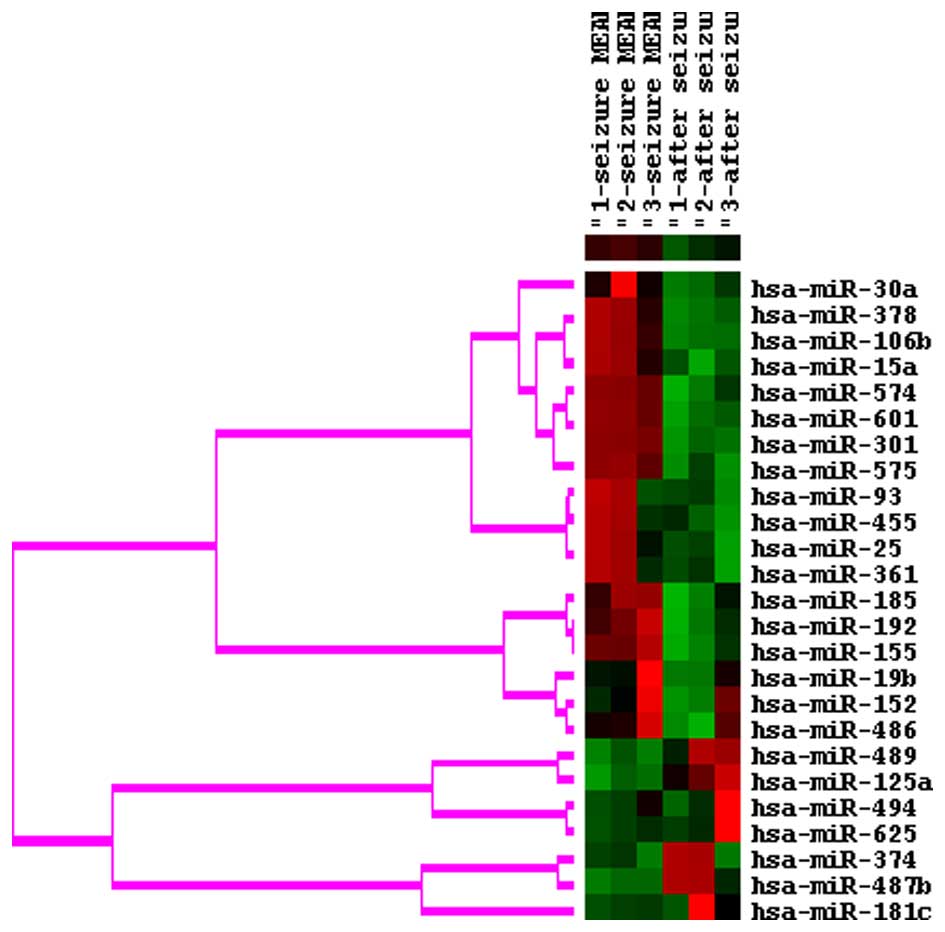
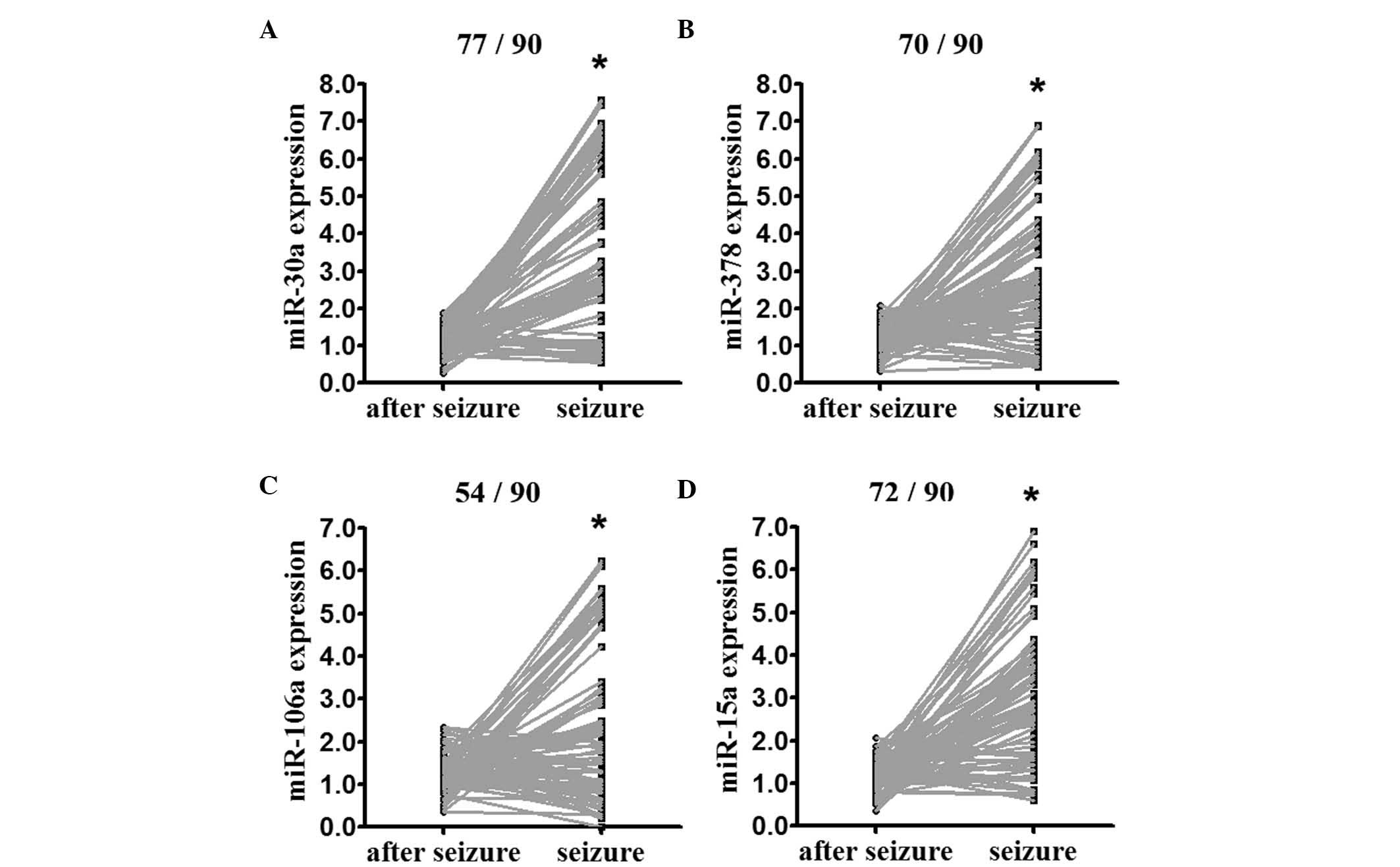
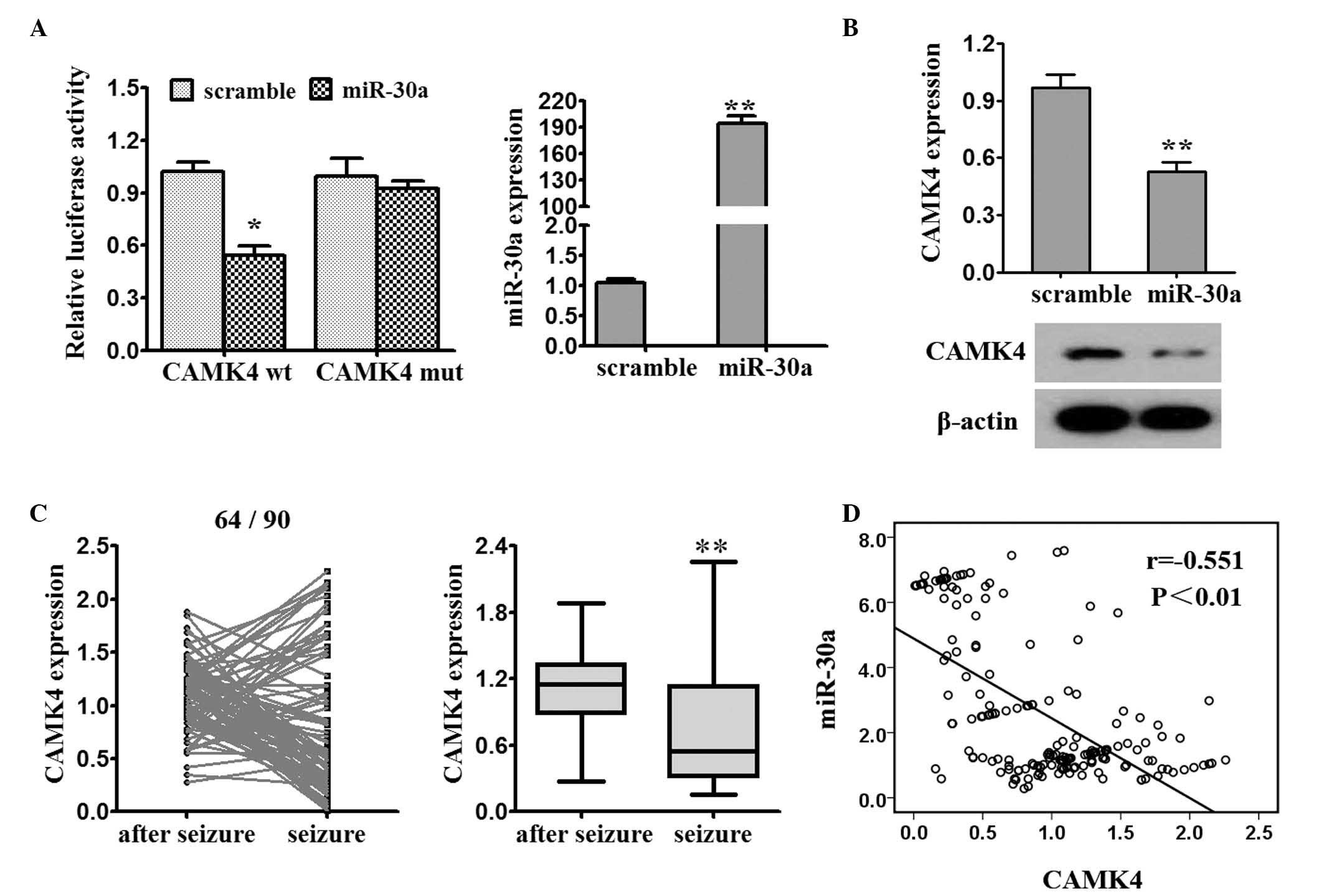
|
1
|
van Graan LA, Lemieux L and Chaudhary UJ:
Methods and utility of EEG-fMRI in epilepsy. Quant Imaging Med
Surg. 5:300–312. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kwan P, Schachter SC and Brodie MJ:
Drug-resistant epilepsy. N Engl J Med. 365:919–926. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ahmad MA, Ayaz Y, Jamil M, Gillani S Omer,
Rasheed MB, Imran M, Khan NA, Majeed W and Javaid N: Comparative
analysis of classifiers for developing an adaptive
computer-assisted EEG analysis system for diagnosing epilepsy.
Biomed Res Int. 2015:6380362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Puttachary S, Sharma S, Stark S and
Thippeswamy T: Seizure-induced oxidative stress in temporal lobe
epilepsy. Biomed Res Int. 2015:7456132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sano T, Reynolds JP, Jimenez-Mateos EM,
Matsushima S, Taki W and Henshall DC: MicroRNA-34a upregulation
during seizure-induced neuronal death. Cell Death Dis. 3:e2872012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Saugstad JA: Non-Coding RNAs in stroke and
neuroprotection. Front Neurol. 6:502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bhalala OG, Srikanth M and Kessler JA: The
emerging roles of microRNAs in CNS injuries. Nat Rev Neurol.
9:328–339. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu DZ, Tian Y, Ander BP, Xu H, Stamova
BS, Zhan X, Turner RJ, Jickling G and Sharp FR: Brain and blood
microRNA expression profiling of ischemic stroke, intracerebral
hemorrhage, and kainate seizures. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
30:92–101. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Henshall DC: MicroRNA and epilepsy:
Profiling, functions and potential clinical applications. Curr Opin
Neurol. 27:199–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zucchini S, Marucci G, Paradiso B, Lanza
G, Roncon P, Cifelli P, Ferracin M, Giulioni M, Michelucci R,
Rubboli G and Simonato M: Identification of miRNAs differentially
expressed in human epilepsy with or without granule cell pathology.
PLoS One. 9:e1055212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li MM, Jiang T, Sun Z, Zhang Q, Tan CC, Yu
JT and Tan L: Genome-wide microRNA expression profiles in
hippocampus of rats with chronic temporal lobe epilepsy. Sci Rep.
4:47342014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McKiernan RC, Jimenez-Mateos EM, Sano T,
Bray I, Stallings RL, Simon RP and Henshall DC: Expression
profiling the microRNA response to epileptic preconditioning
identifies miR-184 as a modulator of seizure-induced neuronal
death. Exp Neurol. 2:346–354. 2013.
|
|
14
|
Zeng X, Xiang J, Wu M, Xiong W, Tang H,
Deng M, Li X, Liao Q, Su B, Luo Z, et al: Circulating miR-17,
miR-20a, miR-29c, and miR-223 combined as non-invasive biomarkers
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e463672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
You G, Yan W, Zhang W, Wang Y, Bao Z, Li
S, Li S, Li G, Song Y, Kang C and Jiang T: Significance of miR-196b
in tumor-related epilepsy of patients with gliomas. PLoS One.
7:e462182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiao S, Yang Z, Lv R, Zhao J, Wu M, Liao Y
and Liu Q: miR-135b contributes to the radioresistance by targeting
GSK3β in human glioblastoma multiforme cells. PLoS One.
9:e1088102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang R, Liang L, Luo D, Feng Z, Huang Q,
He R, Gan T, Yang L and Chen G: Downregulation of miR-30a is
associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer. Med Sci Monit.
21:2514–2520. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Müller AH, Povlsen GK, Bang-Berthelsen CH,
Kruse LS, Nielsen J, Warfvinge K and Edvinsson L: Regulation of
microRNAs miR-30a and miR-143 in cerebral vasculature after
experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. BMC Genomics.
16:1192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wen Y, Han J, Chen J, Dong J, Xia Y, Liu
J, Jiang Y, Dai J, Lu J, Jin G, et al: Plasma miRNAs as early
biomarkers for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
137:1679–1690. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guess MG, Barthel KK, Harrison BC and
Leinwand LA: miR-30 family microRNAs regulate myogenic
differentiation and provide negative feedback on the microRNA
pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01182292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Long G, Wang F, Li H, Yin Z, Sandip C, Lou
Y, Wang Y, Chen C and Wang DW: Circulating miR-30a, miR-126 and
let-7b as biomarker for ischemic stroke in humans. BMC Neurol.
13:1782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Q, Tang Q, Qin D, Yu L, Huang R, Lv
G, Zou Z, Jiang XC, Zou C, Liu W, et al: Role of microRNA 30a
targeting insulin receptor substrate 2 in colorectal tumorigenesis.
Mol Cell Biol. 35:988–1000. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang T, Li F and Tang S: MiR-30a
upregulates BCL2A1, IER3 and cyclin D2 expression by targeting
FOXL2. Oncol Lett. 9:967–971. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang P, Liang J, Li Y and Li J, Yang X,
Zhang X, Han S, Li S and Li J: Down-regulation of miRNA-30a
alleviates cerebral ischemic injury through enhancing beclin
1-mediated autophagy. Neurochem Res. 39:1279–1291. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McCullough LD, Tarabishy S, Liu L,
Benashski S, Xu Y, Ribar T, Means A and Li J: Inhibition of
calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase β and
calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV is detrimental in
cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 44:2559–2566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Koval AV, Vlasov P, Shichkova P,
Khunderyakova S, Markov Y, Panchenko J, Volodina A, Kondrashov FA
and Katanaev VL: Anti-leprosy drug clofazimine inhibits growth of
triple-negative breast cancer cells via inhibition of canonical Wnt
signaling. Biochem Pharmacol. 87:571–578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang C, Hu J, Lu M, Gu H, Zhou X, Chen X,
Zen K, Zhang CY, Zhang T, Ge J, et al: A panel of five serum miRNAs
as a potential diagnostic tool for early-stage renal cell
carcinoma. Sci Rep. 5:76102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Clancy C, Joyce MR and Kerin MJ: The use
of circulating microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Biomark. 15:103–113. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen LT, Xu SD, Xu H, Zhang JF, Ning JF
and Wang SF: MicroRNA-378 is associated with non-small cell lung
cancer brain metastasis by promoting cell migration, invasion and
tumor angiogenesis. Med Oncol. 29:1673–1680. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
You L, Gu W, Chen L, Pan L, Chen J and
Peng Y: MiR-378 overexpression attenuates high glucose-suppressed
osteogenic differentiation through targeting CASP3 and activating
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:7249–7261.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen Z, Li C, Xu Y, Li Y, Yang H and Rao
L: Circulating level of miR-378 predicts left ventricular
hypertrophy in patients with aortic stenosis. PLoS One.
9:e1057022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pan D, Mao C, Quattrochi B, Friedline RH,
Zhu LJ, Jung DY, Kim JK, Lewis B and Wang YX: MicroRNA-378 controls
classical brown fat expansion to counteract obesity. Nat Commun.
5:47252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meenhuis A, van Veelen PA, de Looper H,
van Boxtel N, van den Berge IJ, Sun SM, Taskesen E, Stern P, de Ru
AH, van Adrichem AJ, et al: MiR-17/20/93/106 promote hematopoietic
cell expansion by targeting sequestosome 1-regulated pathways in
mice. Blood. 118:916–925. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fallah P, Amirizadeh N, Poopak B, Toogeh
G, Arefian E, Kohram F, Rad SM Hosseini, Kohram M, Naghadeh H
Teimori and Soleimani M: Expression pattern of key microRNAs in
patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic
phase. Int J Lab Hematol. 37:560–568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shiotani A, Murao T, Kimura Y, Matsumoto
H, Kamada T, Kusunoki H, Inoue K, Uedo N, Iishi H and Haruma K:
Identification of serum miRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for
detection of high risk for early gastric cancer. Br J Cancer.
109:2323–2330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mei Z, Su T, Ye J, Yang C, Zhang S and Xie
C: The miR-15 family enhances the radiosensitivity of breast cancer
cells by targeting G2 checkpoints. Radiat Res. 183:196–207. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Maudet C, Mano M, Sunkavalli U, Sharan M,
Giacca M, Förstner KU and Eulalio A: Functional high-throughput
screening identifies the miR-15 microRNA family as cellular
restriction factors for Salmonella infection. Nat Commun.
5:47182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tijsen AJ, van der Made I, van den
Hoogenhof MM, Wijnen WJ, van Deel ED, de Groot NE, Alekseev S,
Fluiter K, Schroen B, Goumans MJ, et al: The microRNA-15 family
inhibits the TGFβ-pathway in the heart. Cardiovasc Res. 104:61–71.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|