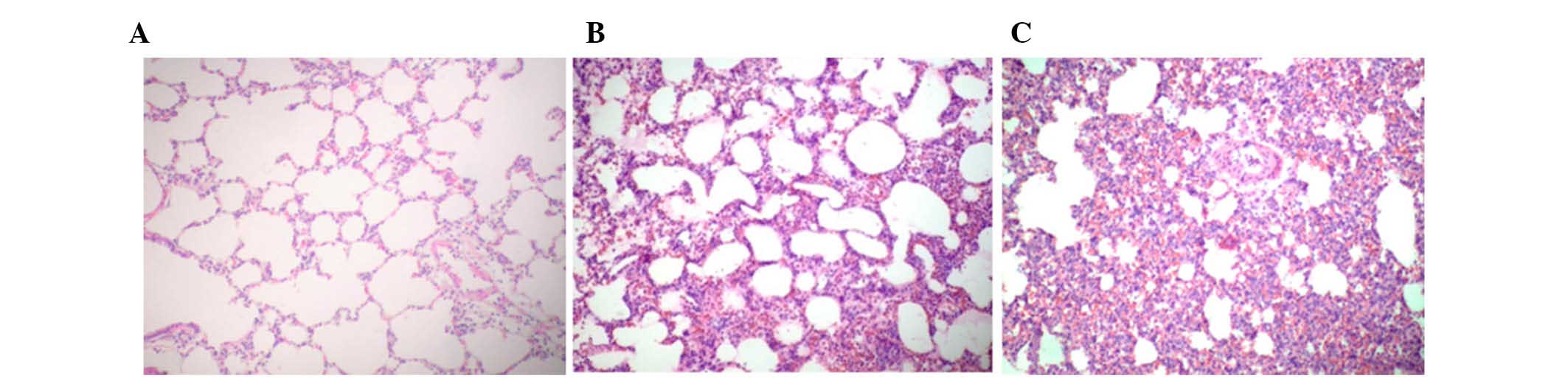
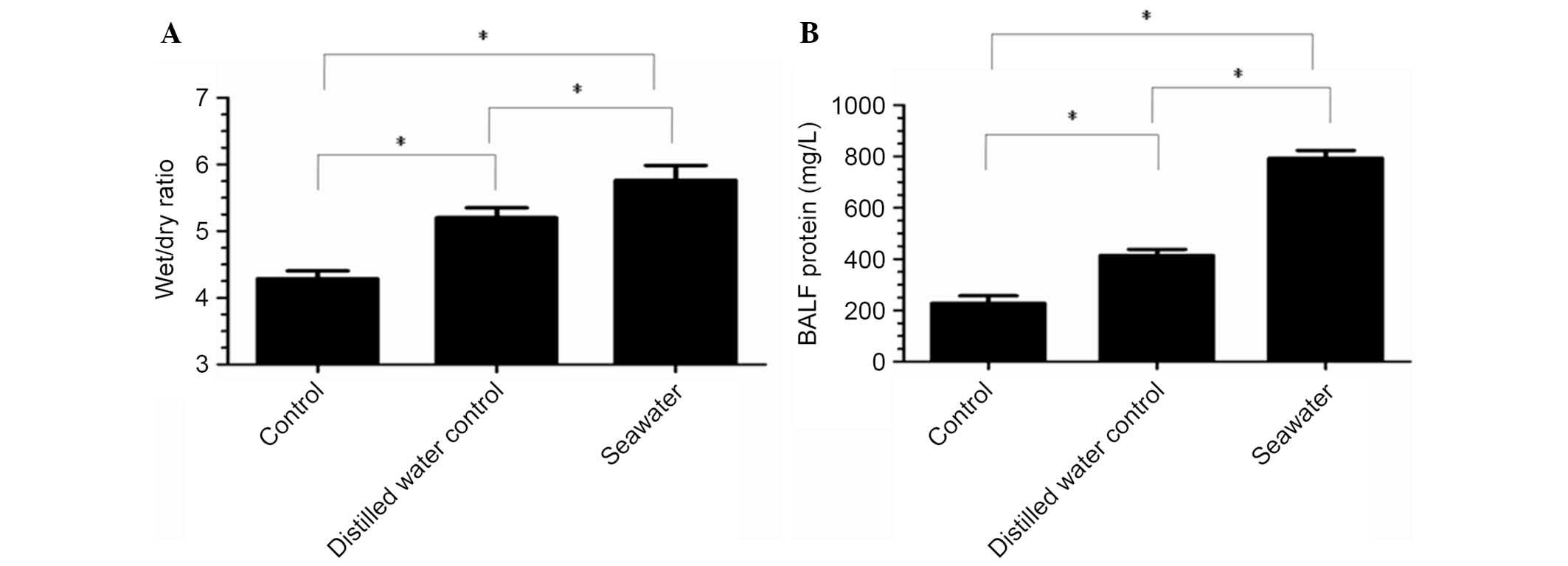
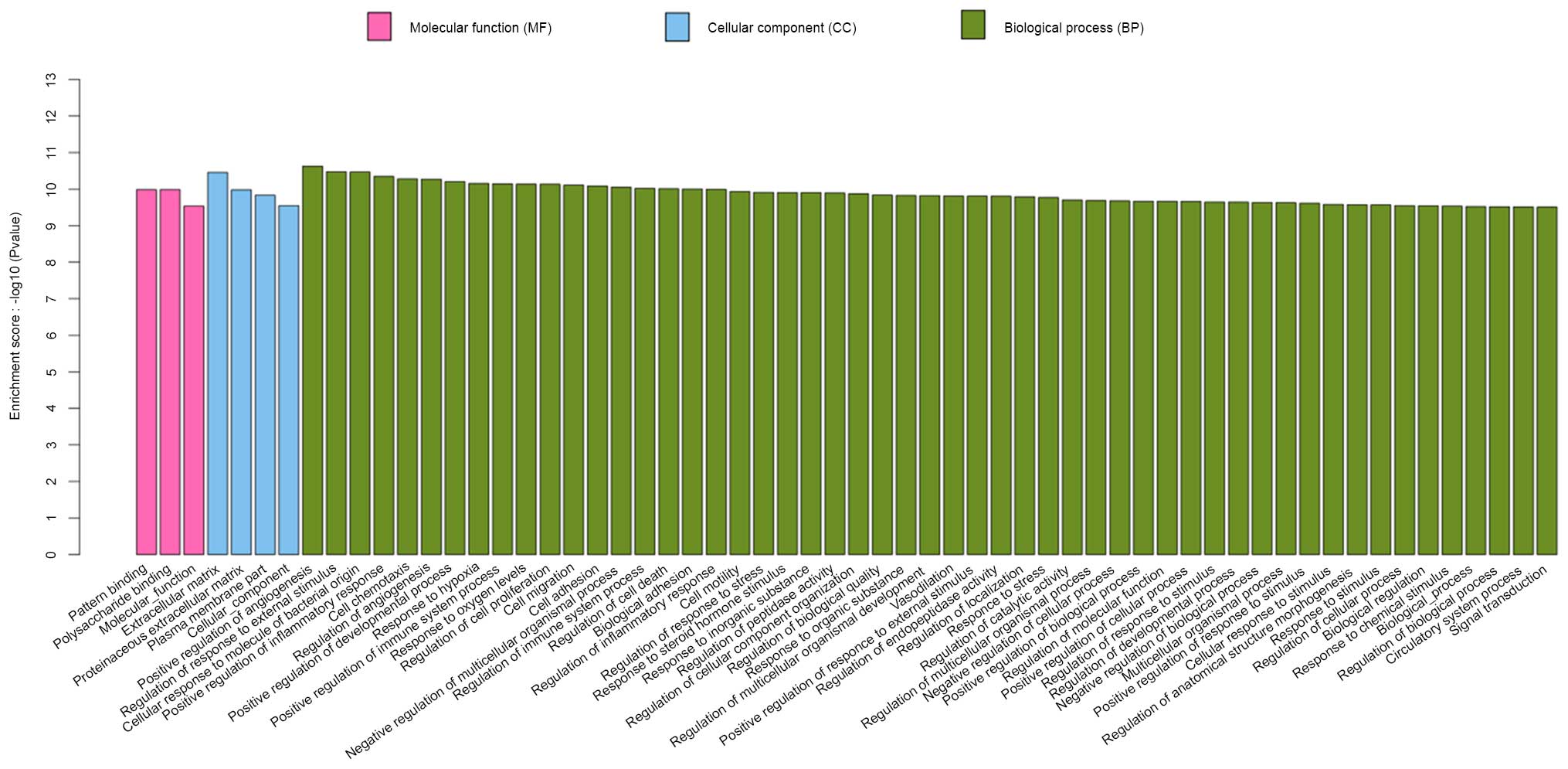
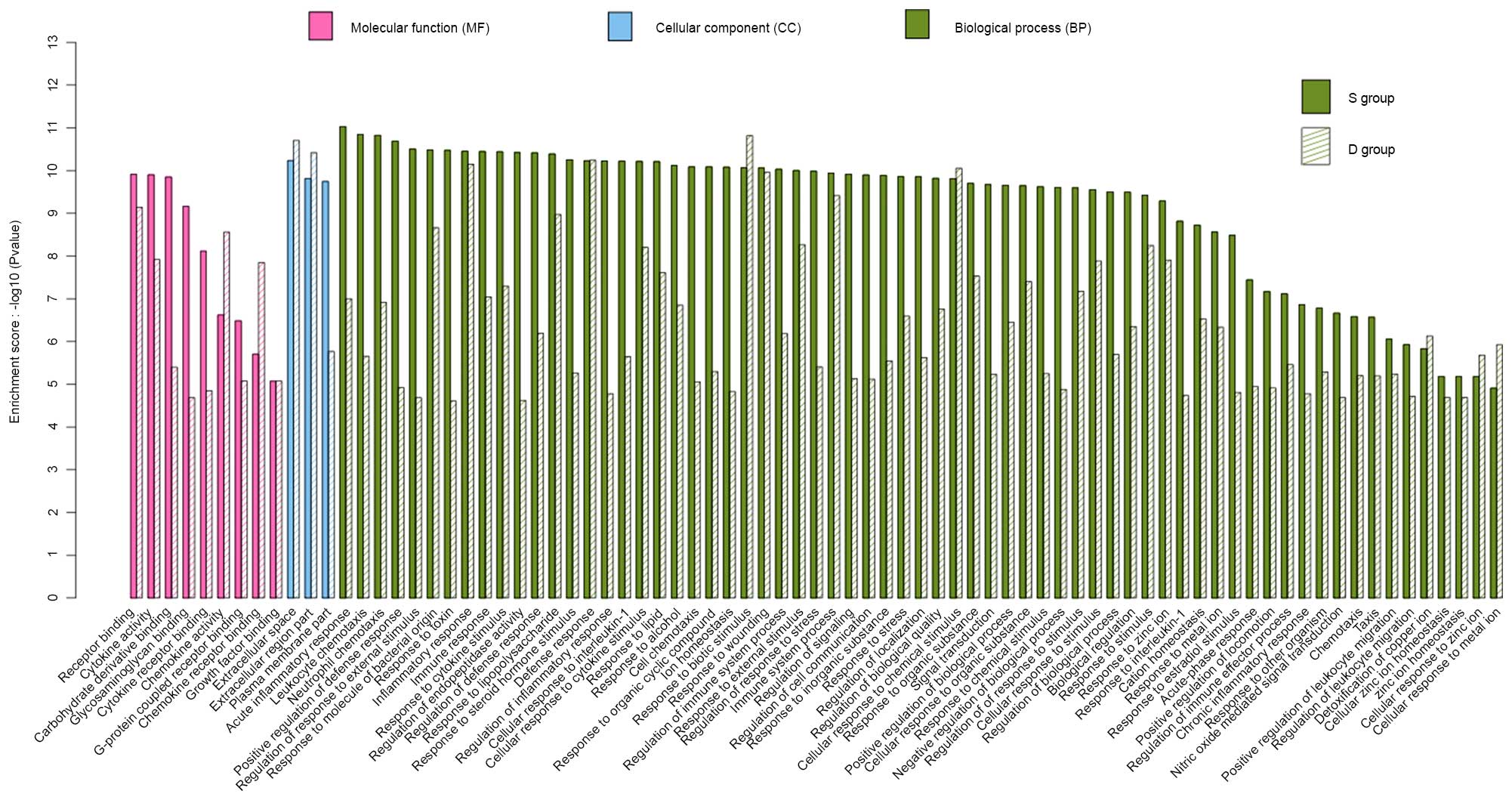
|
1
|
van Beeck EF, Branche CM, Szpilman D,
Modell JH and Bierens JJ: A new definition of drowning: Towards
documentation and prevention of a global public health problem.
Bull World Health Organ. 83:853–856. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Salomez F and Vincent JL: Drowning: A
review of epidemiology, pathophysiology, treatment and prevention.
Resuscitation. 63:261–268. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xinmin D, Yunyou D, Chaosheng P, Huasong
F, Pingkun Z, Jiguang M, Zhiqian X and Qinzhi X: Dexamethasone
treatment attenuates early seawater instillation-induced acute lung
injury in rabbits. Pharmacol Res. 53:372–379. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma L, Li Y, Zhao Y, Wang Q, Nan Y, Mu D,
Li W, Sun R, Jin F and Liu X: 3,5,4′-tri-O-acetylresveratrol
ameliorates seawater exposure-induced lung injury by upregulating
connexin 43 expression in lung. Mediators Inflamm. 2013:1821322013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang Y, Zhang B, Xu DQ, Li WP, Xu M, Li
JH, Xie XY, Fan QX, Liu W, Mu DG, et al: Tanshinone IIA attenuates
seawater aspiration-induced lung injury by inhibiting macrophage
migration inhibitory factor. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1052–1057. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma L, Zhao Y, Li B, Wang Q, Liu X, Chen X,
Nan Y, Liang L, Chang R, Liang L, et al:
3,5,4′-Tri-O-acetylresveratrol attenuates seawater
aspiration-induced lung injury by inhibiting activation of nuclear
factor-kappa B and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Respir Physiol
Neurobiol. 185:608–614. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu W, Dong M, Bo L, Li C, Liu Q, Li Y, Ma
L, Xie Y, Fu E, Mu D, et al: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates
seawater aspiration-induced acute lung injury via regulating
inflammatory cytokines and inhibiting JAK/STAT1 pathway in rats.
Mediators Inflamm. 2014:6125932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li J, Xu M, Fan Q, Xie X, Zhang Y, Mu D,
Zhao P, Zhang B, Cao F, Wang Y, et al: Tanshinone IIA ameliorates
seawater exposure-induced lung injury by inhibiting aquaporins
(AQP) 1 and AQP5 expression in lung. Respir Physiol Neurobiol.
176:39–49. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han F, Luo Y, Li Y, Liu Z, Xu D, Jin F and
Li Z: Seawater induces apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells via
the Fas/FasL-mediated pathway. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 182:71–80.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fan Q, Zhao P, Li J, Xie X, Xu M, Zhang Y,
Mu D, Li W, Sun R, Liu W, et al: 17β-Estradiol administration
attenuates seawater aspiration-induced acute lung injury in rats.
Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 24:673–681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hiroshima Y, Hsu K, Tedla N, Chung YM,
Chow S, Herbert C and Geczy CL: S100A8 induces IL-10 and protects
against acute lung injury. J Immunol. 192:2800–2811. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang M, Dong M, Liu W, Wang L, Luo Y, Li
Z and Jin F: 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 ameliorates seawater
aspiration-induced acute lung injury via NF-κB and RhoA/Rho kinase
pathways. PLoS One. 9:e1045072014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nosotti M, Falleni M, Palleschi A,
Pellegrini C, Alessi F, Bosari S and Santambrogio L: Quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction detection of lymph node lung
cancer micrometastasis using carcinoembryonic antigen marker.
Chest. 128:1539–1544. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi Y, Zhang B, Chen XJ, Xu DQ, Wang YX,
Dong HY, Ma SR, Sun RH, Hui YP and Li ZC: Osthole protects
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by preventing
downregulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Eur J Pharm Sci.
48:819–824. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou ZH, Sun B, Lin K and Zhu LW:
Prevention of rabbit acute lung injury by surfactant, inhaled
nitric oxide, and pressure support ventilation. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 161:581–588. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen XJ, Zhang B, Hou SJ, Shi Y, Xu DQ,
Wang YX, Liu ML, Dong HY, Sun RH, Bao ND, et al: Osthole improves
acute lung injury in mice by upregulating Nrf-2/thioredoxin 1.
Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 188:214–222. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Scharfman A, Hayem A, Lebas J, Laine A and
Sablonnière B: Comparison of three methods for protein measurement:
application to bronchoalveolar lavage fluids. Bull Eur Physiopathol
Respir. 16:785–789. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Saidel-Odes LR and Almog Y: Near-drowning
in the Dead Sea: A retrospective observational analysis of 69
patients. Isr Med Assoc J. 5:856–858. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gregorakos L, Markou N, Psalida V,
Kanakaki M, Alexopoulou A, Sotiriou E, Damianos A and Myrianthefs
P: Near-drowning: Clinical course of lung injury in adults. Lung.
187:93–97. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rui M, Duan YY, Wang HL, Zhang XH and Wang
Y: Differences between seawater- and freshwater-induced lung
injuries. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 21:416–420.
2009.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miyazato T, Ishikawa T, Michiue T and
Maeda H: Molecular pathology of pulmonary surfactants and cytokines
in drowning compared with other asphyxiation and fatal hypothermia.
Int J Legal Med. 126:581–587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McGrath EE, Marriott HM, Lawrie A, Francis
SE, Sabroe I, Renshaw SA, Dockrell DH and Whyte MK: TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) regulates inflammatory neutrophil
apoptosis and enhances resolution of inflammation. J Leukoc Biol.
90:855–865. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Beyer K, Poetschke C, Partecke LI, von
Bernstorff W, Maier S, Broeker BM and Heidecke CD: TRAIL induces
neutrophil apoptosis and dampens sepsis-induced organ injury in
murine colon ascendens stent peritonitis. PLoS One. 9:e974512014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Garcia-Hernández A, Arzate H,
Gil-Chavarria I, Rojo R and Moreno-Fierros L: High glucose
concentrations alter the biomineralization process in human
osteoblastic cells. Bone. 50:276–288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kim JH, Kang SS, Kim ES, Kim JY, Kim MJ
and Tchah H: Osmoprotective effects of supplemental epidermal
growth factor in an ex vivo multilayered human conjunctival model
under hyperosmotic stress. Graefes. Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol.
251:1945–1953. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|