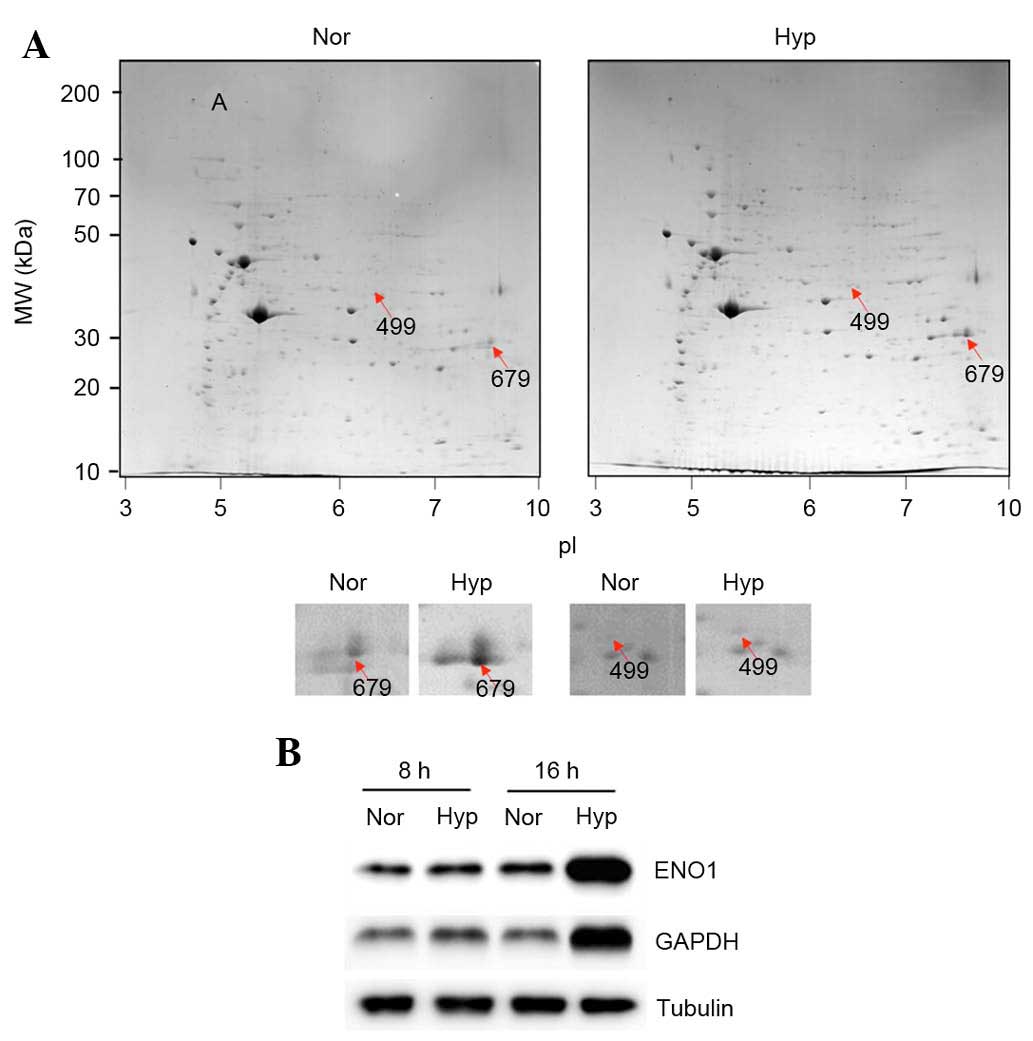
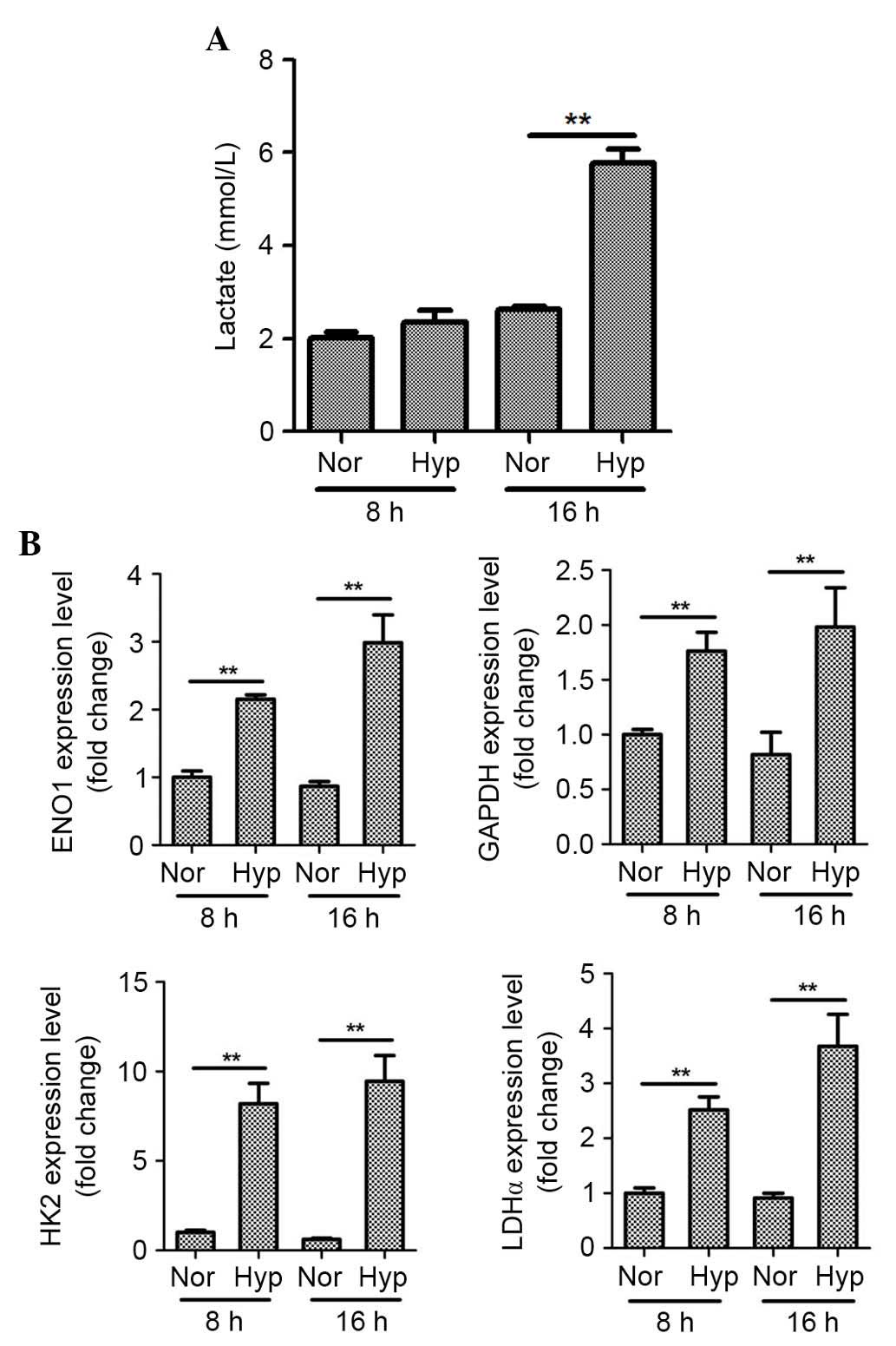
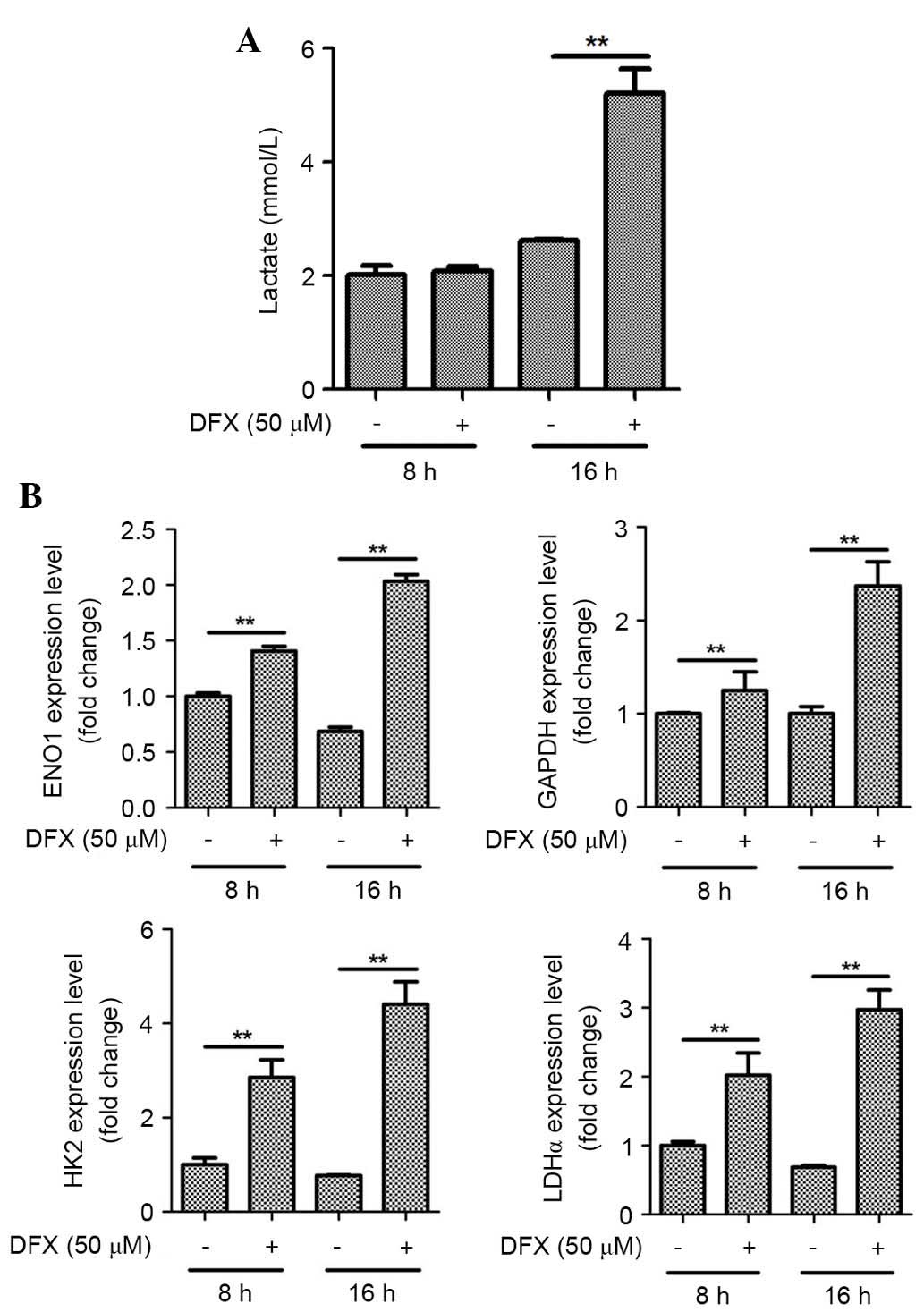
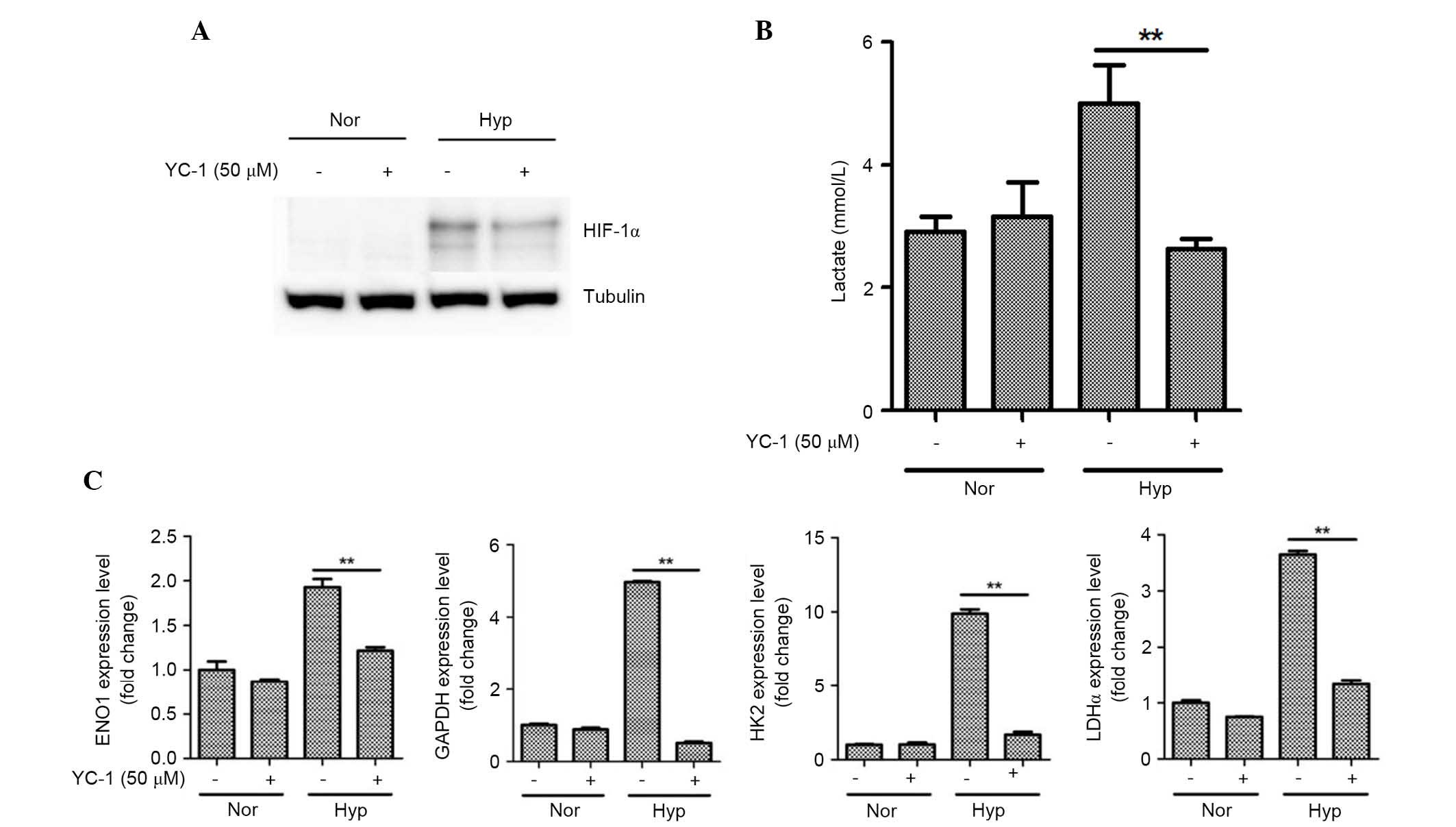
|
1
|
Chung HM, Won CH and Sung JH: Responses of
adipose-derived stem cells during hypoxia: Enhanced
skin-regenerative potential. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 9:1499–1508.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim JH, Park SH, Park SG, Choi JS, Xia Y
and Sung JH: The pivotal role of reactive oxygen species generation
in the hypoxia-induced stimulation of adipose-derived stem cells.
Stem Cells Dev. 20:1753–1761. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee EY, Xia Y, Kim WS, Kim MH, Kim TH, Kim
KJ, Park BS and Sung JH: Hypoxia-enhanced wound-healing function of
adipose-derived stem cells: Increase in stem cell proliferation and
up-regulation of VEGF and bFGF. Wound Repair Regen. 17:540–547.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim JH, Song SY, Park SG, Song SU, Xia Y
and Sung JH: Primary involvement of NADPH oxidase 4 in
hypoxia-induced generation of reactive oxygen species in
adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 21:2212–2221. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kang S, Kim SM and Sung JH: Cellular and
molecular stimulation of adipose-derived stem cells under hypoxia.
Cell Biol Int. 38:553–562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim JH, Kim WK, Sung YK, Kwack MH, Song
SY, Choi JS, Park SG, Yi T, Lee HJ, Kim DD, et al: The molecular
mechanism underlying the proliferating and preconditioning effect
of vitamin C on adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev.
23:1364–1376. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hye Kim J, Gyu Park S, Kim WK, Song SU and
Sung JH: Functional regulation of adipose-derived stem cells by
PDGF-D. Stem Cells. 33:542–556. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim JH, Park SG, Song SY, Kim JK and Sung
JH: Reactive oxygen species-responsive miR-210 regulates
proliferation and migration of adipose-derived stem cells via
PTPN2. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park BS, Kim WS, Choi JS, Kim HK, Won JH,
Ohkubo F and Fukuoka H: Hair growth stimulated by conditioned
medium of adipose-derived stem cells is enhanced by hypoxia:
Evidence of increased growth factor secretion. Biomed Res.
31:27–34. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim JH, Kim SH, Song SY, Kim WS, Song SU,
Yi T, Jeon MS, Chung HM, Xia Y and Sung JH: Hypoxia induces
adipocyte differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells by
triggering reactive oxygen species generation. Cell Biol Int.
38:32–40. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hsu SH, Chen CT and Wei YH: Inhibitory
effects of hypoxia on metabolic switch and osteogenic
differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem cells.
31:2779–2788. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meretoja VV, Dahlin RL, Wright S, Kasper
FK and Mikos AG: The effect of hypoxia on the chondrogenic
differentiation of co-cultured articular chondrocytes and
mesenchymal stem cells in scaffolds. Biomaterials. 34:4266–4273.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gaspar JA, Doss MX, Hengstler JG, Cadenas
C, Hescheler J and Sachinidis A: Unique metabolic features of stem
cells, cardiomyocytes, and their progenitors. Circ Res.
114:1346–1360. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ito K and Suda T: Metabolic requirements
for the maintenance of self-renewing stem cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:243–256. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dong Q, Yang Y, Song L, Qian H and Xu Z:
Atorvastatin prevents mesenchymal stem cells from hypoxia and
serum-free injury through activating AMP-activated protein kinase.
Int J Cardiol. 153:311–316. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suda T, Takubo K and Semenza GL: Metabolic
regulation of hematopoietic stem cells in the hypoxic niche. Cell
Stem Cell. 9:298–310. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mohyeldin A, Garzon-Muvdi T and
Quinones-Hinojosa A: Oxygen in stem cell biology: A critical
component of the stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell. 7:150–161. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Buravkova LB, Rylova YV, Andreeva ER,
Kulikov AV, Pogodina MV, Zhivotovsky B and Gogvadze V: Low ATP
level is sufficient to maintain the uncommitted state of
multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1830:4418–4425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yi T, Kim WK, Choi JS, Song SY, Han J, Kim
JH, Kim WS, Park SG, Lee HJ, Cho YK, et al: Isolation of
adipose-derived stem cells by using a subfractionation culturing
method. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 14:1551–1560. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao W, Qiao X, Ma S and Cui L:
Adipose-derived stem cells accelerate neovascularization in
ischaemic diabetic skin flap via expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α. J Cell Mol Med. 15:2575–2585. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ren BF, Deng LF, Wang J, Zhu YP, Wei L and
Zhou Q: Hypoxia regulation of facilitated glucose transporter-1 and
glucose transporter-3 in mouse chondrocytes mediated by HIF-1alpha.
Joint Bone Spine. 75:176–181. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vannucci SJ, Reinhart R, Maher F, Bondy
CA, Lee WH, Vannucci RC and Simpson IA: Alterations in GLUT1 and
GLUT3 glucose transporter gene expression following unilateral
hypoxia-ischemia in the immature rat brain. Brain Res Dev Brain
Res. 107:255–264. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Roche S, Delorme B, Oostendorp RA, Barbet
R, Caton D, Noel D, Boumediene K, Papadaki HA, Cousin B, Crozet C,
et al: Comparative proteomic analysis of human mesenchymal and
embryonic stem cells: Towards the definition of a mesenchymal stem
cell proteomic signature. Proteomics. 9:223–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim JM, Kim J, Kim YH, Kim KT, Ryu SH, Lee
TG and Suh PG: Comparative secretome analysis of human bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells during osteogenesis. J Cell
Physiol. 228:216–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zeng HL, Zhong Q, Jia HT, Qing YL, Bu QQ,
Han XA and Liu HW: Differential proteomic analysis in human
umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells induced by cobalt chloride.
Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 32:739–743. 2011.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tan SC, Carr CA, Yeoh KK, Schofield CJ,
Davies KE and Clarke K: Identification of valid housekeeping genes
for quantitative RT-PCR analysis of cardiosphere-derived cells
preconditioned under hypoxia or with prolyl-4-hydroxylase
inhibitors. Mol Biol Rep. 39:4857–4867. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chiche J, Pommier S, Beneteau M, Mondragón
L, Meynet O, Zunino B, Mouchotte A, Verhoeyen E, Guyot M, Pagès G,
et al: GAPDH enhances the aggressiveness and the vascularization of
non-Hodgkin's B lymphomas via NF-kB-dependent induction of HIF-1α.
Leukemia. 29:1163–1176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cummings M, Sarveswaran J,
Homer-Vanniasinkam S, Burke D and Orsi NM:
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is an inappropriate
housekeeping gene for normalising gene expression in sepsis.
Inflammation. 37:1889–1894. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
van Dijk A, Naaijkens BA, Jurgens WJ,
Oerlemans R, Scheffer GL, Kassies J, Aznou J, Brouwer M, van Rossum
AC, Schuurhuis GJ, et al: The multidrug resistance protein breast
cancer resistance protein (BCRP) protects adipose-derived stem
cells against ischemic damage. Cell Biol Toxicol. 28:303–315. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gould GW and Holman GD: The glucose
transporter family: Structure, function and tissue-specific
expression. Biochem J. 295:329–341. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mueckler M: Family of glucose-transporter
genes. Implications for glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Diabetes.
39:6–11. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Olson AL and Pessin JE: Structure,
function, and regulation of the mammalian facilitative glucose
transporter gene family. Annu Rev Nutr. 16:235–256. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mobasheri A, Richardson S, Mobasheri R,
Shakibaei M and Hoyland JA: Hypoxia inducible factor-1 and
facilitative glucose transporters GLUT1 and GLUT3: Putative
molecular components of the oxygen and glucose sensing apparatus in
articular chondrocytes. Histol Histopathol. 20:1327–1338.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu H, Chen X and Deng L: Effects of
hypoxic preconditioning on glucose metabolism of rat bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.
25:1004–1007. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kihira Y, Yamano N, Izawa-Ishizawa Y,
Ishizawa K, Ikeda Y, Tsuchiya K, Tamaki T and Tomita S: Basic
fibroblast growth factor regulates glucose metabolism through
glucose transporter 1 induced by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in
adipocytes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 43:1602–1611. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|