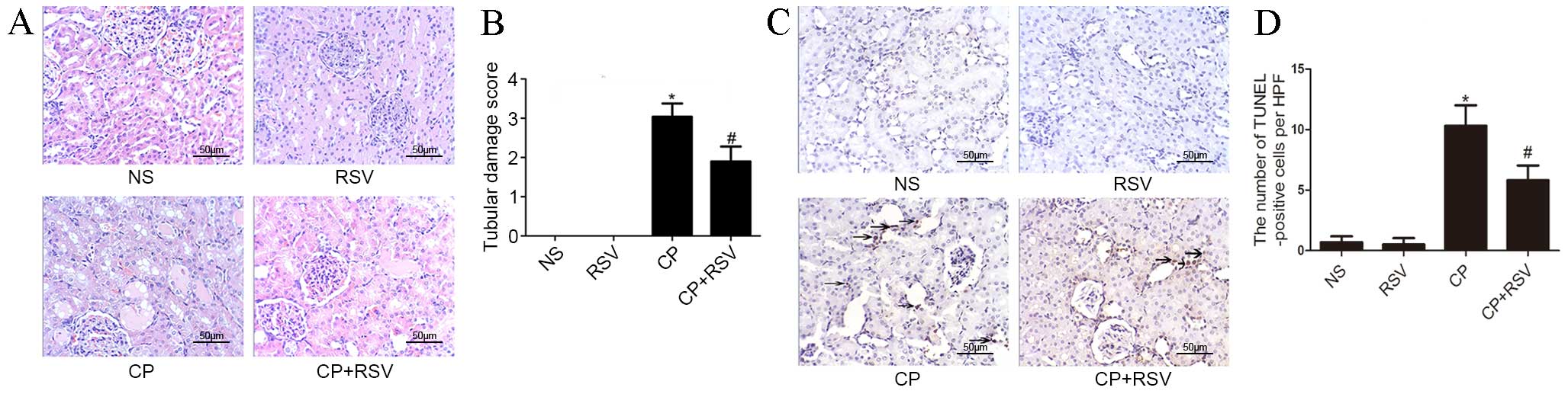
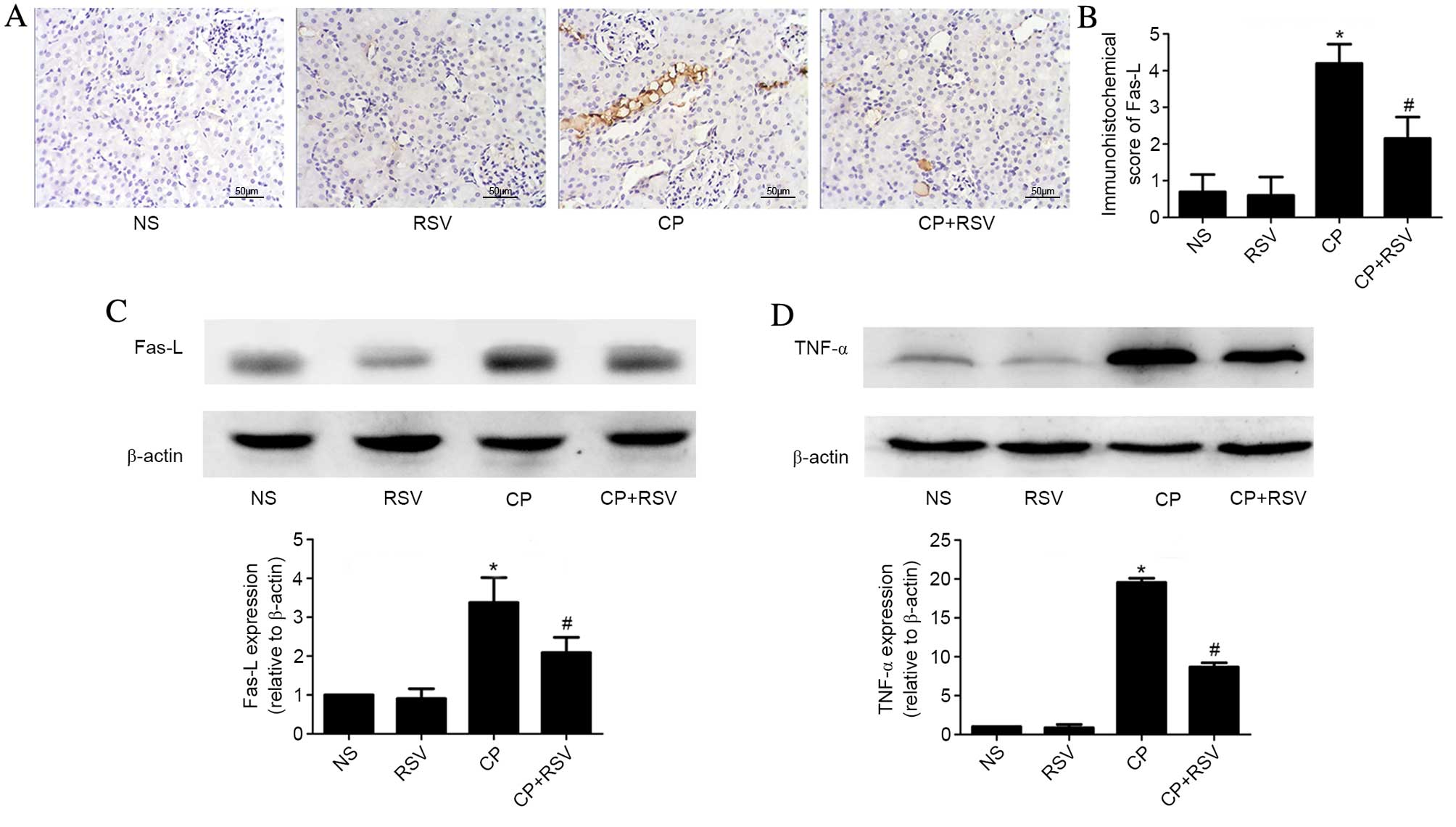
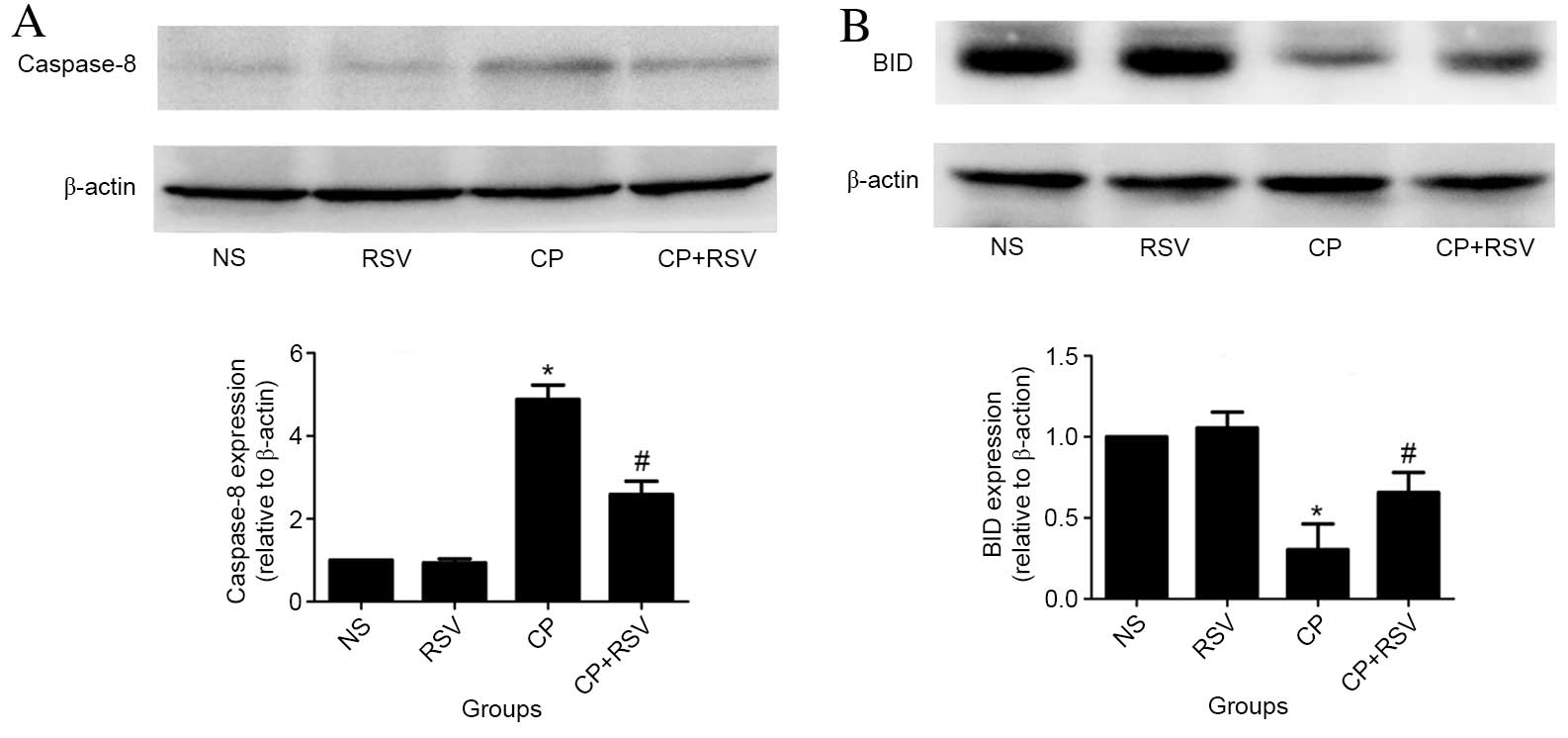
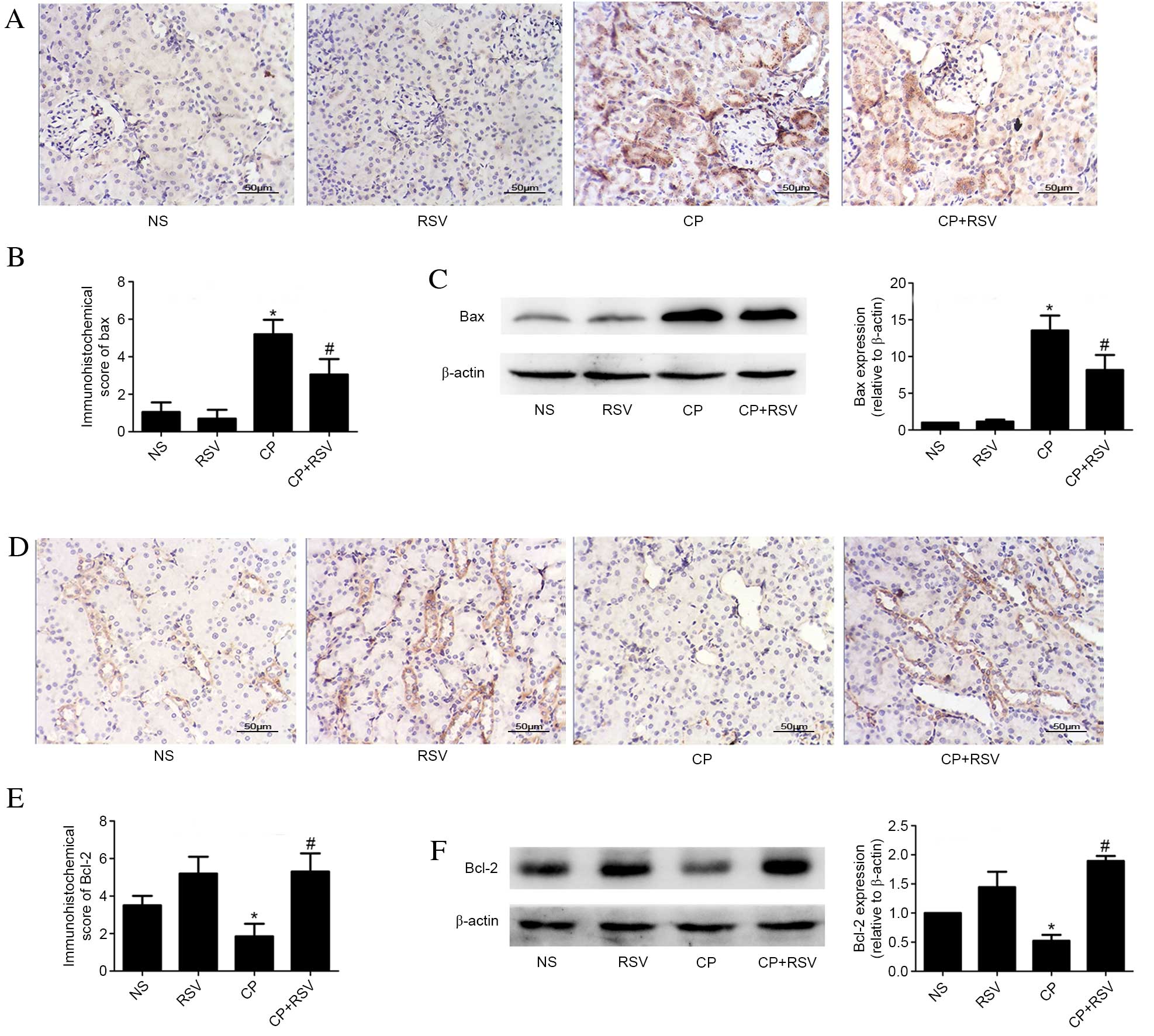
|
1
|
Linkermann A, Chen G, Dong G, Kunzendorf
U, Krautwald S and Dong Z: Regulated cell death in AKI. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 25:2689–2701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bellomo R, Kellum JA and Ronco C: Acute
kidney injury. Lancet. 380:756–766. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Faubel S, Chawla LS, Chertow GM, Goldstein
SL, Jaber BL and Liu KD; Acute Kidney Injury Advisory Group of the
American Society of Nephrology: Ongoing clinical trials in AKI.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 7:861–873. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lameire NH, Bagga A, Cruz D, De Maeseneer
J, Endre Z, Kellum JA, Liu KD, Mehta RL, Pannu N, Van Biesen W and
Vanholder R: Acute kidney injury: An increasing global concern.
Lancet. 382:170–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
dos Santos NA, Carvalho Rodrigues MA,
Martins NM and dos Santos AC: Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and
targets of nephroprotection: An update. Arch Toxicol. 86:1233–1250.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sánchez-González PD, López-Hernández FJ,
López-Novoa JM and Morales AI: An integrative view of the
pathophysiological events leading to cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Crit
Rev Toxicol. 41:803–821. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Karasawa T and Steyger PS: An integrated
view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Toxicol
Lett. 237:219–227. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pabla N and Dong Z: Cisplatin
nephrotoxicity: Mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney
Int. 73:994–1007. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
Signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zou P, Song J, Jiang B, Pei F, Chen B,
Yang X, Liu G and Hu Z: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate protects against
cisplatin nephrotoxicity by inhibiting the apoptosis in mouse. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:4607–4616. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Linkermann A, Himmerkus N, Rölver L,
Keyser KA, Steen P, Bräsen JH, Bleich M, Kunzendorf U and Krautwald
S: Renal tubular Fas ligand mediates fratricide in
cisplatin-induced acute kidney failure. Kidney Int. 79:169–178.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tsuruya K, Ninomiya T, Tokumoto M,
Hirakawa M, Masutani K, Taniguchi M, Fukuda K, Kanai H, Kishihara
K, Hirakata H and Iida M: Direct involvement of the
receptor-mediated apoptotic pathways in cisplatin-induced renal
tubular cell death. Kidney Int. 63:72–82. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tsuruya K, Tokumoto M, Ninomiya T,
Hirakawa M, Masutani K, Taniguchi M, Fukuda K, Kanai H, Hirakata H
and Iida M: Antioxidant ameliorates cisplatin-induced renal tubular
cell death through inhibition of death receptor-mediated pathways.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 285:F208–F218. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen
C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ, Debatin KM, Krammer PH and Peter ME: Two
CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. EMBO J. 17:1675–1687. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang X and Parrish AR: Loss of
α(E)-catenin promotes Fas mediated apoptosis in tubular epithelial
cells. Apoptosis. 20:921–929. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C
and Wang X: Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c
release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface
death receptors. Cell. 94:481–490. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nogae S, Miyazaki M, Kobayashi N, Saito T,
Abe K, Saito H, Nakane PK, Nakanishi Y and Koji T: Induction of
apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion model of mouse kidney: Possible
involvement of Fas. J Am Soc Nephrol. 9:620–631. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schelling JR, Nkemere N, Kopp JB and
Cleveland RP: Fas-dependent fratricidal apoptosis is a mechanism of
tubular epithelial cell deletion in chronic renal failure. Lab
Invest. 78:813–824. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Malhotra A, Bath S and Elbarbry F: An
organ system approach to explore the antioxidative,
anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective actions of resveratrol. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2015:8039712015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kitada M and Koya D: Renal protective
effects of resveratrol. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:5680932013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Catalgol B, Batirel S, Taga Y and Ozer NK:
Resveratrol: French paradox revisited. Front Pharmacol. 3:1412012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kanamori H, Takemura G, Goto K, Tsujimoto
A, Ogino A, Takeyama T, Kawaguchi T, Watanabe T, Morishita K,
Kawasaki M, et al: Resveratrol reverses remodeling in hearts with
large, old myocardial infarctions through enhanced
autophagy-activating AMP kinase pathway. Am J Pathol. 182:701–713.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Turner RS, Thomas RG, Craft S, van Dyck
CH, Mintzer J, Reynolds BA, Brewer JB, Rissman RA, Raman R and
Aisen PS; Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study: A randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of resveratrol for Alzheimer
disease. Neurology. 85:1383–1391. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim DH, Jung YJ, Lee JE, Lee AS, Kang KP,
Lee S, Park SK, Han MK, Lee SY, Ramkumar KM, et al: SIRT1
activation by resveratrol ameliorates cisplatin-induced renal
injury through deacetylation of p53. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
301:F427–F435. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oi N, Jeong CH, Nadas J, Cho YY, Pugliese
A, Bode AM and Dong Z: Resveratrol, a red wine polyphenol,
suppresses pancreatic cancer by inhibiting leukotriene
A4hydrolase. Cancer Res. 70:9755–9764. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Crandall JP, Oram V, Trandafirescu G, Reid
M, Kishore P, Hawkins M, Cohen HW and Barzilai N: Pilot study of
resveratrol in older adults with impaired glucose tolerance. J
Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 67:1307–1312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Palsamy P and Subramanian S: Resveratrol
protects diabetic kidney by attenuating hyperglycemia-mediated
oxidative stress and renal inflammatory cytokines via Nrf2-Keap1
signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1812:719–731. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Do Amaral CL, Francescato HD, Coimbra TM,
Costa RS, Darin JD, Antunes LM and Bianchi Mde L: Resveratrol
attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Arch Toxicol.
82:363–370. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Holthoff JH, Wang Z, Seely KA, Gokden N
and Mayeux PR: Resveratrol improves renal microcirculation,
protects the tubular epithelium, and prolongs survival in a mouse
model of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney Int.
81:370–378. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Liu FC, Tsai HI and Yu HP:
Organ-Protective effects of red wine extract, resveratrol, in
oxidative stress-mediated reperfusion injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2015:5686342015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang B, Ramesh G, Norbury CC and Reeves
WB: Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is mediated by tumor necrosis
factor-alpha produced by renal parenchymal cells. Kidney Int.
72:37–44. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ and Yuan J: Cleavage of
BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas
pathway of apoptosis. Cell. 94:491–501. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schug ZT, Gonzalvez F, Houtkooper RH, Vaz
FM and Gottlieb E: BID is cleaved by caspase-8 within a native
complex on the mitochondrial membrane. Cell Death Differ.
18:538–548. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Ott M, Norberg E, Zhivotovsky B and
Orrenius S: Mitochondrial targeting of tBid/Bax: A role for the TOM
complex? Cell Death Differ. 16:1075–1082. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Korsmeyer SJ, Wei MC, Saito M, Weiler S,
Oh KJ and Schlesinger PH: Pro-apoptotic cascade activates BID,
which oligomerizes BAK or BAX into pores that result in the release
of cytochrome c. Cell Death Differ. 7:1166–1173. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|