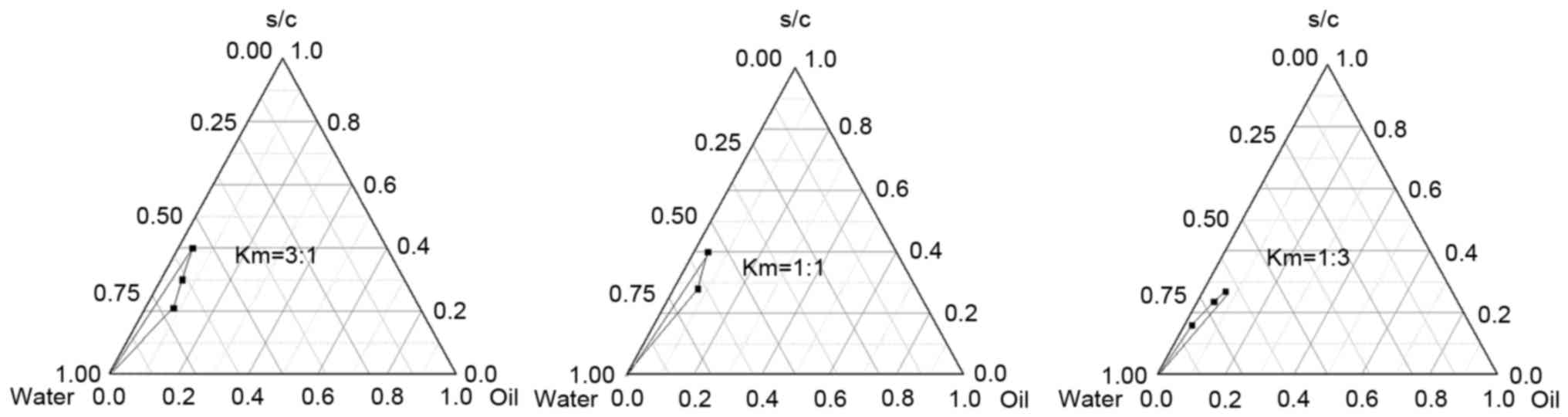
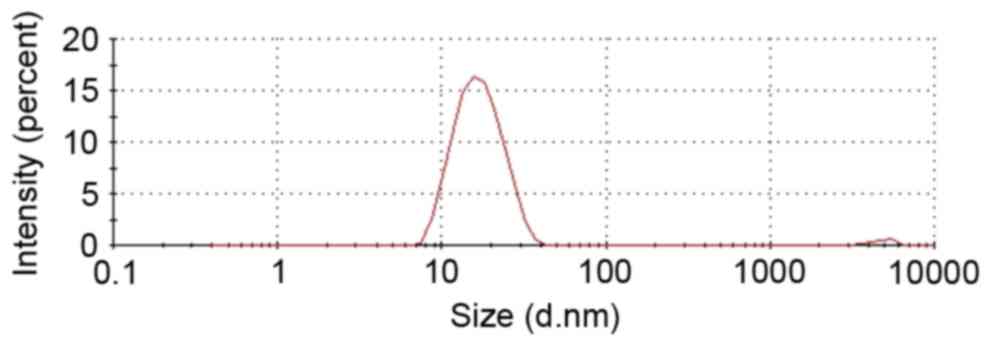
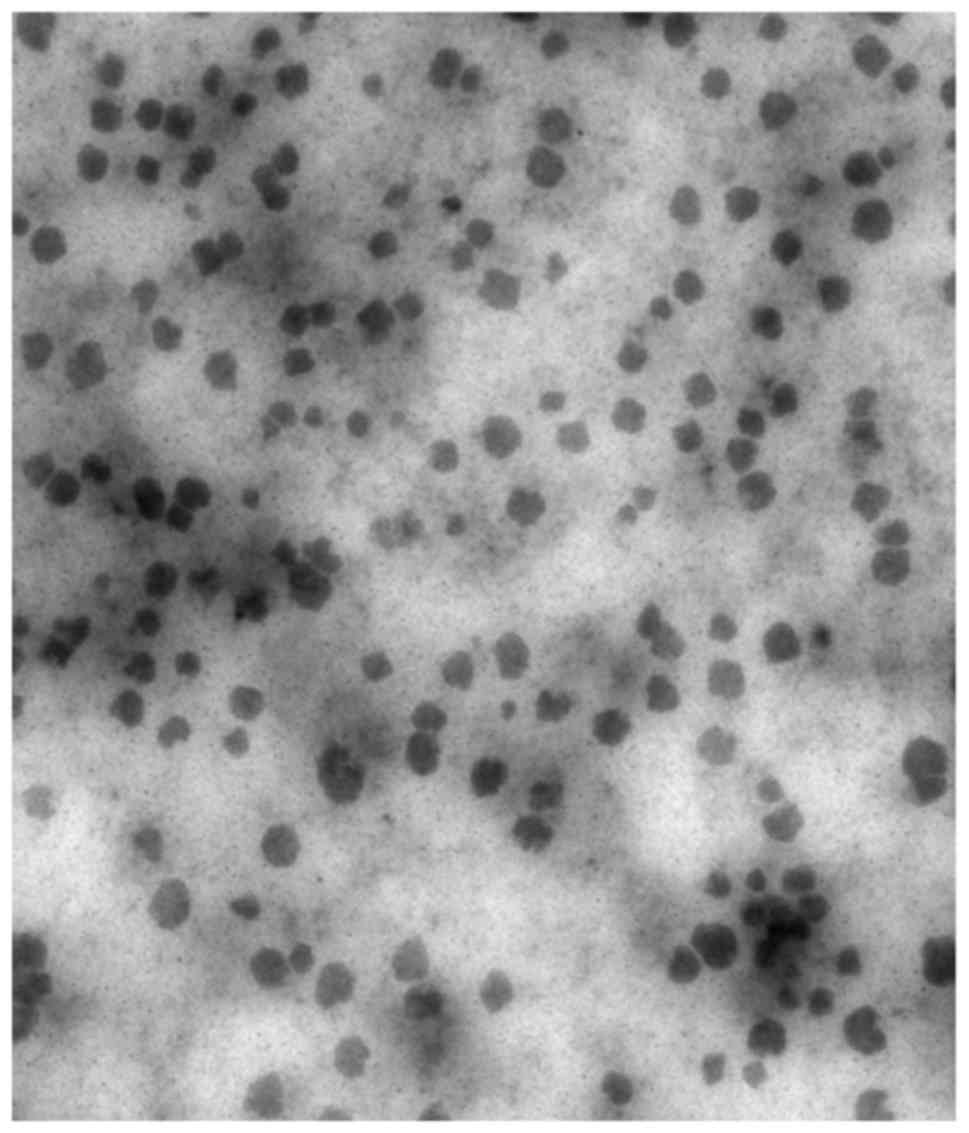
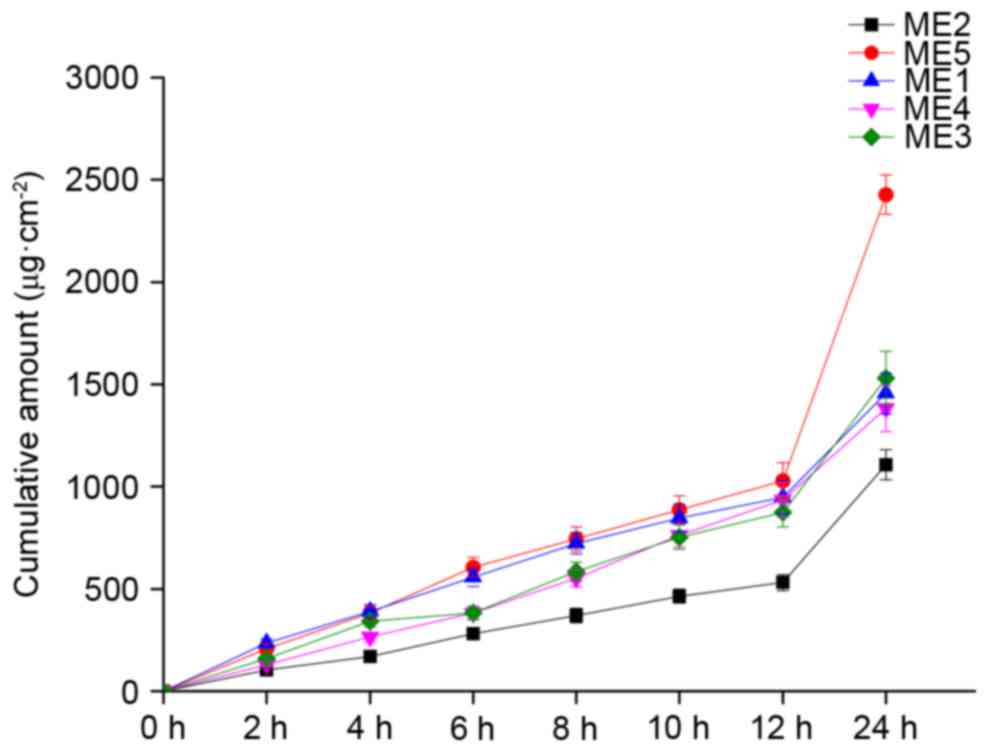
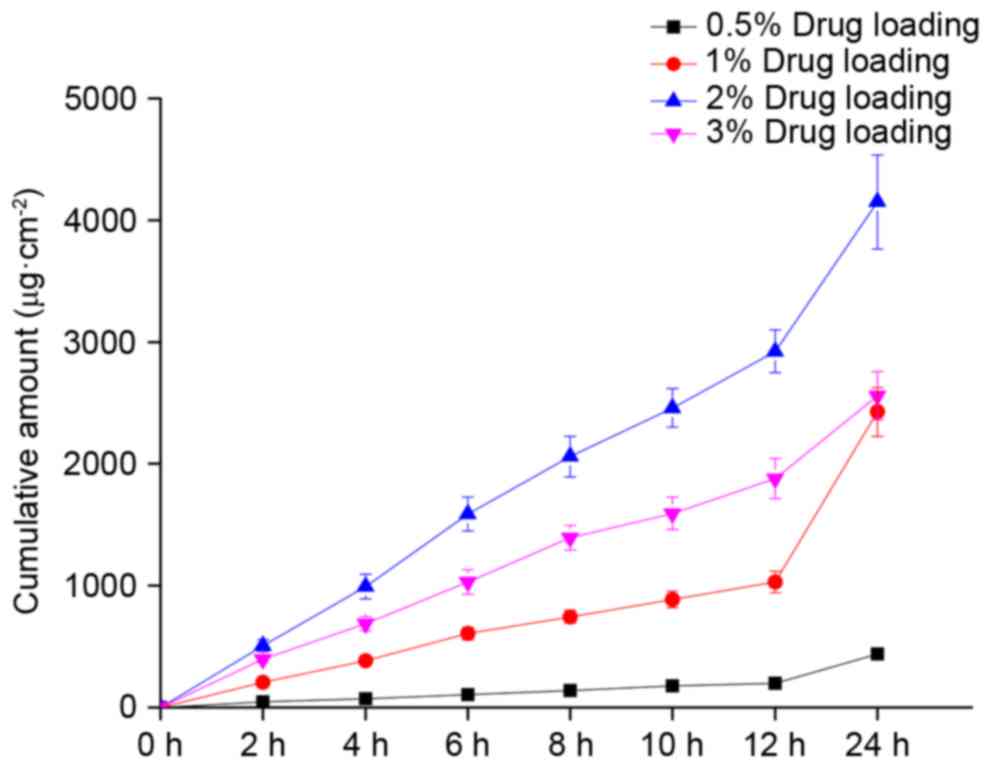
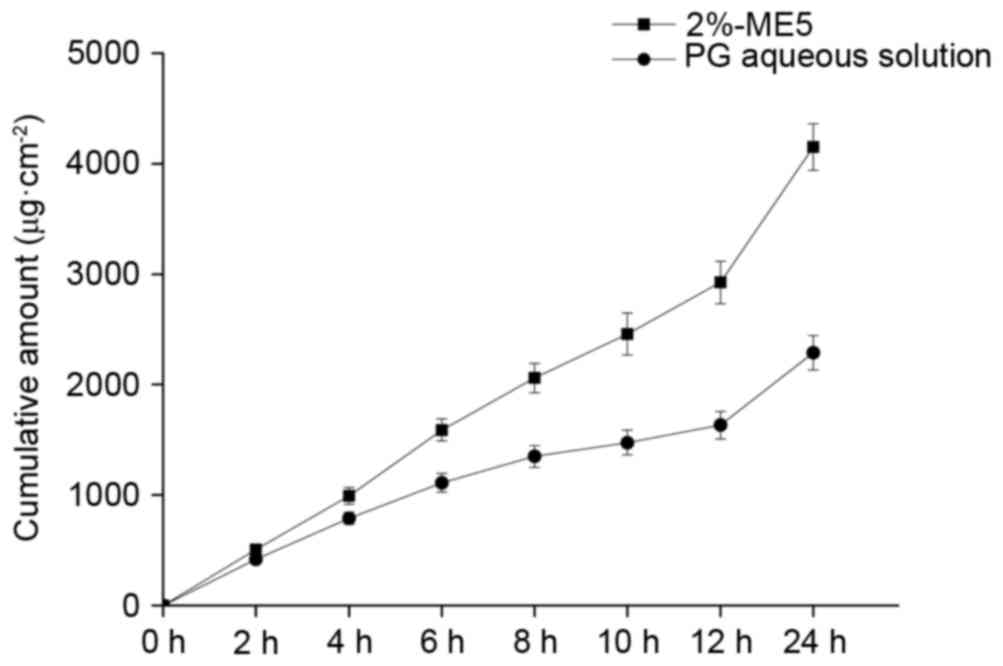
|
1
|
Qiu Y, Chen M, Su M, Xie G, Li X, Zhou M,
Zhao A, Jiang J and Jia W: Metabolic profiling reveals therapeutic
effects of Herba Cistanches in an animal model of
hydrocortisone-induced ‘kidney-deficiency syndrome’. Chin Med.
3:32008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fu G, Pang H and Wong YH: Naturally
occurring phenylethanoid glycosides: Potential leads for new
therapeutics. Curr Med Chem. 15:2592–2613. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saracoglu I, Harput US, Inoue M and
Ogihara Y: New phenylethanoid glycosides from Veronica pectinata
var. glandulosa and their free radical scavenging activities. Chem
Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 50:665–668. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yamaguchi K, Mitsui T, Aso Y and
Sugibayashi K: Structure-permeability relationship analysis of the
permeation barrier properties of the stratum corneum and viable
epidermis/dermis of rat skin. J Pharm Sci. 97:4391–4403. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tandel H, Raval K, Nayani A and Upadhay M:
Preparation and evaluation of cilnidipine microemulsion. J Pharm
Bioallied Sci. 4:(Suppl 1). S114–S115. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
El Maghraby MG: Microemulsions as
transdermal drug delivery systems. Curr Nanoscience. 8:504–511.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mou D, Chen H, Du D, Mao C, Wan J, Xu H
and Yang X: Hydrogel-thickened nanoemulsion system for topical
delivery of lipophilic drugs. Int J Pharm. 353:270–276. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barot BS, Parejiya PB, Patel HK, Gohel MC
and Shelat PK: Microemulsion-based gel of terbinafine for the
treatment of onychomycosis: Optimization of formulation using
D-optimal design. AAPS PharmSciTech. 13:184–192. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsai YH, Lee KF, Huang YB, Huang CT and Wu
PC: In vitro permeation and in vivo whitening effect of topical
hesperetin microemulsion delivery system. Int J Pharm. 388:257–262.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li G, Fan Y, Li X, Wang X, Li Y, Liu Y and
Li M: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a simple microemulsion
formulation for propofol. Int J Pharm. 425:53–61. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang JH, Wu SS, Xu HH, Yan Y, Ju B, Zhu D,
Liang X and Hu J: Inhibitory effects of phenylethanoid glycosides
on melanin synthesis in cultured human epidermal melanocytes. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 9:18019–18025. 2016.
|
|
12
|
Shen LN, Zhang YT, Wang Q, Xu L and Feng
NP: Preparation and evaluation of microemulsion-based transdermal
delivery of total flavone of rhizoma arisaematis. Int J
Nanomedicine. 9:3453–3464. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Draize JH, Woodard G and Calvery HO:
Methods for the study of irritation and toxicity of substances
applied topically to the skin and mucous membranes. J Pharmacol Exp
Therapeutics. 82:377–390. 1944.
|
|
14
|
Sahoo S, Pani NR and Sahoo SK:
Microemulsion based topical hydrogel of sertaconazole: Formulation,
characterization and evaluation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.
120:193–199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Paolino D, Ventura CA, Nisticò S, Puglisi
G and Fresta M: Lecithin microemulsions for the topical
administration of ketoprofen: Percutaneous adsorption through human
skin and in vivo human skin tolerability. Int J Pharm. 244:21–31.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Butani D, Yewale C and Misra A:
Amphotericin B topical microemulsion: Formulation, characterization
and evaluation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 116:351–358. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Acosta EJ, Nguyen T, Witthayapanyanon A,
Harwell JH and Sabatini DA: Linker-based bio-compatible
microemulsions. Environ Sci Technol. 39:1275–1282. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen H, Mou D, Du D, Chang X, Zhu D, Liu
J, Xu H and Yang X: Hydrogel-thickened microemulsion for topical
administration of drug molecule at an extremely low concentration.
Int J Pharm. 341:78–84. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bali V, Ali M and Ali J: Study of
surfactant combinations and development of a novel nanoemulsion for
minimising variations in bioavailability of ezetimibe. Colloids
Surf B Biointerfaces. 76:410–420. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Changez M and Varshney M: Aerosol-OT
microemulsions as transdermal carriers of tetracaine hydrochloride.
Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 26:507–512. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen H, Chang X, Du D, Li J, Xu H and Yang
X: Microemulsion-based hydrogel formulation of ibuprofen for
topical delivery. Int J Pharm. 315:52–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shakeel F, Baboota S, Ahuja A, Ali J, Aqil
M and Shafiq S: Nanoemulsions as vehicles for transdermal delivery
of aceclofenac. AAPS PharmSciTech. 8:E1042007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang YT, Zhao JH, Zhang SJ, Zhong YZ,
Wang Z, Liu Y, Shi F and Feng NP: Enhanced transdermal delivery of
evodiamine and rutaecarpine using microemulsion. Int J
Nanomedicine. 6:2469–2482. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sintov AC: Transdermal delivery of
curcumin via microemulsion. Int J Pharm. 481:97–103. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao L, Wang Y, Zhai Y, Wang Z, Liu J and
Zhai G: Ropivacaine loaded microemulsion and microemulsion-based
gel for transdermal delivery: Preparation, optimization, and
evaluation. Int J Pharm. 477:47–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moreno MA, Frutos P and Ballesteros MP:
Lyophilized lecithin based oil-water microemulsions as a new and
low toxic delivery system for amphotericin B. Pharm Res.
18:344–351. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Panapisal V, Charoensri S and
Tantituvanont A: Formulation of microemulsion systems for dermal
delivery of silymarin. AAPS PharmSciTech. 13:389–399. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qi J, Zhuang J, Wu W, Lu Y, Song Y, Zhang
Z, Jia J and Ping Q: Enhanced effect and mechanism of water-in-oil
microemulsion as an oral delivery system of hydroxysafflor yellow
A. Int J Nanomedicine. 6:985–991. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fouad SA, Basalious EB, El-Nabarawi MA and
Tayel SA: Microemulsion and poloxamer microemulsion-based gel for
sustained transdermal delivery of diclofenac epolamine using
in-skin drug depot: In vitro/in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm.
453:569–578. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gundogdu E, Alvarez IG and Karasulu E:
Improvement of effect of water-in-oil microemulsion as an oral
delivery system for fexofenadine: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int
J Nanomedicine. 6:1631–1640. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao JH, Ji L, Wang H, Chen ZQ, Zhang YT,
Liu Y and Feng NP: Microemulsion-based novel transdermal delivery
system of tetramethylpyrazine: Preparation and evaluation in vitro
and in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 6:1611–1619. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu W, Yu A, Wang W, Dong R, Wu J and Zhai
G: Formulation design of microemulsion for dermal delivery of
penciclovir. Int J Pharm. 360:184–190. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Z, Mu HJ, Zhang XM, Ma PK, Lian SN,
Zhang FP, Chu SY, Zhang WW, Wang AP, Wang WY and Sun KX: Lower
irritation microemulsion-based rotigotine gel: Formulation
optimization and in vitro and in vivo studies. Int J Nanomedicine.
10:633–644. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|