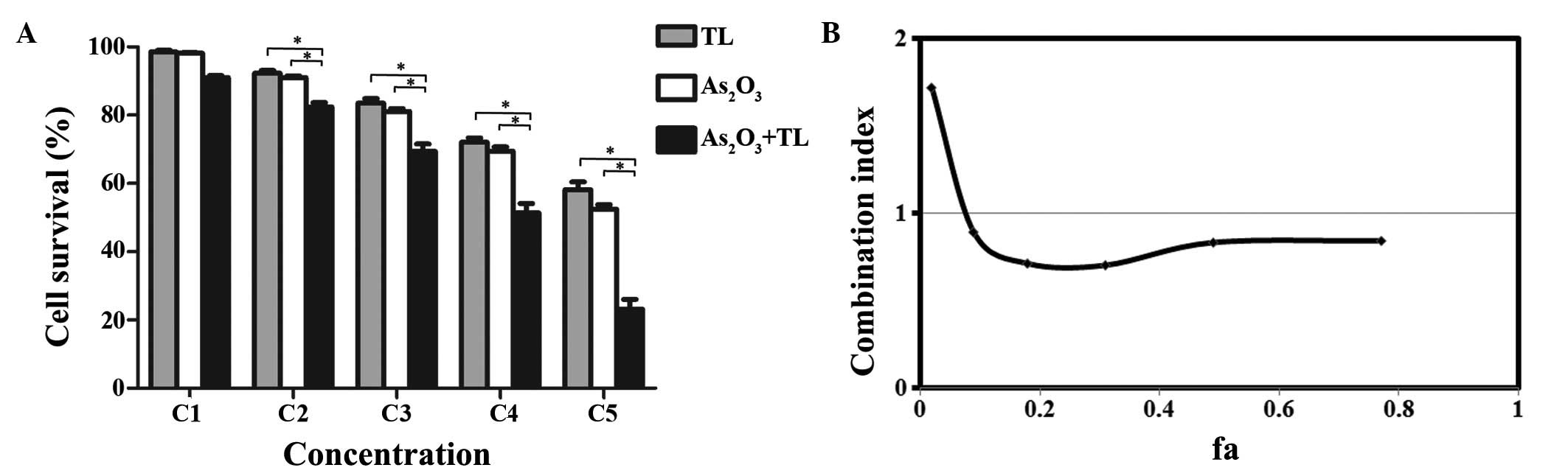
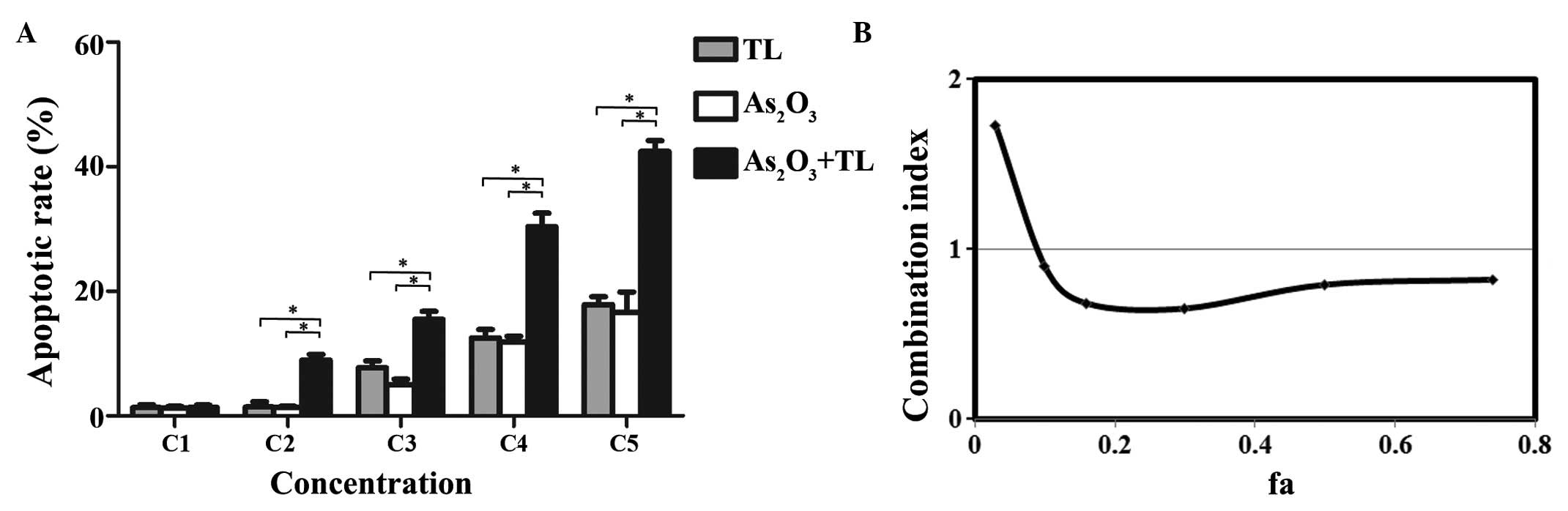
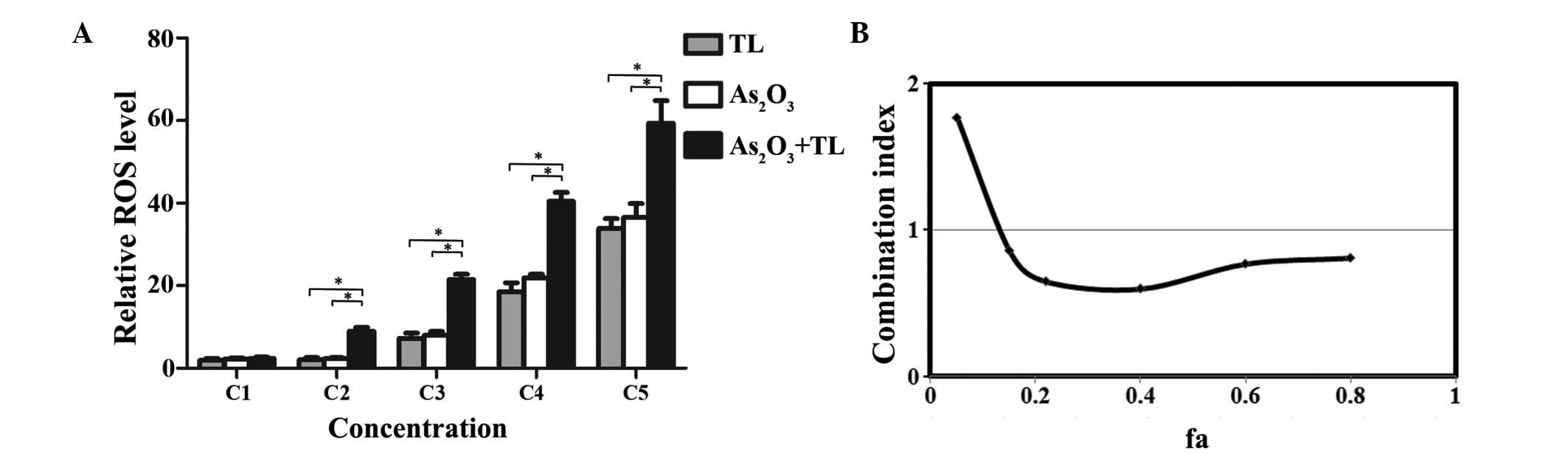
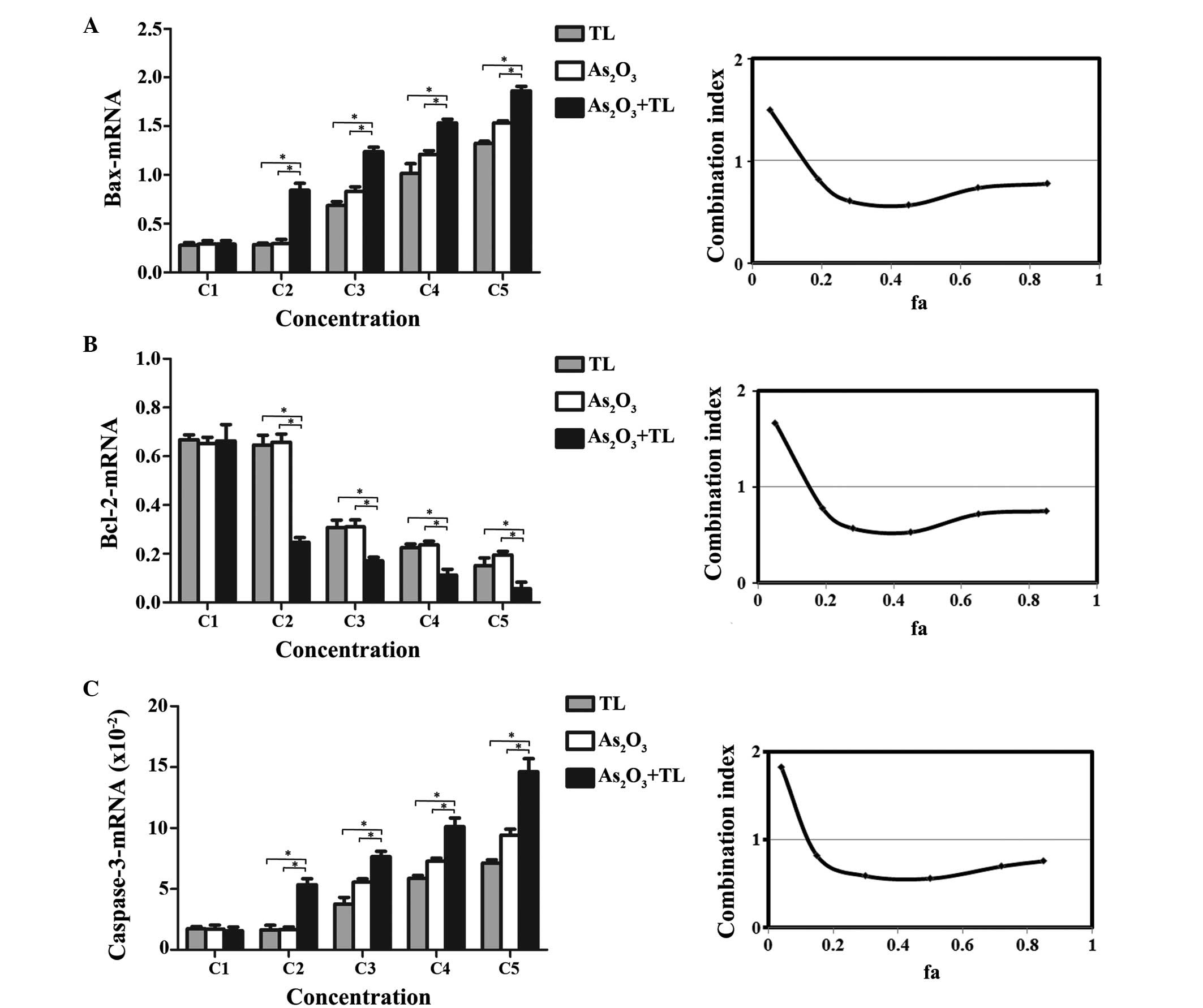
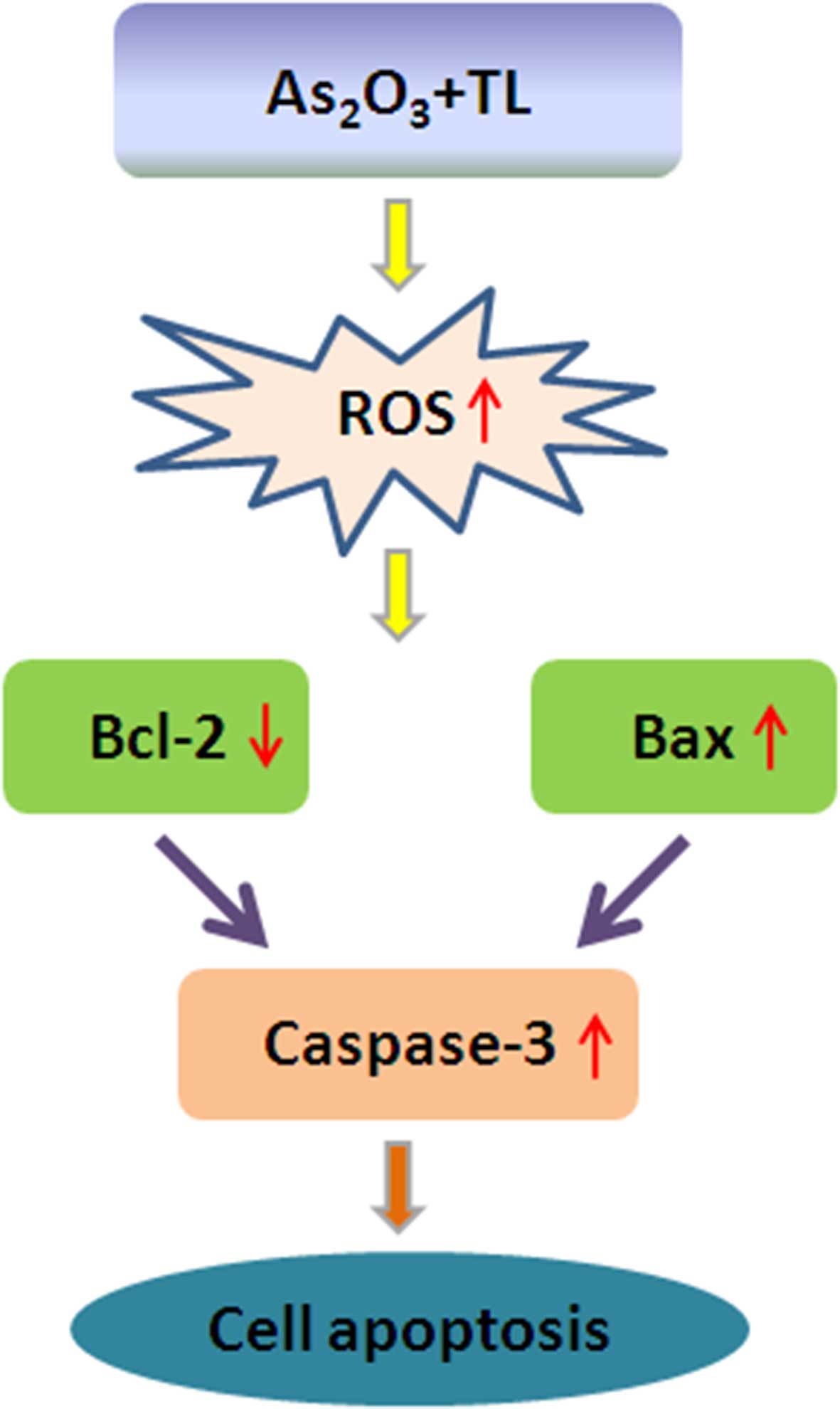
|
1
|
Cogle CR, Craig BM, Rollison DE and List
AF: Incidence of the myelodysplastic syndromes using a novel
claims-based algorithm: High number of uncaptured cases by cancer
registries. Blood. 117:7121–7125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jädersten M and Hellström-Lindberg E:
Myelodysplastic syndromes: Biology and treatment. J Intern Med.
265:307–328. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tefferi A and Vardiman JW: Myelodysplastic
syndromes. N Engl J Med. 361:1872–1885. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gore SD and Hermes-DeSantis ER: Enhancing
survival outcomes in the management of patients with higher-risk
myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer Control. 16:(Suppl). S2–S10.
2009.
|
|
5
|
Chang C, Storer BE, Scott BL, Bryant EM,
Shulman HM, Flowers ME, Sandmaier BM, Witherspoon RP, Nash RA,
Sanders JE, et al: Hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients
with myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia arising
from myelodysplastic syndrome: Similar outcomes in patients with de
novo disease and disease following prior therapy or antecedent
hematologic disorders. Blood. 110:1379–1387. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Warlick ED, Cioc A, Defor T, Dolan M and
Weisdorf D: Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for adults with
myelodysplastic syndromes: Importance of pretransplant disease
burden. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 15:30–38. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fenaux P, Mufti GJ, Hellstrom-Lindberg E,
Santini V, Finelli C, Giagounidis A, Schoch R, Gattermann N, Sanz
G, List A, et al: Efficacy of azacitidine compared with that of
conventional care regimens in the treatment of higher-risk
myelodysplastic syndromes: A randomised, open-label, phase III
study. Lancet Oncol. 10:223–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gore SD, Fenaux P, Santini V, Bennett JM,
Silverman LR, Seymour JF, Hellström-Lindberg E, Swern AS, Beach CL
and List AF: A multivariate analysis of the relationship between
response and survival among patients with higher-risk
myelodysplastic syndromes treated within azacitidine or
conventional care regimens in the randomized AZA-001 trial.
Haematologica. 98:1067–1072. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kantarjian H, Issa JP, Rosenfeld CS,
Bennett JM, Albitar M, DiPersio J, Klimek V, Slack J, de Castro C,
Ravandi F, et al: Decitabine improves patient outcomes in
myelodysplastic syndromes: Results of a phase III randomized study.
Cancer. 106:1794–1803. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zwierzina H, Suciu S, Loeffler-Ragg J,
Neuwirtova R, Fenaux P, Beksac M, Harousseau J, Nuessler V, Cermak
J, Solbu G, et al: Low-dose cytosine arabinoside (LD-AraC) vs.
LD-AraC plus granulocyte/macrophage colony stimulating factor vs.
LD-AraC plus Interleukin-3 for myelodysplastic syndrome patients
with a high risk of developing acute leukemia: Final results of a
randomized phase III study (06903) of the EORTC Leukemia
Cooperative Group. Leukemia. 19:1929–1933. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Beran M, Shen Y, Kantarjian H, O'Brien S,
Koller CA, Giles FJ, Cortes J, Thomas DA, Faderl S, Despa S and
Estey EH: High-dose chemotherapy in high-risk myelodysplastic
syndrome: Covariate-adjusted comparison of five regimens. Cancer.
92:1999–2015. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
List A, Dewald G, Bennett J, Giagounidis
A, Raza A, Feldman E, Powell B, Greenberg P, Thomas D, Stone R, et
al: Lenalidomide in the myelodysplastic syndrome with chromosome 5q
deletion. N Engl J Med. 355:1456–1465. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Badros AZ: Lenalidomide in myeloma-a
high-maintenance friend. N Engl J Med. 366:1836–1838. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lallemand-Breitenbach V, Zhu J, Chen Z and
de Thé H: Curing APL through PML/RARA degradation by As2O3. Trends
Mol Med. 18:36–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM,
Qiu QY, Zhu J, Tang W, Sun GL, Yang KQ, et al: Use of arsenic
trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia
(APL): II. Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics in relapsed
patients. Blood. 89:3354–3360. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schiller GJ, Slack J, Hainsworth JD, Mason
J, Saleh M, Rizzieri D, Douer D and List AF: Phase II multicenter
study of arsenic trioxide in patients with myelodysplastic
syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 24:2456–2464. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vey N, Bosly A, Guerci A, Feremans W,
Dombret H, Dreyfus F, Bowen D, Burnett A, Dennis M, Ribrag V, et
al: Arsenic trioxide in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: A
phase II multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 24:2465–2471. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takahashi S: Combination therapy with
arsenic trioxide for hematological malignancies. Anticancer Agents
Med Chem. 10:504–510. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xia J, Li Y, Yang Q, Mei C, Chen Z, Bao B,
Ahmad A, Miele L, Sarkar FH and Wang Z: Arsenic trioxide inhibits
cell growth and induces apoptosis through inactivation of notch
signaling pathway in breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 13:9627–9641.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hoffman E and Mielicki WP: Arsenic
trioxide: Impact on the growth and differentiation of cancer cells
and possible use in cancer therapy. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online).
67:817–827. 2013.(In Polish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao H, Guo W, Peng C, Ji T and Lu X:
Arsenic trioxide inhibits the growth of adriamycin resistant
osteosarcoma cells through inducing apoptosis. Mol Biol Rep.
37:2509–2515. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li C, Qu X, Xu W, Qu N, Mei L, Liu Y, Wang
X, Yu X, Liu Z, Nie D, et al: Arsenic trioxide induces cardiac
fibroblast apoptosis in vitro and in vivo by up-regulating TGF-β1
expression. Toxicol Lett. 219:223–230. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yedjou C, Tchounwou P, Jenkins J and
McMurray R: Basic mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (ATO)-induced
apoptosis in human leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Hematol Oncol.
3:282010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Han R, Rostami-Yazdi M, Gerdes S and
Mrowietz U: Triptolide in the treatment of psoriasis and other
immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
74:424–436. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng J and Jin J: Study of
triptolide-induced apoptosis in MUTZ-1 cells and its allied
mechanism. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 13:434–439. 2005.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mujumdar N, Mackenzie TN, Dudeja V, Chugh
R, Antonoff MB, Borja-Cacho D, Sangwan V, Dawra R, Vickers SM and
Saluja AK: Triptolide induces cell death in pancreatic cancer cells
by apoptotic and autophagic pathways. Gastroenterology.
139:598–608. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu PP, Liu KC, Huang WW, Ma CY, Lin H,
Yang JS and Chung JG: Triptolide induces apoptosis in human adrenal
cancer NCI-H295 cells through a mitochondrial-dependent pathway.
Oncol Rep. 25:551–557. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Meng HT, Zhu L, Ni WM, You LS, Jin J and
Qian WB: Triptolide inhibits the proliferation of cells from
lymphocytic leukemic cell lines in association with downregulation
of NF-κB activity and miR-16-1*. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:503–511.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sekeres MA, Maciejewski JP, Erba HP,
Afable M, Englehaupt R, Sobecks R, Advani A, Seel S, Chan J and
Kalaycio ME: A Phase 2 study of combination therapy with arsenic
trioxide and gemtuzumab ozogamicin in patients with myelodysplastic
syndromes or secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer.
117:1253–1261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzym Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Takahashi S, Harigae H, Yokoyama H,
Ishikawa I, Abe S, Imaizumi M, Sasaki T and Kaku M: Synergistic
effect of arsenic trioxide and flt3 inhibition on cells with flt3
internal tandem duplication. Int J Hematol. 84:256–261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li M, Ding Y, Mu Y, Ao J and Chen X:
Molecular cloning and characterization of caspase-3 in large yellow
croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 30:910–916.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Clawson KA, Borja-Cacho D, Antonoff MB,
Saluja AK and Vickers SM: Triptolide and TRAIL combination enhances
apoptosis in cholangiocarcinoma. J Surg Res. 163:244–249. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Spampanato C, De Maria S, Sarnataro M,
Giordano E, Zanfardino M, Baiano S, Cartenì M and Morelli F:
Simvastatin inhibits cancer cell growth by inducing apoptosis
correlated to activation of Bax and down-regulation of BCL-2 gene
expression. International J Onco. 40:935–941. 2012.
|
|
36
|
Abdelrahman IY, Helwa R, Elkashef H and
Hassan NH: Induction of P3NS1 myeloma cell death and cell cycle
arrest by simvastatin and/or γ-radiation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
16:7103–7110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Park MT, Kang YH, Park IC, Kim CH, Lee YS,
Chung HY and Lee SJ: Combination treatment with arsenic trioxide
and phytosphingosine enhances apoptotic cell death in arsenic
trioxide-resistant cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:82–92. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|