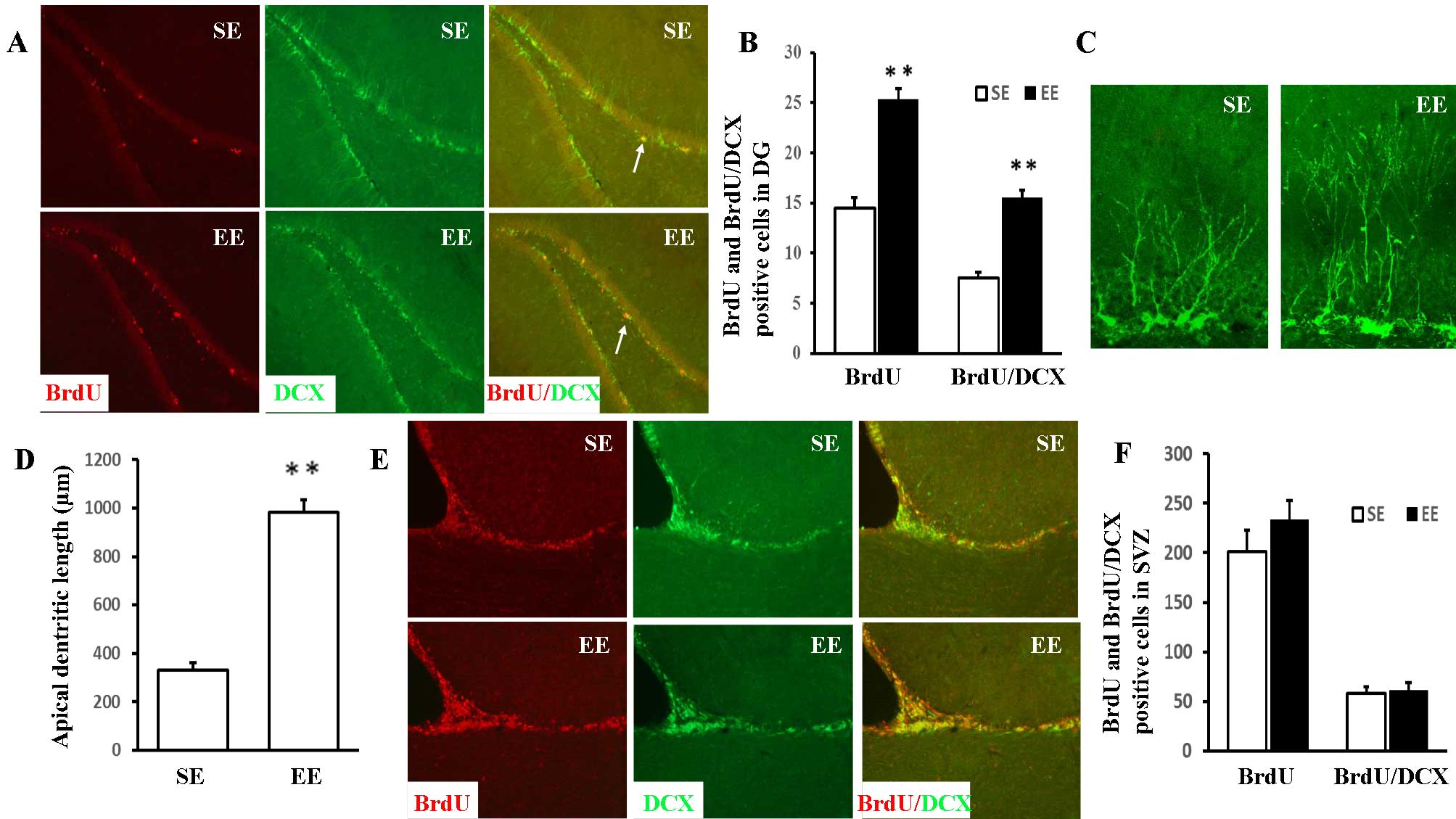
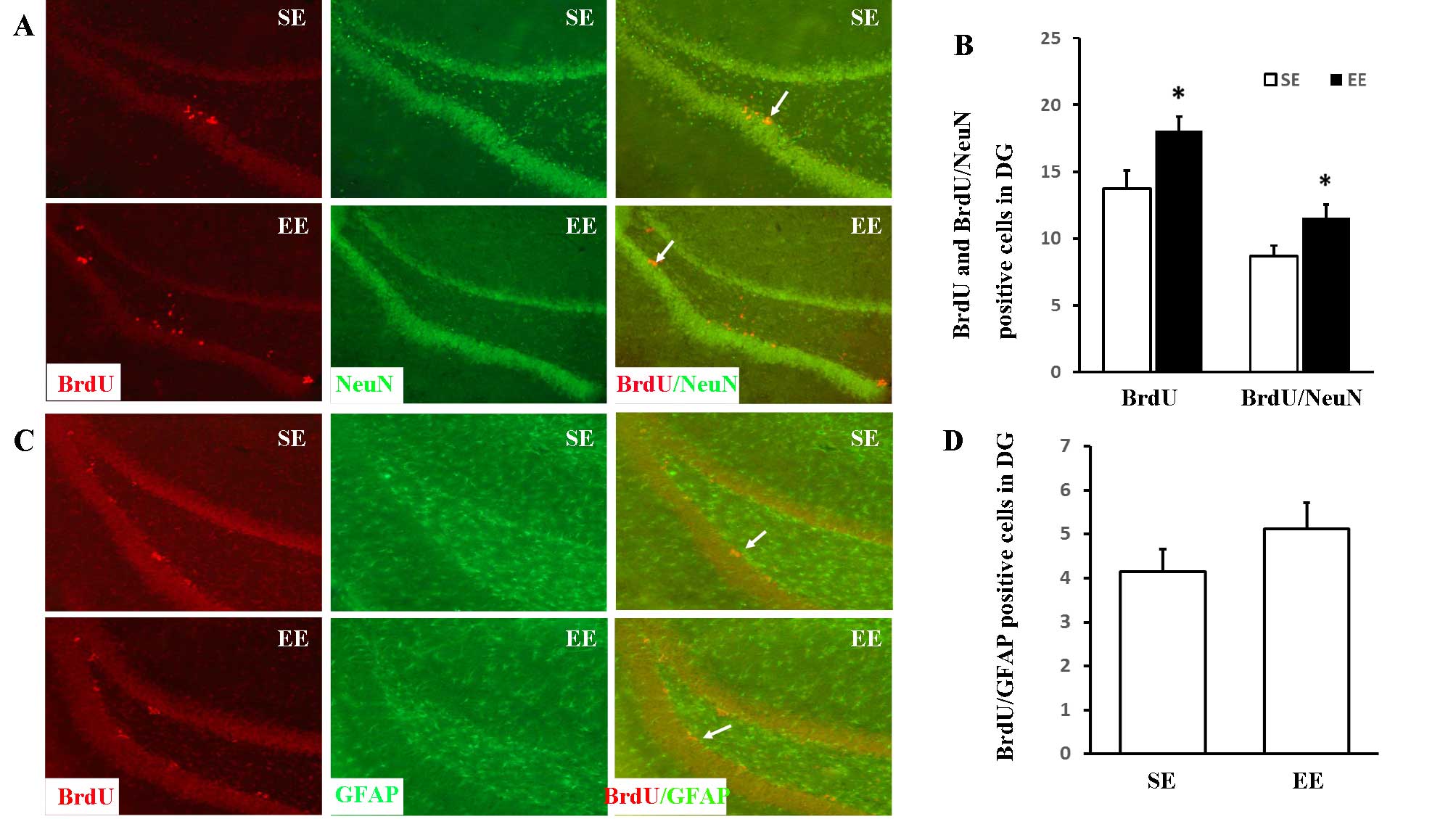
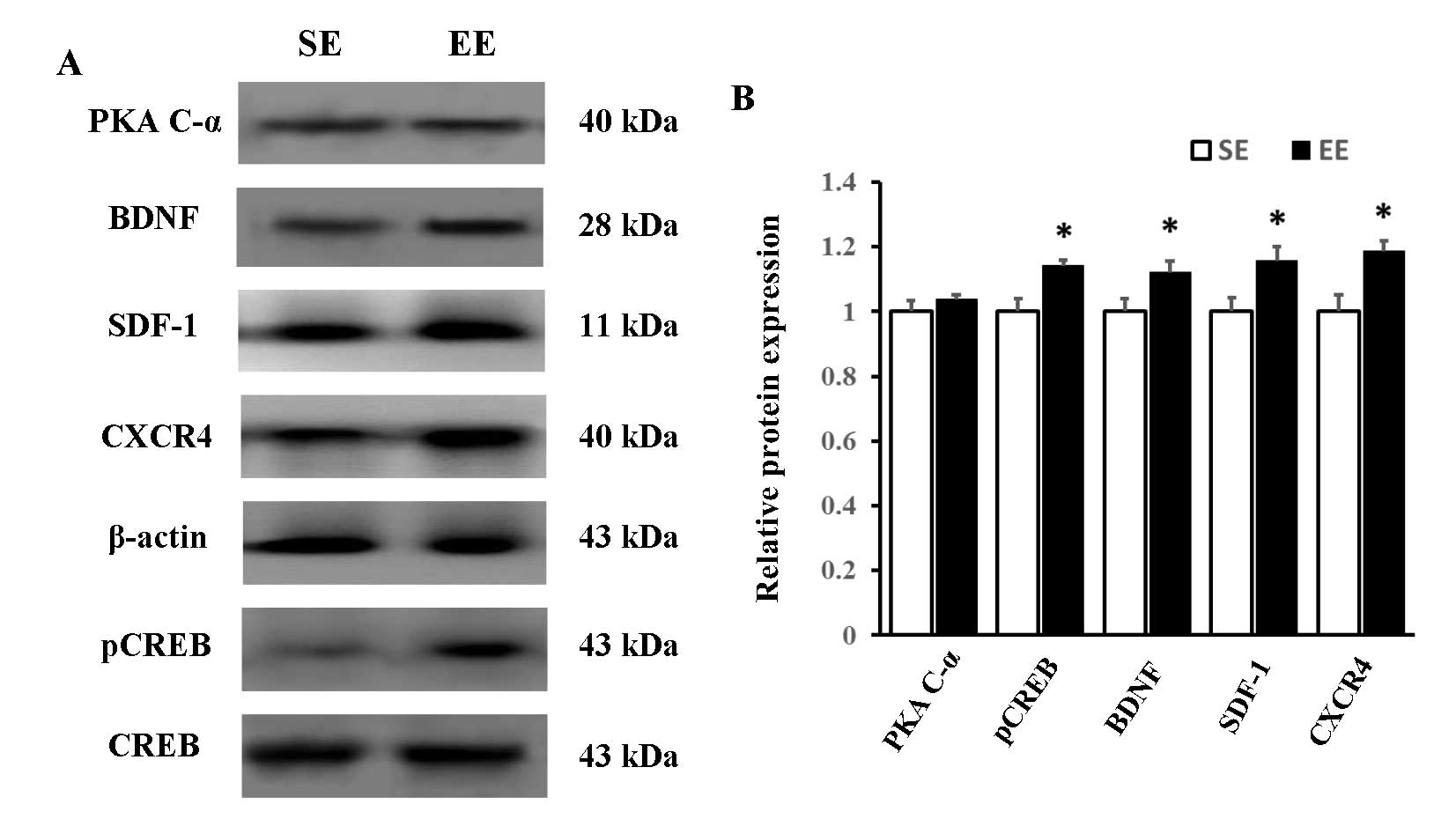
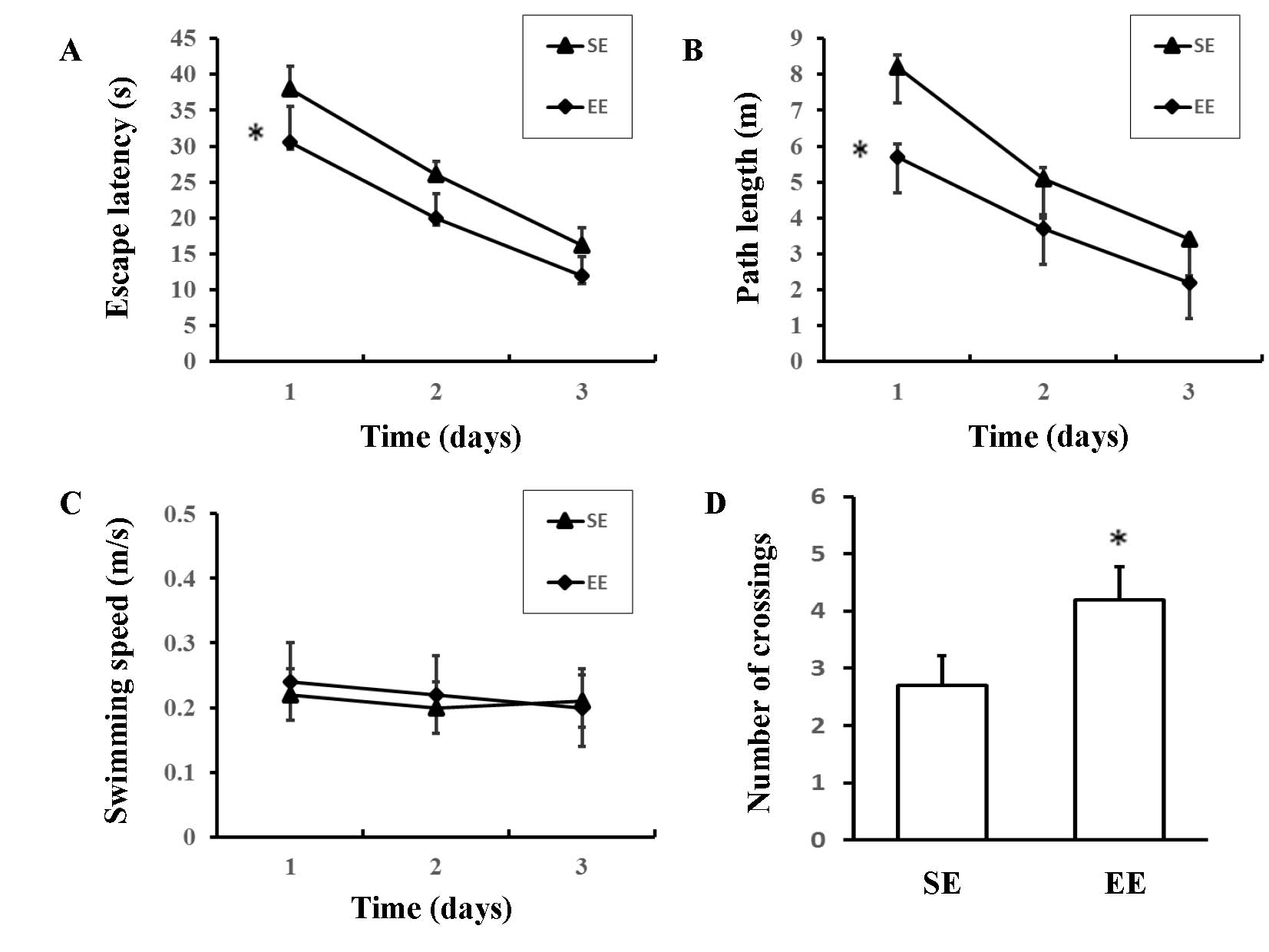
|
1
|
Williamson LL, Chao A and Bilbo SD:
Environmental enrichment alters glial antigen expression and
neuroimmune function in the adult rat hippocampus. Brain Behav
Immun. 26:500–510. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Scharfman H, Goodman J, Macleod A, Phani
S, Antonelli C and Croll S: Increased neurogenesis and the ectopic
granule cells after intrahippocampal BDNF infusion in adult rats.
Exp Neurol. 192:348–356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Serafini G, Hayley S, Pompili M, Dwivedi
Y, Brahmachari G, Girardi P and Amore M: Hippocampal neurogenesis,
neurotrophic factors and depression: Possible therapeutic targets?
CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 13:1708–1721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Son Y, Yang M, Kang S, Lee S, Kim J, Kim
J, Park S, Kim JS, Jo SK, Jung U, et al: Cranial irradiation
regulates CREB-BDNF signaling and variant BDNF transcript levels in
the mouse hippo-campus. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 121:12–19. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gage FH, Kempermann G, Palmer TD, Peterson
DA and Ray J: Multipotent progenitor cells in the adult dentate
gyrus. J Neurobiol. 36:249–266. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
van Praag H, Kempermann G and Gage FH:
Neural consequences of environmental enrichment. Nat Rev Neurosci.
1:191–198. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Murphy M, Greferath U, Nag N,
Nithianantharajah J and Wilson YM: Tracing functional circuits
using c-Fos regulated expression of marker genes targeted to
neuronal projections. Front Biosci. 9:40–47. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nithianantharajah J and Hannan AJ:
Enriched environments, experience-dependent plasticity and
disorders of the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 7:697–709. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nithianantharajah J, Levis H and Murphy M:
Environmental enrichment results in cortical and subcortical
changes in levels of synaptophysin and PSD-95 proteins. Neurobiol
Learn Mem. 81:200–210. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pang TY, Stam NC, Nithianantharajah J,
Howard ML and Hannan AJ: Differential effects of voluntary physical
exercise on behavioral and brain-derived neurotrophic factor
expression deficits in Huntington's disease transgenic mice.
Neuroscience. 141:569–584. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Leger M, Paizanis E, Dzahini K,
Quiedeville A, Bouet V, Cassel JC, Freret T, Schumann-Bard P and
Boulouard M: Environmental enrichment duration differentially
affects behavior and neuroplasticity in adult mice. Cereb Cortex.
25:4048–4061. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Monteiro BM, Moreira FA, Massensini AR,
Moraes MF and Pereira GS: Enriched environment increases
neurogenesis and improves social memory persistence in socially
isolated adult mice. Hippocampus. 24:239–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fan D, Li J, Zheng B, Hua L and Zuo Z:
Enriched environment attenuates surgery-induced impairment of
learning, memory and neurogenesis possibly by preserving BDNF
expression. Mol Neurobiol. 53:344–354. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang JL, Lin YT, Chuang PC, Bohr VA and
Mattson MP: BDNF and exercise enhance neuronal DNA repair by
stimulating CREB-mediated production of apurinic/apyrimidinic
endonuclease 1. Neuromolecular Med. 16:161–174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Kuzumaki N, Ikegami D, Tamura R, Hareyama
N, Imai S, Narita M, Torigoe K, Niikura K, Takeshima H, Ando T, et
al: Hippocampal epigenetic modification at the brain-derived
neurotrophic factor gene induced by an enriched environment.
Hippocampus. 21:127–132. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Williams BM, Luo Y, Ward C, Redd K, Gibson
R, Kuczaj SA and McCoy JG: Environmental enrichment: Effects on
spatial memory and hippocampal CREB immunoreactivity. Physiol
Behav. 73:649–658. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhong L, Yan CH, Lu CQ, Xu J, Huang H and
Shen XM: Calmodulin activation is required for the enhancement of
hippocampal neurogenesis following environmental enrichment. Neurol
Res. 31:707–713. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Marquez-Curtis LA and Janowska-Wieczorek
A: Enhancing the migration ability of mesenchymal stromal cells by
targeting the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. Biomed Res Int. 2013:5610982013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cheng M and Qin G: Progenitor cell
mobilization and recruitment: SDF-1, CXCR4, α4-integrin and c-kit.
Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 111:243–264. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cui L, Qu H, Xiao T, Zhao M, Jolkkonen J
and Zhao C: Stromal cell-derived factor-1 and its receptor CXCR4 in
adult neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia. Restor Neurol Neurosci.
31:239–251. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dwinell MB, Ogawa H, Barrett KE and
Kagnoff MF: SDF-1/CXCL12 regulates cAMP production and ion
transport in intestinal epithelial cells via CXCR4. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 286:G844–G850. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Odemis V, Moepps B, Gierschik P and Engele
J: Interleukin-6 and cAMP induce stromal cell-derived factor-1
chemotaxis in astroglia by up-regulating CXCR4 cell surface
expression. Implications for brain inflammation. J Biol Chem.
277:39801–39808. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang X, Liu T, Zhou Z, Mu X, Song C, Xiao
T, Zhao M and Zhao C: Enriched environment altered aberrant
hippocampal neurogenesis and improved long-term consequences after
temporal lobe epilepsy in adult rats. J Mol Neurosci. 56:409–421.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qu HL, Zhao M, Zhao SS, Xiao T, Song CG,
Cao YP, Jolkkonen J and Zhao CS: Forced limb-use enhanced
neurogenesis and behavioral recovery after stroke in the aged rats.
Neuroscience. 286:316–324. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dhanushkodi A and Shetty AK: Is exposure
to enriched environment beneficial for functional post-lesional
recovery in temporal lobe epilepsy? Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
32:657–674. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fares RP, Belmeguenai A, Sanchez PE,
Kouchi HY, Bodennec J, Morales A, Georges B, Bonnet C, Bouvard S,
Sloviter RS and Bezin L: Standardized environmental enrichment
supports enhanced brain plasticity in healthy rats and prevents
cognitive impairment in epileptic rats. PloS One. 8:e538882013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie H, Wu Y, Jia J, Liu G, Zhang Q, Yu K,
Guo Z, Shen L and Hu R: Enrichment-induced exercise to quantify the
effect of different housing conditions: A tool to standardize
enriched environment protocols. Behav Brain Res. 249:81–89. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Walker MD and Mason G: Female C57BL/6 mice
show consistent individual differences in spontaneous interaction
with environmental enrichment that are predicted by neophobia.
Behav Brain Res. 224:207–212. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ambrogini P, Lattanzi D, Ciuffoli S, Betti
M, Fanelli M and Cuppini R: Physical exercise and environment
exploration affect synaptogenesis in adult-generated neurons in the
rat dentate gyrus: Possible role of BDNF. Brain Res. 1534:1–12.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Madroñal N, López-Aracil C, Rangel A, del
Río JA, Delgado-García JM and Gruart A: Effects of enriched
physical and social environments on motor performance, associative
learning and hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. PloS One.
5:e111302010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Silva CF, Duarte FS, Lima TC and de
Oliveira CL: Effects of social isolation and enriched environment
on behavior of adult Swiss mice do not require hippocampal
neurogenesis. Behav Brain Res. 225:85–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Alvarez PS, Simão F, Hemb M, Xavier LL and
Nunes ML: Effects of undernourishment, recurrent seizures and
enriched environment during early life in hippocampal morphology.
Int J Dev Neurosci. 33:81–87. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shors TJ, Townsend DA, Zhao M,
Kozorovitskiy Y and Gould E: Neurogenesis may relate to some but
not all types of hippocampal-dependent learning. Hippocampus.
12:578–584. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rizzi S, Bianchi P, Guidi S, Ciani E and
Bartesaghi R: Impact of environmental enrichment on neurogenesis in
the dentate gyrus during the early postnatal period. Brain Res.
1415:23–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rochefort C, Gheusi G, Vincent JD and
Lledo PM: Enriched odor exposure increases the number of newborn
neurons in the adult olfactory bulb and improves odor memory. J
Neurosci. 22:2679–2689. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bonzano S, Bovetti S, Fasolo A, Peretto P
and De Marchis S: Odour enrichment increases adult-born
dopaminergic neurons in the mouse olfactory bulb. Eur J Neurosci.
40:3450–3457. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Martončiková M, Lievajová K, Orendáčová J,
Blaško J and Račeková E: Odor enrichment influences neurogenesis in
the rostral migratory stream of young rats. Acta Histochem.
113:326–332. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Petreanu L and Alvarez-Buylla A:
Maturation and death of adult-born olfactory bulb granule neurons:
Role of olfaction. J Neurosci. 22:6106–6113. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Carlezon WA Jr, Duman RS and Nestler EJ:
The many faces of CREB. Trends Neurosci. 28:436–445. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li QQ, Shi GX, Yang JW, Li ZX, Zhang ZH,
He T, Wang J, Liu LY and Liu CZ: Hippocampal cAMP/PKA/CREB is
required for neuroprotective effect of acupuncture. Physiol Behav.
139:482–490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Duffy SN, Craddock KJ, Abel T and Nguyen
PV: Environmental enrichment modifies the PKA-dependence of
hippocampal LTP and improves hippocampus-dependent memory. Learn
Mem. 8:26–34. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xie T, Wang WP, Jia LJ, Mao ZF, Qu ZZ,
Luan SQ and Kan MC: Environmental enrichment restores cognitive
deficits induced by prenatal maternal seizure. Brain Res.
1470:80–88. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chalasani SH, Baribaud F, Coughlan CM,
Sunshine MJ, Lee VM, Doms RW, Littman DR and Raper JA: The
chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1 promotes the survival of
embryonic retinal ganglion cells. J Neurosci. 23:4601–4612.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Opatz J, Küry P, Schiwy N, Järve A,
Estrada V, Brazda N, Bosse F and Müller HW: SDF-1 stimulates
neurite growth on inhibitory CNS myelin. Mol Cell Neurosci.
40:293–300. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Birch AM, McGarry NB and Kelly AM:
Short-term environmental enrichment, in the absence of exercise,
improves memory, and increases NGF concentration, early neuronal
survival, and synaptogenesis in the dentate gyrus in a
time-dependent manner. Hippocampus. 23:437–450. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Young D, Lawlor PA, Leone P, Dragunow M
and During MJ: Environmental enrichment inhibits spontaneous
apoptosis, prevents seizures and is neuroprotective. Nat Med.
5:448–453. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang L, Zhang J, Sun H, Liu H, Yang Y and
Yao Z: Exposure to enriched environment restores the mRNA
expression of mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors in the
hippocampus and ameliorates depressive-like symptoms in chronically
stressed rats. Curr Neurovasc Res. 8:286–293. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|