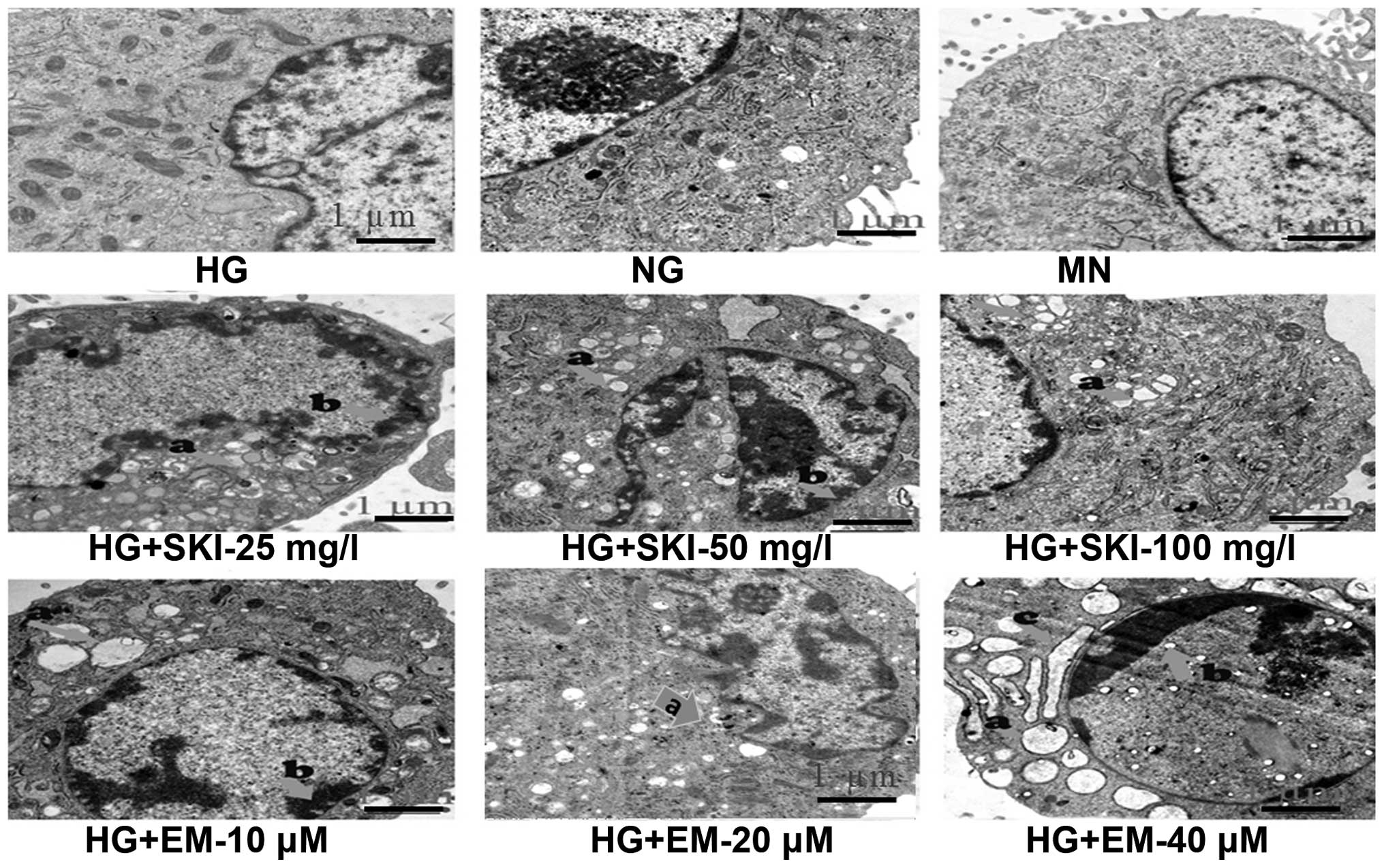
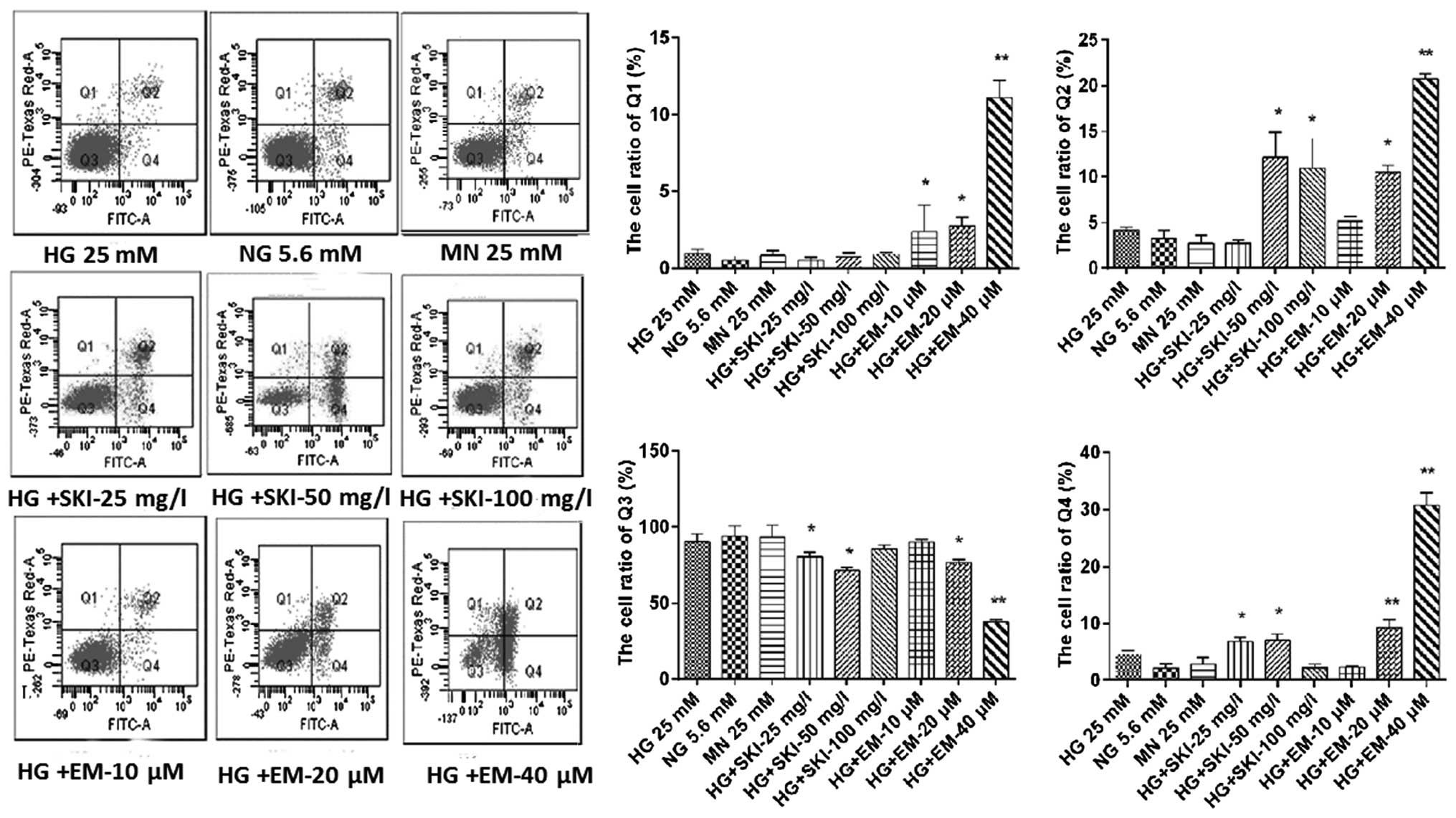
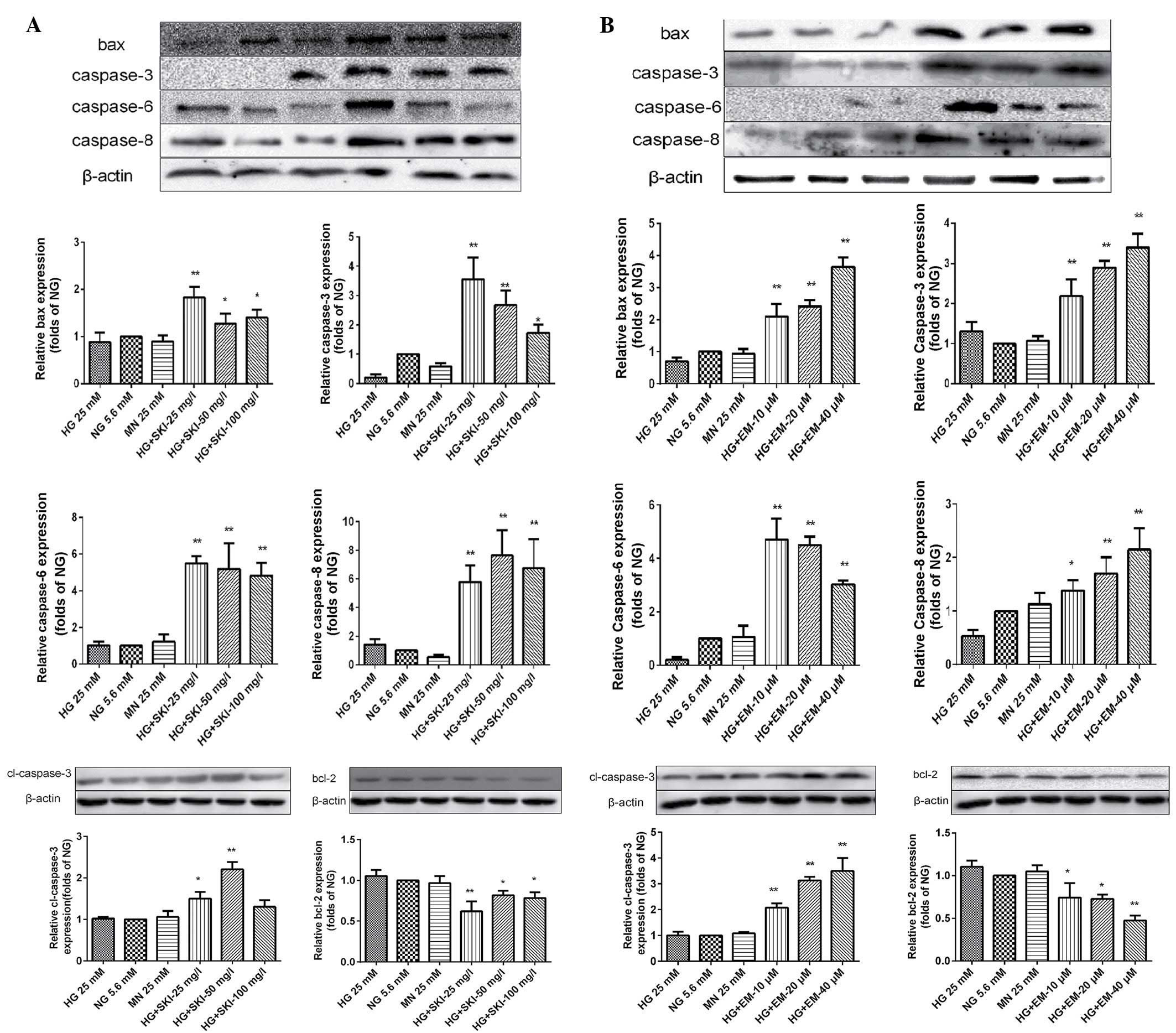
|
1
|
Giunti S, Barit D and Cooper ME: Diabetic
nephropathy: From mechanisms to rational therapies. Minerva Med.
97:241–262. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abboud HE: Mesangial cell biology. Exp
Cell Res. 318:979–985. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Danesh FR, Sadeghi MM, Amro N, Philips C,
Zeng L, Lin S, Sahai A and Kanwar YS: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl
CoA reductase inhibitors prevent high glucose-induced proliferation
of mesangial cells via modulation of Rho GTPase/p21 signaling
pathway: Implications for diabetic nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:8301–8305. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hodgkinson AD, Bartlett T, Oates PJ,
Millward BA and Demaine AG: The response of antioxidant genes to
hyperglycemia is abnormal in patients with type 1 diabetes and
diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 52:846–851. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ye CH, Wu F, Liu TH and Li MQ: Compound
traditional chinese medicine preparation. Chinese Patent
CN103768525A. Filed January 17, 2014; issued May 7, 2014.
|
|
6
|
QY YC and Rui P: Antagonizing effects of
Shenkang Injection on renal interstitial fibrosis in model rat of
chronic aristolochic acid nephropathy. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs.
4:587–592. 2009.
|
|
7
|
Jiang ZW, Lv YY and Xia JL: The phase
clinical observation study of shengkang injection on chronic renal
failure. J China Med Univ. 40:941–945. 2011.
|
|
8
|
Du J, Chen H and Wang XB: Effect of
shenkang injection on hypertrophy and expressions of p21 and p27 in
glomerular mesangial cells of rats cultured in high glucose. Chin J
Integr Tradit West Med. 26(Suppl): 68–71. 2006.In Chinese.
|
|
9
|
Xue J, Ding W and Liu Y: Anti-diabetic
effects of emodin involved in the activation of PPARgamma on
high-fat diet-fed and low dose of streptozotocin-induced diabetic
mice. Fitoterapia. 81:173–177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang LHLF: Effect of emodin and berberine
on gastrointestinal motility in type 2 diabetic rats. World Chin J
Digestol. 13:607–611. 2005.
|
|
11
|
Song B and Liu XZ: Emodin improves insulin
sensitivity in KKAy diabetic mice. Chinese PLA Postgrad Med.
32:1274–1276. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Wang J, Huang H, Liu P, Tang F, Qin J,
Huang W, Chen F, Guo F, Liu W and Yang B: Inhibition of
phosphorylation of p38 MAPK involved in the protection of
nephropathy by emodin in diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol.
553:297–303. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Jia L, Liu ZC, Zhang H, Zhang PJ,
Wan Q and Wang R: Emodin ameliorates high-glucose induced mesangial
p38 over-activation and hypocontractility via activation of
PPARgamma. Exp Mol Med. 41:648–655. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li X, Liu W, Wang Q, Liu P, Deng Y, Lan T,
Zhang X, Qiu B, Ning H and Huang H: Emodin suppresses cell
proliferation and fibronectin expression via p38MAPK pathway in rat
mesangial cells cultured under high glucose. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
307:157–162. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arora MK and Singh UK: Molecular
mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy: An update.
Vascul Pharmacol. 58:259–271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Pang S, Deng B, Qian L, Chen J,
Zou J, Zheng J, Yang L, Zhang C, Chen X, et al: High glucose
induces renal mesangial cell proliferation and fibronectin
expression through JNK/NF-κB/NADPH oxidase/ROS pathway, which is
inhibited by resveratrol. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:629–638.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sodhi CP, Phadke SA, Batlle D and Sahai A:
Hypoxia and high glucose cause exaggerated mesangial cell growth
and collagen synthesis: Role of osteopontin. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 280:F667–F674. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Suzaki Y, Yoshizumi M, Kagami S, Nishiyama
A, Ozawa Y, Kyaw M, Izawa Y, Kanematsu Y, Tsuchiya K and Tamaki T:
BMK1 is activated in glomeruli of diabetic rats and in mesangial
cells by high glucose conditions. Kidney Int. 65:1749–1760. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ye Y, Wang H, Chu JH, Chou GX, Chen SB, Mo
H, Fong WF and Yu ZL: Atractylenolide II induces G1 cell-cycle
arrest and apoptosis in B16 melanoma cells. J Ethnopharmacol.
136:279–282. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li H, Wang P, Liu Q, Cheng X, Zhou Y and
Xiao Y: Cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis induced by Equisetum
hyemale extract in murine leukemia L1210 cells. J Ethnopharmacol.
144:322–327. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ghibelli L and Diederich M: Multistep and
multitask Bax activation. Mitochondrion. 10:604–613. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fuentes-Prior P and Salvesen GS: The
protein structures that shape caspase activity, specificity,
activation and inhibition. Biochem J. 384:201–232. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|