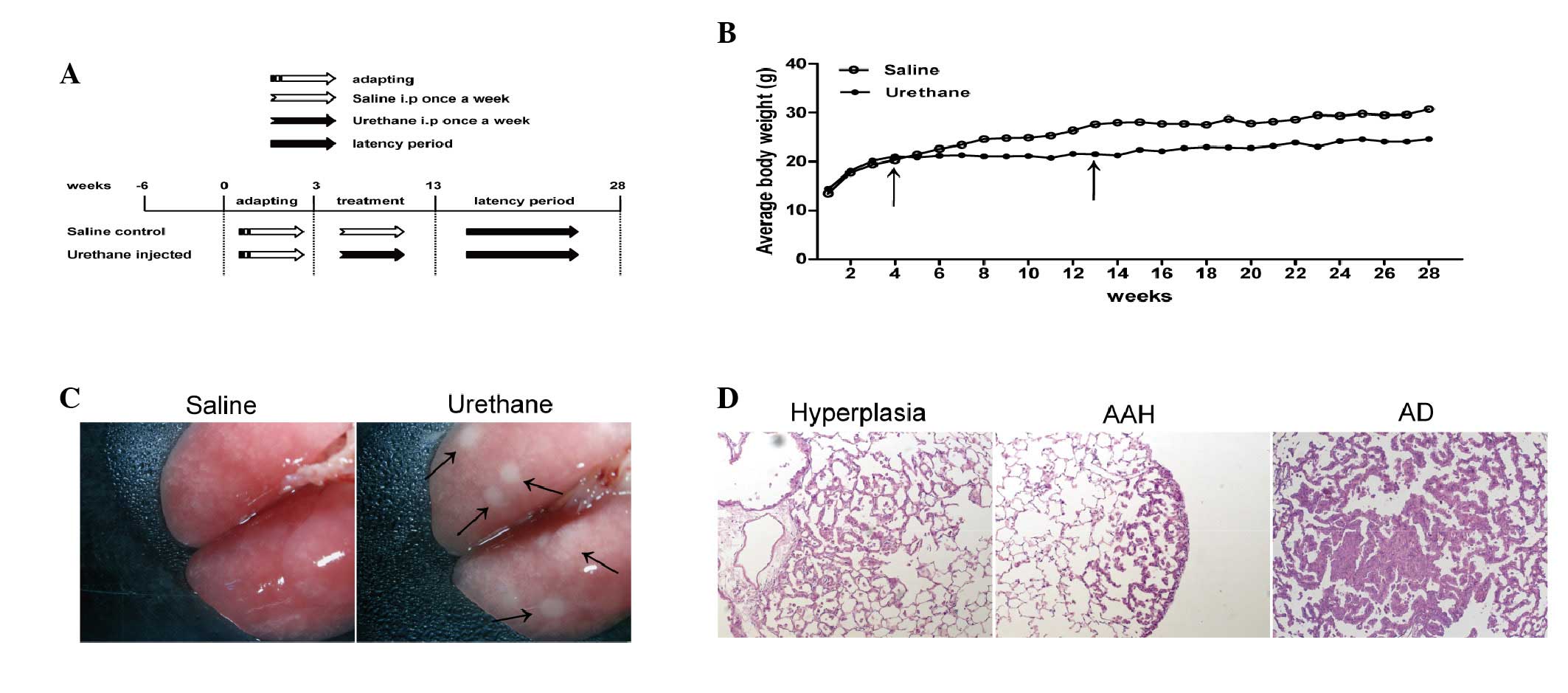
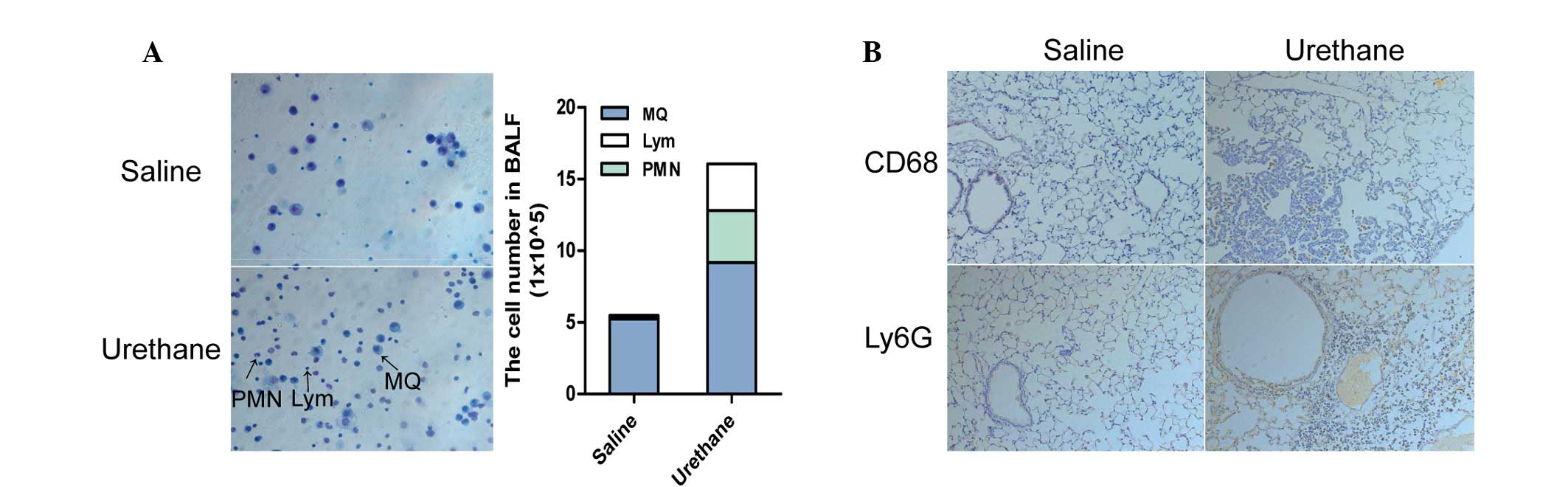
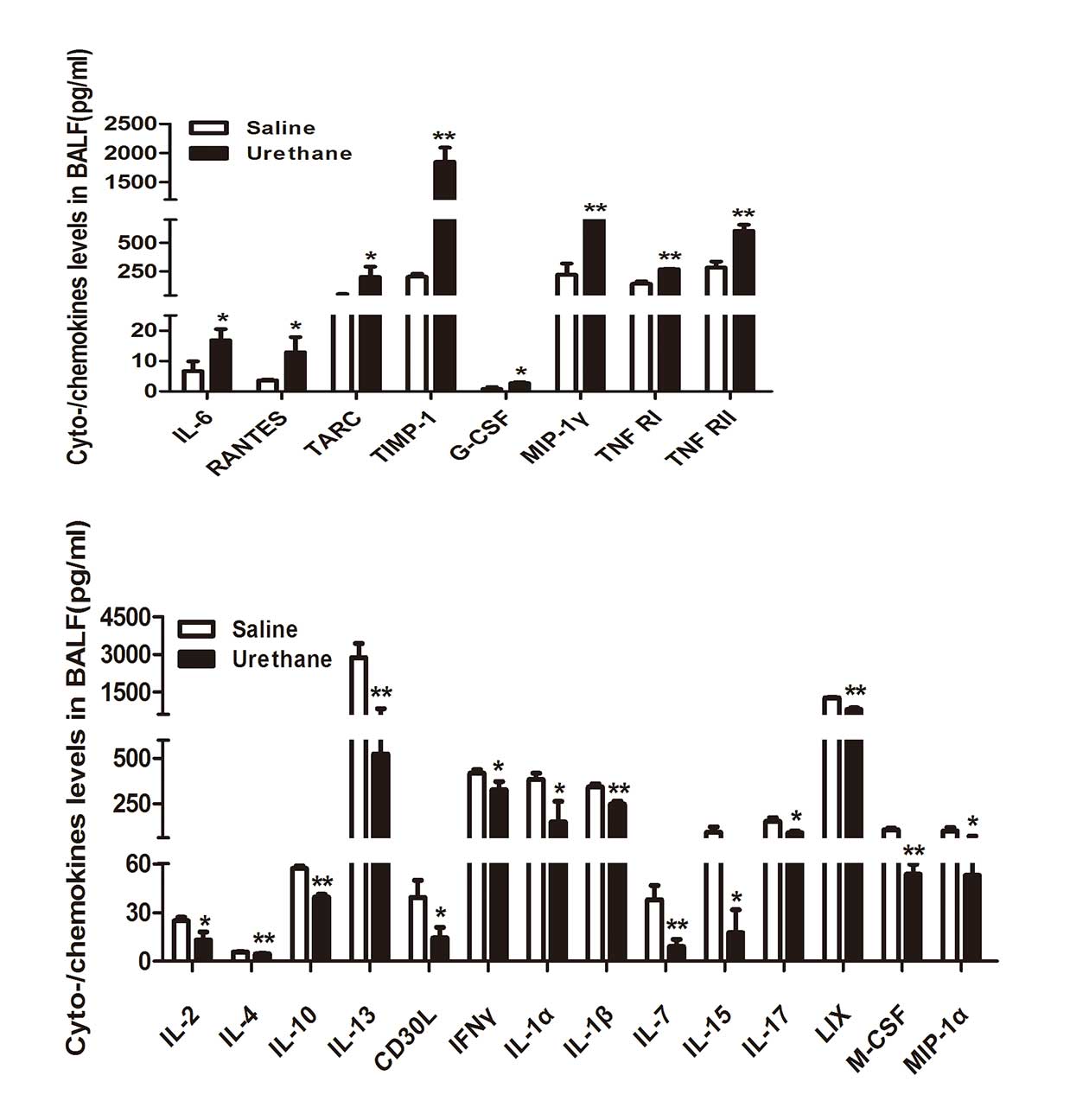
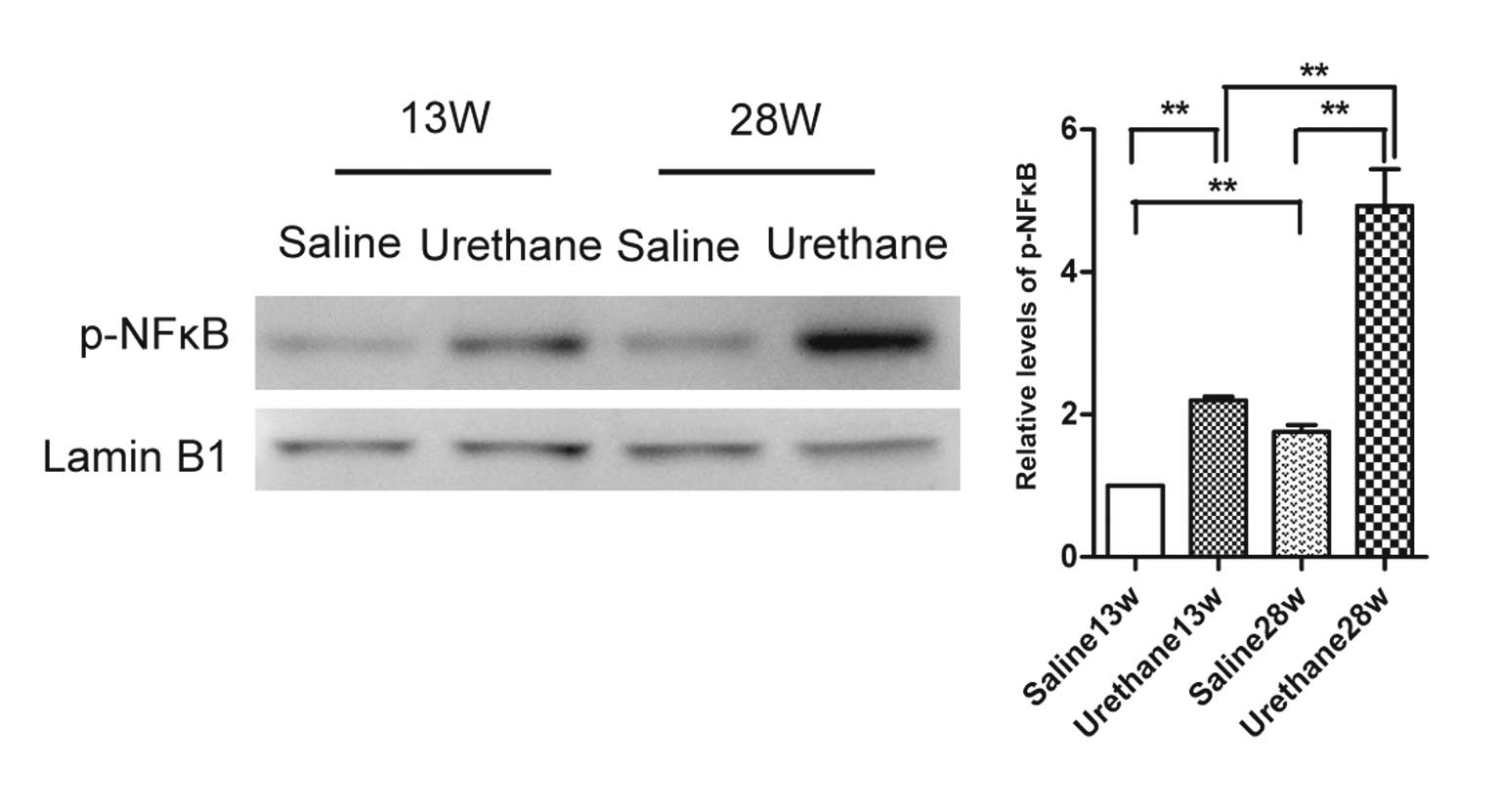
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Malkinson AM: Molecular comparison of
human and mouse pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Exp Lung Res.
24:541–555. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nonas S, Miller I, Kawkitinarong K,
Chatchavalvanich S, Gorshkova I, Bochkov VN, Leitinger N, Natarajan
V, Garcia JG and Birukov KG: Oxidized phospholipids reduce vascular
leak and inflammation in rat model of acute lung injury. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 173:1130–1138. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lagan AL, Melley DD, Evans TW and Quinlan
GJ: Pathogenesis of the systemic inflammatory syndrome and acute
lung injury: Role of iron mobilization and decompartmentalization.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 294:L161–L174. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Moraes TJ, Zurawska JH and Downey GP:
Neutrophil granule contents in the pathogenesis of lung injury.
Curr Opin Hematol. 13:21–27. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Malkinson AM and Beer DS: Major effect on
susceptibility to urethan-induced pulmonary adenoma by a single
gene in BALB/cBy mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 70:931–936.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bernert H, Sekikawa K, Radcliffe RA, Iraqi
F, You M and Malkinson AM: Tnfa and Il-10 deficiencies have
contrasting effects on lung tumor susceptibility: Gender-dependent
modulation of IL-10 haploinsufficiency. Mol Carcinog. 38:117–123.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Doris K, Karabela SP, Kairi CA, Simoes DC,
Roussos C, Zakynthinos SG, Kalomenidis I, Blackwell TS and
Stathopoulos GT: Allergic inflammation does not impact
chemical-induced carcinogenesis in the lungs of mice. Respir Res.
11:1182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartsch H and Nair J: Chronic inflammation
and oxidative stress in the genesis and perpetuation of cancer:
Role of lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, and repair. Langenbecks
Arch Surg. 391:499–510. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Azad N, Rojanasakul Y and Vallyathan V:
Inflammation and lung cancer: Roles of reactive oxygen/nitrogen
species. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 11:1–15. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Candido J and Hagemann T: Cancer-related
inflammation. J Clin Immunol. 33(Suppl 1): S79–S84. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Miller YE, Dwyer-Nield LD, Keith RL, Le M,
Franklin WA and Malkinson AM: Induction of a high incidence of lung
tumors in C57BL/6 mice with multiple ethyl carbamate injections.
Cancer Lett. 198:139–144. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lian X, Qin Y, Hossain SA, Yang L, White
A, Xu H, Shipley JM, Li T, Senior RM, Du H and Yan C:
Overexpression of Stat3C in pulmonary epithelium protects against
hyperoxic lung injury. J Immunol. 174:7250–7256. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Raposo TP, Beirão BC, Pang LY, Queiroga FL
and Argyle DJ: Inflammation and cancer: Till death tears them
apart. Vet J. 205:161–174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kanterman J, Sade-Feldman M and Baniyash
M: New insights into chronic inflammation-induced
immunosuppression. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:307–318. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gonda TA, Tu S and Wang TC: Chronic
inflammation, the tumor microenvironment and carcinogenesis. Cell
Cycle. 8:2005–2013. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Albini A and Sporn MB: The tumour
microenvironment as a target for chemoprevention. Nat Rev Cancer.
7:139–147. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Porta C, Larghi P, Rimoldi M, Totaro MG,
Allavena P, Mantovani A and Sica A: Cellular and molecular pathways
linking inflammation and cancer. Immunobiology. 214:761–777. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Redente EF, Orlicky DJ, Bouchard RJ and
Malkinson AM: Tumor signaling to the bone marrow changes the
phenotype of monocytes and pulmonary macrophages during
urethane-induced primary lung tumorigenesis in A/J mice. Am J
Pathol. 170:693–708. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nguyen DP, Li J and Tewari AK:
Inflammation and prostate cancer: The role of interleukin 6 (IL-6).
BJU Int. 113:986–992. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cho WC, Kwan CK, Yau S, So PP, Poon PC and
Au JS: The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of lung cancer.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 15:1127–1137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Conti P and DiGioacchino M: MCP-1 and
RANTES are mediators of acute and chronic inflammation. Allergy
Asthma Proc. 22:133–137. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Narayan C and Kumar A: Constitutive over
expression of IL-1β, IL-6, NF-κB, and Stat3 is a potential cause of
lung tumorgenesis in urethane (ethyl carbamate) induced Balb/c
mice. J Carcinog. 11:92012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Signaling to
NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 18:2195–2224. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baker RG, Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB,
inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 13:11–22. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pikarsky E, Porat RM, Stein I, Abramovitch
R, Amit S, Kasem S, Gutkovich-Pyest E, Urieli-Shoval S, Galun E and
Ben-Neriah Y: NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in
inflammation-associated cancer. Nature. 431:461–466. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stathopoulos GT, Sherrill TP, Cheng DS,
Scoggins RM, Han W, Polosukhin VV, Connelly L, Yull FE, Fingleton B
and Blackwell TS: Epithelial NF-kappaB activation promotes
urethane-induced lung carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:18514–18519. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|