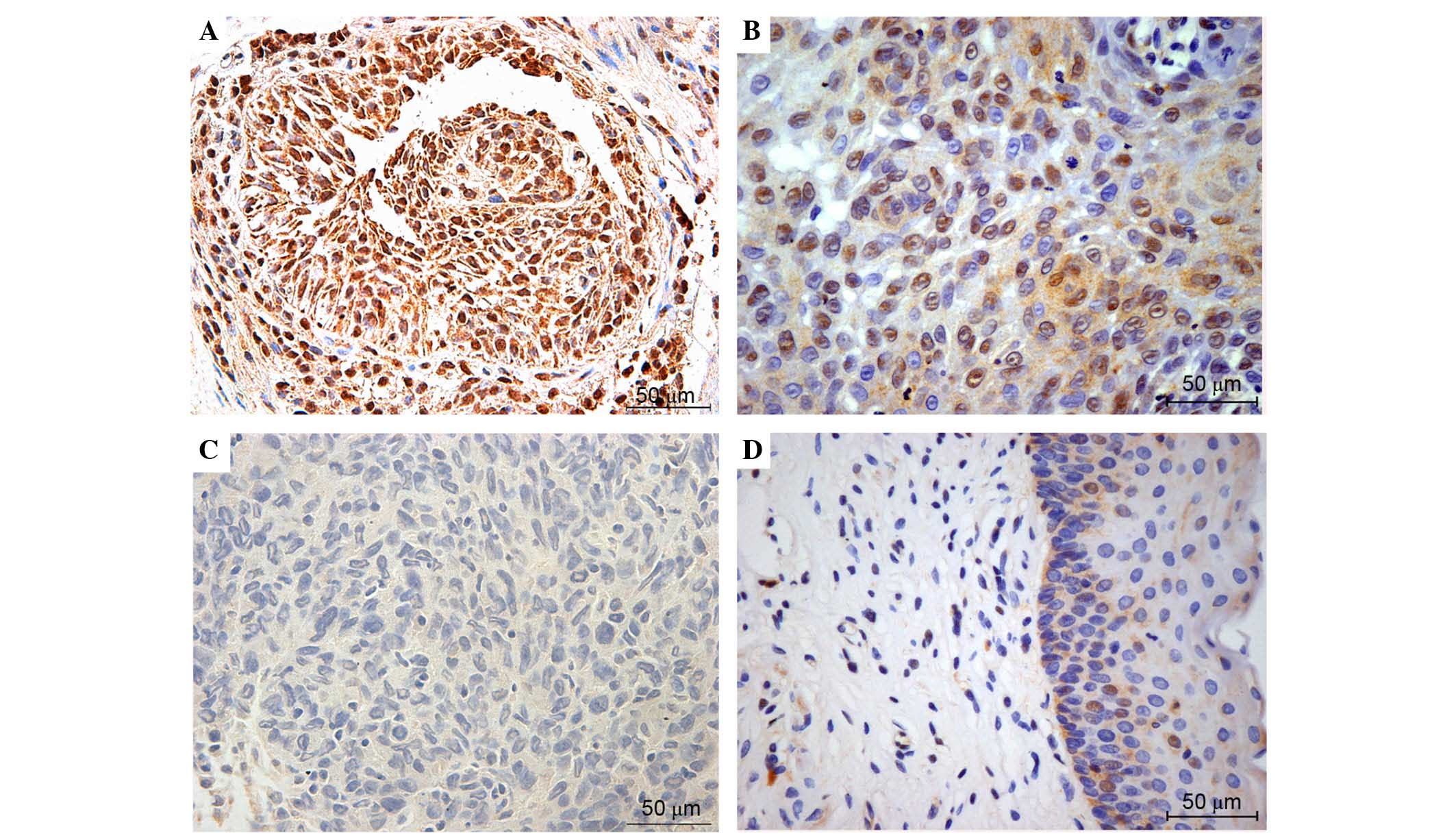
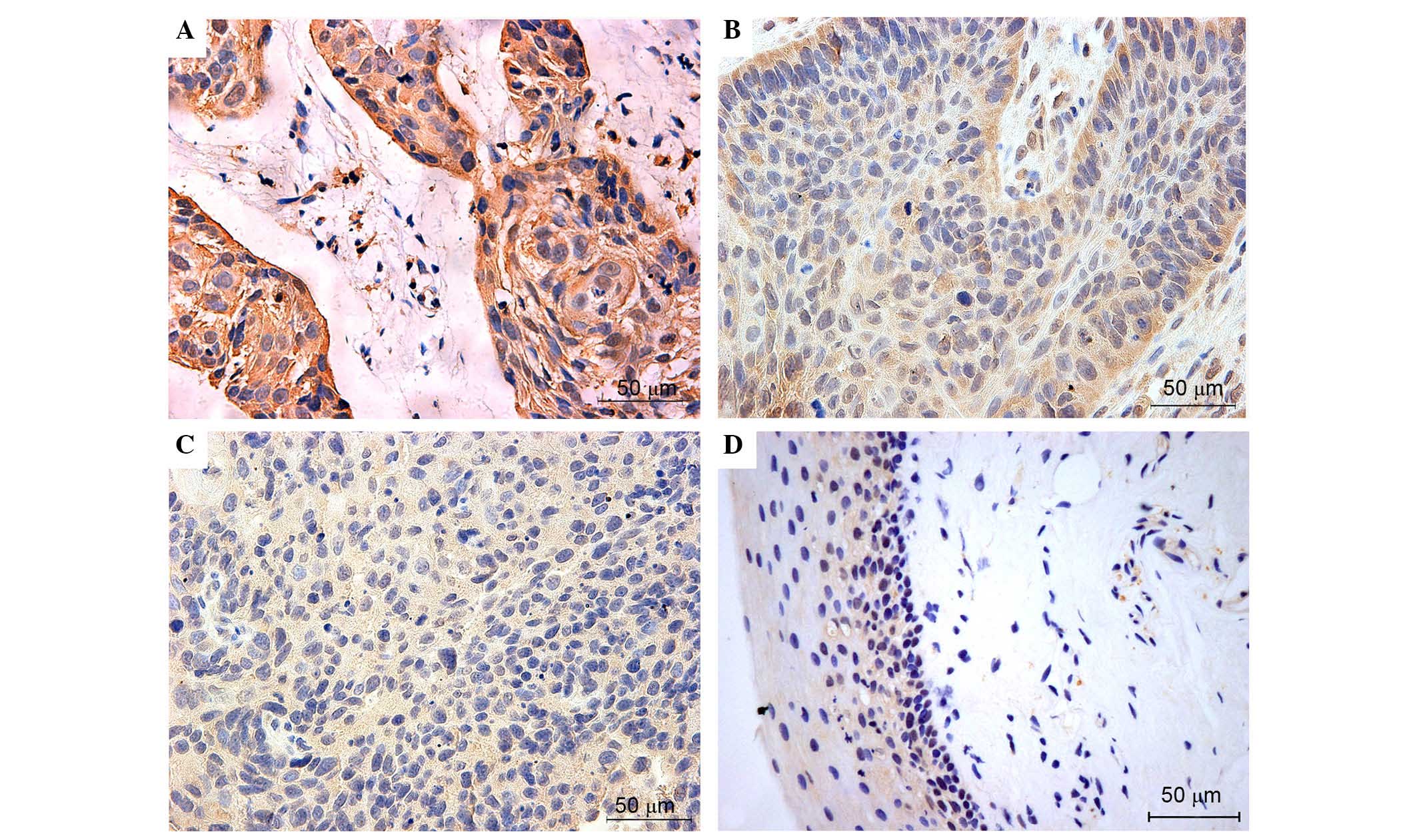
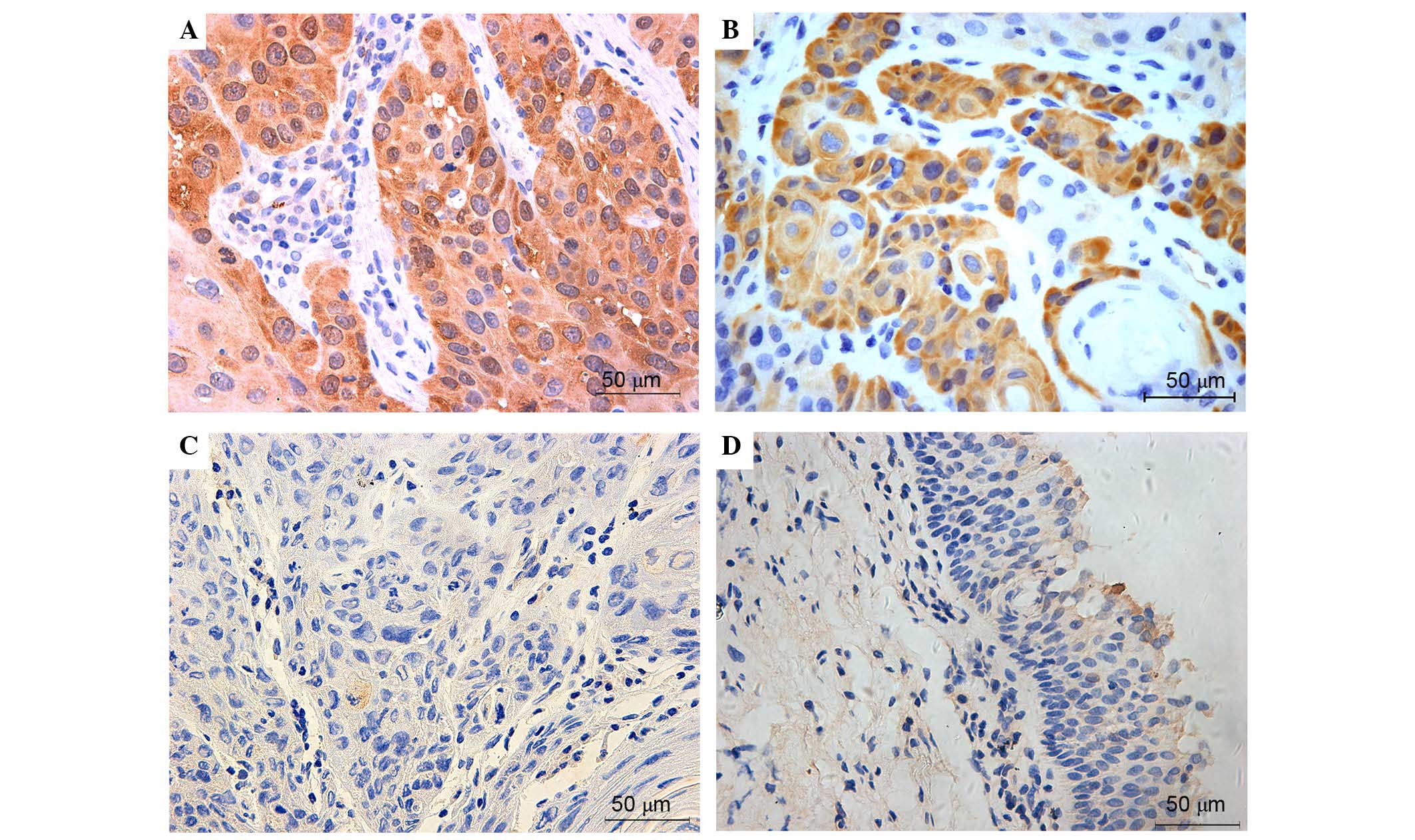
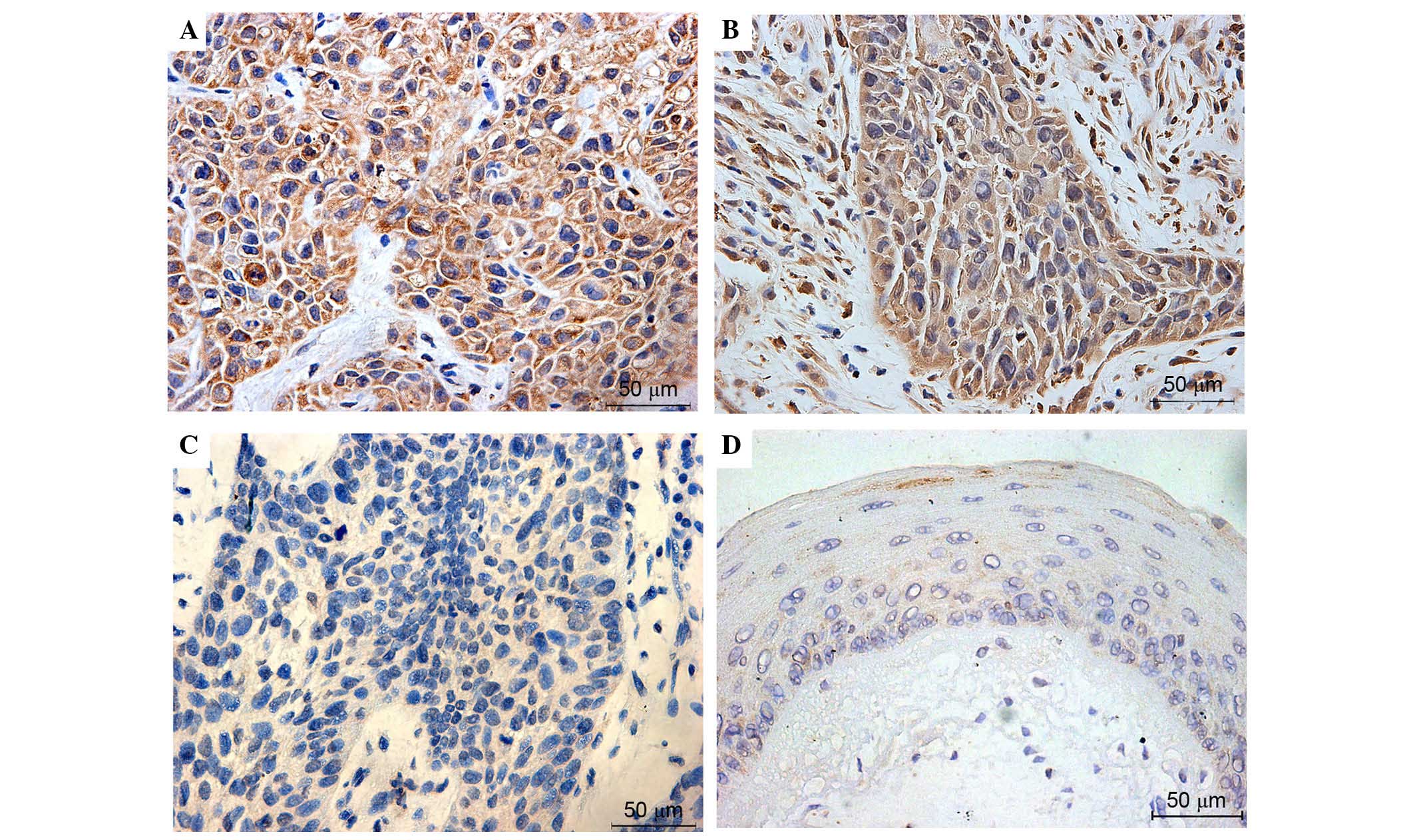
|
1
|
Harrington KJ, Nutting CM and Pandha HS:
Gene therapy for head and neck cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
24:147–164. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
American Society of Clinical Oncology, ;
Pfister DG, Laurie SA, Weinstein GS, Mendenhall WM, Adelstein DJ,
Ang KK, Clayman GL, Fisher SG, Forastiere AA, et al: American
Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline for the
use of larynx-preservation strategies in the treatment of laryngeal
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 24:3693–3704. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cho HY, Reddy SP and Kleeberger SR: Nrf2
defends the lung from oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal.
8:76–87. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Inci E, Civelek S, Seven A, Inci F, Korkut
N and Burçax G: Laryngeal cancer: In relation to oxidative stress.
Tohoku J Exp Med. 200:17–23. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jaramillo MC and Zhang DD: The emerging
role of the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in cancer. Genes Dev.
27:2179–2191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Singh A, Boldin-Adamsky S, Thimmulappa RK,
Rath SK, Ashush H, Coulter J, Blackford A, Goodman SN, Bunz F,
Watson WH, et al: RNAi-mediated silencing of nuclear factor
erythroid-2-related factor 2 gene expression in non-small cell lung
cancer inhibits tumor growth and increases efficacy of
chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 68:7975–7984. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Khor TO, Huang MT, Prawan A, Liu Y, Hao X,
Yu S, Cheung WK, Chan JY, Reddy BS, Yang CS and Kong AN: Increased
susceptibility of NRF2 knockout mice to colitis-associated
colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 1:187–191. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Edge SB and Compton CC; The American Joint
Committee on Cancer, : The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li CJ, Wang SZ, Wang SY and Zhang YP:
Assessment of the effect of local application of amifostine on
acute radiation-induced oral mucositis in guinea pigs. J Radiat
Res. 55:847–854. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Manne U, Myers RB, Moron C, Poczatek RB,
Dillard S, Weiss H, Brown D, Srivastava S and Grizzle WE:
Prognostic significance of Bcl-2 expression and p53 nuclear
accumulation in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer.
74:346–358. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Piyathilake CJ, Bell WC, Oelschlager DK,
Heimburger DC and Grizzle WE: The pattern of expression of Mn and
Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase varies among squamous cell cancers of
the lung, larynx, and oral cavity. Head Neck. 24:859–867. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han Y and Chen JZ: Oxidative stress
induces mitochondrial DNA damage and cytotoxicity through
independent mechanisms in human cancer cells. Biomed Res Int
825065. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
McLean LS, Watkins CN, Campbell P, Zylstra
D, Rowland L, Amis LH, Scott L, Babb CE, Livingston WJ, Darwanto A,
et al: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand 5F 203 induces oxidative
stress that triggers DNA damage in human breast cancer cells. Chem
Res Toxicol. 28:855–871. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dwivedi R, Raturi D, Kandpal N, Dwivedi R,
Singh R and Puri V: Oxidative stress in patients with laryngeal
carcinoma. Indian J Cancer. 45:97–99. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD and
Kensler TW: The role of Keap1 in cellular protective responses.
Chem Res Toxicol. 18:1779–1791. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kensler TW and Wakabayashi N: Nrf2: Friend
or foe for chemoprevention? Carcinogenesis. 31:90–99. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee JM and Johnson JA: An important role
of NRF2-ARE pathway in the cellular defense mechanism. J Biochem
Mol Biol. 37:139–143. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stacy DR, Ely K, Massion PP, Yarbrough WG,
Hallahan DE, Sekhar KR and Freeman ML: Increased expression of
nuclear factor E2 p45-related factor 2 (NRF2) in head and neck
squamous cell carcinomas. Head Neck. 28:813–818. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang CF, Zhang L, Ma SR, Zhao ZL, Wang
WM, He KF, Zhao YF, Zhang WF, Liu B and Sun ZJ: Clinical
significance of KEAP1 and NRF2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
PLoS One. 8:e834792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Solis LM, Behrens C, Dong W, Suraokar M,
Ozburn NC, Moran CA, Corvalan AH, Biswal S, Swisher SG, Bekele BN,
et al: Nrf2 and Keap1 abnormalities in non-small cell lung
carcinoma and association with clinicopathologic features. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:3743–3753. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liao H, Zhou Q, Zhang Z, Wang Q, Sun Y, Yi
X and Feng Y: NRF2 is overexpressed in ovarian epithelial carcinoma
and is regulated by gonadotrophin and sex-steroid hormones. Oncol
Rep. 27:1918–1924. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Soini Y, Eskelinen M, Juvonen P, Kärjä V,
Haapasaari KM, Saarela A and Karihtala P: Nuclear Nrf2 expression
is related to a poor survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pathol
Res Pract. 210:35–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ohta T, Iijima K, Miyamoto M, Nakahara I,
Tanaka H, Ohtsuji M, Suzuki T, Kobayashi A, Yokota J, Sakiyama T,
et al: Loss of Keap1 function activates Nrf2 and provides
advantages for lung cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 68:1303–1309.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Konstantinopoulos PA, Spentzos D,
Fountzilas E, Francoeur N, Sanisetty S, Grammatikos AP, Hecht JL
and Cannistra SA: Keap1 mutations and Nrf2 pathway activation in
epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 71:5081–5089. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yoo NJ, Kim HR, Kim YR, An CH and Lee SH:
Somatic mutations of the KEAP1 gene in common solid cancers.
Histopathology. 60:943–952. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang J, Zhang M, Zhang L, Cai H, Zhou S,
Zhang J and Wang Y: Correlation of Nrf2, HO-1, and MRP3 in
gallbladder cancer and their relationships to clinicopathologic
features and survival. J Surg Res. 164:e99–e105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|