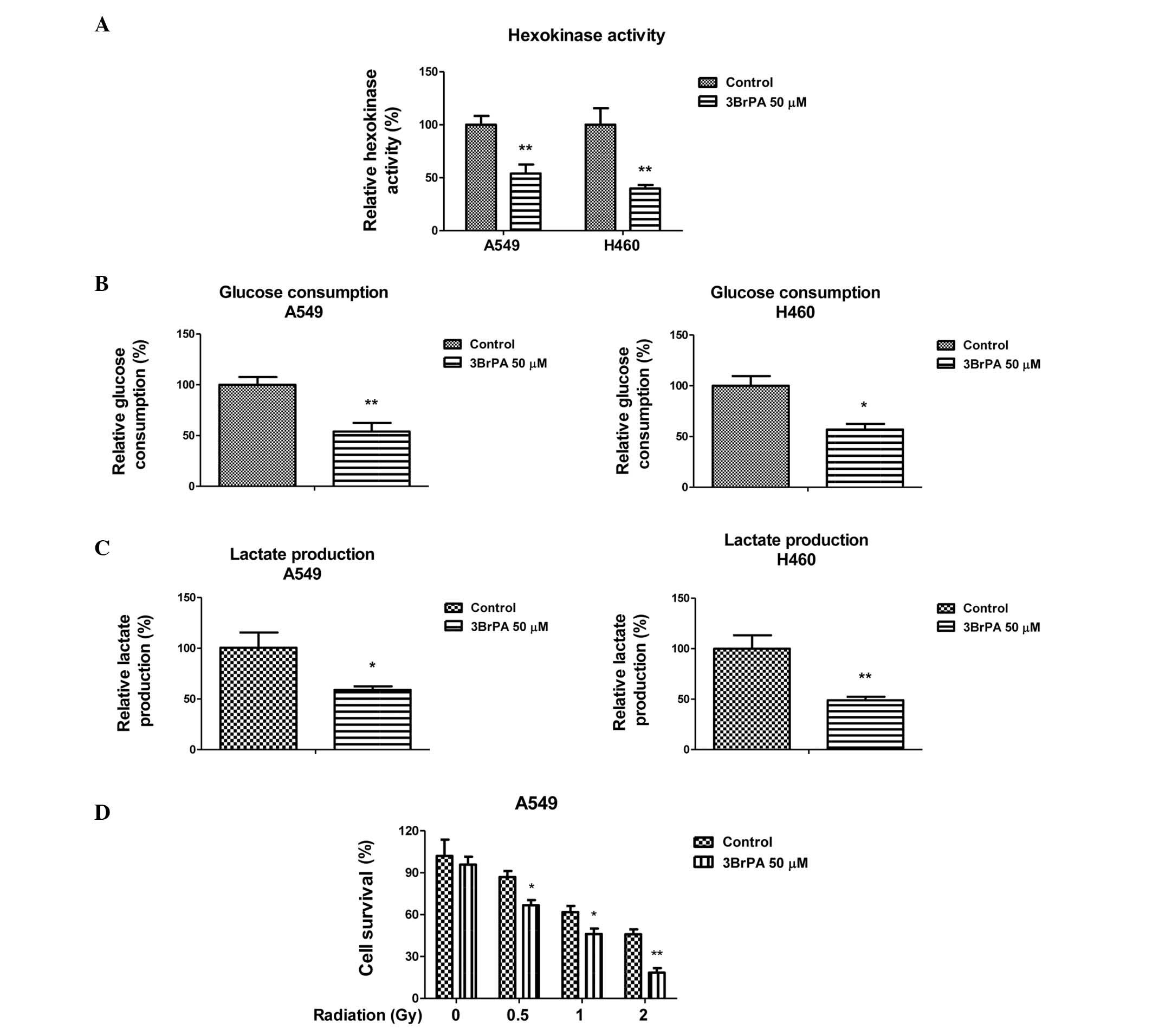
|
1
|
Hayes J, Peruzzi PP and Lawler S:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol
Med. 20:460–469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zheng T, Wang J, Chen X and Liu L: Role of
microRNA in anticancer drug resistance. Int J Cancer. 126:2–10.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ma J, Dong C and Ji C: MicroRNA and drug
resistance. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:523–531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zang YS, Zhong YF, Fang Z, Li B and An J:
MiR-155 inhibits the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to cisplatin
via negative regulation of Apaf-1 expression. Cancer Gene Ther.
19:773–778. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gasparini P, Lovat F, Fassan M, Casadei L,
Cascione L, Jacob NK, Carasi S, Palmieri D, Costinean S, Shapiro
CL, et al: Protective role of miR-155 in breast cancer through
RAD51 targeting impairs homologous recombination after irradiation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:4536–4541. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Habbe N, Koorstra JB, Mendell JT,
Offerhaus GJ, Ryu JK, Feldmann G, Mullendore ME, Goggins MG, Hong
SM and Maitra A: MicroRNA miR-155 is a biomarker of early
pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:340–346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Zhang GJ, Xiao HX, Tian HP, Liu ZL, Xia SS
and Zhou T: Upregulation of microRNA-155 promotes the migration and
invasion of colorectal cancer cells through the regulation of
claudin-1 expression. Int J Mol Med. 31:1375–1380. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li S, Chen T, Zhong Z, Wang Y, Li Y and
Zhao X: microRNA-155 silencing inhibits proliferation and migration
and induces apoptosis by upregulating BACH1 in renal cancer cells.
Mol Med Rep. 5:949–954. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kluiver J, Poppema S, de Jong D, Blokzijl
T, Harms G, Jacobs S, Kroesen BJ and van den Berg A: BIC and
miR-155 are highly expressed in Hodgkin, primary mediastinal and
diffuse large B cell lymphomas. J Pathol. 207:243–249. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xue H, Hua LM, Guo M and Luo JM: SHIP1 is
targeted by miR-155 in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncol Rep.
32:2253–2259. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Czyzyk-Krzeska MF and Zhang X: MiR-155 at
the heart of oncogenic pathways. Oncogene. 33:677–678. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Chen Z, Fillmore CM, Hammerman PS, Kim CF
and Wong KK: Non-small-cell lung cancers: A heterogeneous set of
diseases. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:535–546. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Willers H, Azzoli CG, Santivasi WL and Xia
F: Basic mechanisms of therapeutic resistance to radiation and
chemotherapy in lung cancer. Cancer J. 19:200–207. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Babar IA, Czochor J, Steinmetz A, Weidhaas
JB, Glazer PM and Slack FJ: Inhibition of hypoxia-induced miR-155
radiosensitizes hypoxic lung cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther.
12:908–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao Y, Butler EB and Tan M: Targeting
cellular metabolism to improve cancer therapeutics. Cell Death Dis.
4:e5322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhong J, Rajaram N, Brizel DM, Frees AE,
Ramanujam N, Batinic-Haberle I and Dewhirst MW: Radiation induces
aerobic glycolysis through reactive oxygen species. Radiother
Oncol. 106:390–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shimura T, Noma N, Sano Y, Ochiai Y,
Oikawa T, Fukumoto M and Kunugita N: AKT-mediated enhanced aerobic
glycolysis causes acquired radioresistance by human tumor cells.
Radiother Oncol. 112:302–307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mathupala SP, Ko YH and Pedersen PL:
Hexokinase-2 bound to mitochondria: Cancer's stygian link to the
“Warburg Effectˮ and a pivotal target for effective therapy. Semin
Cancer Biol. 19:17–24. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Suh DH, Kim MA, Kim H, Kim MK, Kim HS,
Chung HH, Kim YB and Song YS: Association of overexpression of
hexokinase II with chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian cancer.
Clin Exp Med. 14:345–353. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jiang S, Zhang LF, Zhang HW, Hu S, Lu MH,
Liang S, Li B, Li Y, Li D, Wang ED and Liu MF: A novel
miR-155/miR-143 cascade controls glycolysis by regulating
hexokinase 2 in breast cancer cells. EMBO J. 31:1985–1998. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|