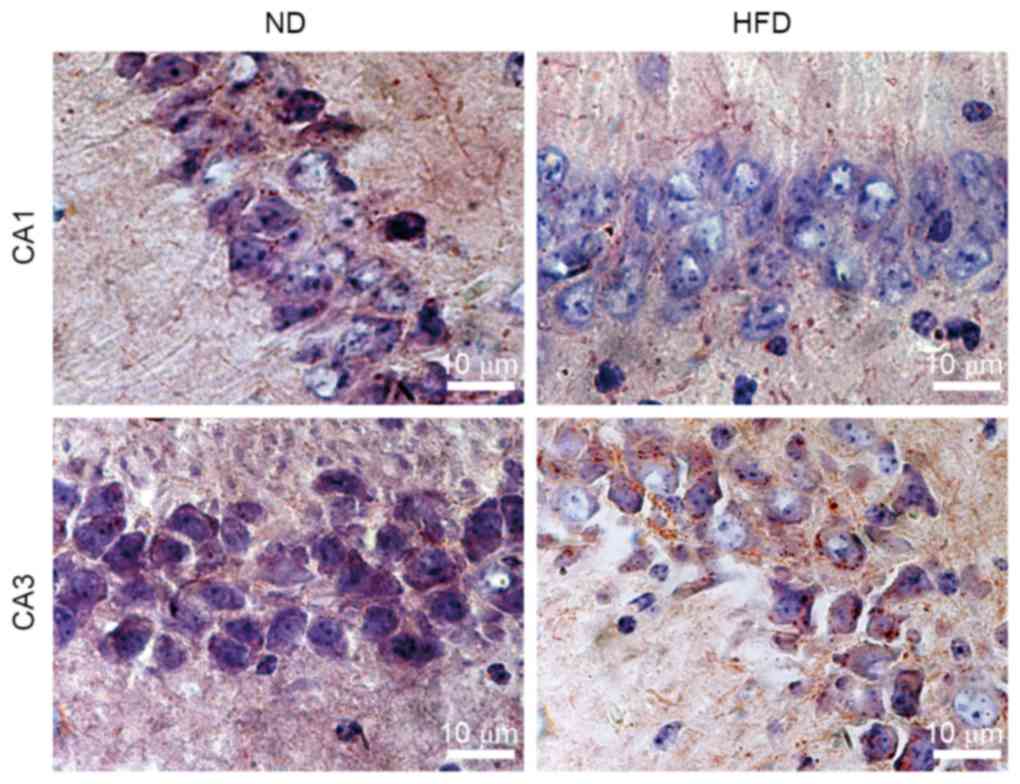
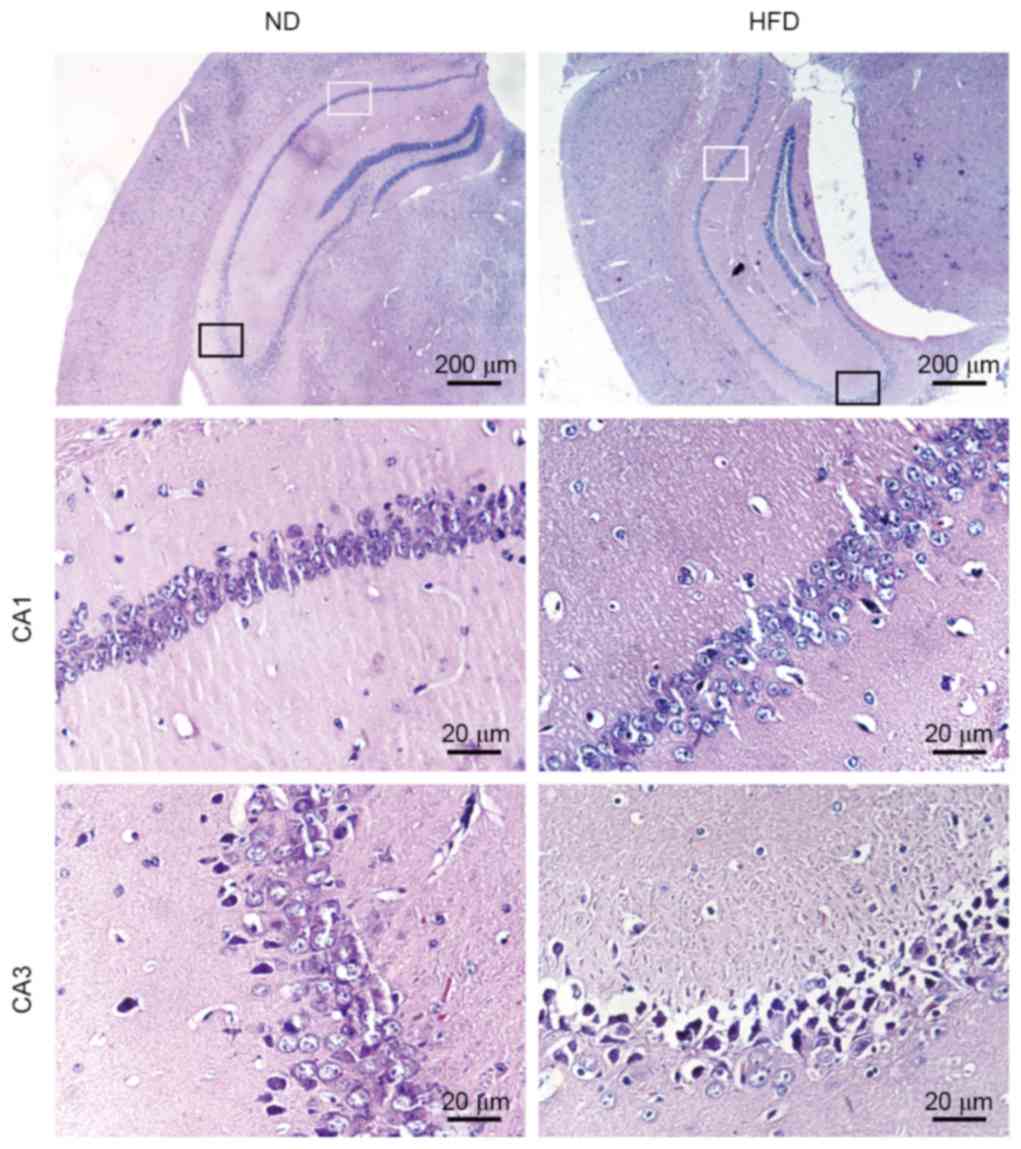
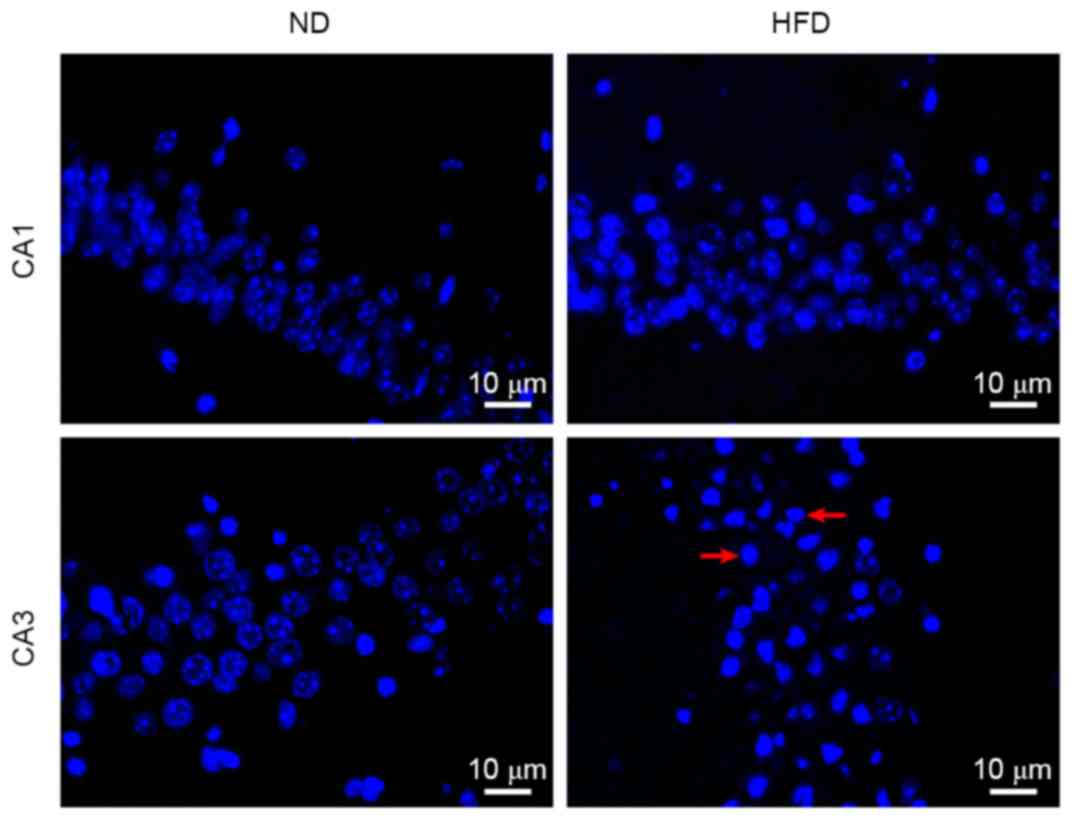
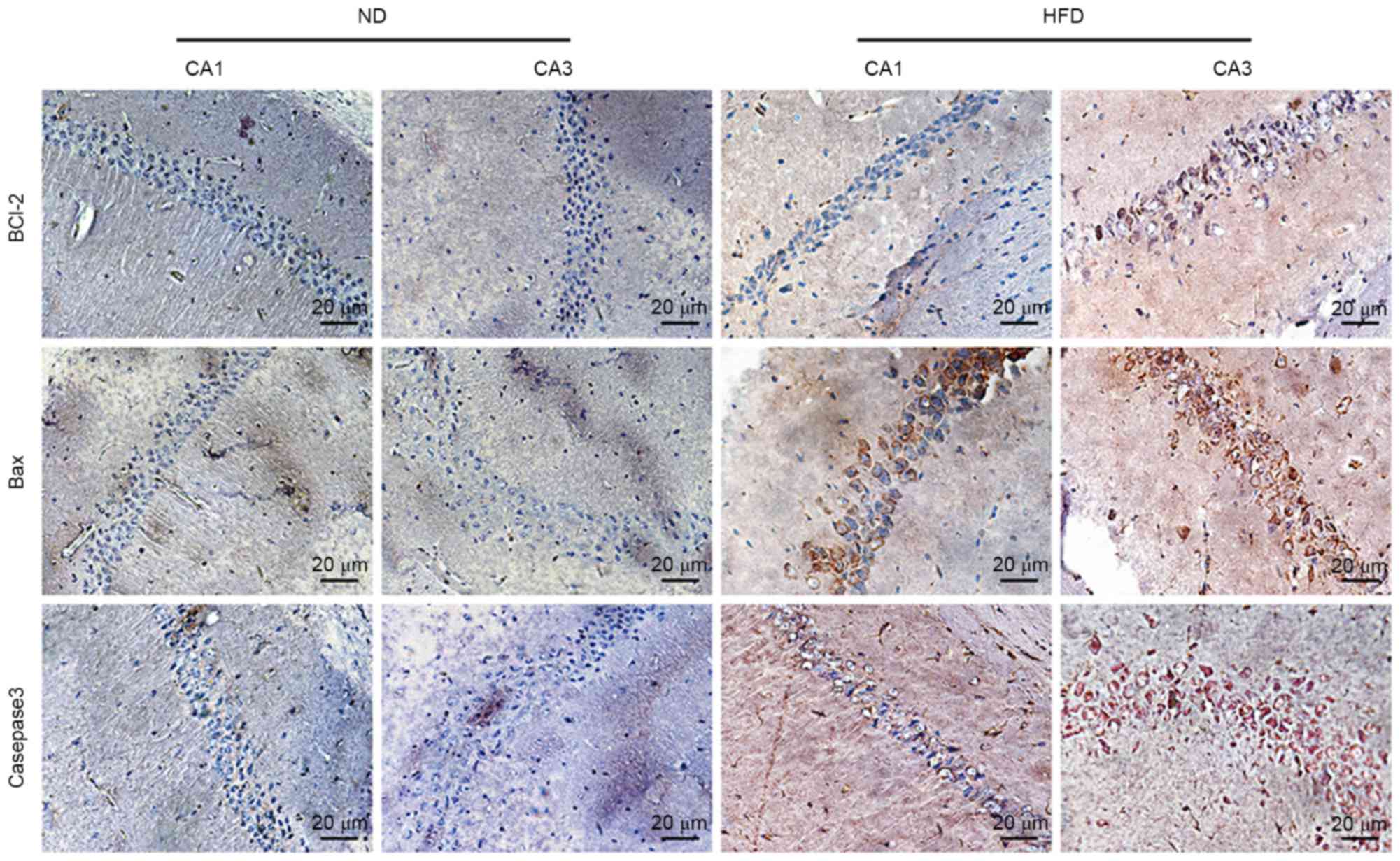
|
1
|
Mawuenyega KG, Sigurdson W, Ovod V,
Munsell L, Kasten T, Morris JC, Yarasheski KE and Bateman RJ:
Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease.
Science. 330:17742010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Akhter R, Sanphui P, Das H, Saha P and
Biswas SC: The regulation of p53 up-regulated modulator of
apoptosis by JNK/c-Jun pathway in β-amyloid-induced neuron death. J
Neurochem. 134:1091–1103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kivipelto M, Helkala EL, Laakso MP,
Hänninen T, Hallikainen M, Alhainen K, Iivonen S, Mannermaa A,
Tuomilehto J, Nissinen A and Soininen H: Apolipoprotein E epsilon4
allele, elevated midlife total cholesterol level, and high midlife
systolic blood pressure are independent risk factors for late-life
Alzheimer disease. Ann Intern Med. 137:149–155. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Solomon A, Kåreholt I, Ngandu T, Winblad
B, Nissinen A, Tuomilehto J, Soininen H and Kivipelto M: Serum
cholesterol changes after midlife and late life cognition:
Twenty-one-year follow-up study. Neurology. 68:751–756. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shepardson NE, Shankar GM and Selkoe DJ:
Cholesterol level and statin use in Alzheimer disease: I. Review of
epidemiological and preclinical studies. Arch Neurol. 68:1239–1244.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pregelj P: Involvement of cholesterol in
the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: Role of statins. Psychiatr
Danub. 20:162–167. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Longenberger J and Shah ZA: Simvastatin
and other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on brain cholesterol levels
in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 8:434–442. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chan RB, Oliveira TG, Cortes EP, Honig LS,
Duff KE, Small SA, Wenk MR, Shui G and Di Paolo G: Comparative
lipidomic analysis of mouse and human brain with Alzheimer disease.
J Biol Chem. 287:2678–2688. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kosari S, Badoer E, Nguyen JC, Killcross
AS and Jenkins TA: Effect of western and high fat diets on memory
and cholinergic measures in the rat. Behav Brain Res. 235:98–103.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
El-Sayyad HI, El Sherbiny MA, Sobh MA, El
Naga AM Abou, Ibrahim MA and Mousa SA: Protective effects of Morus
alba leaves extract on ocular functions of pups from diabetic and
hypercholesterolemic mother rats. Int J Biol Sci. 7:715–728. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen JH, Hsieh CJ, Huang YL, Chen YC, Chen
TF, Sun Y, Wen LL, Yip PK and Chu YM: Genetic polymorphisms of
lipid metabolism gene SAR1 homolog B and the risk of Alzheimer's
disease and vascular dementia. J Formos Med Assoc. 115:38–44. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Seidah NG, Benjannet S, Wickham L,
Marcinkiewicz J, Jasmin SB, Stifani S, Basak A, Prat A and Chretien
M: The secretory proprotein convertase neural apoptosis-regulated
convertase 1 (NARC-1): Liver regeneration and neuronal
differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:928–933. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Benjannet S, Rhainds D, Essalmani R, Mayne
J, Wickham L, Jin W, Asselin MC, Hamelin J, Varret M, Allard D, et
al: NARC-1/PCSK9 and its natural mutants: Zymogen cleavage and
effects on the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor and LDL
cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 279:48865–48875. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu CY, Tang ZH, Jiang L, Li XF, Jiang ZS
and Liu LS: PCSK9 siRNA inhibits HUVEC apoptosis induced by ox-LDL
via Bcl/Bax caspase9-caspase3 pathway. Mol Cell Biochem.
359:347–358. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US); Washington (DC): 2011,
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stranahan AM, Cutler RG, Button C,
Telljohann R and Mattson MP: Diet-induced elevations in serum
cholesterol are associated with alterations in hippocampal lipid
metabolism and increased oxidative stress. J Neurochem.
118:611–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moghadam A Hafezi, Thomas KL and Wagner
DD: ApoE deficiency leads to a progressive age-dependent
blood-brain barrier leakage. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
292:C1256–C1262. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Methia N, André P, Hafezi-Moghadam A,
Economopoulos M, Thomas KL and Wagner DD: ApoE deficiency
compromises the blood brain barrier especially after injury. Mol
Med. 7:810–815. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Frisardi V, Panza F, Seripa D, Farooqui T
and Farooqui AA: Glycerophospholipids and
glycerophospholipid-derived lipid mediators: A complex meshwork in
Alzheimer's disease pathology. Prog Lipid Res. 50:313–330. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thirumangalakudi L, Prakasam A, Zhang R,
Bimonte-Nelson H, Sambamurti K, Kindy MS and Bhat NR: High
cholesterol-induced neuroinflammation and amyloid precursor protein
processing correlate with loss of working memory in mice. J
Neurochem. 106:475–485. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bingham B, Shen R, Kotnis S, Lo CF,
Ozenberger BA, Ghosh N, Kennedy JD, Jacobsen JS, Grenier JM,
DiStefano PS, et al: Proapoptotic effects of NARC 1 (=PCSK9), the
gene encoding a novel serine proteinase. Cytometry A. 69:1123–1131.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klein WL, Krafft GA and Finch CE:
Targeting small Abeta oligomers: The solution to an Alzheimer's
disease conundrum? Trends Neurosci. 24:219–224. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fernández-Vizarra P, Fernández AP,
Castro-Blanco S, Serrano J, Bentura ML, Martínez-Murillo R,
Martínez A and Rodrigo J: Intra- and extracellular Abeta and PHF in
clinically evaluated cases of Alzheimer's disease. Histol
Histopathol. 19:823–844. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shie FS, Jin LW, Cook DG, Leverenz JB and
LeBoeuf RC: Diet-induced hypercholesterolemia enhances brain A beta
accumulation in transgenic mice. Neuroreport. 13:455–459. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Refolo LM, Malester B, LaFrancois J,
Bryant-Thomas T, Wang R, Tint GS, Sambamurti K, Duff K and Pappolla
MA: Hypercholesterolemia accelerates the Alzheimer's amyloid
pathology in a transgenic mouse model. Neurobiol Dis. 7:321–331.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Umeda T, Tomiyama T, Kitajima E, Idomoto
T, Nomura S, Lambert MP, Klein WL and Mori H: Hypercholesterolemia
accelerates intraneuronal accumulation of Aβ oligomers resulting in
memory impairment in Alzheimer's disease model mice. Life Sci.
91:1169–1176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jonas MC, Costantini C and Puglielli L:
PCSK9 is required for the disposal of non-acetylated intermediates
of the nascent membrane protein BACE1. EMBO Rep. 9:916–922. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ko MH and Puglielli L: Two endoplasmic
reticulum (ER)/ER Golgi intermediate compartment-based lysine
acetyltransferases post-translationally regulate BACE1 levels. J
Biol Chem. 284:2482–2492. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu M, Wu G, Baysarowich J, Kavana M,
Addona GH, Bierilo KK, Mudgett JS, Pavlovic G, Sitlani A, Renger
JJ, et al: PCSK9 is not involved in the degradation of LDL
receptors and BACE1 in the adult mouse brain. J Lipid Res.
51:2611–2618. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|