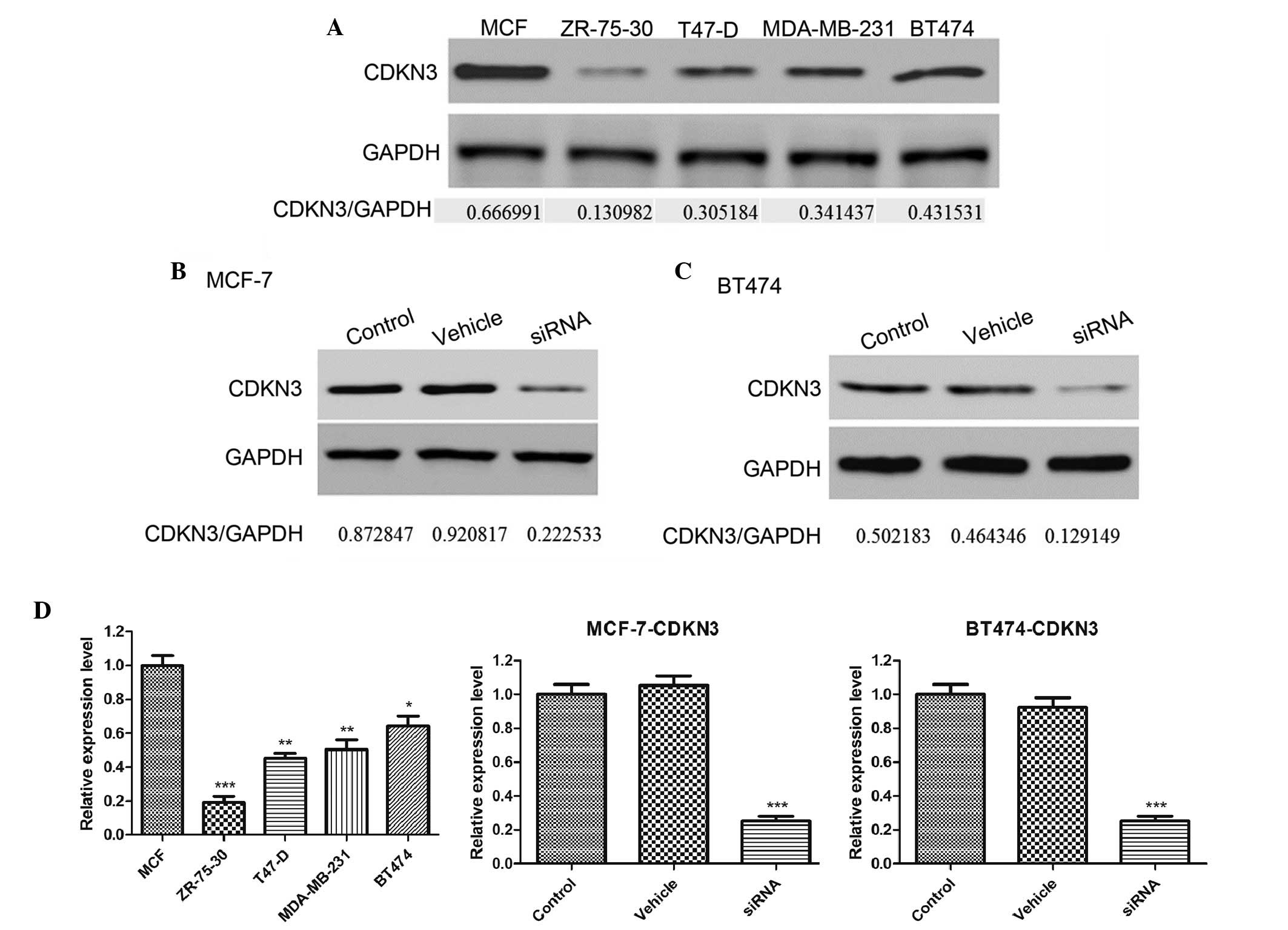
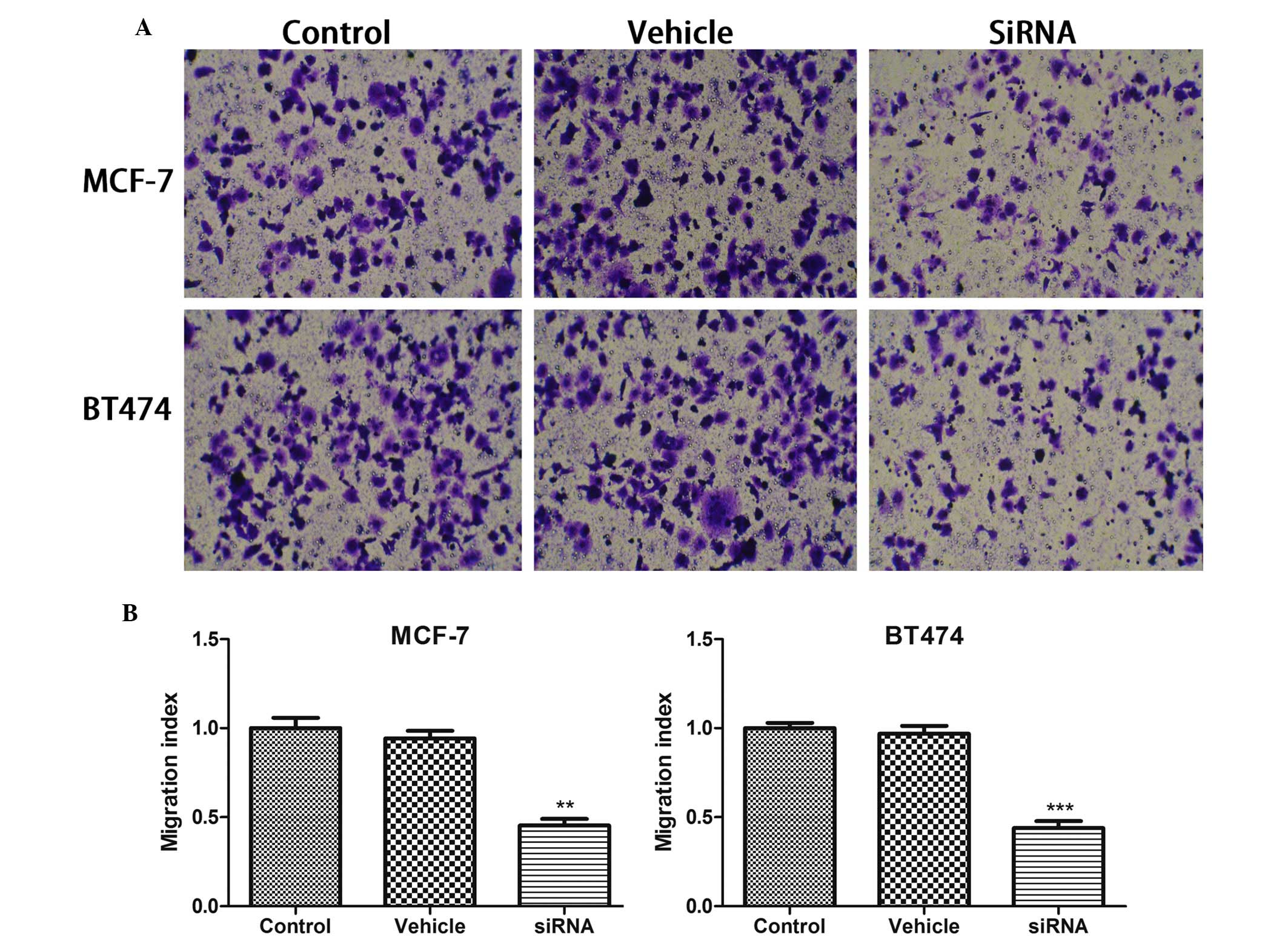
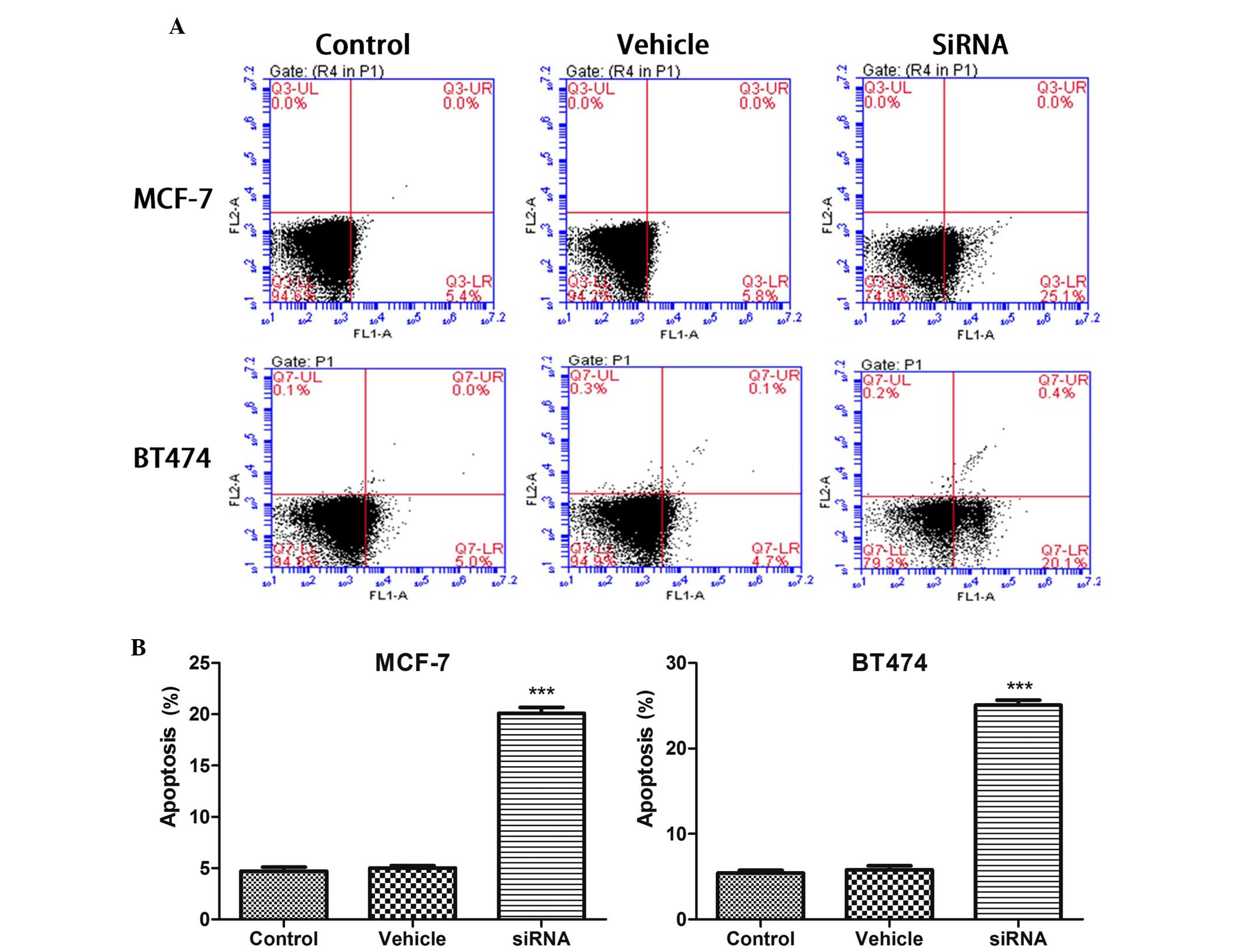
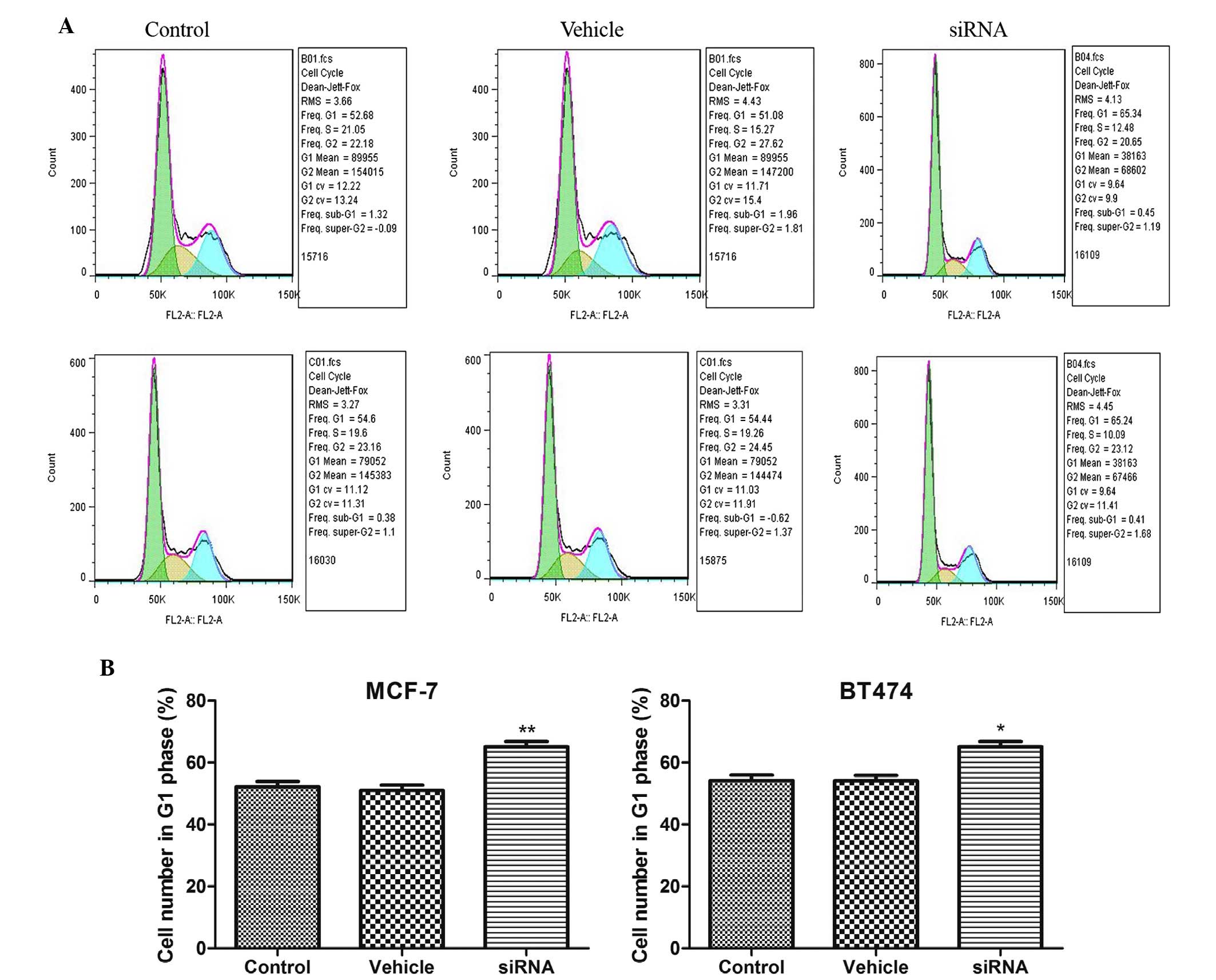
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Baghdassarian N and Ffrench M:
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs) and hematological
malignancies. Hematol Cell Ther. 38:313–323. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Malumbres M: Cyclin-dependent kinases.
Genome Biol. 15:1222014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Berumen J, Espinosa AM and Medina I:
Targeting CDKN3 in cervical cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
18:1149–1162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
García-Escudero R, Martínez-Cruz AB,
Santos M, Lorz C, Segrelles C, Garaulet G, Saiz-Ladera C, Costa C,
Buitrago-Pérez A, Dueñas M and Paramio JM: Gene expression
profiling of mouse p53-deficient epidermal carcinoma defines
molecular determinants of human cancer malignancy. Mol Cancer.
9:1932010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gerald WL: Gene expression analysis of
prostate carcinoma. Expression Profiling of Human Tumors. Ladanyi M
and Gerald WL: Humana Press; New York: pp. 173–197. 2003,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen CF, Feng X, Liao HY, Jin WJ, Zhang J,
Wang Y, Gong LL, Liu JJ, Yuan XH, Zhao BB, et al: Regulation of T
cell proliferation by JMJD6 and PDGF-BB during chronic hepatitis B
infection. Sci Rep. 4:63592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nalepa G, Barnholtz-Sloan J, Enzor R, Dey
D, He Y, Gehlhausen JR, Lehmann AS, Park SJ, Yang Y, Yang X, et al:
The tumor suppressor CDKN3 controls mitosis. J Cell Biol.
201:997–1012. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yeh CT, Lu SC, Chao CH and Chao ML:
Abolishment of the interaction between cyclin-dependent kinase 2
and Cdk-associated protein phosphatase by a truncated KAP mutant.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 305:311–314. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee SW, Reimer CL, Fang L, Iruela-Arispe
ML and Aaronson SA: Overexpression of kinase-associated phosphatase
(KAP) in breast and prostate cancer and inhibition of the
transformed phenotype by antisense KAP expression. Mol Cell Biol.
20:1723–1732. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li H, Jiang X, Yu Y, Huang W, Xing H, Agar
NY, Yang HW, Yang B, Carroll RS and Johnson MD: KAP regulates ROCK2
and Cdk2 in an RNA-activated glioblastoma invasion pathway.
Oncogene. 34:1432–1441. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Drullion C, Trégoat C, Lagarde V, Tan S,
Gioia R, Priault M, Djavaheri-Mergny M, Brisson A, Auberger P,
Mahon FX and Pasquet JM: Apoptosis and autophagy have opposite
roles on imatinib-induced K562 leukemia cell senescence. Cell Death
Dis. 3:e3732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yeh CT, Lu SC, Chen TC, Peng CY and Liaw
YF: Aberrant transcripts of the cyclin-dependent kinase-associated
protein phosphatase in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res.
60:4697–4700. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lai MW, Chen TC, Pang ST and Yeh CT:
Overexpression of cyclin-dependent kinase-associated protein
phosphatase enhances cell proliferation in renal cancer cells. Urol
Oncol. 30:871–878. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yu Y, Jiang X, Schoch BS, Carroll RS,
Black PM and Johnson MD: Aberrant splicing of cyclin-dependent
kinase-associated protein phosphatase KAP increases proliferation
and migration in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 67:130–138. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J,
Baehner FL, Fevr T, Clark L, Bayani N, Coppe JP, Tong F, et al: A
collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of
functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell. 10:515–527.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu YN, Yip GW, Tan PH, Thike AA, Matsumoto
K, Tsujimoto M and Bay BH: Y-box binding protein 1 is up-regulated
in proliferative breast cancer and its inhibition deregulates the
cell cycle. Int J Oncol. 37:483–492. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Padua MB and Hansen PJ: Changes in
expression of cell-cycle-related genes in PC-3 prostate cancer
cells caused by ovine uterine serpin. J Cell Biochem.
107:1182–1188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xing C, Xie H, Zhou L, Zhou W, Zhang W,
Ding S, Wei B, Yu X, Su R and Zheng S: Cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitor 3 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and
promotes tumor cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
420:29–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shibahara K and Stillman B:
Replication-dependent marking of DNA by PCNA facilitates
CAF-1-coupled inheritance of chromatin. Cell. 96:575–585. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pillé JY, Denoyelle C, Varet J, Bertrand
JR, Soria J, Opolon P, Lu H, Pritchard LL, Vannier JP, Malvy C, et
al: Anti-RhoA and anti-RhoC siRNAs inhibit the proliferation and
invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in vitro and in
vivo. Mol Ther. 11:267–274. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Satelli A and Li S: Vimentin in cancer and
its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 68:3033–3046. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|