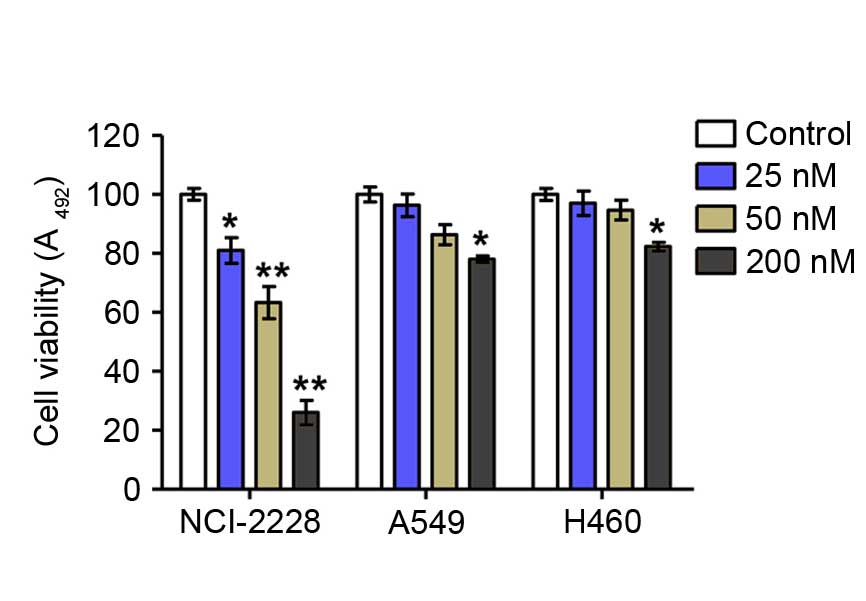
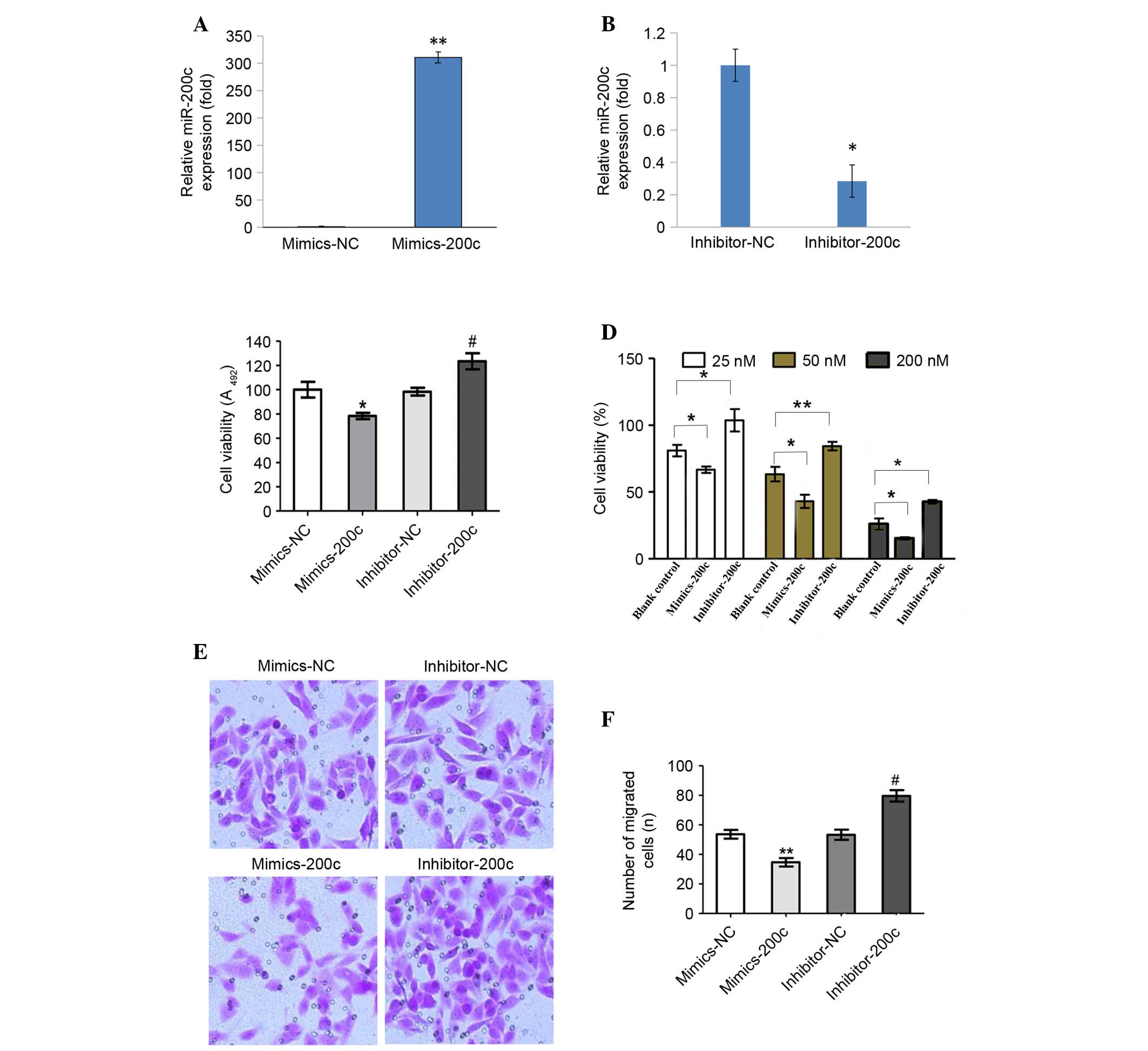
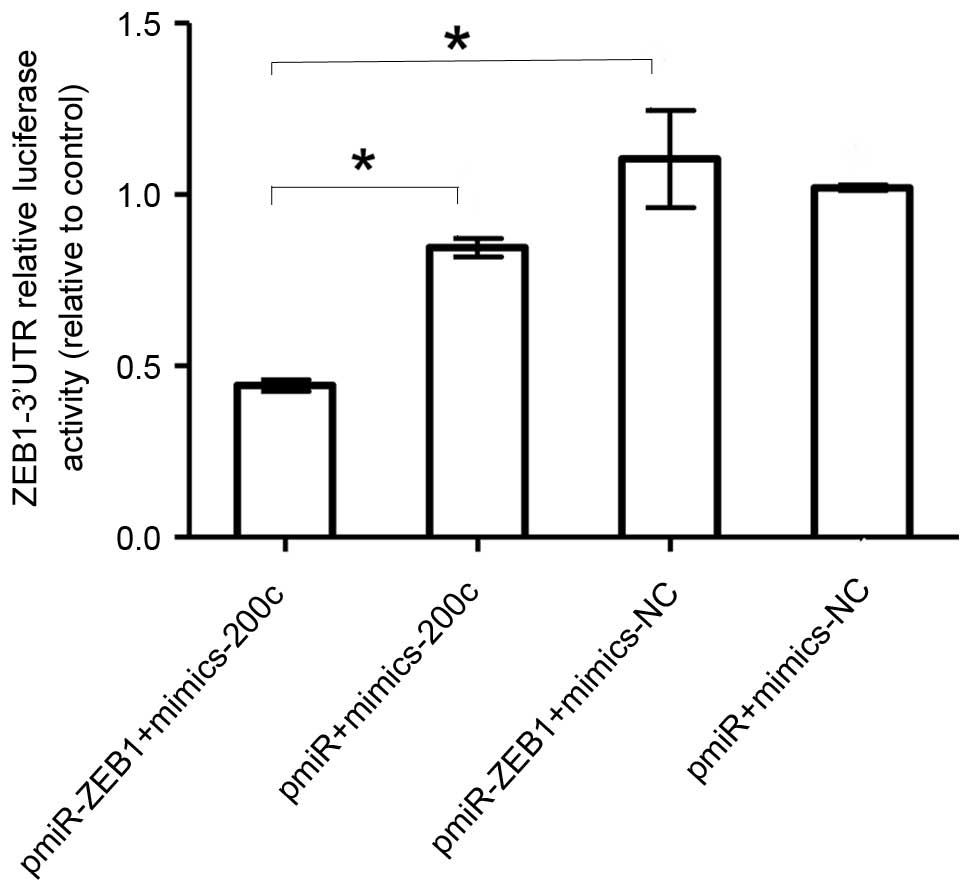
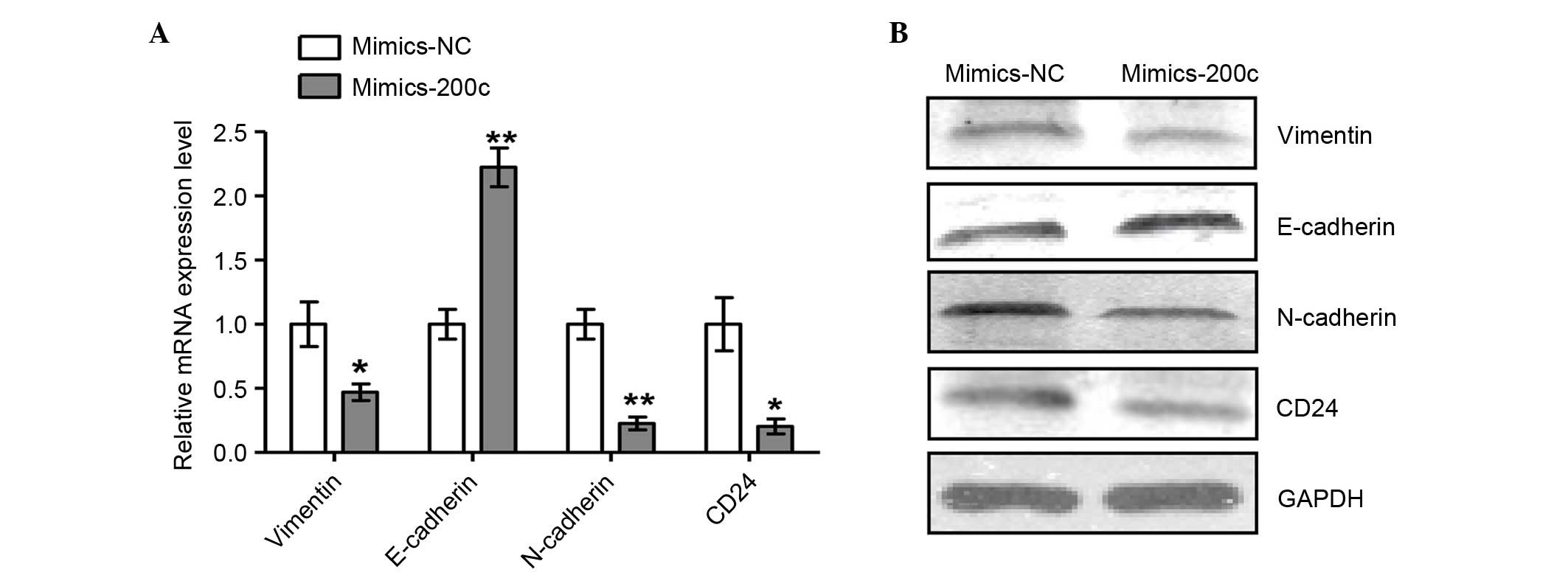
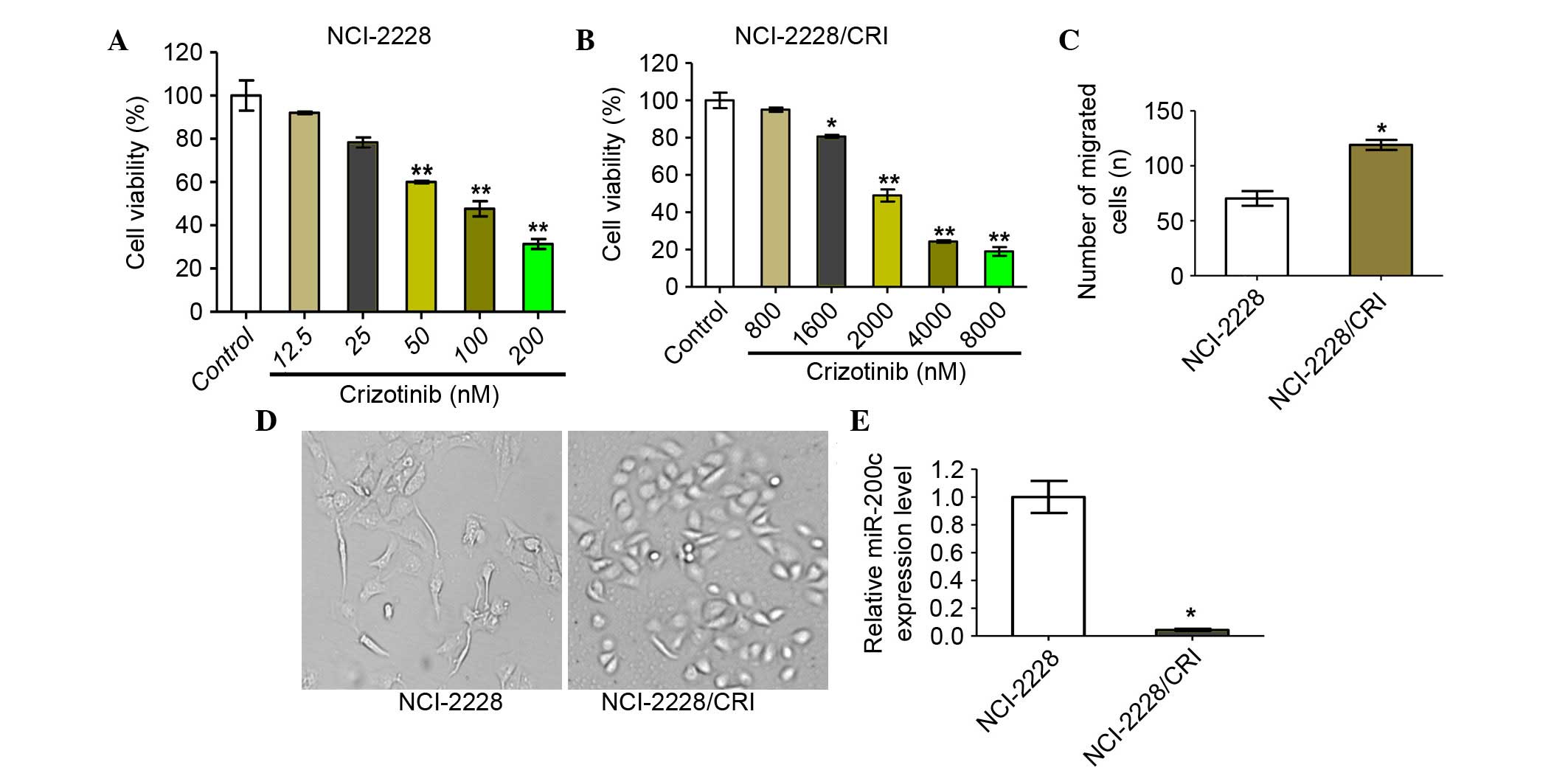
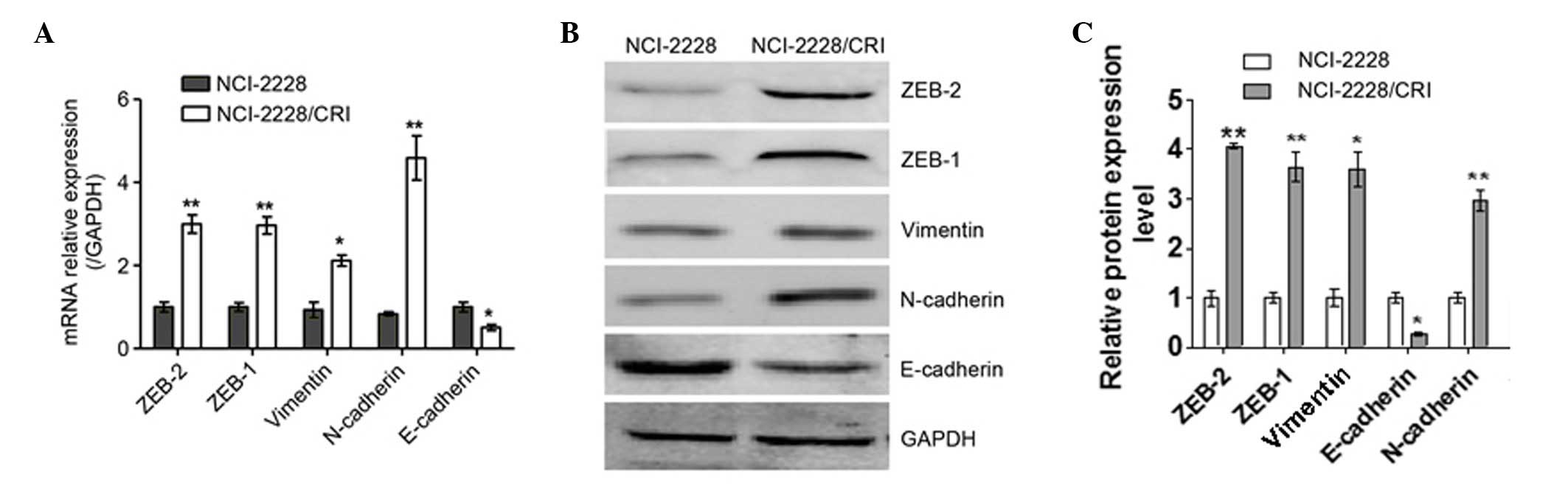
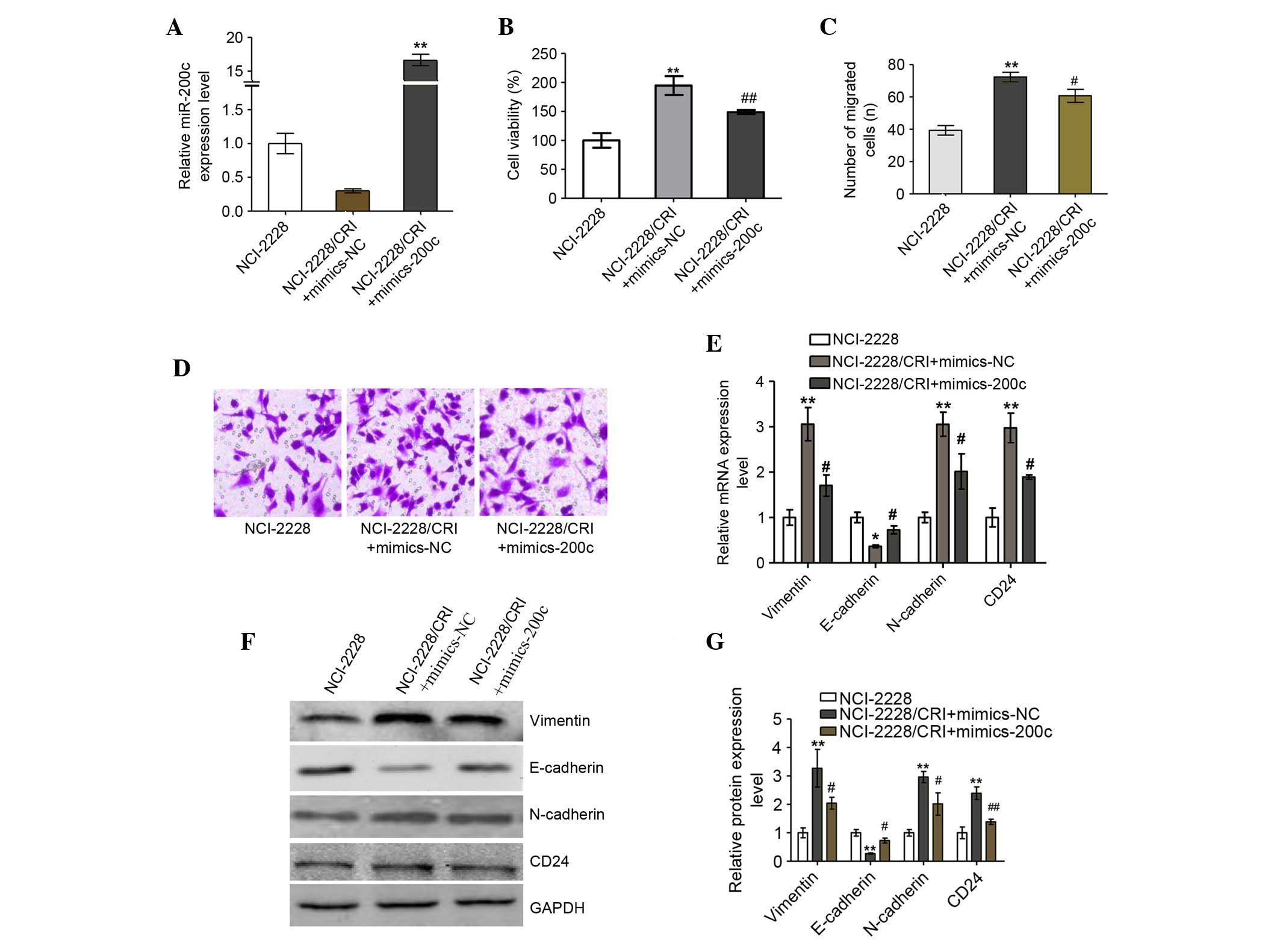
|
1
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blanco R, Maestu I, de la Torre MG,
Cassinello A and Nuñez I: A review of the management of elderly
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 26:451–463.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zimmermann S, Dziadziuszko R and Peters S:
Indications and limitations of chemotherapy and targeted agents in
non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. Cancer Treat Rev.
40:716–722. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rothschild SI and Gautschi O: Crizotinib
in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer.
14:473–480. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT,
Solomon B, Maki RG, Ou SH, Dezube BJ, Jänne PA, Costa DB, et al:
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1693–1703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Malik SM, Maher VE, Bijwaard KE, Becker
RL, Zhang L, Tang SW, Song P, Liu Q, Marathe A, Gehrke B, et al: US
Food and Drug Administration approval: Crizotinib for treatment of
advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer that is
anaplastic lymphoma kinase positive. Clin Cancer Res. 20:2029–2034.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa
K, Mekhail T, Felip E, Cappuzzo F, Paolini J, Usari T, et al:
First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 371:2167–2177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Beasley MB, Chitale
DA, Dacic S, Giaccone G, Jenkins RB, Kwiatkowski DJ, Saldivar JS,
Squire J, et al: Molecular testing guideline for selection of lung
cancer patients for EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors:
Guideline from the college of American pathologists, international
association for the study of lung cancer and association for
molecular pathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 137:828–860. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iacono D, Chiari R, Metro G, Bennati C,
Bellezza G, Cenci M, Ricciuti B, Sidoni A, Baglivo S, Minotti V and
Crinò L: Future options for ALK-positive non-small cell lung
cancer. Lung Cancer. 87:211–219. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N,
Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF and Goodall GJ: A double-negative
feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family
regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res.
68:7846–7854. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G and Kang Y: The
miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin
transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem.
283:14910–14914. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cochrane DR, Spoelstra NS, Howe EN,
Nordeen SK and Richer JK: MicroRNA-200c mitigates invasiveness and
restores sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic
agents. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1055–1066. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bryant JL, Britson J, Balko JM, Willian M,
Timmons R, Frolov A and Black EP: A microRNA gene expression
signature predicts response to erlotinib in epithelial cancer cell
lines and targets EMT. Br J Cancer. 106:148–156. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi L, Zhang S, Wu H, Zhang L, Dai X, Hu
J, Xue J, Liu T, Liang Y and Wu G: MiR-200c increases the
radiosensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cell line A549 by
targeting VEGF-VEGFR2 pathway. PloS One. 8:e783442013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer
cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Dev. 22:894–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tang H, Deng M, Tang Y and Xie X, Guo J,
Kong Y, Ye F, Su Q and Xie X: miR-200b and miR-200c as prognostic
factors and mediators of gastric cancer cell progression. Clin
Cancer Res. 19:5602–5612. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C (T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou X, Wang Y, Shan B, Han J, Zhu H, Lv
Y, Fan X, Sang M, Liu XD and Liu W: The downregulation of
miR-200c/141 promotes ZEB1/2 expression and gastric cancer
progression. Med Oncol. 32:4282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Paterson EL, Kazenwadel J, Bert AG,
Khew-Goodall Y, Ruszkiewicz A and Goodall GJ: Down-regulation of
the miRNA-200 family at the invasive front of colorectal cancers
with degraded basement membrane indicates EMT is involved in cancer
progression. Neoplasia. 15:180–191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tamagawa S, Beder LB, Hotomi M, Gunduz M,
Yata K, Grenman R and Yamanaka N: Role of miR-200c/miR-141 in the
regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 33:879–886.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van Jaarsveld MT, Helleman J, Boersma AW,
van Kuijk PF, van Ijcken WF, Despierre E, Vergote I, Mathijssen RH,
Berns EM, Verweij J, et al: miR-141 regulates KEAP1 and modulates
cisplatin sensitivity in ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene.
32:4284–4293. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gregory PA, Bracken CP, Smith E, Bert AG,
Wright JA, Roslan S, Morris M, Wyatt L, Farshid G, Lim YY, et al:
An autocrine TGF-beta/ZEB/miR-200 signaling network regulates
establishment and maintenance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Mol Biol Cell. 22:1686–1698. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vrba L, Jensen TJ, Garbe JC, Heimark RL,
Cress AE, Dickinson S, Stampfer MR and Futscher BW: Role for DNA
methylation in the regulation of miR-200c and miR-141 expression in
normal and cancer cells. PloS One. 5:e86972010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu Y, Brenn T, Brown ER, Doherty V and
Melton DW: Differential expression of microRNAs during melanoma
progression: miR-200c, miR-205 and miR-211 are downregulated in
melanoma and act as tumour suppressors. Br J Cancer. 106:553–561.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Hulf T, Dyrskjøt
L, Ramanathan R, Hansen TB, Villadsen SB, Gao S, Ostenfeld MS,
Borre M, et al: Coordinated epigenetic repression of the miR-200
family and miR-205 in invasive bladder cancer. Int J Cancer.
128:1327–1334. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim HR, Kim WS, Choi YJ, Choi CM, Rho JK
and Lee JC: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition leads to crizotinib
resistance in H2228 lung cancer cells with EML4-ALK translocation.
Mol Oncol. 7:1093–1102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kogita A, Togashi Y, Hayashi H, Sogabe S,
Terashima M, De Velasco MA, Sakai K, Fujita Y, Tomida S, Takeyama
Y, et al: Hypoxia induces resistance to ALK inhibitors in the H3122
non-small cell lung cancer cell line with an ALK rearrangement via
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Oncol. 45:1430–1436.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shen W, Pang H, Liu J, Zhou J, Zhang F and
Liu L, Ma N, Zhang N, Zhang H and Liu L: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition contributes to docetaxel resistance in human non-small
cell lung cancer. Oncol Res. 22:47–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li J, Li X, Ren S, Chen X, Zhang Y, Zhou
F, Zhao M, Zhao C, Chen X, Cheng N, et al: miR-200c overexpression
is associated with better efficacy of EGFR-TKIs in non-small cell
lung cancer patients with EGFR wild-type. Oncotarget. 5:7902–7916.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li X, Gao D, Wang H, Li X, Yang J, Yan X,
Liu Z and Ma Z: Negative feedback loop between p66Shc and ZEB1
regulates fibrotic EMT response in lung cancer cells. Cell Death
Dis. 6:e17082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Singh AB, Sharma A, Smith JJ, Krishnan M,
Chen X, Eschrich S, Washington MK, Yeatman TJ, Beauchamp RD and
Dhawan P: Claudin-1 up-regulates the repressor ZEB-1 to inhibit
E-cadherin expression in colon cancer cells. Gastroenterology.
141:2140–2153. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chua HL, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Clare SE,
Morimiya A, Badve S and Nakshatri H: NF-kappaB represses E-cadherin
expression and enhances epithelial to mesenchymal transition of
mammary epithelial cells: Potential involvement of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2.
Oncogene. 26:711–724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|