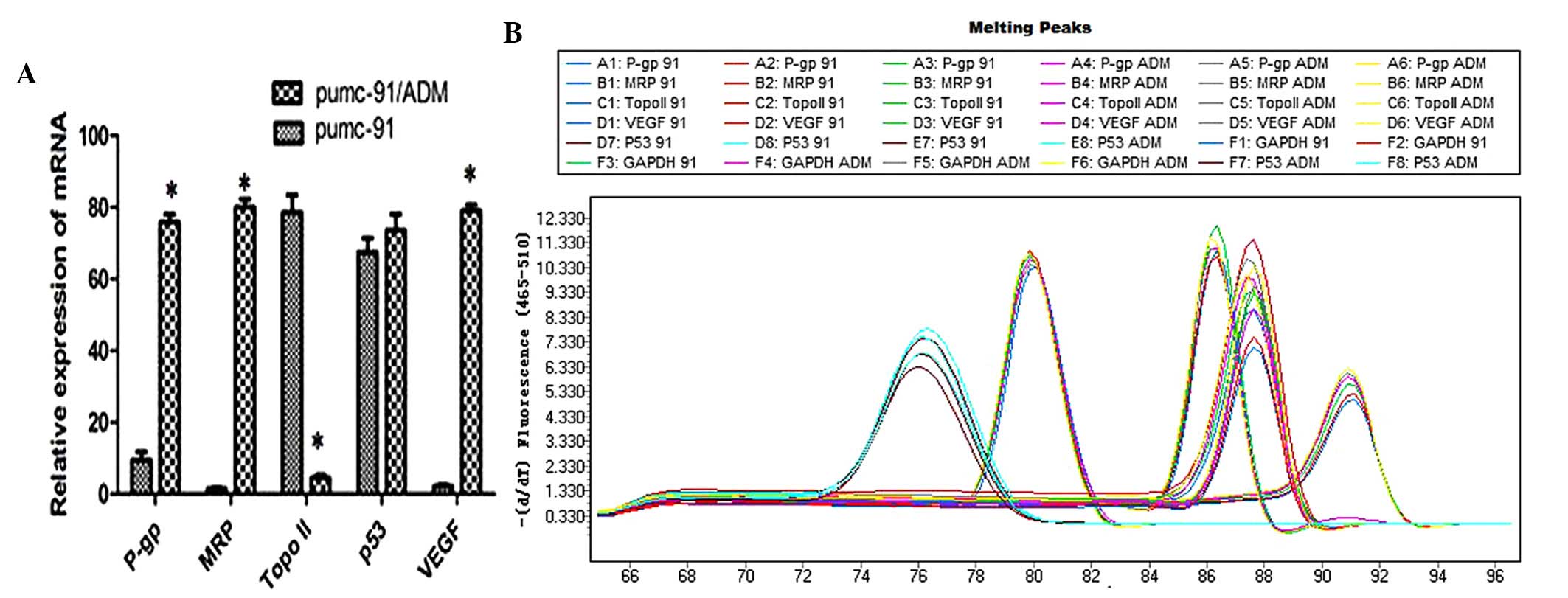
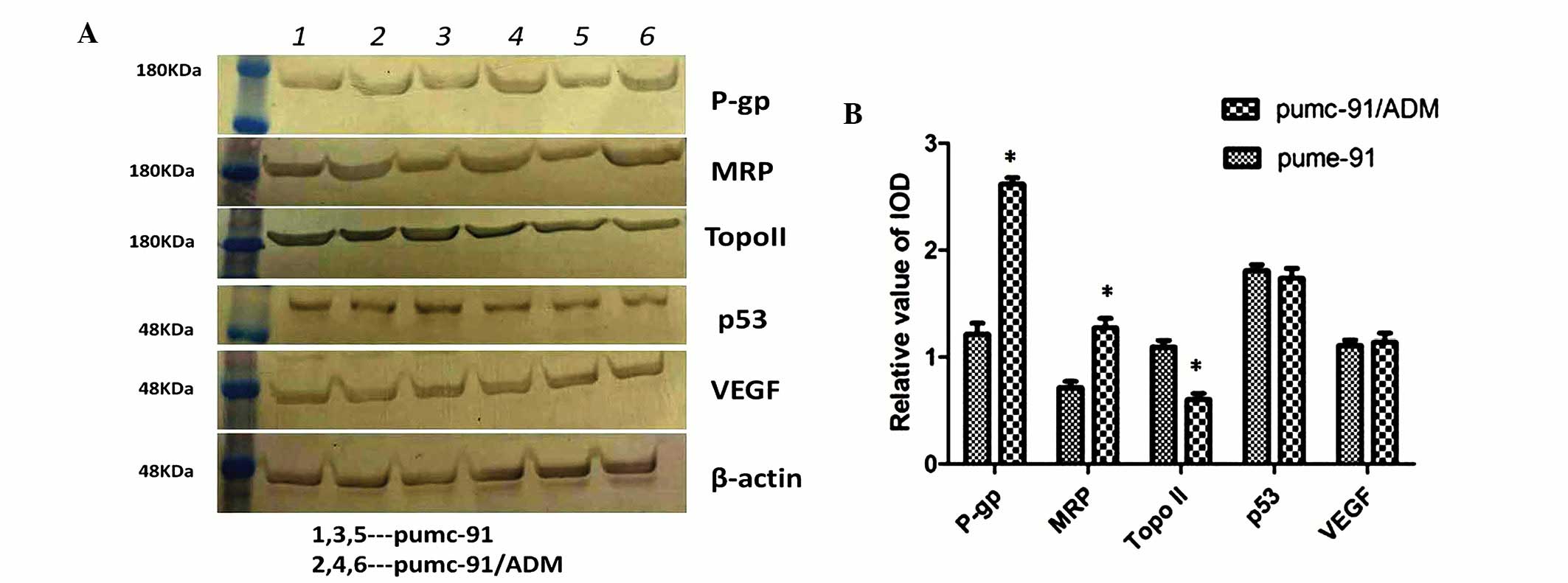
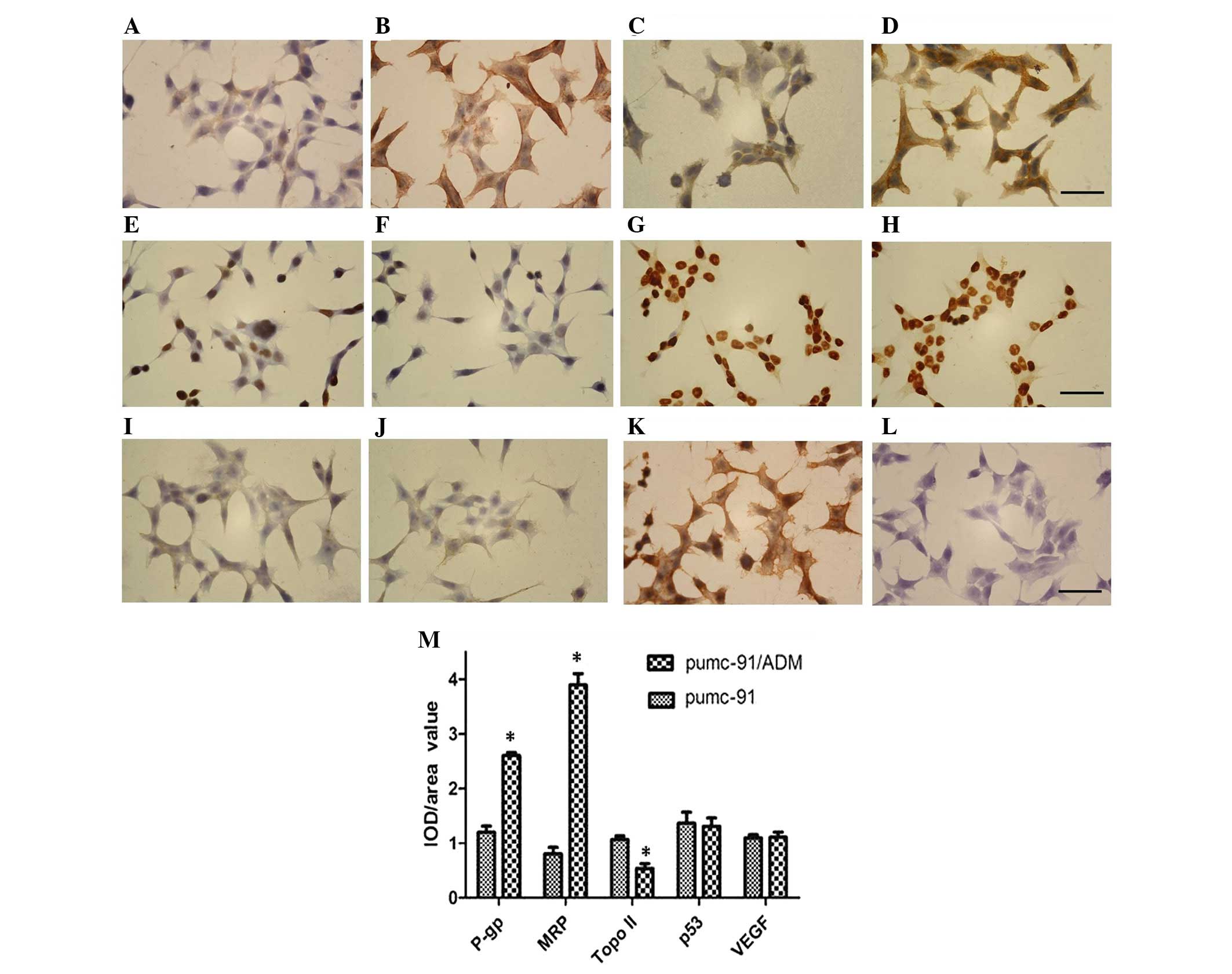
|
1
|
Lei T, Zhao X, Jin S, Meng Q, Zhou H and
Zhang M: Discovery of potential bladder cancer biomarkers by
comparative urine proteomics and analysis. Clin Genitourin Cancer.
11:56–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meng Q, Lei T and Zhang M, Zhao J, Zhao XH
and Zhang M: Identification of proteins differentially expressed in
adriamycin-resistant (pumc-91/ADM) and parental (pumc-91) human
bladder cancer cell lines by proteome analysis. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 139:509–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sacerdote C, Guarrera S, Ricceri F,
Pardini B, Polidoro S, Allione A, Critelli R, Russo A, Andrew AS,
Ye Y, et al: Polymorphisms in the XRCC1 gene modify survival of
bladder cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. Int J Cancer.
133:2004–2009. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zeekpudsa P, Kukongviriyapan V,
Senggunprai L, Sripa B and Prawan A: Suppression of NAD(P)H-quinone
oxidoreductase 1 enhanced the susceptibility of cholangiocarcinoma
cells to chemotherapeutic agents. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:112014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zandvliet M, Teske E and Schrickx JA:
Multi-drug resistance in a canine lymphoid cell line due to
increased P-glycoprotein expression, a potential model for
drug-resistant canine lymphoma. Toxicol In Vitro. 28:1498–1506.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li W and Song M: Expression of multidrug
resistance proteins in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast.
Oncol Lett. 8:2103–2109. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Semiglazova TIu, Klimenko VV, Filatova LV,
Chubenko VA, Krivorot'ko PV, Ivanov VG, Turkevich EA, Ivantsov AO,
Novikov SN, Semiglazov VV, et al: Markers of effectiveness of
preoperative taxane-based chemotherapy for locally advanced breast
cancer. Vopr Onkol. 59:363–367. 2013.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grosset AA, Labrie M, Gagné D, Vladoiu MC,
Gaboury L, Doucet N and St-Pierre Y: Cytosolic galectin-7 impairs
p53 functions and induces chemoresistance in breast cancer cells.
BMC Cancer. 14:8012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ki CS, Lin TY, Korc M and Lin CC:
Thiol-ene hydrogels as desmoplasia-mimetic matrices for modeling
pancreatic cancer cell growth, invasion, and drug resistance.
Biomaterials. 35:9668–9677. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang M, Jin S and Zhang M: Establishing
human multi-drug resistant bladder cancer cell lines Pumc-91/ADM
and evaluating its biological characteristics. J Med Res. 38:70–72.
2009.
|
|
11
|
Yu S, Meng Q, Hu H and Zhang M:
Correlation of ANXA1 expression with drug resistance and relapse in
bladder cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:5538–5548. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu H, Meng Q, Lei T and Zhang M:
Nucleophosmin1 associated with drug resistance and recurrence of
bladder cancer. Clin Exp Med. 15:361–369. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pappas JJ, Petropoulos S, Suderman M,
Iqbal M, Moisiadis V, Turecki G, Matthews SG and Szyf M: The
multidrug resistance 1 gene Abcb1 in brain and placenta:
Comparative analysis in human and guinea pig. PLoS One.
9:e1111352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu P, Du Y, Cheng X, Yu Q, Huang L and
Dong R: Expression of multidrug resistance-associated proteins and
their relation to postoperative individualized chemotherapy in
gastric cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 12:3072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kodiakov DS, Klimachëv VV, Avdalian AM,
Bobrov IP, Lazarev AF, Lushnikova EL and Nepomiashchikh LM:
Topoisomerase IIa expression in correlation with clinical and
morphological parameters and proliferation (based on argyrophilic
proteins of nucleolar organizer regions and Ki-67 antigen) in lung
adenocarcinoma. Vopr Onkol. 60:63–68. 2014.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Llovet JM: Focal gains of VEGFA: Candidate
predictors of sorafenib response in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Cell. 25:560–562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tonigold M, Rossmann A, Meinold M, Bette
M, Märken M, Henkenius K, Bretz AC, Giel G, Cai C, Rodepeter FR, et
al: A cisplatin-resistant head and neck cancer cell line with
cytoplasmic p53(mut) exhibits ATP-binding cassette transporter
upregulation and high glutathione levels. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
140:1689–1704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
An J, Wang X, Guo P, Zhong Y, Zhang X and
Yu Z: Hexabromocyclododecane and polychlorinated biphenyls increase
resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to cisplatin through
the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway. Toxicol
Lett. 229:265–272. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kovalev AA, Tsvetaeva DA and Grudinskaja
TV: Role of ABC-cassette transporters (MDR1, MRP1, BCRP) in the
development of primary and acquired multiple drug resistance in
patients with early and metastatic breast cancer. Exp Oncol.
35:287–290. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee YK, Lin TH, Chang CF and Lo YL:
Galectin-3 silencing inhibits epirubicin-induced ATP binding
cassette transporters and activates the mitochondrial apoptosis
pathway via β-catenin/GSK-3β modulation in colorectal carcinoma.
PLoS One. 8:e824782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Copsel S, Garcia C, Diez F, Vermeulem M,
Baldi A, Bianciotti LG, Russel FG, Shayo C and Davio C: Multidrug
resistance protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4) regulates cAMP cellular levels
and controls human leukemia cell proliferation and differentiation.
J Biol Chem. 286:6979–6988. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Su W and Pasternak GW: The role of
multidrug resistance-associated protein in the blood-brain barrier
and opioid analgesia. Synapse. 67:609–619. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu P, Du Y, Cheng X, Yu Q, Huang L and
Dong R: Expression of multidrug resistance-associated proteins and
their relation to postoperative individualized chemotherapy in
gastric cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 12:3072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsang WP, Kong SK and Kwok TT: Epidermal
growth factor induction of resistance to topoisomerase II toxins in
human squamous carcinoma A431 cells. Oncol Rep. 16:789–793.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Campiglio M, Somenzi G, Olgiati C, Beretta
G, Balsari A, Zaffaroni N, Valagussa P and Ménard S: Role of
proliferation in HER2 status predicted response to doxorubicin. Int
J Cancer. 105:568–573. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fillmore CM, Xu C, Desai PT, Berry JM,
Rowbotham SP, Lin YJ, Zhang H, Marquez VE, Hammerman PS, Wong KK
and Kim CF: EZH2 inhibition sensitizes BRG1 and EGFR mutant lung
tumours to TopoII inhibitors. Nature. 520:239–242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chin KV and Kong AN: Application of DNA
microarrays in pharmacogenomics and toxicogenomics. Pharm Res.
19:1773–1778. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Garufi A and D'Orazi G: High glucose
dephosphorylates serine 46 and inhibits p53 apoptotic activity. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin J, Shen A, Chen H, Liao J, Xu T, Liu
L, Lin J and Peng J: Nitidine chloride inhibits hepatic cancer
growth via modulation of multiple signaling pathways. BMC Cancer.
14:7292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mésange P, Poindessous V, Sabbah M,
Escargueil AE, de Gramont A and Larsen AK: Intrinsic bevacizumab
resistance is associated with prolonged activation of autocrine
VEGF signaling and hypoxia tolerance in colorectal cancer cells and
can be overcome by nintedanib, a small molecule angiokinase
inhibitor. Oncotarget. 5:4709–4721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Baranasic D, Oppermann T, Cheaib M, Cullum
J, Schmidt H and Simon M: Genomic characterization of variable
surface antigens reveals a telomere position effect as a
prerequisite for RNA interference-mediated silencing in paramecium
tetraurelia. MBio. 5:e013282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Luo B, Ju S, Muneri CW and Rui R: Effects
of histone acetylation status on the early development of in vitro
porcine transgenic cloned embryos. Cell Reprogram. 17:41–48. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|