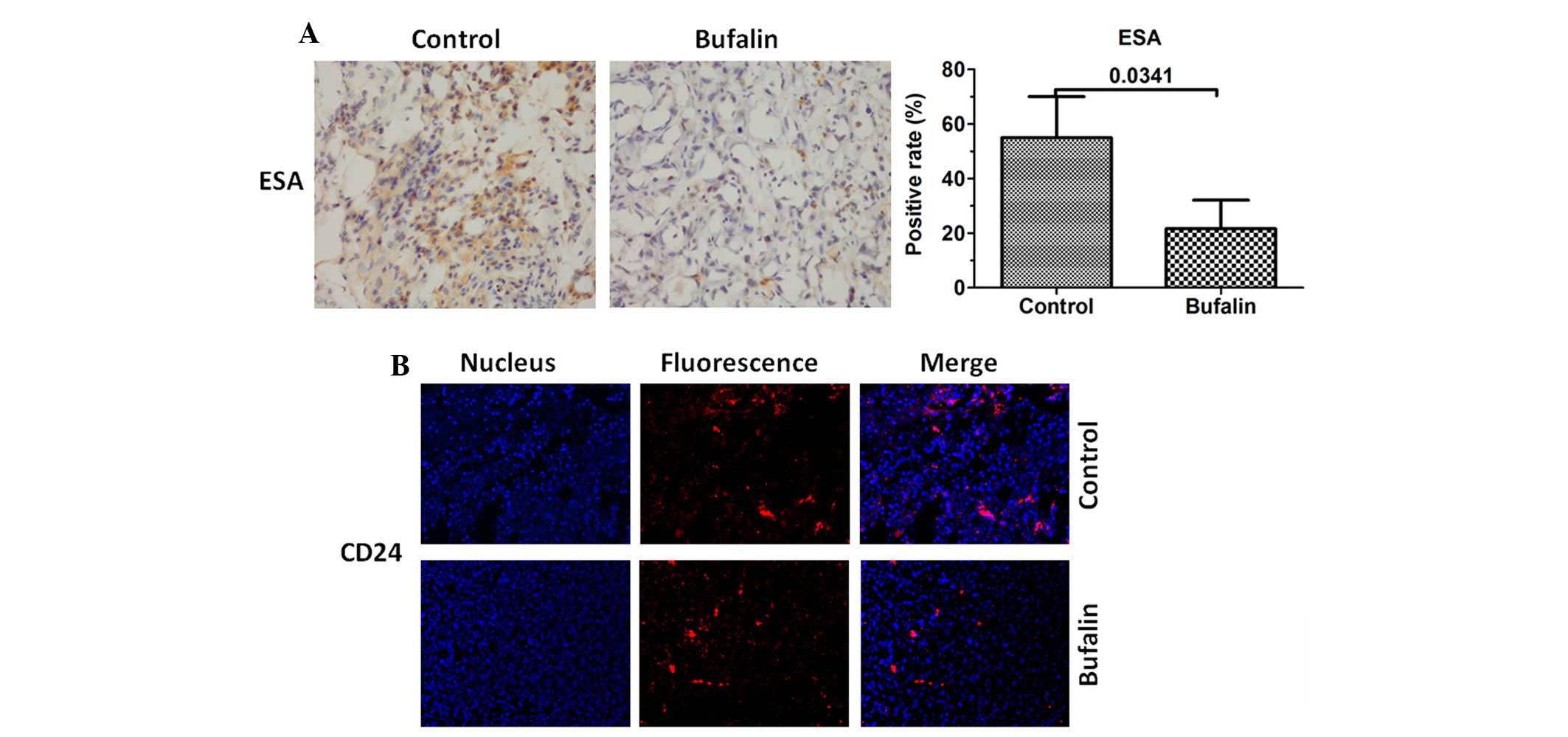
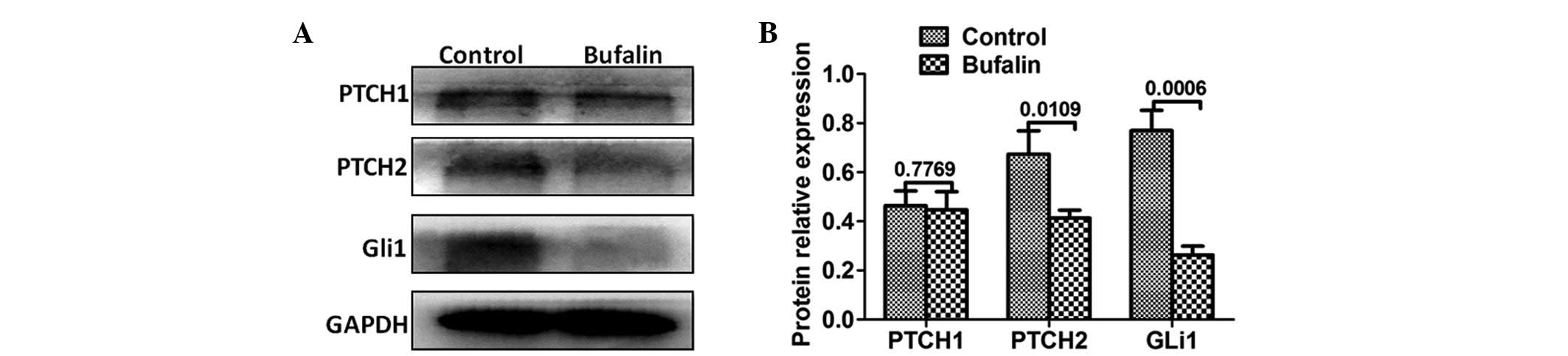
|
1
|
Pandol S, Gukovskaya A, Edderkaoui M,
Dawson D, Eibl G and Lugea A: Epidemiology, risk factors, and the
promotion of pancreatic cancer: Role of the stellate cell. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27(Suppl 2): S127–S134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Onkendi EO, Boostrom SY, Sarr MG, Farnell
MB, Nagorney DM, Donohue JH, Kendrick ML, Reid-Lombardo KM, Harmsen
WS and Que FG: 15-year experience with surgical treatment of
duodenal carcinoma: A comparison of periampullary and
extra-ampullary duodenal carcinomas. J Gastrointest Surg.
16:682–691. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tanase CP, Neagu AI, Necula LG, Mambet C,
Enciu AM, Calenic B, Cruceru ML and Albulescu R: Cancer stem cells:
Involvement in pancreatic cancer pathogenesis and perspectives on
cancer therapeutics. World J Gastroenterol. 20:10790–10801. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumours: Accumulating evidence and unresolved
questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:755–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sureban SM, May R, Qu D, Weygant N,
Chandrakesan P, Ali N, Lightfoot SA, Pantazis P, Rao CV, Postier RG
and Houchen CW: DCLK1 regulates pluripotency and angiogenic factors
via microRNA-dependent mechanisms in pancreatic cancer. PLoS One.
8:e739402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Kong D, Ahmad A, Bao B and Sarkar
FH: Pancreatic cancer stem cells: Emerging target for designing
novel therapy. Cancer Lett. 338:94–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li C, Heidt DG, Dalerba P, Burant CF,
Zhang L, Adsay V, Wicha M, Clarke MF and Simeone DM: Identification
of pancreatic cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 67:1030–1037. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A, Montes
De Oca R, Gerstenblith MR, Briggs K, Parker AR, Shimada Y, Eshleman
JR, Watkins DN and Beachy PA: Widespread requirement for Hedgehog
ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract tumours. Nature.
425:846–851. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Olive KP, Jacobetz MA, Davidson CJ,
Gopinathan A, McIntyre D, Honess D, Madhu B, Goldgraben MA,
Caldwell ME, Allard D, et al: Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling
enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic
cancer. Science. 324:1457–1461. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abetov D, Mustapova Z, Saliev T and
Bulanin D: Biomarkers and signaling pathways of colorectal cancer
stem cells. Tumour Biol. 36:1339–1353. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang F, Ma L, Zhang Z, Liu X, Gao H,
Zhuang Y, Yang P, Kornmann M, Tian X and Yang Y: Hedgehog Signaling
Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Pancreatic Cancer
Stem-Like. Cells J Cancer. 7:408–417. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Meng Z, Yang P, Shen Y, Bei W, Zhang Y, Ge
Y, Newman RA, Cohen L, Liu L, Thornton B, et al: Pilot study of
huachansu in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, nonsmall-cell
lung cancer, or pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 115:5309–5318. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Luan J, Duan H, Zhang F,
Yagasaki K and Zhang G: Effects of bufalin on the proliferation of
human lung cancer cells and its molecular mechanisms of action.
Cytotechnology. 62:573–583. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang L, Zhao MN, Liu TY, Wu XS, Weng H,
Ding Q, Shu YJ, Bao RF, Li ML, Mu JS, et al: Bufalin induces cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in gallbladder carcinoma cells. Tumour
Biol. 35:10931–10941. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu SH, Hsiao YT, Chen JC, Lin JH, Hsu SC,
Hsia TC, Yang ST, Hsu WH and Chung JG: Bufalin alters gene
expressions associated DNA damage, cell cycle, and apoptosis in
human lung cancer NCI-H460 cells in vitro. Molecules. 19:6047–6057.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chueh FS, Chen YY, Huang AC, Ho HC, Liao
CL, Yang JS, Kuo CL and Chung JG: Bufalin-inhibited migration and
invasion in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells is carried out by
suppression of the matrix metalloproteinase-2, ERK, and JNK
signaling pathways. Environ Toxicol. 29:21–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gao Y, Li HX, Xu LT, Wang P, Xu LY, Cohen
L, Yang PY, Gu K and Meng ZQ: Bufalin enhances the
anti-proliferative effect of sorafenib on human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells through downregulation of ERK. Mol Biol Rep.
39:1683–1689. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang P, Chen Z, Meng ZQ, Fan J, Luo JM,
Liang W, Lin JH, Zhou ZH, Chen H, Wang K, et al: Dual role of Ski
in pancreatic cancer cells: Tumor-promoting versus
metastasis-suppressive function. Carcinogenesis. 30:1497–1506.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Uchida S, Yokoo S, Yanagi Y, Usui T,
Yokota C, Mimura T, Araie M, Yamagami S and Amano S: Sphere
formation and expression of neural proteins by human corneal
stromal cells in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:1620–1625.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li C, Lee CJ and Simeone DM:
Identification of human pancreatic cancer stem cells. Methods Mol
Biol. 568:161–173. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu J, He J, Liu Y, Simeone DM and Lubman
DM: Identification of glycoprotein markers for pancreatic cancer
CD24+CD44+ stem-like cells using nano-LC-MS/MS and tissue
microarray. J Proteome Res. 11:2272–2281. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim EJ, Sahai V, Abel EV, Griffith KA,
Greenson JK, Takebe N, Khan GN, Blau JL, Craig R, Balis UG, et al:
Pilot clinical trial of hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449
(vismodegib) in combination with gemcitabine in patients with
metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5937–5945. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wright MH, Calcagno AM, Salcido CD,
Carlson MD, Ambudkar SV and Varticovski L: Brca1 breast tumors
contain distinct CD44+/CD24− and
CD133+ cells with cancer stem cell characteristics.
Breast Cancer Res. 10:R102008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, Gong
C, Huang Y, Hu X, Su F, Lieberman J and Song E: Let-7 regulates
self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell.
131:1109–1123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Eyler CE and Rich JN: Survival of the
fittest: Cancer stem cells in therapeutic resistance and
angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 26:2839–2845. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hadnagy A, Gaboury L, Beaulieu R and
Balicki D: SP analysis may be used to identify cancer stem cell
populations. Exp Cell Res. 312:3701–3710. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mizuno N, Yatabe Y, Hara K, Hijioka S,
Imaoka H, Shimizu Y, Ko SB and Yamao K: Cytoplasmic expression of
LGR5 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Front Physiol. 4:2692013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matsuda Y, Kure S and Ishiwata T: Nestin
and other putative cancer stem cell markers in pancreatic cancer.
Med Mol Morphol. 45:59–65. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chefetz I, Alvero AB, Holmberg JC,
Lebowitz N, Craveiro V, Yang-Hartwich Y, Yin G, Squillace L, Gurrea
Soteras M, Aldo P and Mor G: TLR2 enhances ovarian cancer stem cell
self-renewal and promotes tumor repair and recurrence. Cell Cycle.
12:511–521. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Croker AK and Allan AL: Inhibition of
aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activity reduces chemotherapy and
radiation resistance of stem-like ALDHhiCD44+
human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 133:75–87.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rich JN: Cancer stem cells in radiation
resistance. Cancer Res. 67:8980–8984. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Q, Shi S, Yen Y, Brown J, Ta JQ and
Le AD: A subpopulation of CD133(+) cancer stem-like cells
characterized in human oral squamous cell carcinoma confer
resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 289:151–160. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Huang P, Wang CY, Gou SM, Wu HS, Liu T and
Xiong JX: Isolation and biological analysis of tumor stem cells
from pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
14:3903–3907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang L, Zhao MN, Liu TY, Wu XS, Weng H,
Ding Q, Shu YJ, Bao RF, Li ML, Mu JS, et al: Bufalin induces cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in gallbladder carcinoma cells. Tumour
Biol. 35:10931–10941. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu SH, Wu TY, Hsiao YT, Lin JH, Hsu SC,
Hsia TC, Yang ST, Hsu WH and Chung JG: Bufalin induces cell death
in human lung cancer cells through disruption of DNA damage
response pathways. Am J Chin Med. 42:729–742. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yan S, Qu X, Xu L, Che X, Ma Y, Zhang L,
Teng Y, Zou H and Liu Y: Bufalin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis
by redistributing death receptors in lipid rafts in breast cancer
cells. Anticancer Drugs. 25:683–689. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yin PH, Liu X, Qiu YY, Cai JF, Qin JM, Zhu
HR and Li Q: Anti-tumor activity and apoptosis-regulation
mechanisms of bufalin in various cancers: New hope for cancer
patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:5339–5343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Qi F, Li A, Inagaki Y, Kokudo N, Tamura S,
Nakata M and Tang W: Antitumor activity of extracts and compounds
from the skin of the toad Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:342–349. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Tang SN, Fu J, Nall D, Rodova M, Shankar S
and Srivastava RK: Inhibition of sonic hedgehog pathway and
pluripotency maintaining factors regulate human pancreatic cancer
stem cell characteristics. Int J Cancer. 131:30–40. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fu J, Rodova M, Roy SK, Sharma J, Singh
KP, Srivastava RK and Shankar S: GANT-61 inhibits pancreatic cancer
stem cell growth in vitro and in NOD/SCID/IL2R gamma null mice
xenograft. Cancer Lett. 330:22–32. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Singh BN, Fu J, Srivastava RK and Shankar
S: Hedgehog signaling antagonist GDC-0449 (Vismodegib) inhibits
pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics: Molecular mechanisms.
PLoS One. 6:e273062011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|