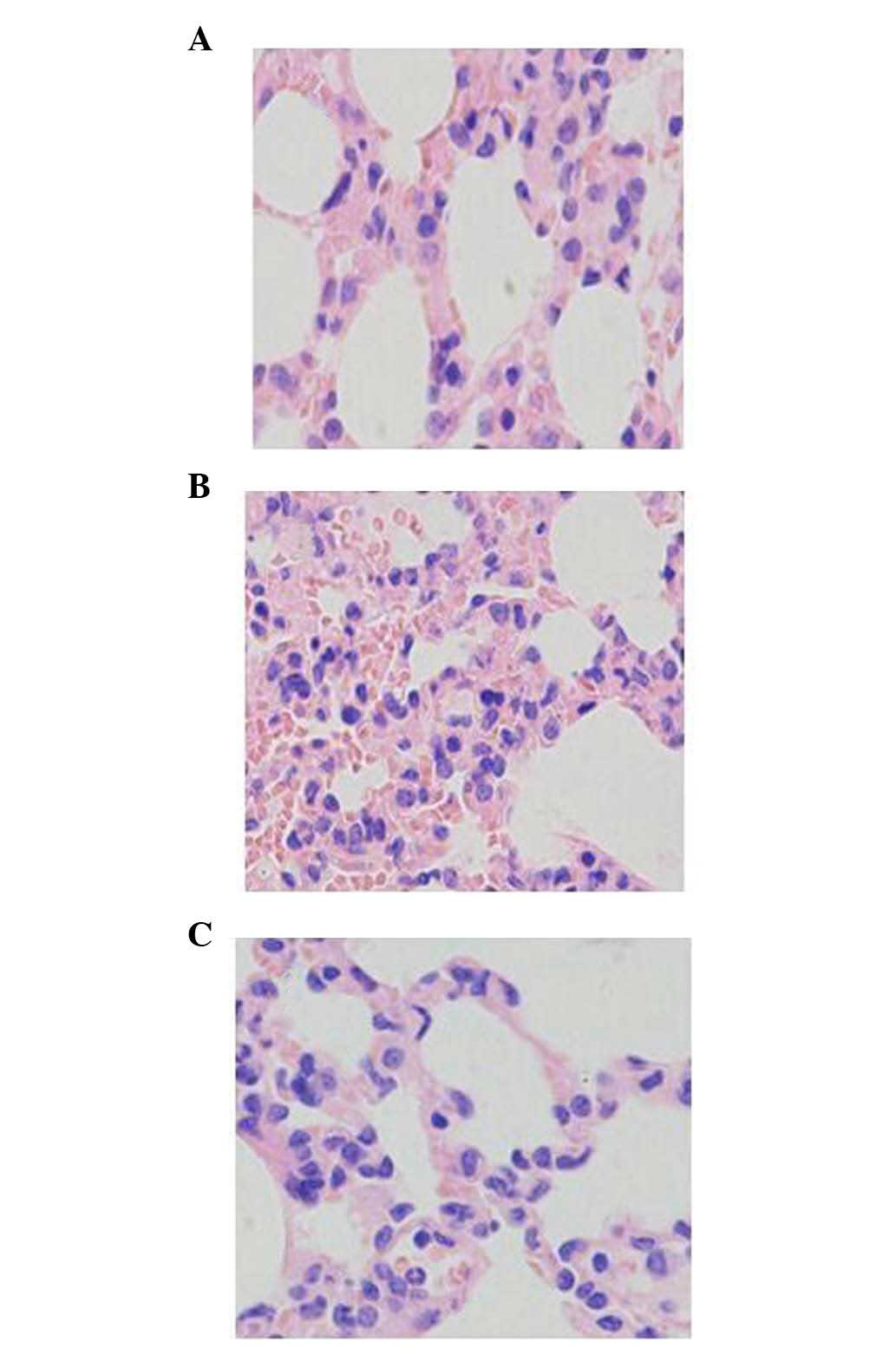
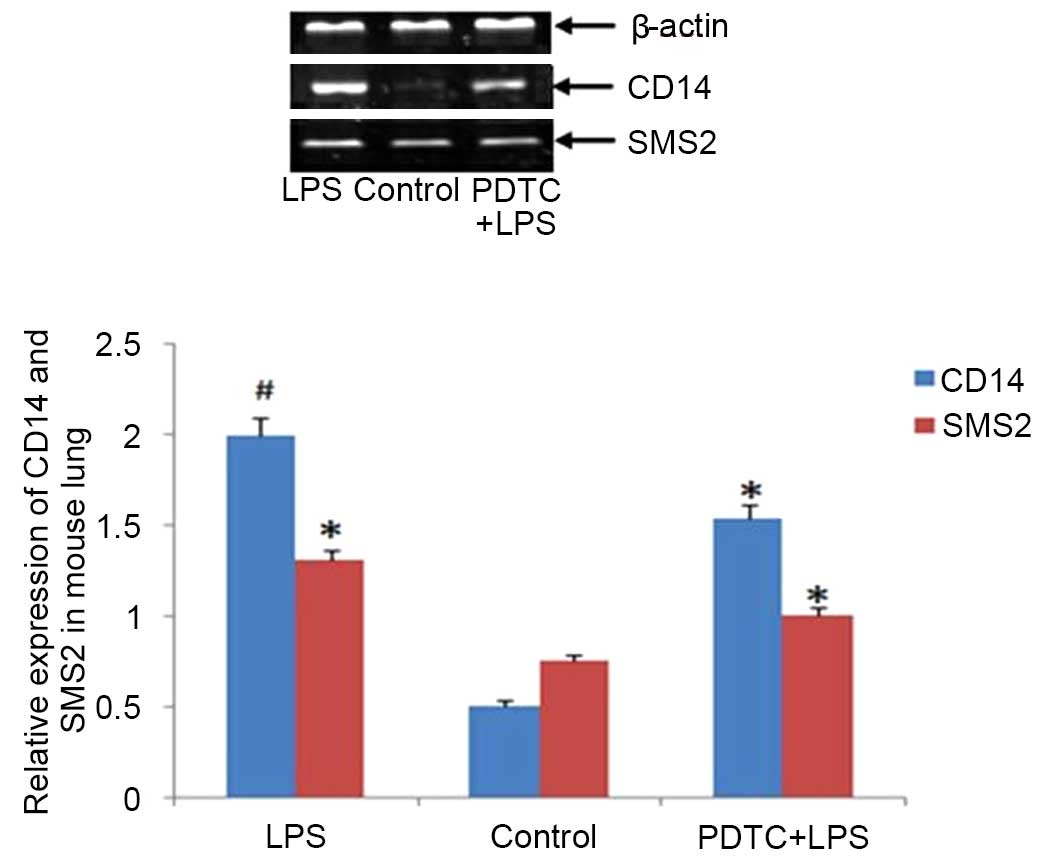
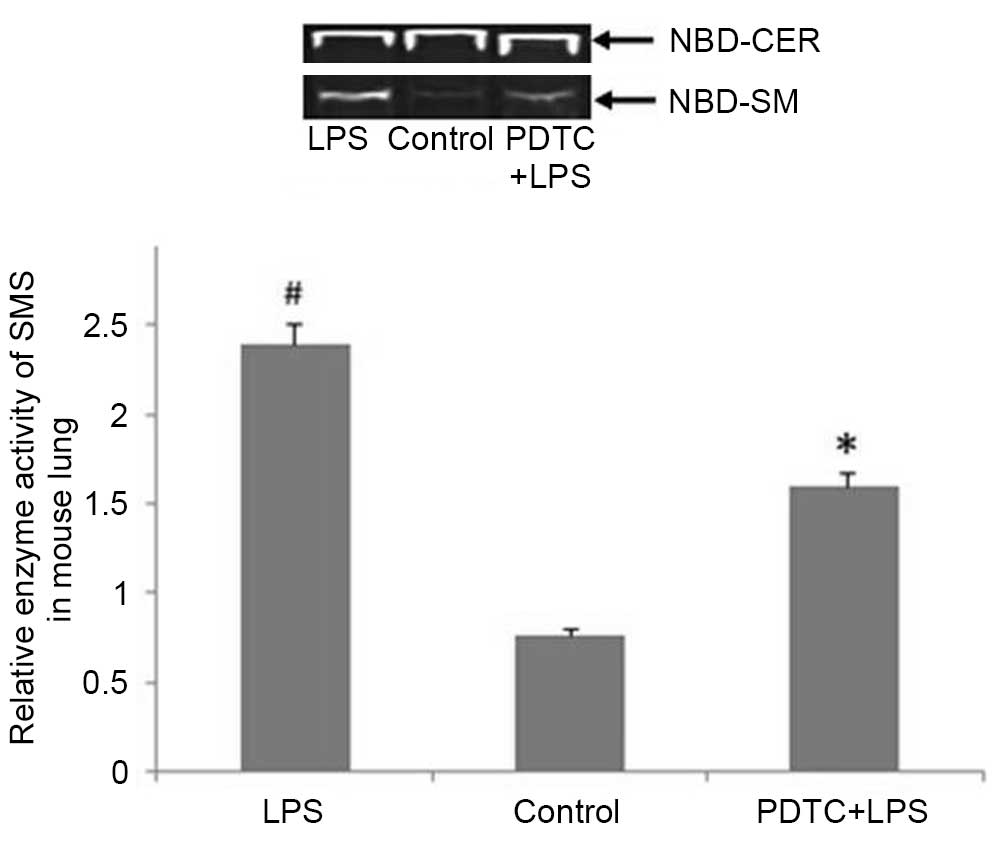
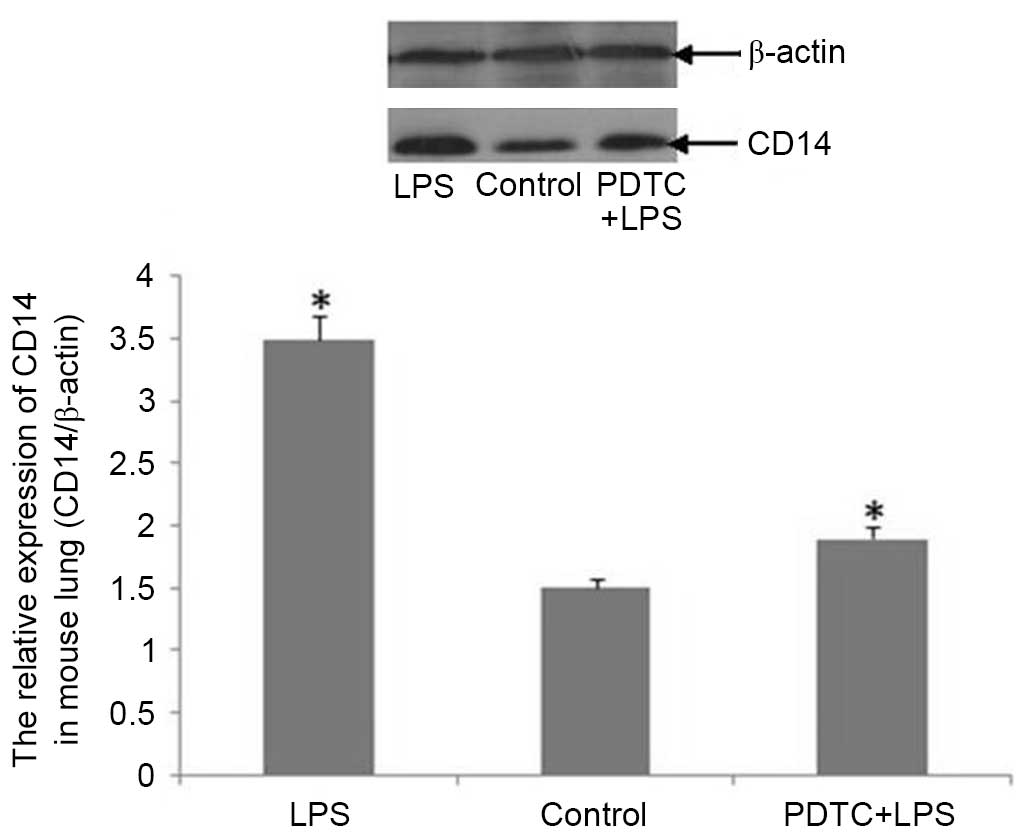
|
1
|
Zhang L, Wang L, Jiang J, Zheng D, Liu S
and Liu C: Lipopolysaccharides upregulate calcium concentration in
mouse uterine smooth muscle cells through the T-type calcium
channels. Int J Mol Med. 35:784–790. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vianna RC, Gomes RN, Bozza FA, Amâncio RT,
Bozza PT, David CM and Castro-Faria-Neto HC: Antibiotic treatment
in a murine model of sepsis: Impact on cytokines and endotoxin
release. Shock. 21:115–120. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen Y, Zhou X and Rong L: Analysis of
mechanical ventilation and lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury using DNA microarray analysis. Mol Med Rep. 11:4239–4245.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J,
Clermont G, Carcillo J and Pinsky MR: Epidemiology of severe sepsis
in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and
associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 29:1303–1310. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang Y and Guangxiong Y: Research progress
of epidemiology on sepsis. J Clin Emer Call. 6:416–420. 2015.In
Chinese.
|
|
6
|
Tadros T, Traber DL, Heggers JP and
Herndon DN: Effects of interleukin-1alpha administration on
intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury, mucosal permeability,
and bacterial translocation in burn and sepsis. Ann Surg.
237:101–109. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ulevitch RJ and Tobias PS:
Receptor-dependent mechanisms of cell stimulation by bacterial
endotoxin. Annu Rev Immunol. 13:437–457. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lloyd KL and Kubes P: GPI-linked
endothelial CD14 contributes to the detection of LPS. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 291:473–481. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gitlin JM and Loftin CD: Cyclooxygenase-2
inhibition increases lipopolysaccharide-induced atherosclerosis in
mice. Cardiovasc Res. 81:400–407. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Liu S, Wang H, Qiu C, Zhang J, Zhang T,
Zhou W, Lu Z, Rausch-Fan X and Liu Z: Escin inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in human periodontal
ligament cells. Mol Med Rep. 6:1150–1154. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Majdalawieh A and Ro HS: LPS-induced
suppression of macrophage cholesterol efflux is mediated by
adipocyte enhancer-binding protein 1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
41:1518–1525. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wong MC, van Diepen JA, Hu L, Guigas B, de
Boer HC, van Puijvelde GH, Kuiper J, van Zonneveld AJ, Shoelson SE,
Voshol PJ, et al: Hepatocyte-specific IKKβ expression aggravates
atherosclerosis development in APOE*3-Leiden mice.
Atherosclerosis. 220:362–368. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Miyaso H, Morimoto Y, Ozaki M, Guigas B,
de Boer HC, van Puijvelde GH, Kuiper J, van Zonneveld AJ, Shoelson
SE and Voshol PJ: Obstructive jaundice increases sensitivity to
lipopolysaccharide via TLR4 upregulation: Possible involvement in
gut-derived hepatocyte growth factor-protection of hepatocytes. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:1859–1866. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xie GQ, Jiang JX, Chen YH, Liu DW, Zhu PF
and Wang ZG: Induction of acute hepatic injury by endotoxin in
mice. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 1:558–564. 2002.
|
|
15
|
Merrill AH Jr and Jones DD: An update of
the enzymology and regulation of sphingomyelin metabolism. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1044:1–12. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Meng A, Luberto C, Meier P, Bai A, Yang X,
Hannun YA and Zhou D: Sphingomyelin synthase as a potential target
for D609-induced apoptosis in U937 human monocytic leukemia cells.
Exp Cell Res. 292:385–392. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Triantafilou M, Miyake K, Golenbock DT and
Triantafilou K: Mediators of innate immune recognition of bacteria
concentrate in lipid rafts and facilitate
lipopolysaccharide-induced cell activation. J Cell Sci.
115:2603–2611. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huitema K, van den Dikkenberg J, Brouwers
JF and Holthuis JC: Identification of a family of animal
sphingomyelin synthases. EMBO J. 23:33–44. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yamaoka S, Miyaji M, Kitano T, Umehara H
and Okazaki T: Expression cloning of a human cDNA restoring
sphingomyelin synthesis and cell growth in sphingomyelin
synthase-defective lymphoid cells. J Biol Chem. 279:18688–18693.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Anjum F, Joshi K, Grinkina N, Gowda S,
Cutaia M and Wadgaonkar R: Role of sphingomyelin synthesis in
pulmonary endothelial cell cytoskeletal activation and
endotoxin-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
47:94–103. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
National Research Council Committee for
the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals;
The National Academies Collection; Reports funded by National
Institutes of Health: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. National Academies Press (US) National Academy of
Sciences; Washington (DC): 2011
|
|
22
|
Bao Y, Geng Y and Jing H: Effect of
hirudin on the levels of acute lung injury rat tumor necrosis
factor-α and matrix metal-loproteinase-12. Mol Med Rep. 5:873–875.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Le Roy D, Di Padova F, Adachi Y, Glauser
MP, Calandra T and Heumann D: Critical role of
lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and CD14 in immune responses
against gram-negative bacteria. J Immunol. 167:2759–2765. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abalsamo L, Spadaro F, Bozzuto G, Paris L,
Cecchetti S, Lugini L, Iorio E, Molinari A, Ramoni C and Podo F:
Inhibition of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C results
in loss of mesenchymal traits in metastatic breast cancer cells.
Breast Cancer Res. 14:R502012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Adams JM II, Pratipanawatr T, Berria R,
Wang E, DeFronzo RA, Sullards MC and Mandarino LJ: Ceramide content
is increased in skeletal muscle from obese insulin-resistant
humans. Diabetes. 53:25–31. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Górska M, Dobrzyń A, Zendzian-Piotrowska M
and Górski J: Effect of streptozotocin-diabetes on the functioning
of the sphingomyelin-signalling pathway in skeletal muscles of the
rat. Horm Metab Res. 36:14–21. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Straczkowski M, Kowalska I, Nikolajuk A,
Dzienis-Straczkowska S, Kinalska I, Baranowski M,
Zendzian-Piotrowska M, Brzezinska Z and Gorski J: Relationship
between insulin sensitivity and sphingomyelin signaling pathway in
human skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 53:1215–1221. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen HC, Smith SJ, Ladha Z, Jensen DR,
Ferreira LD, Pulawa LK, McGuire JG, Pitas RE, Eckel RH and Farese
RV Jr: Increased insulin and leptin sensitivity in mice lacking
acyl CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1. J Clin Invest.
109:1049–1055. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lou B, Dong J, Li Y, Ding T, Bi T, Li Y,
Deng X, Ye D and Jiang XC: Pharmacologic inhibition of
sphingomyelin synthase (SMS) activity reduces apolipoprotein-B
secretion from hepatocytes and attenuates endotoxin-mediated
macrophage inflammation. PLoS One. 9:e1026412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Akashi S, Ogata H, Kirikae F, Kirikae T,
Kawasaki K, Nishijima M, Shimazu R, Nagai Y, Fukudome K, Kimoto M
and Miyake K: Regulatory roles for CD14 and phosphatidylinositol in
the signaling via toll-like receptor 4-MD-2. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 268:172–177. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dinarello CA: Interleukin-1 and the
pathogenesis of the acute-phase response. N Engl J Med.
311:1413–1418. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Heinrich PC, Castell JV and Andus T:
Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem J. 265:621–636.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Beutler B and Cerami A: Cachectin/tumor
necrosis factor: An endogenous mediator of shock and inflammation.
Immunol Res. 5:281–293. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|